DigiNerve is constantly evolving to enhance your experience while you’re on your journey to becoming a Top Doc. We are excited to bring you the latest updates with our commitment to ensure a seamless journey on the go.
Read on the July edition (Vol – 1) of our monthly newsletter to know the latest updates.
CONTENT UPDATES
PostGrad Course Updates
Dermatology MD:-
1. Chat show on ‘Discussion on Leprosy’ by Dr. Vivek Vasudev Pai, Dr. Shraddha Mahobia, and Dr. Samira Siddiqui Khatoon Mohd. Hanif has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- To learn the approach to a patient with leprosy.
- To understand the current scenario of leprosy and the National Strategic Plan for 2023-2027 for India.
- To learn the approach to patients with lepra reactions and relapse.
- To understand the management of patients with ENL reactions and relapse.
Pediatrics MD:-
1. Chat show on ‘Approach to a Child with Asthma’ by Dr. Piyush Gupta and Dr. Prawin Kumar has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Clinical presentation of asthma in children.
- How can a diagnosis of asthma in children be established?
- What is the role of the Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) in the diagnosis of asthma.
- Management of Asthma in Children.
Medicine MD:-
1. 8 new topics have been added to the following modules:
| Module | Section | Topic |
| Rheumatology | Long Case Discussions | Gout |
| Infectious Diseases | Clinical Scenarios | Amoebic Liver Abscess |
| Systemic Fungal Infections | ||
| Japanese Encephalitis | ||
| Critical Care Medicine | Decision Making | Central Venous Line |
| Intubation in Critically Ill Patients | ||
| Cardiology | Basic Sciences | Treadmill Test |
| Endocrinology and Diabetes | Long Case Discussions | Approach and Management of Hyponatremia |
Note: The topics mentioned above also include 39 new self-assessment and 16 benchmark trials.
Update Your DigiNerve App for Better Experience.
To read the updates shared in the Monthly Newsletter June (Vol-2), click here.
DigiNerve is constantly evolving to enhance the user experience while you’re on their journey to becoming a Top Doc. We are excited to bring the latest updates with our commitment to ensure a seamless journey on the go.
Read our monthly newsletter’s June edition (Vol – 2) for the latest updates.
CONTENT UPDATES
PostGrad Course Updates
OBGYN MD:-
1. 5 new topics have been added to the following modules:
| Section | Module | Topic |
| Gynecology | Menstrual Abnormalities | Menopause Hormonal Therapy |
| Obstetrics | Procedural Videos | Caesarean Section |
| Third Stage of Labour and its Complications | Postpartum Psychiatric Illness | |
| Medical Disorders in Pregnancy | Case Discussion: Pregnancy Induced Hypertension | |
| Labour (Normal and Abnormal) | Management of Abnormal Labour |
Note: The topics mentioned above also include 25 new MCQs and 10 benchmark trials.
2. Chat show on ‘Primary Amenorrhea’ by Dr. Aswath Kumar and Dr. Lilly Varghese has been added to the course:
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Different etiologies of primary amenorrhea
- Important subtypes: Clinical features
- Investigations
- Management: Hormonal and surgical treatment
Surgery MS:-
1. Chat show on ‘Management of Head Injury’ by Prof. (Dr.) Nilay Mandal and Dr. Arjun Dasgupta has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Initial assessment of a head injury patient
- Prevention of secondary injury and management of raised ICP
- Types of head injury and their radiological findings
Professional Course Updates
MRCOG Part 2:-
1. Webinar on ‘Discussion of Important Questions and Doubt Clearance (MRCOG-2 EMQs)’ by Dr. Richa Saxena has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the webinar were:
- To discuss important questions of MRCOG part 2 exam.
- To prepare for exam with the help of carefully curated questions with detailed explanations, images and flowcharts.
- To ease the journey of clearing MRCOG exam.
- To understand latest patterns of questions as per RCOG curriculum (EMQs).
Technology Updates
1. Inclusion of HYQs
A new section of High Yield Questions has been included in the courses- Cracking MRCOG- PART 1 and Part 2. It comprises HYQs from the year 2016-2022.
2. Free Access to Dr. Wise
An additional benefit of 10 queries for non-subscribers.
3. Customised Question Bank Generator
- A new feature of Customised Question Bank Generator has been added, under the course of Cracking MRCOG Part-1.
- Beneath the ‘Test’ section, users can generate questions in the ‘Practice’ or ‘Test Mode’ as per the choice of difficulty level and as per the number of questions required.
Update Your DigiNerve App for Better Experience.
To read the updates shared in the Monthly Newsletter July (Vol-1), click here.
The result of the INI-CET exam held on 05.11.2023 for admission to the July session 2024 was declared on 19.05.2024 and is available on the AIIMS official website, www.aiimsexams.ac.in.
After the declaration of the result, the institute released the schedule of online seat allocation for admission to PG courses of INIs [MD/MS/DM(6yrs.)/MCh(6yrs.)/MDS].
For admission to PG courses at INIs for the January 2024 session, the schedule of online seat allocation at INI Institutes (including Mock Round), as per the official notification, is provided below:
Schedule for 1st Round of Online Seat Allocation (including Mock Round)
| S.No. | Particulars | Date |
| 1 | Exercising of Choices (Institute and Subject/Speciality) for Mock Round | From 11.06.2024 (Tuesday) to 13.06.2024 upto 05.00 pm (Thursday) |
| 2 | Announcement of Seat Allocation for 1st Mock Round | 15.06.2024 (Saturday) |
| 3 | Exercising of Choices (Institute and Subject/Speciality) for 1st Round | From 16.06.2024 (Sunday) to 18.06.2024 up to 05:00 pm (Tuesday) |
| 4 | Announcement of Seat Allocation of 1stRound | 22.06.2024 (Saturday) |
| 5 | Online Acceptance of Allocated Seat | From: 24.06.2024, 11.00 am (Monday) to 27.06.2024 up to 05.00 pm (Thursday) |
| 6 | Reporting and Submission of Documents/Security Deposit | From: 24.06.2024, 11.00 am (Monday) to 27.06.2023 up to 05.00 pm (Thursday) |
Schedule for 2nd Round of Online Seat Allocation
| S. No. | Particulars | Date |
| 1 | Announcement of Seat Allocation of 2nd Round | 13.07.2024 (Staurday) |
| 2 | Online Acceptance of Allocated Seat | From 15.07.2024, 11.00 am (Monday) to 19.07.2024 up to 05.00 pm (Friday) |
| 3 | Reporting and Submission of Documents/Security Deposit | From 15.07.2024, 11.00 am (Monday) to 19.07.2024 up to 05.00 pm (Friday) |
Only eligible candidates will have access to the portal link on “My Page”, on the AIIMS website, www.aiimsexams.ac.in. It can be accessed by logging in with the credentials used for completing the application form INI-CET for admission to PG programs for the July 2024 session.
Here’s a list of participating INI-CET institutes for the January 2024Session.
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi
- AIIMS, Bhopal
- AIIMS, Bhubaneshwar
- AIIMS, Jodhpur
- AIIMS, Nagpur
- AIIMS, Patna
- AIIMS, Raipur
- AIIMS, Rishikesh
- AIIMS, Bibinagar
- AIIMS, Bhatinda
- AIIMS, Deoghar
- AIIMS, Mangalagiri
- AIIMS, Raebareli
- AIIMS, Kalyani
- AIIMS, Bilaspur
- AIIMS, Gorakhpur
- AIIMS, Guwahati
- Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry
- National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bengaluru
- Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh
- Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), Trivandrum
DNB-PDCET is Diplomate of National Board- Post Diploma Centralized Entrance Test. It is a single-window entrance examination for admission to Post Diploma DNB Broad Specialty Courses. The duration of the Post Diploma DNB course is 2 years.
The DNB-PDCET entrance examination is conducted by the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS). A consistent national standard for assessing the minimal level of knowledge and skills required for postgraduate and doctorate courses is provided by NBEMS.
The DNB PDCET examination will held on 28th July 2024 for a total of 1073 seats for 14 different specialties. The DNB-PDCET 2024 result has been released on 21st August 2024 and can be downloaded from the NBEMS official website, natboard.edu.in.
DNB-PDCET Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria for admission to the Post Diploma DNB courses are as follows:
- Candidates can apply for the DNB PDCET 2024 in the desired broad specialty using the online application system available at the NBEMS website, https://nbe.edu.in or https:// natboard.edu.in if they have completed the final examination leading to the award of a Post Graduate Diploma from Indian Universities that have been duly recognized by NMC.
- The final test result for the mentioned Post Graduate Diploma certification should have been released on or around February 28, of the academic year.
- Those who are already enrolled in an MD, MS, or DNB programme are not eligible to take the DNB-PDCET until they have finished the ongoing program or have been released from it.
- You must provide documented verification of their registration with the NMC, the former Medical Council of India, or the State Medical Council on the day of the exam and during counselling/admission.
DNB-PDCET Exam Scheme
| Particulars | Description |
| Scheme | Single-day and single session exam |
| Mode of Exam | Computer-based Test |
| Type of questions | Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |
| Language of Question Paper | English |
| Total number of questions | 120 |
| Total time allotted | 120 minutes |
| Marking Scheme | +4 is given for every correct answer.
-1 is given for every incorrect answer. Zero mark for every unattempted answer. Questions marked for review are evaluated according to the marking scheme. |
| Total Marks | 480 |
| Organizing Body | NBEMS (National Board of Examinations In Medical Sciences) |
List of Post Diploma DNB Courses
Following is the list of Post Diploma DNB Courses in which admission is done through DNB-PDCET:
| S.No. | Post Diploma DNB Courses | Prior Entry Eligible Qualification |
| 1 | DNB (Anaesthesiology) | DA |
| 2 | DNB (Dermatology, Venereology & Leprosy) | DVD |
| 3 | DNB (Nuclear Medicine) | DNM |
| 4 | DNB (Obstetrics and Gynaecology) | DGO |
| 5 | DNB (Ophthalmology) | DOMS |
| 6 | DNB (Orthopaedics) | DORTHO |
| 7 | DNB (Otorhinolaryngology) | DLO |
| 8 | DNB (Paediatrics) | DCH |
| 9 | DNB (Psychiatry) | DPM |
| 10 | DNB (Radio Diagnosis) | DMRD |
| 11 | DNB (Radiation Oncology) | DMRT |
| 12 | DNB (Respiratory Medicine) | DTCD |
| 13 | DNB (Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation) | DPMR |
| 14 | DNB (Pathology) | DCP |
DNB PDCET Online Application Form
Steps to fill in an online DNB-PDCET application form.
- You are required to fill out the user registration form to generate a User ID/Application ID and Password.
- You will receive an SMS and Email with the User ID and Password.
- Then you must complete the application form and upload your photograph, scanned signature, thumb impression, and other required documents. You must fill in the information correctly to avoid any discrepancies later.
- While filling in the form, you need to choose your Exam Centre/Test City and pay the examination fee.
- After completing the form and carefully checking it, agree to the declaration and submit the application.
- You must submit the DNB-PDCET online application form before the last date.
- After completing the payment, check the payment status to be mentioned as ‘S’ (Successful) on the application form.
- You must take a printout of the filled Application form with the transaction ID printed on it and payment status should be mentioned as Successful.
Instruction to Fill Online DNB-PDCET Online Application Form
New User Registration: You are required to create an online profile to generate a User ID and Password.
Applicant Login: You can login and register an online application using the User ID and Password that has been set. Following user creation, the “Go to Application” link enables you to carry on with the application submission.
Fill out the application form correctly: You are required to fill in details like name, gender, nationality, email id, contact, and more.
Nationality can be chosen from the following options: Indian, Non-Resident Indian (NRI), Overseas Citizen of India (OCI)/PIO, and Non-OCI Foreign Nationals. If you are a Foreign National along with an Overseas Citizen of India, choose OCI/PIO as your nationality. If you are a foreign national and not an OCI, then choose Non-OCI Foreign National as your Nationality.
Upload Images: Upload your photograph, signature, and thumb impression in the application form.
Instruction for Uploading the Images
| Images to be uploaded | Instructions |
| Photograph | Candidate must upload two photographs:
1. Real time photograph- taken by the inbuilt system while filling out the PDCET application form. 2. Recent Photograph- in this case, the photograph should not be more than 3 months old. · Do not wear spectacles, cap goggles, or ornaments while getting clicked. · Photograph should be colored with white background. · The size of the image should be less than 80kb. · The image should be in .jpg/.jpeg format. |
| Signature |
The signature can be made in two ways: 1. Uploading the signature using a digital device: (i.e., camera) · Draw a box of size 1.5 cm (height) x 3.5 cm (width). · Sign with a black or blue ink pen. · Scan the image through scanner and then crop the image to the box. · Resize the image to 20-100kb. 2. Uploading the scanned signature · Signature should be done on a blank white page with blue/black pen. · Set the scanner to 200 dpi. · Scanned image should be in .jpeg/.jpg format. · Size of the image should be less than 80kb. |
| Thumb impression |
· Draw a box of 3.5 cm x 1.5 cm (width x height) on white paper. · Use a blue/black ink pad and take the left thumb impression. · Scanner should be set at 200 dpi. · Scanned image of the thumbprint must be in .jpg/.jpeg format. · Size of the image should be less than 80kb. |
Choose Examination City: You must choose the Test City from the given options. The exam centres are allotted according to a first come first serve basis.
Exam Centres
The tentative list of exam centres for the DNB-PDCET exam:
- Ahmedabad
- Bengaluru
- Bhopal
- Chandigarh/Mohali
- Chennai
- Delhi NCR
- Guwahati
- Hyderabad
- Jaipur
- Jammu
- Kolkata
- Kozhikode
- Lucknow
- Mumbai
- Patna
- Pune
- Ranchi
- Thiruvananthapuram
- Visakhapatnam
Pay the Examination Fee: The DNB-PDCET examination fee is Rs. 5000 (excluding additional payment gateway charges and tax). After making the payment make sure the confirmation is reflected as ‘S’ (Successful) in the application form.
Application Form Submission: Carefully preview your application form and agree to the declaration and submit the application form.
Acknowledgment of Application Submission: An acknowledgment email is sent to the registered email ID which confirms the successful application.
If any detail/field in the application form mentioned is incorrect, you can only edit it during the Edit Window. However, the following fields remain non-editable:
- Name of the Candidate
- Email ID
- Mobile number
- Nationality
- Test City
List of Barred Items
- Mobiles phones and other electronic devices like earphones, Bluetooth, wristwatches, etc.
- Any stationary item like a pen, textual material, notebook, writing pad, pouch, eraser, etc.
- Any ornaments like rings, earrings, bracelets, chains, brooches, etc.
- Any other wearables and accessories like caps, goggles, wallets, handbags, etc.
DNB PDCET Admit Card
The DNB-PDCET admit cards can be downloaded from the NBEMS website, natboard.edu.in.
You must download their admit cards from the NBEMS website and firmly paste their most recent (not older than three months) passport-size photo in the designated spot on the card. The image must adhere to the following requirements:
- The size of the photograph must be a minimum of 35×45 mm with a clear face and head of the candidate.
- The photograph should be coloured with white background.
- No caps, goggles, or ornaments should be worn.
- The photo must be printed on fine paper with a resolution of at least 600 dpi.
- The admit card mentions the exact address and location of the exam centres. You are urged to become familiar with the location of the test centres at least one day before the exam and make sure you report for the exam at the appointed time.
Documents to Carry on Exam Day
Candidates must bring the following documents to the test centre on the exam day:
- A printed copy of your barcoded or QR coded admit card with a recent colored photo attached.
- Permanent SMC/MCI/NMC registration photocopy, later retained by the test centre.
- Any one of the government-issued photo IDs listed below:
- PAN Card
- Aadhar Card (with the photograph)
- Voter ID
- Driving License
- Passport
DNB PDCET 2024 Result Declaration
The DNB PDCET 2024 result has been declared on 21st August 2024. The Cut-off date for qualifying for the final examination of PG Medical Diploma qualification towards eligibility for DNB-PDCET 2024 is 31st May 2024.
Steps to Check Your DNB PDCET 2024 Result
Step 1: Go to the official NBEMS website, ntaboard.edu.in.
Step 2: Click on the DNB PDCET 2024 result link available on the homepage.
Step 3: Enter your login details and click on the submit button.
Step 4: DNB PDCET Result 2024 PDF will appear on the screen.
Step 5: Check and download the PDCET 2024 result.
Step 6: Take a printout of the same for further counselling and admission purposes.
The merit list of the DNB-PDCET entrance examination is generated specialty wise and there are no minimum qualifying criteria. Questions asked in the examination can be challenged only within the 3 calendar days after the exam day.
Any candidates found indulging in unfair practices will be expelled for the next 14 attempts or the next 7 years or as decided by the Examination Ethics Committee after considering a particular case.
The DNB PDCET official answer key can be downloaded from the official NBEMS official website once released.
Validation of DNB-PDCET Result 2024
The PDCET result is valid only for the current year i.e., the year in which the examination has been attempted. The merit and score cannot be carried forward to the next admission sessions.
Tie-breaker Criteria
In case of two or more candidates score the same, the merit is determined using the following criteria in descending order:
- Candidates who have marked more correct responses are placed above in the merit.
- Candidates with a lesser number of negative responses in the question paper are placed in a better position in the merit.
- Older candidates are placed in better positions on merit.
Publication of Merit List
- All students who take the DNB Post Diploma CET test will be ranked according to the scores they received in comparison to other applicants who applied for the same broad specialty.
- For each Broad specialty for which the Post Diploma CET test is held, a distinct merit will be created. For instance, only Post DGO applicants will be eligible for the merit list for DNB Obstetrics and Gynecology Post Diploma seats. Specialty-based merit lists will be released separately.
DNB PDCET 2024 Counselling
- The registration for the counseling is conducted by the designated authority.
- Candidates who have secured merit positions in the NBEMS-conducted DNB Post Diploma Centralized Entrance Test (DNB-PDCET) 2024 and who meet the requirements for admission to DNB (Post Diploma) programs (2024 admission session) at various NBEMS-accredited Medical Colleges, Institutions, and Hospitals in India are invited to participate in the counselling for the allocation of seats solely based on merit and student preference.
- For Scheduled Castes (SC), Schedule Tribes (ST), Persons with Disabilities (PwD), Other Backward Classes (OBC), and EWS, the status of any Post Diploma DNB seats that are subject to appropriate reservations will be declared at the time of counselling.
- Candidates are required to show their category certificate at the time of counselling.
- The PwD candidates must get themselves certified at one of the Disability Assessment Boards, before the counselling date and are required to carry their treatment documents at the time of counselling.
Important Dates for DNB-PDCET Entrance Examination
| Particulars | Tentative Timelines |
| Submission of Online Application Form | 28th May 2024 (3 PM Onwards) to 17th June 2024 (Till 11:55PM) |
| Application Edit Window | 20th June 2024 to 23rd June 2024 |
| Selective Edit Window to rectify images (Photograph/Signatures/Thumb Impression) | 3rd July 2024 to 7th July 2024 |
| Admit Card Issue Date | 16th July 2024 |
| Examination Date | 21st July 2024 |
| Result Declaration | By 21st August 2024 |
| The cut-off date for qualifying for the final examination of PG Medical Diploma qualification towards eligibility for DNBPDCET | 31st May 2024 |
Things to keep in mind
- Know the DNB PDCET Exam Pattern before starting the preparation.
- Remember to regularly check the DNB PDCET Registration Date and DNB PDCET online application form release date and submit it on time to get to the desired exam centre.
- Go through the DNB PDCET syllabus before preparation and solve the PDCET previous year’s question papers and sample papers to enhance the preparation.
- Solve DNB PDCET mock test papers during revision time to evaluate your progress and understanding of the topic.
- Don’t forget to affix the photograph on the admit card.
- Verify and check all the required documents for the exam day.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is PDCET?
Ans. DNB-PDCET is Diplomate of National Board- Post Diploma Centralized Entrance Test. It is a single-window entrance examination for admission to Post Diploma DNB Broad Specialty Courses. It is conducted by the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS).
Q2. What is the duration of the PDCET exam?
Ans. The duration of the PDCET exam is 120 minutes.
Q3. When is the DNB-PDCET 2024 result declared?
Ans. The DNB-PDCET 2024 result has been declared on 21st August 2024 and can be checked on the official NBEMS website, natboard.edu.in, and nbe.edu.in.
Q4. What is the exam pattern of DNB PDCET?
Ans. The DNB-PDCET is a computer-based exam with multiple choice type questions. It is Single-day and single session exam. The exam has a total of 120 MCQs to be completed in 120 minutes.
MRCP (Membership of the Royal Colleges of Physicians) is a postgraduate diploma awarded by the Federation of Royal Colleges of Physicians of the United Kingdom.
The MRCP exam comprises three parts:
- MRCP(UK) Part 1: This written exam consists of multiple-choice questions (MCQs), and is intended to evaluate a candidate’s grasp of the fundamental sciences as well as their capacity to apply that knowledge in clinical settings.
- MRCP(UK) Part 2: This section also has multiple-choice questions and is geared toward clinical medical knowledge and abilities. It assesses the candidate’s capacity to use clinical comprehension and knowledge for patient diagnosis, research, and management.
- MRCP(UK) Part 2 Clinical (PACES): PACES stands for Practical Assessment of Clinical Examination Skills. The PACES is an objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) used to evaluate applicants’ clinical abilities. Candidates are evaluated at a number of stations on their capacity to effectively communicate, obtain information, and perform clinical procedures.
The MRCP Part 1 and 2 are held four times a year whereas the frequency of PACES varies with the location.
After the successful completion of all three parts of the MRCP exam, you will be awarded with MRCP(UK) diploma that paves the way to your specialist internal medicine training in the UK. The certification for the MRCP(UK) is approved by the General Medical Council (GMC) as a part of the UK postgraduate medical training programme and it follows the UK curricula and guidelines.
The blog mentions the MRCP Part 1 dates, MRCP Part 2 dates and MRCP PACES dates along with the schedule and MRCP exam fees of all three parts.
MRCP PART 1 WRITTEN EXAMINATION
MRCP Part 1 Exam Dates
The MRCP exam dates for Part 1 2024 are as follows:
- 24 January 2024
- 17 April 2024
- 14 August 2024
- 16 Oct 2024
MRCP Part 1 Exam Schedule and Fees
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Reasonable Adjustment Deadline | Results by | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 06 Nov 2023- 13 Nov 2023 | 24 Jan 2024 | 20 Nov 2023 | 23 Feb 2024 | £460(UK) £616(Int.) |
| 2024/2 | 05 Feb 2024- 12 Feb 2024 | 17 Apr 2024 | 19 Feb 2024 | 17 May 2024 | £460(UK) £616(Int.) |
| 2024/3 | 03 Jun 2024- 10 Jun 2024 | 14 Aug 2024 | 17 Jun 2024 | 13 Sep 2024 | £460(UK) £616(Int.) |
| 2024/4 | 05 Aug 2024-12 Aug 2024 | 16 Oct 2024 | 19 Aug 2024 | 15 Nov 2024 | £460(UK) £616(Int.) |
Note: The application process and fee for the Hong Kong centres are different.
MRCP Part 1 Exam Centres in India
- Chennai
- Hyderabad
- Kerala
- Kolkata
- Mumbai
- New Delhi
Must Read: How to Pass MRCP Part 1 in First Attempt?
MRCP PART 2 WRITTEN EXAMINATION
MRCP Part 2 Exam Dates
The exam dates for MRCP Part 2 are as follows:
- 21 Feb 2024
- 15 May 2024
- 11 Sep 2024
- 20 Nov 2024
MRCP Part 2 Exam Schedule and Fees
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Reasonable Adjustment Deadline | Exam Date | Results by |
| 2024/1 | 04 Dec 2023-11 Dec 2023 | 18 Dec 2023 | 21 Feb 2024 | 22 Mar 2024 |
| 2024/2 | 18 Mar 2024-25 Mar 2024 | 01 Apr 2024 | 15 May 2024 | 14 Jun 2024 |
| 2024/3 | 08 Jul 2024-15 Jul 2024 | 22 Jul 2024
|
11 Sep 2024 | 11 Oct 2024
|
| 2024/4 | 16 Sep 2024-23 Sep 2024 | 30 Sep 2024 | 20 Nov 2024 | 20 Dec 2024 |
MRCP Part 2 Exam Centres in India
- Chennai
- Hyderabad
- Kerala
- Kolkata
- Mumbai
- New Delhi
Click here to know about the MRCP exam in detail.
MRCP PART 2 CLINICAL (PACES)
Following points to note:
- The exam dates for the MRCP 2 PACES exam are different for the different countries and centres. You must choose the exam centre and dates according to your feasibility.
- MRCP Part 2 PACES fees also vary from country to country.
MRCP Part 2 PACES Exam Schedule and Fees
The following table mentions the application dates according to the exam centre in India:
Bengaluru
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Dates | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 29 Feb 2024 – 2 Mar 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | Centre not running in this assessment period | |||
| 2024/3 | 17 Jun 2024 – 24 Jun 2024 | 24 Oct 2024- 26 Oct 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
Chennai
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 18 Mar 2024- 22 Mar 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | Centre not running in this assessment period | |||
Hyderabad
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 15 Mar 2024 – 17 Mar 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | To be confirmed | |||
Kochi
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 22 Feb 2024- 24 Feb 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | To be confirmed | |||
Kolkata
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 5 Apr 2024- 7 Apr 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | To be confirmed | |||
New Delhi
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 28 Mar 2024- 31 Mar 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | To be confirmed | |||
Pondicherry
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 8 Feb 2024- 10 Feb 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | To be confirmed | |||
| 2024/3 | To be confirmed | |||
Pune
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 9 Oct 2023- 16 Oct 2023 | 12 Mar 2024- 17 Mar 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/2 | Centre not running in this assessment period | |||
Thiruvananthapuram
| MRCP Exam 2024 | Application Period | Exam Date | Admission Documents Sent | Fees |
| 2024/1 | Centre not running during this assessment period | |||
| 2024/2 | 19 Feb 2024- 26 Feb 2024 | 5 Jun 2024- 8 Jun 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date | £1202 |
| 2024/3 | 17 Jun 2024- 24 Jun 2024 | 27 Nov 2024 – 30 Nov 2024 | Approximately 4 weeks prior to the exam date
|
£1202 |
UK 2024 Application Dates
| Diets | Application Open | Application Close | Assessment Period | Fees |
| 2024/1 | 13 Nov 2023 | 20 Nov 2023 | Late January – End of March | £657 |
| 2024/2 | 25 March 2024 | 01 April 2024 | Early June- Early August | £657 |
| 2024/3 | 22 July 2023 | 29 July 2024 | Late September – Early December
|
£657 |
Exam Centres for MRCP 2 PACES in India
- Bengaluru
- Chennai
- Hyderabad
- Kochi
- Kolkata
- New Delhi
- Pondicherry
- Pune
- Thiruvananthapuram
Cracking MRCP will be a significant achievement in the field of medicine that opens up various career opportunities. To ace your MRCP Part 1 preparation, you can enroll in the ‘Cracking MRCP Part 1’ online course by eminent faculty, Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander and Dr. Archith Boloor. The course is crafted based on the curriculum designed by The Royal College of Physicians. It provides access to video lectures, webinars & video archives, practice assessments, notes, high-yield questions, e-chapters, mock papers and performance tracking assistance by providing a leaderboard.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. Is MRCP done after MBBS?
Ans. Yes, you can sit in the MRCP exam only after completing the MBBS. Along with the MBBS degree, you must have a minimum of 12 months of postgraduate experience in medicine.
Q2. What is the fee for the MRCP exam for Indian students?
Ans. The fee for the MRCP Part 1 and 2 is £616 for candidates other than UK (including Indian students )while for MRCP Part 2 Clinical (PACES), the fee is £1202 for Indian students.
Q3. Can we take the MRCP exam in India?
Ans. Yes, you can take the MRCP exam in India. In India, you can take the MRCP exam at the following locations: Chennai, Hyderabad, Kerala, Kolkata, Mumbai, and New Delhi. In addition to these, MRCP PACES is also conducted at Bengaluru, Kochi, Pondicherry, Pune, and Thiruvananthapuram.
FMGE (Foreign Medical Graduate Examination) is a screening test for an Indian citizen or an overseas Indian citizen who holds a primary medical degree from a medical institution outside of India in order to be eligible for provisional or permanent registration with the Medical Council of India or any State Medical Council on or after 15th March, 2002.
According to the 2002 Screening Test Regulations, the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS) conducts the Screening Test. The National Medical Commission and all State Medical Councils get the results once the exam has been administered, published, and distributed by NBEMS.
The NBEMS administers the screening test twice a year. The FMGE 2023 exams were held on 20th January, 2023 and 30th July, 2023.
For 2024, the FMGE application process commenced on 23rd November, 2023. The FMGE 2024 exam will be held on 20th January, 2024.
FMGE 2024 Important Dates
| Process | Timelines |
| Submission of Online Application | 29th April 2024 to 20th May 2024 (Till 11:55 PM) |
| Edit Window | 24th May 2024 to 28th May 2024 |
| Edit Window to rectify images | 7th June 2024 to 10th June 2024 |
| Edit Window to rectify discrepancies related to documents uploaded in the application | Through Online Deficient Document Submission Portal (http://exam.natboard.edu.in/fmge.php) The portal will close on 14th June 2024 at 11:55 PM |
| Final opportunity to rectify deficiencies related to documents upload in the application | 21st June 2024 (11AM onwards) to 24th June (Till 11:55PM) |
| Admit Card Issue Date | 1st July 2024 |
| FMGE Exam Date 2024 | 6th July 2024 |
| Result Declaration Date | 6th August 2024 |
FMGE 2024 Eligibility Criteria
- A candidate must be an Indian/Overseas Citizen of India.
- The candidate must hold a primary medical qualification that has been verified by the Indian Embassy for registration as a medical practitioner.
- The applicant must hold an “Eligibility Criteria” from the National Medical Commission (or the former Medical Council of India). This condition is not necessary for Indian nationals or Indian residents living abroad who received their medical degrees from foreign institutions or who were admitted to such institutions before March 15, 2002.
- The final examination result of the mentioned primary medical qualification must have been declared on or before 31st October 2023 and the candidate is required to submit the documentary proof for the same.
- To enroll in any medical program outside of India, Indian citizens or Indian citizens living abroad must pass the “National-Eligibility-cum Entrance Test for Admission to MBBS course” by May 2018 or later. If a person meets the requirements for admission to the MBBS course as outlined in the Regulations on Graduate Medical Education, 1997, the outcome of the “National- Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test for Admission to MBBS course” shall be deemed to be treated as the eligibility certificate.
- Only qualified applicants who possess both the Provisional Pass Certificate/Degree Certificate of Primary Medical Qualification and the Eligibility Certificate (if applicable) will be permitted to appear in the FMGE.
- Three (3) years from the date of result declaration, the NEET result is considered legitimate.
- If the applicant has an Under Graduate medical qualification from Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, or the United States of America and has also been awarded a Post Graduate medical qualification in Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, or the United States of America and has been recognised for enrolment as a medical practitioner in that country, they will not need to pass the screening test in order to seek provisional or permanent registration in India.
- The candidates belonging to Pakistan or Indian students who have gained their medical degree from Pakistan must go through the updated guidelines and security clearance from the official NBEMS website to check their eligibility.
FMGE 2024 Application Form
Application forms can only be filled out once.
Instruction for filling out the FMGE 2024 Application Form
-
- Complete the user registration form to create a password and a user ID/application ID.
- User ID and Password will be communicated by email and text message.
- Login as an applicant for FMGE December 2023 session and fill the form from the “Go To Application” link.
- Fill out the application form completely, and submit your photo, scanned signature, thumbprint, and other papers. You are also required to mention Identification details, details of Primary Medical Qualification, and eligibility certificate.
- Select your test city and pay the exam fee.
- Accept the declaration and submit the application.
- Print off the completed application form with the Transaction ID and “S” (Successful) payment status for your records.
Instructions for Uploading Images
1. Photograph:
Candidates are required to upload two photographs.
a. Real-time Photograph: This photograph is to be taken while filling out the form by the webcam/in-built camera of the system. Take a photograph with a white background and the face must be clearly visible.
b. Recent Photograph: Candidates are required to upload a recent photograph that too not more than 3 months old. Keep the following things in mind while taking and uploading a photograph:
-
- The background must be white.
- The face must be clearly visible.
- The image size must be less than 80 kb.
- The image must be in .jpg/.jpeg format.
- The face must take up 70-80% of the frame.
- You must not wear heavy ornaments, spectacles, caps, goggles, and other accessories.
2. Signature:
Candidates are required to upload their signature and the digital image of the signature can be made in two ways:
a. Using a camera/digital device to directly image:
-
- Draw a box of 1.5 cm (height) x 3.5 cm (width) on a white sheet and use blue/black ink to sign within the box.
- Transfer the signed image using a digital device/scanner to the computer/laptop.
- Crop and resize the image to 20-100 kb.
b. Scanning the Signature:
-
- Draw a box of 3.5 x 1.5 cm (width x height) on a white sheet and sign with black/blue ink.
- Set the scanner to 200 dpi.
- The scanned image should be saved in the .jpg/.jpeg format.
- Crop and resize the image to less than 80 kb.
3. Thumb Impression:
On a white sheet of paper, draw a box of 3.5 cm x 1.5 cm (width x height).
Using a black/blue color ink pad, take a clear impression of the left thumb.
a. Prepare a digital image of the thumb impression using a digital device (Camera):
-
- Transfer thumb impression from camera to computer.
- Then, crop and resize the image to less than 80 kb.
b. Scanning the thumb impression:
-
- Set the scanner to 200 dpi and save the scanned image of the thumbprint in .jpg/.jpeg format.
- The size of the image should be less than 80 kb.
The following is a list of documents to be submitted by the candidates if required by NBEMS to determine eligibility:
- Copy of Address Proof (PAN Card/Voter ID/Passport/ Driving License/ Aadhar Card).
- Latest Passport size Photographs
- Copy of Date of Birth Proof (Certificate of Matriculation).
- Copy of 10+2 passing certificate.
- Copy of 10+2 mark sheet.
- Copy of internship certificate (if done abroad).
- Copy of failed certificate/ result for Ex-candidates.
- Proof of Category (SC, ST, OBC, etc.)
- Equivalence Certificate: From the Association of Indian Universities (for candidates who have done 10+2 abroad).
List of Documents allowed for Proof of Citizenship
- Valid Passport for Indian Citizens/NRI
- OCI Card and Valid Passport of the citizenship country for Overseas Citizens of India
- Indian Govt. issued ID for Nepalese Candidates and for Indian candidates who have completed their Primary Medical Qualification from Nepal and govt. has not issued any passports to them.
Things to keep in mind while filling out the FMGE application form
- Candidates might need to upload the Eligibility Certificate (EC) issued by MCI/NMC. If you were admitted during a time when the government of India did not require or exempt you from getting an EC from MCI, you will need to submit a copy of your admission letter to prove your enrollment in the main medical degree. This will serve as a substitute for the EC.
- If admission to Primary Medical Qualification has been gained on or after May 2018, the candidate can be asked to provide the qualifying NEET-UG scorecard in place of the EC.
- Online Deficient Document Submission Portal: If any document(s) provided by applicants do not meet requirements (such as an EC, passport, proof of passing, etc.), the applicant will be notified via an online deficient document submission portal.
- Documents CANNOT be submitted in any other way, including by email, the Communication Web Portal, or in person at the NBEMS office. The following URL will take you to the Online Deficient Document Submission Portal: http://exam.natboard.edu.in/fmge.php
FMGE 2024 Examination Fee
The FMGE 2024 entrance examination fee is Rs. 6000 (excluding GST and payment gateway charges). The total FMGE entrance exam fee is Rs. 7080 after adding GST.
You must make sure that the payment made is successful and that the application form reflects the status as “S” (for Successful).
FMGE 2024 Exam Centres
The tentative list of Exam centres for the FMGE:
- Ahmedabad/Gandhinagar
- Aizawl
- Ajmer
- Aligarh
- Bengaluru
- Bhilai Nagar
- Bhopal
- Bhubaneswar
- Bikaner
- Chennai
- Coimbatore
- Delhi NCR
- Ernakulum
- Guntur
- Hamirpur
- Hyderabad
- Jalandhar
- Jammu
- Jodhpur
- Kannur
- Kohima
- Kolkata
- Kollam
- Kottayam
- Kozhikode
- Lucknow
- Madurai
- Mangaluru
- Meerut
- Mehsana
- Mumbai/Navi Mumbai/Thane
- Nagpur
- Patna
- Pune
- Rajkot
- Shillong
- Sikar
- Surat
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupathi
- Udupi
- Vadodara
- Vellore
- Visakhapatnam
FMGE 2024 Admit Card
- Candidates can download the admit card from the NBEMS website. The FMGE admit card release date is 15th Jan, 24.
- Candidates must affix the postcard size on the space provided in the admit card.
- Candidate must bring the following documents to the exam centre:
- PAN Card
- Driving License
- Voter ID
- Passport
- Aadhaar Card (with Photograph)
FMGE 2024 Exam Scheme
| Particulars | Description |
| Exam Type | Computer-based Test |
| Exam Pattern | The exam comprises one paper delivered in two parts comprising 150 questions to be attempted in 150 minutes. There is a break between both parts. |
| Types of Questions | Multiple Choice Questions |
| Total number of questions | 300 |
| Language | English |
| Marking Scheme | One mark is given for every correct answer. There is no negative marking. |
There are no restrictions on the number of attempts to be availed by a candidate.
FMGE 2024 Exam Schedule
| Activities | Part-I
(9:00 AM – 11:30 AM) |
Part-II
(2:00 PM – 04:30 PM) |
| Entry at Examination Centre and Registration Commencement | 07:00 AM | 12:00 PM |
| Entry Closes at Examination Centre | 08:30 AM | 01:30 PM |
| Candidate Login Time | 08:45 AM | 01:45 PM |
| Candidate login to read instructions | 08:50 AM | 01:50 PM |
| Exam Start Time | 09:00 AM | 02:00 PM |
| Exam End Time | 11:30 AM | 04:30 PM |
FMGE Subject-wise Marks Distribution and Syllabus
The following is the blueprint for the FMGE Screening Test:
A. Pre and Para clinical Subjects
| S.No. | Pre & Para Clinical Subjects | Distribution of Marks |
| 1 | Anatomy | 17 |
| 2 | Physiology | 17 |
| 3 | Biochemistry | 17 |
| 4 | Pathology | 13 |
| 5 | Microbiology | 13 |
| 6 | Pharmacology | 13 |
| 7 | Forensic Medicine | 10 |
| TOTAL | 100 | |
B. Clinical Subjects
| S.No. | Clinical Subjects | Distribution of Marks |
| 1 | Medicine and Allied Subjects | |
| a. | Medicine | 33 |
| b. | Psychiatry | 5 |
| c. | Dermatology & STD | 5 |
| d. | Radiotherapy | 5 |
| 2 | General Surgery and Allied Subjects | |
| a. | General Surgery | 32 |
| b. | Anaesthesiology | 5 |
| c. | Orthopaedics | 5 |
| d. | Radiodiagnosis | 5 |
| 3 | Pediatrics | 15 |
| 4 | Ophthalmology | 15 |
| 5 | Otorhinolaryngology | 15 |
| 6 | Obstetrics and Gynecology | 30 |
| 7 | Community Medicine | 30 |
| TOTAL | 200 | |
Syllabus for FMGE
Following is the FMGE Exam syllabus:
ANATOMY
- General Anatomy: Basic tissues to the body, Terminology & Nomenclature
- Elements of Anatomy: Osteology, Arthrology, Myology, Angiology, Neurology
- Regional Anatomy: Upper limb, Lower limb Thorax-including diaphragm Abdomen and Pelvis, Head, Neck Brain, and Spinal cord
- Embryology: Development of individual organs and systems, Postnatal growth & development
- Histology: General Histology Microanatomy of individual organs and systems
- Human Genetics: Principles of Human Genetics and Molecular Biology
- Radiological Anatomy: Skiagrams, Special X-rays, Principles of imaging techniques.
- Surface Anatomy: In cadavers, in the living
- Sectional Anatomy: Thorax, Abdomen, Head, Neck, and Brain
PHYSIOLOGY
- General Physiology
- Body fluids – Blood
- Nerve and Muscle
- Gastrointestinal Tract
- Kidney
- Skin and Body temperature
- Endocrine Glands
- Reproduction
- Cardiovascular System
- Respiratory System
- Central Nervous Systems
- Special Senses
BIOCHEMISTRY
- Cell and Sub-cellular structures
- Hydrogen Ion concentration Acid, Bases, Buffers, Handerson-Haselbach equation
- Isotopes and their Application
- Carbohydrates
- Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
- Lipids
- Nuclear Acids
- Enzymes
- Vitamins
- Biological Oxidation
- Digestion and Absorption from GI Tract
- Intermediary Metabolism
- Carbohydrate Metabolism
- Lipid Metabolism
- Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism
- Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
- Minerals
- Biochemical Genetics and Protein Biosynthesis
- Tissue Biochemistry
- Liver Functions
- Nutrition and Energy Metabolism
PATHOLOGY
- Cell injury
- Inflammation and Repair
- Immunopathology
- Infectious diseases
- Circulatory disturbances
- Growth disturbances and Neoplasia
- Nutritional and other disorders
- Genetic disorder
- Hematology
- Cardiovascular Pathology
- Respiratory Pathology
- Pathology of Kidney and Urinary Tract
- Hepato-Biliary Pathology
- Lymphoreticular System/Spleen
- Reproductive System (Male & Female)
- Diseases of the Breast
- Musculoskeletal System
- Endocrine pathology
- Neuropathology
- Dermato-Pathology
- Ocular Pathology
MICROBIOLOGY
- General Microbiology
- Immunology
- Bacteriology
- General Virology
- Systemic Virology
- Mycology
- Parasitology
- Clinical/Applied Microbiology
PHARMACOLOGY
- General Pharmacology
- Autonomic Nervous System
- Cardiovascular System
- Diuretics
- Drugs affecting blood and blood formation
- Autocoids and related drugs
- Respiratory System
- Gastro-intestinal System
- Endocrine pharmacology
- Central Nervous System
- Psychopharmacology
- Drugs in Anaesthetic practice
- Chemotherapy
- Toxicology
- Clinical Pharmacology and Rational drug use
FORENSIC MEDICINE
- Definitions
- Courts of India
- Court procedures
- Medical Certifications & medico-legal reports including the dying declaration
- Death
- Changes after death Inquest by police, magistrate, and coroner Identification
- Examination of mutilated human remains
- Medico-legal autopsies
- Mechanical injuries and wounds
- Examination of an injury case
- Injuries due to physical agents & their medico-legal importance
- Asphyxial death
- Death due to malnutrition, neglect battered babies
- Dowry death
- Virginity, sexual offences, sexual perversions
- Legitimacy
- Pregnancy and delivery
- Infanticide
- Biological fluids
- Seminal stains
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Medical Jurisprudence
- Toxicology
GENERAL SURGERY
- Hemorrhage and shock
- Fluid, electrolyte, and Acid balance, nutrition Skin tumors, burns, skin grafting
- Arterial diseases
- Venous diseases
- Lymphatic and Lymph nodes
- Wounds
- Specific and non-specific injections
- Tumors, Cysts, Ulcers, Sinuses, and Fistulae
- Infections of the Hand and Foot
- Diseases of muscle, tendons, bursae, and fascia Hernia
- Umbilical granuloma, fistula, adenoma
- Abdominal Wall
- Face, Teeth, Gums, Mouth, Tongue, Salivary glands, Neck
- Thyroid Glands, Thyroglossal Tract and Endocrines
- Breast
- Sympathetic System
- Cranio-Cerebral injuries
- Brain, Nerves
- Genito-Urinary System
- Kidneys and Ureters
- Urinary Bladder
- Prostrate
- Urethra
- Penis, Testis, and Scrotum
- Vasectomy and Recanalisation
- Cardiothoracic System
- Oesophagus, Stomach, and Duodenum
- Spleen, Liver, Gall Bladder and bile ducts Pancreas
- Peritoneum
- Intestines, intestinal obstruction
- Appendix
- Rectum and Anal Canal
ANESTHESIA
- Anatomy of upper airway
- Physiology of Respiration O2/CO2
- Methods of oxygen therapy.
- Pre-operative evaluation/pre-medication
- Anaesthetic agents, stages of Anaesthesia
- Principles and mechanism of administration of general anaesthetics, balanced Anaesthesia
- IPPV, Endotracheal Intubations
- Muscle Relaxants
- Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia
- Local Anesthesia
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation basic, use of simple ventilators
- Monitoring
- ICU, the role of anaesthesiologist in ICU
- Shock
- Blood Transfusion and Fluid Electoral
- Balance Sites of respiratory obstruction and Management of the Airway in an unconscious patient
- Poisoning
- Role of anaesthesiologist in acute and chronic relief.
ORTHOPEDICS
- Traumatology
- Injuries to bones and joints
- Injuries of the Lower Extremities
- Injuries of the Spine Vascular Injuries
- Cold Orthopedics
- Regional Conditions
- Neuro-Muscular Disorder
- Bone and Joint Tuberculosis
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
RADIO- DIAGNOSIS
- Respiratory System
- Cardiovascular System
- Gastrointestinal System
- Obstetrics &Gynaecology
- Skeletal System
- Central Nervous System
- Excretory System
RADIOTHERAPY
- Principles of Radiotherapy
- Principles of Chemotherapy
- Prevention and Early Diagnosis of Cancer
- Principles of Nuclear Medicine
- Common radiation reactions and management
- Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in commonly seen cancers
- Radio-isotopes in diagnosis and therapy
PEDIATRICS
- Vital statistic
- Neonatology Growth & Development
- Nutrition
- Infections
- Genetics
- Pediatric Emergencies
- Central Nervous System
- Gastroenterology
- Nephrology
- Endocrinology
- Respiratory System
MEDICINE
- Clinical Methods in the Practice of Medicine
- Common symptoms of the disease
- Nutrition/Exposure to Physical & Chemical Agents
- Infections
- Hematology
- Respiratory System
- Cardio-Vascular System
- Gastro-Intestinal Tract
- Emergency Medicine
- Neurological System
- Nephrology & Urinary system connected to Tissue Disorders
- Endocrine System
- Geriatrics
TUBERCULOSIS AND RESPIRATORY DISEASES
Diagnosis and management of common ailments affecting the chest with special emphasis on management and prevention of Tuberculosis and National Tuberculosis Control Programme.
PSYCHIATRY
- History aspects and diagnosis & treatment of mental illness
- Conduction of Mental Status Examination
- Behavioral Sciences
- Different psychoses
- Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of:
- Schizophrenia
- Mania and depression
- Anxiety disorders and hysteria
- Dementia
- Alcoholism Drug Abuse
- Psychiatric emergencies
- Clinical features, diagnosis, and management of psychiatric disorders of childhood and adolescence
- Personality disorder
DERMATOLOGY AND SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES
- Dermatological therapy
- Lichen Planus
- Diseases caused by Nutritional and Environmental Factors
- Infective Disorders
- Melanocytes, pigment metabolism, and other disorders of Pigmentation
- Allergic Disorders
- Dermatitis and Eczema
- Vesiculobullous Diseases
- Alopecia and Hirsutism
- Structure and Functions of Sebaceous Glands and Disease
- Leprosy
- Psoriasis
- STD
OPHTHALMOLOGY
- Basic sciences – Anatomy, Physiology, Pharmacology, Pathology, Elementary Optics, Diseases of the Eye
- Conjunctiva
- Cornea
- Sclera
- Uveal Tract
- Lens
- Vitreous
- Glaucoma
- Retina
- Optic Nerve
- Intra-Ocular Tumors
- Squint
- Orbit
- Lacrimal System
- Lids
- Refractive Errors
- Injuries
- Ophthalmic Surgery
- Community Ophthalmology
- Miscellaneous
OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY
- Diseases of the Ear
- Diseases of the Nose and Para Nasal sinuses
- Diseases of Nasopharynx
- Diseases of Trachea
- Oesophagus
OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
- Anatomy of the Female Reproductive Tract
- Physiology of conception
- Development of fetus and placenta Diagnosis of pregnancy
- Maternal changes in pregnancy
- Antenatal care
- Abnormal obstetrics
- Normal labor
- Normal puerperium
- Breast Feeding
- Care of newborn
- Medical termination of pregnancy
- Family planning
- Operative obstetrics
- Post caesarian pregnancy
- Pharmacotherapeutics in obstetrics
- Safe motherhood
- Maternal morbidity and morality
- Medico-legal aspects
- RCH
- Current topics
- Vaginal discharge
- Menstrual disorder Fertility, infertility
- Endometriosis and the Allied States
- Genital injuries and fistulae
- Genital infections
- Genital prolapse
- Tumors
- Carcinoma
- Radiotherapy in gynecology
- Chemotherapy in gynecology
- Endoscopy
- Diseases of breast
- Operative gynecology
COMMUNITY MEDICINE
- Evaluation of Public Health and Concepts of Health
- Environment and Health Health Education
- Nutrition and Dietetics
- Occupational Health
- Medical Sociology and Community Mental Health
- Fundamentals of Biostatistics
- Basic Epidemiology
- Epidemiology of Specific Diseases
- Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases
- Demography Reproductive and Child Health
- School Health
- Urban Health
- Health System in India
- Health Planning and Management including Disaster Management
- International Health
FMGE 2024 Result
- The FMGE January 2024 exam result was most probably declared by 20th February 2024 and can be seen on the website, natboard.edu.in.
- An applicant will only be considered to have passed the FMGE if they score at least 150 out of 300. The result of the FMGE 2023 exam is indicated as Pass/Fail.
- Any question from the FMGE Examination may be challenged for any technical inaccuracies using relevant medical literature within five calendar days after the examination’s conclusion but before the results are announced.
- Only genuine applicants who took the exam using their registered email address from the NBEMS Communication Web Portal are eligible to submit such a challenge.
- There won’t be any Re-examination, verification, or re-totaling.
- The applicants must login with their User ID and Password to download their score card.
- The “in-person” verification of credentials, including finger biometrics and Face ID, is required for qualified candidates. After the results are announced, a distribution schedule for FMGE PASS certificates will be posted on the NBEMS website.
- The admission slip for collecting the PASS certificate must include information about the papers that must be brought for “in-person” verification.
- After in-person document and identification verification, qualified applicants will get Pass Certificates. This process is expected to take four weeks after the results are announced, but it may take longer or shorter depending on the situation.
- The National Medical Commission and all State Medical Councils get a signed office copy of the FMGE results to verify that the FMGE Pass Certificates given to qualifying applicants by NBEMS are accurate.
MRCOG (Member of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists) is an RCOG membership examination, which is globally recognized as the gold standard qualification in the obstetrics & gynecology specialty. An aspirant needs to go through a three-part assessment to complete the MRCOG membership exam.
MRCOG Part 1
MRCOG Part 1 is the first stage of the RCOG’s membership exam. The aim of this part is basically to assess the understanding of a medico in the basic and clinical sciences relevant to Obstetrics and Gynecology.
MRCOG Part 1 Exam Pattern
- MRCOG Part 1 comprises two papers, SBA paper 1 and SBA paper 2.
- Both are Computer-based tests (CBT).
- Each paper is of 100 questions with a single best response (SBAs).
- Each paper receives the same number of points, so paper 1 receives 50% of the total, and paper 2 also counts for 50% of the total marks.
- There is no minimum score requirement for both papers.
- A candidate’s overall (combined) mark is the only factor in determining their outcome.
Timetable of MRCOG Part 1
| SBA Paper 1 and SBA Paper 2 | |
| Particulars | Description |
| Duration | 2.5 hours (150 minutes) for each paper |
| Number of questions | 100 SBAs for each paper |
| Lunch break (approximately one hour) between both the papers | |
Steps to remember
- Create online RCOG account.
- Get your eligibility checked by emailing the application form.
- After getting eligibility approval, complete an ‘Expression of Interest form’.
- Check the exam timetable and book your exam country slot and pay the exam fee.
- Book Pearson VUE slot.
How to Apply?
Eligibility for MRCOG Part 1
- After obtaining an undergraduate medical degree, the candidate becomes eligible for the MRCOG Part 1 exam.
- Postgraduate training is not required to appear for the part 1 exam.
- Candidates applying for the first time will have to submit a complete eligibility application form and get it approved.
- No more than 6 attempts are allowed for both parts 1 and 2.
Eligibility approval and application submission
- To get the eligibility approval, an aspirant needs to first write an email.
- Mention the subject line as “Part 1 Eligibility Assessment Application (enter your college number)”.
- Attach the application form available in the “Part 1 MRCOG Eligibility application form” section on the official website.
- Also, attach a scan or photo of your original primary medical degree certificate or, if your medical degree certificate does not list your primary medical degree and university, then attach a scan or photo of your medical registration certificate.
- Email at part1eligibility@rcog.org.uk with your submission. Following that, an automated response describing what to do next will appear.
- Make sure your application is complete and all the mentioned details are correct.
- If a candidate is re-appearing for the exam so, they must have got their eligibility approved on the first attempt, and hence, they can directly book an exam, and complete the Expression of Interest form.
Medical Degree Certificate
You must affix a copy of your degree certificate or a medical registration certificate, which attests to your primary medical qualification and university if you are not GMC-registered. You do not have to send a copy of your medical degree certificate if you are GMC-registered. Your medical degree certificate must be in English.
It takes around 4 weeks to process your Part 1 Eligibility application following the advertised closing date. If accepted, you’ll be able to reserve a spot on the Part 1 MRCOG exam.
How to book MRCOG Part 1 exam?
- Expression of Interest Form
- You need to submit an Expression of Interest form within the stipulated time, available on the official website. It’s only afterwards that you will be able to book an exam when the window opens.
- While filling out the Expression of Interest form, it is the responsibility of a candidate to confirm that the email address and College account number they have filled in on this form are accurate and correspond to the information on their individual RCOG accounts. You will not be able to reserve a spot on the following exam if any of the information you enter in this form does not comply with this requirement.
- After submitting the form, the candidate will see a confirmation screen on their web browser. It is advised to take a screenshot of this confirmation screen for records. Please be aware that email confirmation will not be sent by the RCOG for submitting the form.
- When the application window opens, the eligible candidates will receive an email along with instructions to book an exam place at available Pearson VUE test centres.
- Exam Calendar
The MRCOG Part 1 exam is conducted twice a year, one in the month of January (was held on 16th January 2024) and the other in the month of July (to be held on 2nd July 2024).
a. MRCOG Part 1 Exam calendar for January
| Opening Date for Booking window application | 14 November 2023, (Tuesday) |
| Closing Date for Booking window application | 14 December 2023, (Thursday) |
| MRCOG Part 1 Exam Date | 16 January 2024, (Tuesday) |
| Result Declaration | 13 February 2024, (Tuesday) |
b. Exam Calendar for the Upcoming MRCOG Part 1 Exam in July 2024
| Part 1 Eligibility Approval Deadline | 15 March 2024, (Friday) |
| Closing Date for Expression of Interest form | 29 March 2024, (Friday) |
| Opening Date for Booking window application | 23 April 2024, (Tuesday) |
| Closing Date for Booking window application | 30 May 2024, (Thursday) |
| MRCOG Part 1 Exam Date | 2 July 2024, (Tuesday) |
| Result Declaration | 31 July 2024, (Wednesday) |
MRCOG Part 1 Examination Fee
| Location | Fees (2024) |
| UK and Republic of Ireland | £534 |
| Band A | £644 |
| Band B (India comes under this category) | £555 |
| Band C | £443 |
Points to Note for the fee structure:
- India comes under B and B. Thus, the fee for the candidates having exam centres in India is £544 which is equivalent to INR 49,583.15. The amount in the Indian currency varies as per the currency change.
- Payments are linked to the country’s bandings of international membership fees.
- Banding applies to the center where you take the exam, not the candidate’s country of residence.
- You can check out on the official website that in which band your exam centre country falls under.
- Search and book the country location
- Applicants who have accepted eligibility and submitted an Expression of Interest will receive a Booking token.
- Reservation ID does not guarantee a place for the next exam, but the possibility to reserve free places when the reservation window opens.
- At this stage, candidates have the option to book an exam from a country that is available at the time of booking.
- Book Pearson VUE centre
After booking a country location, candidates will be contacted to book an exam slot at one of Pearson VUE’s test centres in the country which you have chosen and paid for.
MRCOG Pass Marks
- The standard setting is done to ensure fair examination and to accurately determine the candidate’s performance. The pass marks and the pass rate vary from exam sitting to exam sitting as there is no fixed level or quota.
- For Part 1 MRCOG, Ebel’s Method is used for the standard setting.
- This approach considers the level of difficulty and the question’s applicability to ST3 practice.
- Ebel’s research focuses on estimating the percentage of questionable candidates who would properly answer each exam question.
- Ebel’s method divides problems into nine different categories by classifying them as easy, medium, or hard, and by classifying their relevance as essential, important or acceptable. The standard-setting panel then determines what proportion of questions from each category they feel a borderline applicant would correctly respond to.
- The borderline candidate is a fictitious test taker who is of average intelligence, has a fair bit of clinical knowledge, and has made a respectable amount of preparation. This candidate should be just at the right level to pass.
How long should you wait to take the following MRCOG Part?
- Candidates who passed the Part 1 MRCOG after March 2013 must retake the exam within seven years after the Part 2 MRCOG exam date.
- The seven-year period is pro rata. This indicates that for trainees enrolled in less than full-time training or who take a break from training, the 7-year duration is proportionally extended, up to a maximum of 10 years.
- Candidates who passed Part 1 of the MRCOG in March 2013 or earlier must sit for Part 2 of the MRCOG within ten years of passing Part 1.
- Candidates who complete MRCOG Part 2 must take Part 3 of the MRCOG within seven years (prorated) of the Part 2 exam date.
- It is possible to take the MRCOG Part 1 before beginning UK specialist training.
- The MRCOG Part 2 must be taken within 10 years of the exam date when the candidate passed Part 1 MRCOG, if they do not desire to be included in the UK Specialist Register.
- There is no time limit on how frequently applicants may retake Part 2 or Part 3 MRCOG if they do not want to be added to the UK Specialist Register.
Preparation Tips:
- An aspirant must practice with a range of revision resources available in the support material section on the official website.
- All the aspirants are also advised to register with RCOG college to get access to a lot of benefits to support their preparation.
- You can enroll in the online MRCOG preparation courses by top faculty.
- Time management and an effective preparation strategy are must.
NEET UG is a single window entrance examination for admission to undergraduate medical courses (MBBS, BDS, BAMS, BSMS, BUMS, and BAMS courses) in all medical institutions, including government or private colleges and universities.
Since 2020, admission to AIIMS and JIPMER for MBBS/BDS courses is also done through the NEET UG exam. In 2022, approximately 18.7 lakh aspirants were registered for NEET UG entrance examination. All nationalities are eligible to participate in NEET (UG)-2024, including Indians, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), and Foreign Nationals.
NEET UG 2024 Conducting Body
National Testing Agency (NTA) is a conducting body for the NEET UG entrance examination since 2019. To determine a candidate’s aptitude for admission to prestigious higher education institutions, NTA, a top testing organization, conducts effective, transparent, and standard examinations.
Important Dates
| Particulars | Date |
| NEET UG 2024 Application Form Release Date | 09 February 2024 |
| Last Date to Submit Online Application Form | 10 April 2024 (up to 09:00 PM) |
| Last Date of successful transaction of fee | 10 April 2024 (up to 11:50 PM) |
| NEET UG 2024 Admit Card Release Date | 01 May 2024 |
| NEET UG 2024 Exam Date and Timing | 05 May 2024, 02:00 PM to 05:20 PM (IST) |
| NEET UG 2024 Result Date | 14 June 2024 |
NEET UG 2024 Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility Criteria for MBBS and BDS Course
- Candidate must have completed the age of 17 at the time of admission or will attain that age on or before 31 December of the admission year to the first year of the UG medical course.
- To enroll in undergraduate medical programs at a foreign medical or dental institutes, Indian citizens, and Overseas Citizens of India (OCI) candidates must also pass the NEET (UG) exam.
- Moreover, in order to qualify for NEET (UG) – 2024, the applicant must have earned at least 50% aggregate in Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English in addition to passing in each of these subjects separately. For admission to undergraduate medical programmes, they to have a rank on the NEET (UG)-2022 merit list.
- For candidates from Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes (NCL) or Unreserved and General-EWS, the minimum marks in the qualifying examination taken together for Physics, Chemistry, and Biology/Biotechnology shall be 40%.
- In addition to fulfilling the above mentioned eligibility criteria, NRI and OCI applicants must attach a Certificate from the relevant Indian Diplomatic Mission in the nation of their residency with their online NEET UG application form to confirm their claim that they are an NRI or OCI candidate and save the original proof of such document to present it when applying for admission to NEET-eligible courses at the time of counselling.
- In a similar vein, a foreign applicant for NEET (UG) 2024 must submit Documentary Proof in support of their nationality along with their online application form (for example, current passport or a certificate from the competent authority in their country regarding their citizenship status).
- OCI cardholders can only take up the admission against the availability of NRI seat or any supernumerary seat.
Common Services Centre/Facilitation Centres
As part of the Hon. Prime Minister’s Digital India efforts, candidates who are unable to submit their applications online owing to a variety of obstacles can use the services of the Common Services Centre by Government of India. The Common Services Center (CSC) programme is run at the village panchayat level by a village-level entrepreneur as part of the ambitious National e-Governance Plan (NeGP) of the Government of India (VLE).
They will assist applicants from urban and rural regions in submitting their application forms online and making payment using an e-wallet. The website www.csc.gov.in has a list of the Common Services Center. More than 1.5 lakh Common Services Centers (CSC) are located throughout the nation. The website www.csc.gov.in has a list of the Common Services Center.
NEET UG 2024 Application Form: Step by Step Procedure
Step 1: NEET UG 2024 Registration
- Applicants are required to sign up and register with the correct phone number and mail id. Signup for the Online Application Form and write down the Application Number that the system generates.
- The applicant must complete the registration with all necessary information. Moreover, select Security and generate a password.
- You are required to choose security question and enter an answer.
- An Application number will be produced upon the successful submission of the personal information; use it to complete the next steps of the application form and refer to it in any future contact.
- The applicant will be able to log in directly for subsequent times using the system-generated Application Number and Password they created.
Step 2: NEET UG 2024 Application form
- Candidates can log in using the system-generated Application Number and pre-created Password.
- Complete the application form, which includes filling out personal information, selecting the medium of the question paper and the examination cities, educational information and uploading pictures and applicable documents.
- The application form comprises of:
- Registration Page which includes personal details, present address, permanent address, password, security pin.
- Application page which includes, personal details, category, choice of exam city, educational details of class 10th, 12th, parent’s income details along with uploading the original and scanned documents.
- Fee payment page, which includes submitting the application form fee, which is the last procedure of successful submission of the application form.
- Candidates must download, save, and print a copy of confirmation Page of Application Form for the records (which will only be downloaded upon successful payment of fee).
List of Documents to be Uploaded while filling NEET UG 2024 Application Form
Candidates are required to upload the scanned images/documents of the below mentioned documents:
| Particulars | Size | Instructions | Format |
| Recent Passport size Photograph | 10 kb to 200 kb | The photograph can be coloured or black and white with white background and 80% of the face (without mask) must be visible including ears.
Spectacles are allowed only if used regularly. |
JPG format |
| Postcard size
Photograph (4”x6”) |
10 kb – 200 kb | (4”x6”) | JPG format |
| Signature | 4 kb to 30 kb | The signature must be done in running hand on white paper with a Black Ink pen. | JPG format |
| Left and Right hand Fingers and Thumb Impression | 10 kb to 200 kb | – | JPG format |
| Category
Certificate (if applicable) |
50 kb to 300 kb | – | PDF format |
| Citizenship Certificate (if applicable) | 50 kb to 300 kb | – | PDF format |
| PwD Certificate (wherever
applicable) |
50 kb to 300 kb | – | PDF format |
| Class 10th Pass Certificate | 50 kb to 300 kb | – | JPG format |
All the uploaded documents must be clearly legible.
Here’s a list of permissible IDs for Identity Proof:
| Category of Candidates | Types of permissible IDs |
| Indian Nationals of all States | Class 12 Admit Card, Election Card (EPIC No.), Ration Card, Bank Account Passbook with Photograph, Passport Number or Number of any other Photo Identity Card issued by Government. |
| NRIs | Passport Number |
| Foreign Nationals/OCI | Passport Number/Citizenship Certificate Number |
Step 3: Application Form Fee Payment
- The applicants must pay the required examination cost after finishing Step 1 and 2.
- Only Net Banking, Credit Card, Debit Card, UPI, or Paytm Services may be used to submit the fee online.
Below mentioned is the NEET UG 2024 application fee required to be submitted by all the candidates for the successful submission of their application form.
| Category of Candidate | Application Fee in India (in Rs.) | Application Fee outside India (in Rs.) |
| General | Rs. 1700 | Rs. 9500 |
| General-EWS/ OBC-NCL | Rs. 1600 | |
| SC/ST/PwBD/Third Gender | Rs. 1000 |
Processing Fee & GST are paid additionally as applicable.
- All applicants must verify that their email address and mobile number are accurate.
- Candidates are required to enter the OTP sent to their registered email address or phone number before submitting their payment.
- The online application form’s confirmation page won’t be created until the candidate has successfully made their payment.
- If the Confirmation Page is not created after fee payment, the applicant may need to contact the relevant Bank/Payment Gateway (at the helpline number/ email) to ensure the successful payment or to request a refund for duplicate or repeated payments.
NEET UG 2024 Examination and Marking Scheme
| Particulars | Description |
| Mode of Examination | Pen & Paper based test |
| Type of Questions | Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |
| Total number of marks | 720 |
| Total number of questions | 180 |
| Marking Scheme |
|
| Duration of the Exam | 03 hours and 20 minutes |
| Medium of the Question Paper | NEET UG exam can be attempted in any one of the following 13 languages: English, Hindi, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Malayalam, Marathi, Kannada, Odia, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Punjabi |
NEET UG 2024 Exam Pattern
The NEET UG 2023 exam paper comprises of 4 subjects, which additional has two sections. Section A comprise of 35 questions and section B comprise of 15 questions, out of which 10 are to be answered.
| S.No. | Subject | Section | Number of Questions | Marks (Each question carries 04 marks) | Type of questions |
| 1
|
Physics | Section A | 35 | 140 | MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) |
| Section B | 15 | 40 | |||
| 2 | Chemistry | Section A | 35 | 140 | |
| Section B | 15 | 40 | |||
| 3 | Botany | Section A | 35 | 140 | |
| Section B | 15 | 40 | |||
| 4 | Zoology | Section A | 35 | 140 | |
| Section B | 15 | 40 |
NEET UG 2024 Exam Centres
Candidates who want to appear for the NEET UG Entrance Examination can opt for the nearest examination city centre. While filling out the application form, candidates will get options for the cities (examination centres) from the respective state they choose. There are a total of 557 examination centres, from which 543 are in India and 14 are outside India. Be careful while opting for the medium/language of question paper. Once chosen while filling the application form, a candidate cannot change the option.
Apart from the examination centres across country, option of regional languages will be available at the following centres only:
| S. No. | Medium of Question Paper | Examination Centres |
| 1 | English | All Examination Centres |
| 2 | English and Hindi | All Examination Centres in India |
| 3 | English and Assamese | Examination Centres in Assam |
| 4 | English and Bengali | Examination Centres in West Bengal, Tripura,
and Andaman & Nicobar Islands |
| 5 | English and Gujarati | Examination Centres in Gujarat, Daman &
Diu and Dadra & Nagar Haveli |
| 6 | English and Kannada | Examination Centres in Karnataka |
| 7 | English and Malayalam | Examination Centres in Kerala and
Lakshadweep |
| 8 | English and Marathi | Examination Centres in Maharashtra |
| 9 | English and Odia | Examination Centres in Odisha |
| 10 | English and Punjabi | Examination Centres in Punjab, Chandigarh,
Delhi/New Delhi (including Faridabad, Ghaziabad, Gurugram, Meerut and Noida/Greater Noida) |
| 11 | English and Tamil | Examination Centres in Tamil Nadu,
Puducherry, and Andaman & Nicobar |
| 12 | English and Telugu | Examination Centres in Andhra Pradesh and
Telangana |
| 13 | English and Urdu | All Examination Centres in India |
Overseas candidates/Foreign National Candidates desirous to pursue undergraduate medical education in India can also opt for an International examination centre.
List of International Examination Centres for NEET UG 2024 Exam:
| S. No. | City Code | Country | City |
| 1 | 9901 | Kuwait | Kuwait City |
| 2 | 9902 | UAE | Dubai |
| 3 | 9903 | UAE | Abu Dhabi |
| 4 | 9904 | Thailand | Bangkok |
| 5 | 9905 | Sri Lanka | Colombo |
| 6 | 9906 | Qatar | Doha |
| 7 | 9907 | Nepal | Kathmandu |
| 8 | 9908 | Malaysia | Kuala Lumpur |
| 9 | 9909 | Nigeria | Lagos |
| 10 | 9910 | Bahrain | Manama |
| 11 | 9911 | Oman | Muscat |
| 12 | 9912 | Saudi Arabia | Riyadh |
| 13 | 9913 | UAE | Sharjah |
| 14 | 9914 | Singapore | Singapore |
NEET UG 2024 Exam Syllabus
The core subjects included in the NEET UG exam pattern are Physics, Chemistry and Biology of 11th and 12th standard.
Mentioned below is the syllabus for the NEET UG entrance examination:
Units from the Physics Subject:
| Physics Syllabus (Class 11th) | Physics Syllabus (Class 12th) |
|
|
Units from the Chemistry Subject:
| Chemistry Syllabus (Class 11th) | Chemistry Syllabus (Class 12th) |
|
|
Units from the Biology Subject:
| Biology Syllabus (Class 11th) | Biology Syllabus (Class 12th) |
|
|
Aspirants must start NEET exam preparation along with the 11th and 12th standard and make a strict NEET study plan to score well and secure a good rank in the entrance examination. It is also advised to solve NEET prep mock test.
NEET UG 2024 Admit Card
- Admit cards can be downloaded from the NTA website by logging in to the ‘Candidates Login’ page.
- Candidate must read all the instructions mentioned in the admit card carefully.
- The admit card includes all the details, such as exam date, timing, and centre.
- Candidate must check the exam centre and location prior to avoid any travelling issues later on the examination day.
- Candidates must affix the photograph on the space provided on the admit card.
- The following papers must be retained by candidates for future correspondence as references:
- Printouts of the online application’s confirmation page.
- Evidence of remittance (i.e., Bank transaction details supported by confirmation page). Candidates should be aware that a simple fee deduction from a bank account does not constitute proof of fee payment. The payment must be accompanied by an updated fee on the candidate’s account. The creation of the confirmation page serves as evidence that the application form was successfully submitted.
- A minimum of 4-6 identical passport-size and postcard-size photos that were scanned and uploaded for the online application.
- A copy of the self-declaration created by the system for candidates from the U.T. of J&K who have chosen seats under the 15% All India Quota.
Things to carry at the day of Examination
Candidates must carry the following documents at the day of examination:
- Printed copy of admit card with the passport size photograph affixed on it (photograph must be same as the one uploaded on the application form)
- Passport size photograph
- One coloured postcard size photograph (4” * 6”) with white background (to be pasted on proforma downloaded with the admit card).
- Any photo ID issued by government
- PwBD certificate, if applicable.
If any candidate is found indulged in the unfair practices, will be booked under UFM case and will be debarred for 3 years and shall also be liable for the criminal action.
Post Examination Activities and Result Declaration
Display of OMR sheets and responses on the website
After the exam, OMR Answer Sheets will be posted on the NTA website. Candidates will have the option to lodge an appeal against the OMR grade by paying a processing fee of Rs. 20 per question.
Display of Answer Sheets
Once the provisional NEET UG answer key is released, candidates will have the chance to dispute the provisional Answer Key online by paying a non-refundable processing fee of Rs.200 per answer challenged.
NEET UG 2024 Results
The result, score card and Merit List are released by NTA on the official website as per the qualifying criteria and other norms. NEET scorecard displays NEET UG cut-off marks, total marks scored, percentile, AIR, marks scored in each subject (PCB), AIQ Rank (All India Quota), and category rank.
Applicants are urged to keep a copy of their confirmation page, admit card, and score card for the NEET (UG) – 2024 exam because these documents may not be accessible online after a month or two of result declaration date.
Merit List and Qualifying Criteria
In accordance with the qualifying requirements established by the National Medical Commission and Dental Council of India, the National Testing Agency releases an All India Merit List of successful applicants for NEET (UG).
The minimum pass marks required in NEET UG for admission to UG Medical courses for the candidates belonging to:
- General and General EWS category: 50th percentile
- SC/ST/OBC: 40th percentile
- Candidates with Benchmark disabilities: 40th percentile
- SC/ST/OBC-NCL candidates: 40th percentile
The highest score obtained in the NEET UG All India Common Merit List will be used to calculate the percentile for admission to Undergraduate Medical Courses.
NEET UG Cut Off 2024
NEET cut off is the minimum score required by the candidate to successfully qualify the entrance examination to get admission into the medical colleges.
Mentioned below are the cut off range of the previous years’ which will provide the aspirants an idea for NEET UG 2023 cut-off range:
NEET UG Cut off 2022
| Category | Marks Range | Qualifying Criteria |
| UR/EWS | 715-117 | 50th Percentile |
| OBC/SC/ST | 116-93 | 40th Percentile |
| UR/EWS & PH | 116-105 | 45th Percentile |
| OBC/SC/ST & PH | 104-93 | 40th Percentile |
NEET UG Cut off 2021
| Category | Marks Range | Qualifying Criteria |
| UR/EWS | 720-138 | 50th Percentile |
| OBC/SC/ST | 137-108 | 40th Percentile |
| UR/EWS & PwD | 137-122 | 45th Percentile |
| OBC/SC/ST & PwD | 121-108 | 40th Percentile |
Counselling Procedure for NEET UG 2024
Counselling session is conducted by Medical Counselling Committee (MCC). The seats available under the following quotas:
- All India Quota Seats
- State Government Quota Seats
- Central Institutions/Universities/Deemed Universities
- State/Management/NRI Quota Seats in Private Medical/Dental Colleges or any
- Private University
- Central Pool Quota Seats
- All seats including NRI Quota as well as Management Quota, are in private unaided/aided minority/non-minority medical colleges
- AIIMS Institutes across India/JIPMER
In case of admission to AFMC College, MCC just completes the AFMC registration process and provides the AFMC Authorities with the information of registered candidates for the admissions procedure. The score may be used by DU/BHU and other universities for any further pertinent courses they offer.
Click here to know about the complete admission procedure for MBBS at AFMC, Pune.
Reservation Policy for admission to MBBS and BDS Course
The categories and extent of reservation are as follows:
| Category | Percentage of Reservation |
| General Category belonging to Economically Weaker Section (GEN-EWS) | 10% of seats in every course. |
| Other Backward Classes belonging to the Non-Creamy Layer (OBC- NCL) | 27% of seats in every course. |
| Scheduled Caste (SC) | 15% of seats in every course. |
| Scheduled Tribe (ST) | 7.5% of seats in every course. |
| Persons with Disability (PwD) | 5% seats in each of OPEN, GEN-EWS, OBC-NCL, SC, and ST category seats. |
Merit List in case of tie-breaking situations:
If two or more candidates obtain equal marks/percentile scores in the NEET UG, then the inter-se-merit is determined as follows:
- Candidate with higher marks/percentile in Biology subject in the entrance exam, followed by,
- Candidate who achieved higher scores/percentile in chemistry, followed by,
- Candidate with higher physics score/percentile, followed by
- Candidate with a lower percentage of attempted incorrect answers and correct answers across all test participants, followed by
- Candidate with a lower percentage of attempted incorrect responses to correct answers in Biology section in the exam, followed by
- Candidate with a lower percentage of attempted incorrect responses to correct answers in Chemistry in the exam, followed by
- Candidate with a lower percentage of attempted incorrect responses to correct answers in Physics in the exam, followed by
- Candidate Older in Age, followed by
- Application Number in ascending order
For the updates, applicants must often check the https://neet.nta.nic.in/, www.MoH&FW.gov.in & www.mcc.nic.in websites for MBBS/BDS Courses, and https://neet.nta.nic.in/, www.ayush.gov.in & www.aaccc.gov.in for BAMS/BSMS/BUMS/BHMS Courses.
The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test for Post-Graduation is a qualifying and ranking test in India for candidates interested in doing MD, MS, or PG Diploma. This year’s NEET PG Exam is scheduled for 23rd June’24.
Let’s go into the eligibility, Application fee updates, marking scheme, and other details.
NEET PG 2024 Eligibility Criteria:
- According to the Indian Medical Council Act 1956, the candidates are required to have an MBBS degree or a Provisional MBBS Pass Certificate.
- Candidates must have a permanent or provisional MCI or SMC-issued MBBS qualification registration.
- The candidates must have completed a year of internship before applying.
Application and Fees:
As per the NEET PG 2024 fees have been reduced, and the General and OBC applicants must pay Rs. 3,500 to fill out the NEET PG application form, while SC/ST/PWD candidates must pay Rs. 2,500.
Duration:
The exam will be 3.5 hours long.
Exam Format:
The exam will be computer-based and administered at the designated locations.
Test Pattern & Marks:
14 subjects are classified under 3 parts in the paper:
Part A – Pre-clinical subjects
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Biochemistry
Part B – Para-clinical subjects
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Forensic medicine
- Social & preventive medicine
Part C – Clinical subjects
- General medicine including
- Dermatology & venereology
- Psychiatry
- General surgery including
- Orthopedics, anaesthesia & radiodiagnosis
- Obstetrics & gynecology
- Pediatrics
- ENT
- Ophthalmology
Marking scheme:
Incorrect answers will incur a penalty of 25% through negative marking. No deductions will be made for questions left unanswered.
- +4 marks for correct response
- -1 for incorrect response
- No marks for unattempted question
Important Dates: NBEMS has published the official exam calendar having dates of NEET PG 2024.
| Events | Dates |
| NEET PG 2024 Application form release | 16-April-2024 |
| Last Date to submit an application | 6-May-2024 |
| Cut-off Release | 15-Aug-2024 |
| NEET PG 2024, Exam Date | 23-June-2024 |
| Result Declaration | 15-July-2024 |
Note: Candidates should be aware that admit cards will not be provided to those who are found ineligible before the examination.
How to prepare for NEET PG 2024?
It’s time for you to make the most of the preparation period. Revise as much as you can. Whatever you’ve studied to date, it’s now time to test yourself and prepare for the bigger one. Always keep in mind that your perspective defines your reality.
Here are the 7 Tips to crack NEET PG 2024:
- Create and Stick by a Plan: Decide for the next day before you go to bed and stick to it no matter what. Wake up and stick to your plan so you’re prepared and don’t waste time deciding what to study.
- Prioritize the subjects where you need conceptual clarity: Focus on conceptual clarity with the help of trusted content only. Finding the right content can be a hassle so choose DigiNerve, an app by Jaypee Brothers who have published most of your textbooks. This online app provides video lectures by India’s top faculty which include your textbook authors.
- Revision and MCQs: The more you revise, the better; devote the first two months to clarifying concepts of the topics you’re having trouble with, and the last month to solving MCQs.
- Question papers from previous years: This will assist you in comprehending the NEET PG Exam structure and identifying essential topics that may appear in the exam.
- Notes: You probably have read everything, and you have the knowledge so now the only thing left is to go through your notes, it will help you recall important points.
- ITD method: Memorize with the help of the ITD Method- Importance of the topic, Time consumption, and Detailing.
- Enroll for Mock Tests: Attending mock tests will help you assess your knowledge. This will help you know the subjects where you need clarity. On its official website, the NBE publishes practice tests. One of the most important components of the exam preparation approach is the mock test. You must conduct mock tests after concluding their revision to assess their preparation. You will get to learn what else must be done to increase a particular topic’s score. To access the sample test, you must first log in to the NBE’s official website. Before beginning the online mock test, candidates should carefully read all the instructions. Recalibrate your strategy by taking a mock test and weighing your results.
To prepare for NEET PG 2024, subscribe to DigiNerve’s courses by India’s top faculty today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. When will NEET PG be in 2024?
Ans. The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test-Postgraduate (NEET PG 2024) will now be held on June 23, 2024.
Q2. Is PG necessary after MBBS?
Ans. For doctors to be successful in their specialties, they must have a postgraduate degree in medicine.
Q3. How do I pay the fees for NEET PG 2024?
Ans. Fees can be paid using a debit/credit card or a net banking service. Candidates should print the confirmation page after successfully paying the application fees.
INI-CET is the Institute of National Importance-Combined Entrance Test. It is a combined medical entrance examination conducted for admission to PG courses [MD, MS, DM (6 yrs), MCh (6 yrs) & MDS] at INI institutes.
INI-CET typically assesses candidates’ knowledge, skills, and competencies in the medical field, and it includes multiple-choice questions (MCQs) on subjects included in the undergraduate medical programme.
The INI-CET 2024 exam date for the July session is 19th May 2024.
INI-CET 2024: List of Participating Institutes
The list of participating institutes for the INI-CET July 2024 Session is as follows:
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi
- AIIMS, Bhopal
- AIIMS, Bhubaneshwar
- AIIMS, Jodhpur
- AIIMS, Nagpur
- AIIMS, Patna
- AIIMS, Raipur
- AIIMS, Rishikesh
- AIIMS, Bibinagar
- AIIMS, Bhatinda
- AIIMS, Deoghar
- AIIMS, Mangalagiri
- AIIMS, Raebareli
- AIIMS, Kalyani
- AIIMS, Bilaspur
- AIIMS, Gorakhpur
- AIIMS, Guwahati
- Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry
- National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bengaluru
- Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh
- Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), Trivandrum
INI-CET 2024: Eligibility Criteria
To be eligible to sit in the INI-CET, an applicant must be an Indian National (IN), an Overseas Citizen of India (OCI), or a Foreign National under the permitted categories but the eligibility criteria vary.
The general eligibility criteria to appear for the INI-CET 2024 exam are as follows:
1. Eligibility Criteria for Indian Nationals
Indian Nationals include the candidates who are citizens of India.
a. The prime eligibility qualification for admission to PG courses at INIs is an MBBS degree from an NMC/MCI-recognised medical college and one must have completed 12 months of compulsory rotatory internship/practical training on or before 31st January 2024.
Minimum Aggregate Marks:
- General/OBC/EWS candidates must have a minimum of 55% aggregate in MBBS/BDS to appear for INI-CET whereas SC/ST candidates must have a minimum of 50% marks in aggregate.
- The minimum aggregate required for PwBD candidates depends on the category they fall into, say, 55% aggregate marks if they belong to GEN/OBC/EWS and 50% aggregate marks if they belong to SC/ST.
Make sure to consider the aggregate of all the professional MBBS/BDS exams to calculate the minimum eligibility aggregate required. In the case of supplementary exams, consider only the marks obtained for successful completion.
b. Sponsored candidates: In addition to the above criteria mentioned, sponsored candidates are required to upload a sponsored certificate during the application procedure and submit the original document at the time of admission.
c. For Indian Nationals who have graduated from foreign universities, the marks obtained in FMGE conducted by NBE will be considered in place of aggregate marks, in addition to the general eligibility criteria mentioned above.
Candidates are not eligible to apply for seats under both Indian National and Foreign National categories.
The eligibility criteria for admission to PG courses in different INIs may vary.
2. Eligibility Criteria for Foreign Nationals
Foreign Nationals include the candidates who are not citizens of India.
Candidate must have completed their MBBS degree for admission to MD/MS/DM(6yrs)/MCh(6yrs) and BDS for admission to MDS course along with the successful completion of 12 months of rotational internship/practical training.
Foreign Nationals desirous to appear for INI-CET are required to calculate the aggregate according to the grading system of the applicable university/institution and hence, they must obtain a grading system certificate from the applicable university/institute. Then accordingly fill in the “Marks Column” for completion of the Application Form for INI-CET July session 2024.
Minimum Aggregate Marks: To be eligible for INI-CET, the minimum marks in aggregate in all the professional exams of MBBS/BDS must be 55% aggregate or equivalent.
No Objection Certificate (NOC) Foreign National must be obtained from the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Govt. of India, and should be submitted to the Examination Section on or before the last date.
For the 2024 session, the Last date of receiving the application form duly recommended & forwarded with “No Objection Certificate” from the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Govt. of India for Foreign Nationals to apply and appear in the INI-CET for PG courses –July 2024 session is 17th May 2024.
Candidates would only be eligible for open category (unreserved) seats for Indian Nationals if they were born before 04.03.2021 and have obtained their OCI card before 04.03.2021. They will not be taken into account for seats reserved for foreigners.
According to the ruling of the Hon’ble Supreme Court of India in Writ Petition (Civil) 891 / 2021 dated February 03, 2023, OCI/PIO card holders who are not to be treated as Indian Nationals should be deemed considered Foreign Nationals. They will not be considered for seats reserved for Indian citizens.
It is highly advised to check your eligibility for the INI-CET exam and submit the relevant documents on time to avoid the cancellation of the application form.
Being aware of the process flow is crucial so that you don’t miss out on any step and to ease out the INI-CET journey, the process flow map is provided in this blog.
INI-CET 2024: Process Map
The INI-CET 2024 admission process steps are categorized into three phases:
Phase I: Application Procedure
It includes the registration procedures & basic candidate information, generation of EUC, followed by completion of the application.
While filling out the application form, make sure to upload the necessary documents and the earliest issued valid OCI card(if applicable) on the portal. The required documents vary depending on your nationality and category.
Phase II: Examination
The examination phase includes the release of admit card, a computer-based test followed by result declaration, and filling of college choice and order preference for counselling.
Phase III: Seat Allocation
This phase includes counselling procedures for all the rounds, say the Mock round, 1st round, and 2nd round. In addition to these, depending upon the requirements, additional rounds, open rounds, and spot rounds are also conducted.
INI-CET is a challenging exam but is worth every effort you make to get admission into your dream medical college.
The Institute of National Importance Super Speciality (INI-SS) stands as a beacon of excellence in medical education within India. Renowned for its top-notch programs, AIIMS hosts this prestigious INI Super Speciality (SS) entrance exam annually. This exam is the gateway to exclusive medical courses offered by esteemed institutions like AIIMS in New Delhi and other Institutes of National Importance across the country.
As we approach the INI-SS Exam 2024, medical professionals and aspiring doctors are eagerly gearing up to highlight their skills and knowledge. This exam holds immense significance, paving the way for individuals to pursue a specialisation in medical courses such as DM/M.Ch./MD Hospital Administration.
Here is a list of institutions that participate in the INI-SS exam:
1. AIIMS, New Delhi
2. AIIMS, Bhopal
3. AIIMS, Bhubaneswar
4. AIIMS, Jodhpur
5. AIIMS, Patna
6. AIIMS, Raipur
7. AIIMS, Rishikesh
8. AIIMS, Bhatinda
9. AIIMS, Nagpur
10. AIIMS, Bilaspur
11. AIIMS, Mangalagiri
12. AIIMS, Rajkot
13. AIIMS, Gorakhpur
14. AIIMS, Bibinagar
15. JIPMER, Puducherry
16. NIMHANS, Bengaluru
17. PGIMER, Chandigarh
18. SCTIMST, Kerala
Eligibility Criteria for DM Courses
| S. No. | Course Type | Participating Institutes | Educational Qualification |
| 1. | DM – ADDICTION PSYCHIATRY | AIIMS |
MD/DNB in Psychiatry
|
| PGIMER | |||
| NIMHANS | |||
| 2. | DM – CARDIAC SURGICAL INTENSIVE CARE | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Anaesthesia/Pediatrics/Medicine |
| 3. | DM – CARDIAC-ANAESTHESIOLOGY/DM -CARDIOTHORACIC& VASCULAR ANAESTHESIA/CARDIAC ANAESTHESIA & INTENSIVE CARE | AIIMS |
MD/DNB in Anaesthesiology |
| PGIMER | |||
| NIMHANS | |||
| JIPMER | |||
| 4. | DM – CARDIOLOGY | AIIMS |
MD/DNB in Medicine/Pediatrics |
| SCTIMST | |||
| PGIMER | |||
| JIPMER | MD/DNB in General Medicine/Pediatrics/Pulmonary Medicine | ||
| 5. | DM – CLINICAL HEMATOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Medicine/Pediatrics
|
| PGIMER | MD in Medicine or equivalent | ||
| 6. | DM – CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Medicine/Pharmacology/Pediatrics
|
| PGIMER | MD in Pharmacology or equivalent
|
||
| JIPMER | MD/DNB in General Medicine/Pharmacology/Pediatrics | ||
| 7. | DM – CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE/CRITICAL CARE/DM-INTENSIVE CARE | AIIMS | MD in Anaesthesiology/Medicine/Chest Medicine
|
| JIPMER | MD in Anaesthesiology/General Medicine/Pulmonary Medicine
|
||
| PGIMER | MD in Anaesthesia/Internal Medicine | ||
| 8. | DM -ENDOCRINOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Medicine/Pediatrics |
| JIPMER | |||
| PGIMER | MD in Medicine or equivalent | ||
| 9. | DM -GASTROENTEROLOGY/MEDICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY | AIIMS | MD/ DNB in Medicine |
| PGIMER | MD in Medicine or equivalent | ||
| JIPMER | MD/ DNB in General Medicine /Pediatrics | ||
| 10. | DM -HEMATOPATHOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Pathology/Lab. Medicine |
| PGIMER | MD in Pathology or equivalent | ||
| 11. | DM – INFECTIOUS DISEASES/CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Medicine/Pediatrics/Microbiology/Tropical Medicine |
| AIIMS (Raipur) | M.D/DNB in Medicine/Pediatrics /Tropical Medicine | ||
| 12. | DM – MEDICAL GENETICS | AIIMS | MD in Pediatrics/Medicine/Obstetrics and Gynecology
|
| PGIMER | MD in Pediatrics or equivalent | ||
| 13.
|
DM – MEDICAL ONCOLOGY
|
AIIMS | MD/DNB in Medicine/Pediatrics |
| PGIMER | |||
| JIPMER | MD/DNB in Medicine / Pediatrics /Radiotherapy | ||
| 14. | DM – NEONATOLOGY | AIIMS |
MD in Pediatrics |
| PGIMER | |||
| JIPMER | |||
| 15. | DM-NEPHROLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Medicine/Pediatrics |
| JIPMER | |||
| PGIMER | MD in Medicine or equivalent | ||
| 16. | DM – PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY | AIIMS | MD in Pediatrics |
| PGIMER | |||
| SCTIMST | |||
| 17. | DM – PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY & INTENSIVE CARE | AIIMS | MD in Pediatrics |
| 18.
|
DM – NEURO-ANAESTHESIOLOGY & CRITICAL CARE/DM-NEURO ANAESTHESIA/NEURO ANAESTHESIA AND NEUROCRITICAL CARE
|
AIIMS |
MD/DNB in Anaesthesiology |
| PGIMER | |||
| SCTIMST | |||
| NIMHANS | |||
| JIPMER | |||
| 19. | DM-NEUROLOGY | AIIMS |
MD in General Medicine/Pediatrics |
| JIPMER | |||
| SCTIMST | |||
| NIMHANS | M.D./DNB in Internal (General) Medicine/Pediatrics | ||
| PGIMER | MD in Medicine or equivalent | ||
| 20. | DM – NEUROIMAGING AND INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY/NEUROIMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS | AIIMS |
MD/DNB in Radiodiagnosis |
| NIMHANS | |||
| JIPMER | |||
| PGIMER | MD/DNB in Radiology or equivalent | ||
| SCTIMST | MD/DNB in Radiodiagnosis/Radiology | ||
| 21. | DM – ONCO -ANAESTHESIA | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Anaesthesiology |
| 22. | DM – PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Pediatrics |
| PGIMER | |||
| 23. | DM – PULMONARY CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | AIIMS | MD in Medicine/Pulmonary Medicine/Chest Medicine/Respiratory Medicine
|
| PGIMER | MD in Medicine/Respiratory Diseases or equivalent | ||
| 24. | DM – REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE | AIIMS | MD/MS in Obstetrics and Gynecology |
| 25. | DM – THERAPEUTIC NUCLEAR MEDICINE | AIIMS | MD in Nuclear Medicine |
| 26. | DM -CARDIOVASCULAR RADIOLOGY & ENDOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS/DM- CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING AND VASCULAR INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY | AIIMS | MD /DNB in Radio-Diagnosis or equivalent degree |
| PGIMER | |||
| SCTIMST | MD /DNB in Radio-Diagnosis/Radiology | ||
| 27. | DM – PEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY | AIIMS | MD in Pediatrics |
| 28.
|
DM – CHILD AND ADOLESCENT PSYCHIATRY
|
PGIMER | MD/DNB in Psychiatry or equivalent |
| NIMHANS | |||
| 29. | DM – CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY & RHEUMATOLOGY | AIIMS | MD in Medicine/Pediatrics
|
| PGIMER | MD in Medicine or equivalent | ||
| JIPMER | MD/DNB in General Medicine/Pediatrics | ||
| 30. | DM – PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY & HEPATOLOGY/PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Pediatrics or equivalent |
| JIPMER | |||
| 31. | DM – HEPATOLOGY | PGIMER | MD in Medicine/Pediatrics or equivalent |
| 32. | DM -HISTOPATHOLOGY | PGIMER | MD in Pathology or equivalent |
| 33. | DM – PEDIATRIC CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY | PGIMER | MD in Pediatrics or equivalent |
| 34. | DM – PEDIATRICS CRITICAL CARE | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Pediatrics or equivalent |
| PGIMER | |||
| JIPMER | |||
| 35. | DM – PEDIATRIC HAEMATOLOGY -ONCOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Pediatrics or equivalent |
| PGIMER | |||
| 36. | DM – PEDIATRIC ENDOCRINOLOGY | AIIMS | MD in Pediatrics or equivalent |
| PGIMER | |||
| 37. | DM – TRAUMA ANAESTHESIA & ACUTE CARE | PGIMER | MD in Anaesthesia or equivalent |
| 38. | DM – PEDIATRIC ANAESTHESIA & INTENSIVE CARE | PGIMER | MD in Anaesthesia or equivalent |
| 39. | DM – ACUTE CARE-EMERGENCY MEDICINE | PGIMER | MD in Internal Medicine/General Medicine/ Emergency Medicine or Equivalent |
| 40. | DM – PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY | AIIMS | MD in Pediatrics or equivalent |
| PGIMER | |||
| 41. | DM -NEUROPATHOLOGY | NIMHANS | MD/DNB in Pathology |
| 42. | DM – FORENSIC PSYCHIATRY | NIMHANS | MD/DNB in Psychiatry |
| 43. | DM – GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY | NIMHANS | MD/DNB in Psychiatry |
| 44. | DM -INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY | AIIMS | MD in Interventional Radiology
|
| PGIMER | MD/DNB in Radio-diagnosis or equivalent | ||
| 45. | DM – PAIN MEDICINE | AIIMS | MD in Anaesthesiology or equivalent |
| 46. | DM – METABOLISM MEDICINE | AIIMS | MD in Biochemistry/Medicine/Pediatrics/Internal Medicine |
| 47. | DM – HOSPITAL MEDICINE & CRITICAL CARE | AIIMS | MD in Internal Medicine/Geriatric Medicine |
| 48. | DM – MEDICAL AND FORENSIC TOXICOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Forensic Medicine or Forensic Medicine & Toxicology/Pharmacology/Emergency Medicine/Internal/General
Medicine/Pediatrics |
| 49. | DM – PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Pediatrics or Emergency Medicine |
| 50. | DM – FORENSIC PATHOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Forensic Medicine/Forensic Medicine and Toxicology |
| 51. | DM – FORENSIC RADIOLOGY & VIRTUAL AUTOPSY | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Forensic Medicine/Forensic Medicine and Toxicology |
| 52. | DM – HIGH ALTITUDE MEDICINE | AIIMS | MD/DNB in Internal Medicine/Physiology/Anaesthesia/Community Medicine |
Eligibility Criteria for M.Ch. Courses
| S.No. | Course Type | Participating Institutes | Educational Qualification |
| 1. | M.Ch. – BREAST, ENDOCRINE AND GENERAL SURGERY | AIIMS | MS in Surgery |
| 2. | M.Ch. – CTVS/CVTS* | AIIMS | MS/DNB in Surgery/General Surgery |
| PGIMER | |||
| JIPMER | |||
| SCTIMST* | |||
| 3. | M.Ch. – G.I. SURGERY/SURGICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY | AIIMS | MS in Surgery/General Surgery |
| JIPMER | |||
| PGIMER | |||
| 4. | M.Ch. – GYNECOLOGIC ONCOLOGY | AIIMS | MD/MS in Obstetrics & Gynecology |
| JIPMER | |||
| 5. | M.Ch. – HEAD-NECK SURGERY AND ONCOLOGY/HEAD & NECK SURGERY* | AIIMS | MS in Surgery/ENT |
| PGIMER* | |||
| 6. | M.Ch. – MINIMAL ACCESS SURGERY & GENERAL SURGERY | AIIMS | MS in Surgery |
| 7. | M.Ch. – NEURO-SURGERY | AIIMS | MS/DNB in Surgery |
| PGIMER | |||
| NIMHANS | MS/DNB in General Surgery | ||
| JIPMER | |||
| SCTIMST | |||
| 8. | M. Ch. – PEDIATRIC SURGERY | AIIMS | MS in Surgery/General Surgery |
| JIPMER | |||
| PGIMER | |||
| 9. | M.Ch. – PLASTIC AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY/PLASTIC SURGERY | AIIMS | MS in Surgery/ENT/Orthopaedics |
| PGIMER | |||
| JIPMER | MS/DNB in General Surgery | ||
| 10. | M.Ch. – SURGICAL ONCOLOGY | AIIMS | MS in Surgery/ENT
|
| JIPMER | MS/DNB in General Surgery/Obstetrics & Gynecology/Otolaryngology (E.N.T)/ Orthopaedics Surgery | ||
| 11. | M.Ch. – TRAUMA SURGERY AND CRITICAL CARE | AIIMS | MS in Surgery/Trauma and Emergency Surgery |
| 12. | M.Ch. – UROLOGY | AIIMS | MS in Surgery/General Surgery |
| PGIMER | |||
| JIPMER | |||
| 13. | M.Ch. – CORNEA, CATARACT, AND REFRACTIVE SURGERY | PGIMER | MD/MS in Ophthalmology or equivalent |
| 14. | M.Ch. – RENAL TRANSPLANT SURGERY | PGIMER | MS in Surgery or equivalent |
| 15. | M.Ch.- VITREORETINAL SURGERY | PGIMER | MD/MS in Ophthalmology or equivalent |
| 16. | M.Ch. – PEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS SURGERY/PEDIATRIC ORTHOPAEDICS | AIIMS | MS/DNB in Orthopaedics or an equivalent |
| PGIMER | |||
| 17. | M.Ch. – JOINT REPLACEMENT & RECONSTRUCTION | AIIMS | MS/DNB in Orthopaedics or an equivalent degree |
| 18. | M.Ch. – SPINE SURGERY | AIIMS | MS/DNB in Orthopaedics or an equivalent |
| 19. | M.Ch. – VASCULAR SURGERY | SCTIMST | MS/DNB in Surgery/General Surgery |
| 20. | M.Ch. – HAND AND MICROVASCULAR SURGERY | AIIMS | MS in General Surgery/Orthopaedics |
| 21. | M.Ch. – SPORTS INJURY | AIIMS | MS/DNB in Orthopaedics |
Age Relaxation Criteria for General Category
| Institute | Upper Age Limit | Date of Birth (for admission to the 2024 session) |
| AIIMS New Delhi & Other AIIMS | 35 years | Born on or after 01.01.1989 |
| PGIMER, Chandigarh | 45 years | Born on or after 01.01.1979 |
| NIMHANS, Bengaluru | 37 years | Born on or after 01.01.1987 |
| SCTIMST, Thiruvananthapuram | 40 years | Born on or after 01.01.1984 |
| JIPMER, Puducherry | No Upper Age Limit | – |
Age Relaxation Criteria for Other Categories
| Category | Maximum Relaxation |
| OBC Candidates | Maximum of 3 years |
| SC/ST Candidates | Maximum of 5 years |
| Ex-Serviceman | Maximum of 5 years |
| Commissioned Officers | Maximum of 5 years |
| Sponsored Candidates | Upper age limit not applicable |
| Persons with Disabilities | Upper age relaxation of 5 years (DM/M.Ch.) |
| All Category Candidates at NIMHANS Bengaluru | The upper age limit of 37 years as of 01.01.2024 |
FAQs
Q1. What is the eligibility criteria for AIIMS?
Ans. The eligibility criteria for admission to AIIMS varies by course. For admission to a medical undergraduate course, you must complete your 12th standard with science stream, and for admission to PG medical courses, you need to have an MBBS degree. Moreover, for admission to super specialty courses (DM/M.Ch.), you need to have a PG degree (MD/MS/DNB).
Q2. Who is eligible for INI-SS 2024?
Ans. Candidates with MD, MS, or DNB degrees in specific medical fields are eligible, with age restrictions and relaxations based on institution and category.
Q3. How does age relaxation work for different categories of candidates applying for the INI-SS exam?
Ans. Age relaxation varies by category, with OBC, SC, ST, Ex-Serviceman, and Persons with Disabilities candidates eligible for up to 3 to 5 years’ relaxation.
In India, medical entrances are among the toughest exams. At each level of medical education, be it graduation, postgraduation, super-specialisation, or fellowship courses, aspirants must crack the entrances to get admission at medical colleges.
Among the various entrance exams conducted in India, the “Institute of National Importance Super-Speciality” (INI-SS) is an entrance examination conducted for admission to various super-specialty courses (DM, M.Ch., and MD Hospital Administration) offered by Institutes of National Importance (INIs). It is highly competitive and evaluates candidates’ knowledge and skills in the medical field. It typically covers subjects related to various medical specialties such as cardiology, neurology, oncology, nephrology, etc. The examination aims to select the most qualified medical candidates for advanced training in super-specialty disciplines, thereby ensuring the highest standards of healthcare in the country. Enrolling in online medical PG courses paves the way to success in MD/MS exams and also multifolds competitive exam preparation.
The higher the education, the fewer the seats. This is always a challenge to secure a seat at a medical college and get on the merit list. For this, which college has your desired specialty? How many seats are there in which medical college? How many seats are available for your desired specialty? These are some important questions that come to the mind of every aspirant. This blog answers all these questions. It mentions the list of DM and M.Ch. courses along with a total number of seats for both the General and Sponsored Categories at all the INIs. Also, seat distribution for each INI is mentioned separately.
List of DM Courses and Total Number of DM Seats at INI-Institutes
| 1. DM – Acute Care-Emergency Medicine | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | ACUTE CARE-EMERGENCY
MEDICINE |
3 | 2 |
| 2. DM – Addiction Psychiatry | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | ADDICTION PSYCHIATRY (NDDTC) | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | ADDICTION PSYCHIATRY | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | ADDICTION PSYCHIATRY | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | AIIMS GORAKHPUR | ADDICTION PSYCHIATRY | 1 | 0 |
| 3. DM – Cardiac Surgical Intensive Care | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | CARDIAC SURGICAL INTENSIVE
CARE |
5 | 3 |
| 4. DM – Cardiac Anesthesiology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | CARDIAC ANAESTHESIOLOGY | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | CARDIOTHORACIC ANAESTHESIA | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS RAIPUR | CARDIAC ANAESTHESIA | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | CARDIAC ANESTHESIOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | CARDIOTHORACIC ANAESTHESIA & INTENSIVE CARE | 1 | 4 |
| 6 | SCTIMST, TRIVANDRUM | CARDIOTHORACIC & VASCULAR ANAESTHESIA | 0 | 2 |
| 5. DM-Cardiology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | CARDIOLOGY | 3 | 2 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | CARDIOLOGY | 4 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS PATNA | CARDIOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS RAIPUR | CARDIOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | CARDIOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 6 | AIIMS JODHPUR | CARDIOLOGY | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | CARDIOLOGY | 0 | 2 |
| 8 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | CARDIOLOGY | 2 | 3 |
| 9 | SCTIMST, TRIVANDRUM | CARDIOLOGY | 0 | 3 |
| 10 | AIIMS NAGPUR | CARDIOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 11 | AIIMS BATHINDA | CARDIOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 12 | AIIMS, BILASPUR | CARDIOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 6. DM – Cardiovascular Radiology & Endovascular Interventions | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | CARDIOVASCULAR RADIOLOGY AND ENDOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS | 3 | 2 |
| 2 | SCTIMST, TRIVANDRUM | CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING AND VASCULAR INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 7. DM – Child and Adolescent Psychiatry | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | CHILD AND ADOLESCENT
PSYCHIATRY |
2 | 2 |
| 2 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | CHILD AND ADOLESCENT
PSYCHIATRY |
2 | 2 |
| 8. DM – Clinical Haematology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | CLINICAL HAEMATOLOGY | 1 | 3 |
| 9. DM – Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY AND
RHEUMATOLOGY |
1 | 0 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY AND
RHEUMATOLOGY |
1 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS MANGALAGIRI | CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY AND
RHEUMATOLOGY |
1 | 0 |
| 10. DM – Clinical Pharmacology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | 1 | 3 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS RAIPUR | CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 6 | AIIMS JODHPUR | CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY | 1 | 3 |
| 11. DM – Critical Care Medicine/Intensive Care | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | CRITICAL CARE
MEDICINE/INTENSIVE CARE |
5 | 1 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | CRITICAL CARE | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS RAIPUR | CRITICAL CARE | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE
(ANAESTHESIOLOGY) |
3 | 2 |
| 6 | AIIMS JODHPUR | CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE | 3 | 0 |
| 7 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | CRITICAL CARE | 0 | 1 |
| 8 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | INTENSIVE CARE | 0 | 1 |
| 12. DM – Endocrinology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | ENDOCRINOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | ENDOCRINOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | ENDOCRINOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS RAIPUR | ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | ENDOCRINOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | AIIMS JODHPUR | ENDOCRINOLOGY | 2 | 3 |
| 7 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | ENDOCRINOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 8 | AIIMS, BILASPUR | ENDOCRINOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 13. DM – Forensic Pathology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS JODHPUR | FORENSIC PATHOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 14. DM – Forensic Psychiatry | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | FORENSIC PSYCHIATRY | 0 | 2 |
| 15. DM – Forensic Radiology & Virtual Autopsy | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | FORENSIC RADIOLOGY & VIRTUAL
AUTOPSY |
1 | 0 |
| 16. DM – Gastroenterology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | GASTROENTEROLOGY | 4 | 8 |
| 2 | AIIMS PATNA | GASTROENTEROLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | GASTROENTEROLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS JODHPUR | GASTROENTEROLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | MEDICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY | 1 | 2 |
| 6 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | GASTROENTEROLOGY | 3 | 6 |
| 17. DM – Geriatric Psychiatry | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY | 2 | 0 |
| 18. DM – Haematopathology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | HAEMATO-PATHOLOGY | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | HAEMATO-PATHOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | AIIMS JODHPUR | HAEMATO-PATHOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | HAEMATO-PATHOLOGY | 0 | 3 |
| 19. DM – Hepatology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | HEPATOLOGY | 1 | 2 |
| 20. DM – High Altitude Medicine | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | HIGH ALTITUDE MEDICINE | 1 | 2 |
| 21. DM – Histopathology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | HISTOPATHOLOGY | 1 | 2 |
| 22. DM – Hospital Medicine & Critical Care | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | HOSPITAL MEDICINE & CRITICAL CARE | 1 | 1 |
| 23. DM – Infectious Diseases | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | INFECTIOUS DISEASES | 11 | 3 |
| 2 | AIIMS RAIPUR | CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | INFECTIOUS DISEASES | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS JODHPUR | INFECTIOUS DISEASES | 2 | 1 |
| 5 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES | 1 | 2 |
| 24. DM – Interventional Radiology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS PATNA | INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | AIIMS RAIPUR | INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | AIIMS JODHPUR | INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 25. DM – Medical and Forensic Toxicology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RAIPUR | MEDICAL AND FORENSIC
TOXICOLOGY |
1 | 0 |
| 26. DM – Medical Genetics | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | MEDICAL GENETICS | 5 | 3 |
| 2 | AIIMS JODHPUR | MEDICAL GENETICS | 3 | 1 |
| 3 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | MEDICAL GENETICS | 1 | 2 |
| 27. DM – Gastroenterology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | MEDICAL ONCOLOGY | 4 | 0 |
| 2 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | MEDICAL ONCOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS JODHPUR | MEDICAL ONCOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | MEDICAL ONCOLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | MEDICAL ONCOLOGY | 0 | 3 |
| 6 | AIIMS, BILASPUR | MEDICAL ONCOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 28. DM – Neonatology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | NEONATOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 2 | AIIMS PATNA | NEONATOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS RAIPUR | NEONATOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | NEONATOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | AIIMS JODHPUR | NEONATOLOGY | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | NEONATOLOGY | 0 | 2 |
| 7 | AIIMS NAGPUR | NEONATOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | NEONATOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | AIIMS, BILASPUR | NEONATOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 29. DM – Nephrology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 5 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS PATNA | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 5 | AIIMS RAIPUR | NEPHROLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | NEPHROLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | AIIMS NAGPUR | NEPHROLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 8 | AIIMS JODHPUR | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 1 |
| 9 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | NEPHROLOGY | 0 | 2 |
| 10 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 3 |
| 11 | AIIMS, BILASPUR | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 1 |
| 12 | AIIMS MANGLAGIRI | NEPHROLOGY | 2 | 0 |
x
| 30. DM – Neuro-Anaesthesiology & Critical Care | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | NEURO-ANESTHESIOLOGY & CRITICAL CARE | 4 | 0 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | NEURO-ANESTHESIOLOGY & CRITICAL CARE | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | NEURO-ANESTHESIOLOGY & CRITICAL CARE | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | NEURO-ANESTHESIOLOGY & CRITICAL CARE | 1 | 1 |
| 5 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | NEURO-ANESTHESIOLOGY & CRITICAL CARE | 2 | 5 |
| 6 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | NEURO-ANESTHESIOLOGY & CRITICAL CARE | 4 | 2 |
| 7 | SCTIMST, TRIVANDRUM | NEUROANAESTHESIA | 0 | 2 |
| 31. DM – Neuroimaging and Interventional Neuroradiology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | NEUROIMAGING AND
INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY |
2 | 3 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | NEUROIMAGING AND INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | NEUROIMAGING AND INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY | 4 | 1 |
| 32. DM – Neurology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | NEUROLOGY | 6 | 0 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | NEUROLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | NEUROLOGY | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | NEUROLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | AIIMS JODHPUR | NEUROLOGY | 2 | 1 |
| 6 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | NEUROLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 7 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | NEUROLOGY | 3 | 4 |
| 8 | SCTIMST, TRIVANDRUM | NEUROLOGY | 5 | 1 |
| 9 | AIIMS MANGLAGIRI | NEUROLOGY | 0 | 2 |
| 10 | AIIMS MANGALAGIRI | NEUROLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 33. DM – Neuropathology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | NIMHANS, BENGALURU | NEUROPATHOLOGY | 1 | 1 |
| 34. DM – Onco-Anesthesia | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | ONCO-ANESTHESIA, DR.BRAIRCH | 4 | 3 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | ONCO-ANAESTHESIOLOGY &
PALLIATIVE CARE |
2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | ONCO-ANAESTHESIOLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 35. DM – Pediatric Anaesthesia & Intensive Care | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC ANAESTHESIA &
INTENSIVE CARE |
0 | 1 |
| 36. DM – Pediatric Cardiology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY | 0 | 3 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 37. DM – Pediatric Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY | 0 | 3 |
| 38. DM – Pediatric Emergency Medicine | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RAIPUR | PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY MEDICINE | 1 | 0 |
| 39. DM – Pediatric Endocrinology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | PEDIATRIC ENDOCINROLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC ENDOCINROLOGY | 0 | 0 |
| 40. DM – Pediatric Gastroenterology and Hepatology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | PEDIATRICS
GASTEROENTEROLOGY |
1 | 0 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC GASTROENTEROLOGY
AND HEPATOLOGY |
0 | 2 |
| 41. DM – Pediatric Haematology-Oncology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS BHOPAL | PEDIATRIC HAEMATOLOGYONCOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | PEDIATRIC HAEMATOLOGYONCOLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC HAEMATOLOGYONCOLOGY | 3 | 2 |
| 42. DM – Pediatric Nephrology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY | 0 | 3 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 3 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 43. DM – Pediatric Neurology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGY | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGY | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGY | 1 | 3 |
| 44. DM – Pediatric Oncology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | PEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY | 3 | 2 |
| 45. DM – Pediatric Oncology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY & INTENSIVE CARE | 0 | 1 |
| 46. DM – Pediatric Pulmonology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS JODHPUR | PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC PULMONOLOGY | 0 | 2 |
| 47. DM – Pediatric Critical Care | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RAIPUR | PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | JIPMER, PUDUCHERRY | PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE | 2 | 4 |
| 4 | AIIMS NAGPUR | PEDIATRIC CRITICAL CARE | 1 | 0 |
| 48. DM – Pain Medicine | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | PAIN MEDICINE (ANAESTHESIOLOGY) | 0 | 1 |
| 49. DM – Pulmonary, Critical Care & Sleep Medicine | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | AIIMS BHOPAL | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 2 | 0 |
| 3 | AIIMS BHUBANESHWAR | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 3 | 0 |
| 4 | AIIMS PATNA | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | AIIMS RAIPUR | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 2 | 0 |
| 6 | AIIMS RISHIKESH | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 3 | 1 |
| 7 | AIIMS JODHPUR | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 3 | 1 |
| 8 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 2 | 5 |
| 9 | AIIMS RAJKOT | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 2 | 0 |
| 10 | AIIMS GORAKHPUR | PULMONARY, CRITICAL CARE & SLEEP MEDICINE | 1 | 0 |
| 11 | AIIMS MANGALAGIRI | PULMONARY MEDICINE | 1 | 0 |
| 50. DM – Reproductive Medicine | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | REPRODUCTIVE MEDICINE | 1 | 1 |
| 51. DM – Therapeutic Nuclear Medicine | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | THERAPEUTIC NUCLEAR MEDICINE | 1 | 3 |
| 52. DM – Trauma Anaesthesia & Acute Care | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | TRAUMA ANAESTHESIA & ACUTE CARE | 0 | 1 |
| 53. DM – Virology | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS, RISHIKESH | VIROLOGY | 1 | 0 |
| 54. DM – Breast, Endocrine and General Surgery | ||||
| S.No. | Institute | Subject | General | Sponsored |
| 1 | AIIMS NEW DELHI | BREAST, ENDOCRINE AND GENERAL SURGERY | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | PGIMER, CHANDIGARH | ENDOCRINE & BREAST SURGERY | 1 | 2 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the difference between INI-SS and INI-CET?
Ans. INI-CET is an entrance examination conducted for admission to medical PG courses, that includes MD, MS, DM (6 yrs), MCh (6 yrs), and MDS courses whereas INI-SS is an entrance exam conducted for admission to medical super specialty courses that includes admission to DM, M.Ch. and MD in Hospital Administration courses.
Q2. How many years is super-specialty after MD?
Ans. After MD, superspecialty courses (DM and M.Ch. courses) are of three-year duration.
MD Medicine has a vast curriculum that comprises the study of basic medical sciences, systemic medicine, allied medicine specialties, tropical medicine infectious medicine, and recent advances in medicine. It also involves rotations through various specialties, allowing students to gain practical experience in different areas of medicine such as cardiology, oncology, and neurology. Throughout the curriculum, students learn and practice clinical skills such as patient examination, history-taking, diagnostic reasoning, and communication with patients and colleagues. Emphasis is placed on the development of professionalism, ethical conduct, and communication skills necessary for practicing medicine.
Students also need to pass written exams, practical exams, clinical assessments, and thesis writing in their MD degree to demonstrate competency and progress toward completion of the degree.
MD Medicine student is expected to know the in-depth of the subject with an emphasis on the most prevalent diseases/health problems. To become a skilled doctor, having comprehensive knowledge of the subject along with the recent advances is crucial. And for gaining this comprehensive knowledge, it is important to refer to a variety of books, such as textbooks, atlases, handbooks, review books, clinical cases, OSCE preparation books, and books pertaining to particular systems. It is always advised to refer to the latest edition of the books.
Here’s a list of the best books on Medicine for PG residents:
- An Insider’s Guide to Clinical Medicine
An Insider’s Guide to Clinical Medicine by Archith Boloor and Anudeep Padakanti is among the best books when it comes to clinicals.
Winner of the Award for Excellence in Book Production by the Federation of Indian Publishers 2020, this book is an amazing learning aid for practical examinations for medical students. It comprises x-rays, spotters, common drugs, instruments, and ECGs. It serves as a ready reckoner for medicine practical examinations. Comprehensive section on history taking and decision making, complete case sheets on all organ systems, visual memory aids, and conceptual explanations – all these features make it one of the best books for medicine.
- Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
Harrison’s book is one of the most recommended books for MD medicine students and residents. It serves as a reference for understanding the fundamentals of internal medicine and for guidance in clinical decision-making. It’s known for its depth of content, clear explanations, and evidence-based approach.
Extensive visual support, updated clinical trial results, recommended guidelines, comprehensive content on therapeutic approaches, specific treatment regimens, clinical decision trees, and algorithms – these are some of the key features of this 2-volume book.
- API Textbook of Medicine
An ideal learning tool for medical students, clinicians, and practitioners, this book has been regularly updated by the Association of Physicians of India (API) for more than 50 years now. From bedside clinics to the clinical management of cases – everything is well explained in the book.
It includes medical guidelines applicable to Indian standards. A new part on SARS-COVID-19 under the ‘Viral Infections’ section has been added. Also, new chapters on Covid Vaccination, DNA-Repair Deficiency & Lysosomal Storage Disorders, and the Impact of COVID-19 on the Hospital Environment have been added in the latest edition of the book.
- CMC Vellore Handbook of Emergency Medicine
Previously known as ‘Emergency Medicine Best Practices at CMC (EMAC)’, this book is written by KPP Abhilash. This book is an amazing learning resource for ICU postings and learning critical care protocols. Through its comprehensive yet concise text, this book simplifies all the basics of commonly encountered medical and surgical emergencies. It also features the latest techniques and procedures to tackle a health emergency along with incorporating recent evidence-based recommendations. It serves as the best learning text to provide better patient care.
- South Asian Edition of ‘The Washington Manual of Medical Therapeutics’
The editor of the south asian edition of this renowned book is Dr. Archith Boloor. The book is filled with case scenarios and casualties that help to cater patients during residency. It strengthens the clinical abilities and enhances the resident’s knowledge of treatment modalities. It provides practical solutions and expert guidance for the challenges faced by medical students, residents, and interns while practicing internal medicine. Its easy-to-follow format covers pathophysiology, clinical presentation, diagnostics, therapeutics, and other practical solutions.
- Practical Guidelines on Fluid Therapy
This book by Dr. Sanjay Pandya is a must-have for learning practical information about fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base disorders. It is an excellent handbook for every MD Medicine student and resident. Considering the importance of fluid management topics in medical sciences, the features of the book such as the case presentation method, easy-to-follow approach, and easy language make it a commendable resource that has made its place on shelves of all medical students and residents.
- Hutchison’s Clinical Methods
Hutchinson’s Clinical Methods: An Integrated Approach to Clinical Practice is a must-have reference book for practicals. The latest edition is a go-to guide for medical students and practitioners to learn about core clinical skills. It includes basic principles, different patient groups, and all main body systems. It is a super amazing learning resource to learn clinical skills and understand doctor-patient relationships.
- Manual of Practical Medicine
Written by R Alagappan, this book is an amazing learning resource for medical students and practitioners. The content is mentioned in a sequential manner. The latest edition of the book has enhanced its content with a lot of topics such as Coivd 19, Gout, antiviral drugs in the management of hepatitis B and C, newer drug therapy for multiple sclerosis, and newer monoclonal antibodies for the management of various systemic disorders.
A quick glimpse at some more recommended books for MD Medicine students and residents:
MD Medicine Textbooks (Latest Edition)
- Oxford Textbook of Medicine
- Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine
- Cecil: Textbook of Medicine
- Clinical Examination in Cardiology
- Kumar & Clark: Book of Clinical Medicine
Reference books
- Marriot’s Practical Electrocardiography
- Hurst: The Heart
- Crofton and Douglas: Respiratory Diseases
- Brain’s Diseases of the Nervous System
- Adam’s Principles of Neurology
- Braunwald – Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine
- William’s Textbook of Endocrinology
- De Gruchi’s Clinical Hematology in Medical Practice
- Slesenger & Fordtran: Gastrointestinal and Liver disease
- Manson’s Tropical Diseases
- Kelly’s Textbook of Rheumatology
Books for Clinical Methods
- Hutchinson’s Clinical Methods
- Macleod’s Clinical examination
- John Patten: Neurological Differential Diagnosis
- Neurological Examination in Clinical Practice by Bickerstaff
Click here to complement your studies with our Medicine MD online course.
Pathology is a comprehensive subject, included in the 2nd year of the MBBS curriculum. It covers various aspects of disease processes, their causes, and the resulting changes in the structure and function of the body. The subject serves as the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine, helping medical professionals understand the underlying processes of diseases.
Medical students must have a sound knowledge of the pathology subject, as it provides a foundation for understanding disease processes, making accurate diagnoses, and formulating appropriate treatment plans. The subject also plays a crucial role in research and contributes significantly to medical knowledge and patient care advancements.
The Pathology course curriculum in MBBS includes an introduction to pathology, cellular pathology, hematology, general pathology, systemic pathology, common pathogens and their mechanisms, histopathology, clinical pathology, autopsy, and forensic pathology.
Subject Weightage of Pathology in Competitive Exams
Approximately 12 questions are asked in the NEET-PG exam, and in the INI-CET, approximately, 13-16 questions are asked from the Pathology subject.
The competitive exams mainly assess the understanding of the aspirant regarding disease processes, diagnostic principles, and the application of pathology in clinical scenarios.
Getting familiar with the subject weightage of subjects in exams, exam patterns, high-yield topics, and reliable preparation tips multiplies the chances of gaining conceptual clarity over a subject and scoring high in the exams.
Important Topics of Pathology in MBBS
Hematology
- Coagulation Pathway
- Hemophilia
- Blood Bank
- Megaloblastic Anemia
- Multiple Myeloma
- Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Hemolytic Anemia
- Lymphoma
- Hypercoagulability
- Thalassemia
- Acute Leukemia (AML/ALL)
- CML & MDS
- Waldenstrom’s Disease and Heavy Chain Disorders
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
- Stain
Cell Biology
- Cell Injury Concept
- Cellular Adaption
- Irreversible Injury 1 and 2
- Free Radical Injury
- Pigmentation
- Necrosis
GIT
- Jaundice
- Fatty Liver
- Hepatitis
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Celiac Disease
- Whipple Disease
- GI Polyps
- Liver disorders
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Acute and Chronic Gastritis
- GIT Tumor
- Congenital GIT Anomalies
- Mesothelioma
Renal
- PSGN
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- ADPKD
- Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Glomerular Nephritis
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Alport Syndrome
- Renal Spotters
- Renal Stones
CNS
- Malformations of Brain
- CSF Analysis
- Prion Disease
- Medulloblastoma
- Meningioma
- CNS Degenerative Disease
- Meningitis
- CNS Tumor
- Neuroblastoma
Lung
- ARDS
- Emphysema
- TB Lung Lesions
- Adenocarcinoma
- Occupational Disease
- Obstructive Lung Disorders
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Infective Lung Disorders
- Lung Abscess
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Lung Cancer
- COPD
- Asbestosis
CVS
- Myocardial Infarction
- DCM & HCM
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Rheumatic Heart Disease
- Vasculitis
- Infective Endocarditis
- Vascular Sclerosis
- Bleeding Disorders
- Clotting Factor Disorders
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Grouping
- Platelets Disorders
Breast
- Fibroadenoma
- Breast Oncogenesis
- Breast Cancer
- TNM Staging
Endocrine
- Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Follicular Carcinoma
- Pheochromocytoma
- Parathyroid and Thyroid Disorders
- Adrenal Gland Disorders
Inflammation
- Plasma Chemical Mediators
- Coagulation Cascade
- Chronic Inflammation
- Neutrophil Extracellular Trap
- Inflammatory Markers
Malignancy
- Tumor Marker
- Tumor Suppressor Gene
- Molecular Hallmark of Cancer
- Bone Tumors
- Melanoma
- Hodgkin & Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Seminoma
Genetics
- Gene Repair Defects
- Inheritance Pattern
- Down Syndrome
- Turner Syndrome
- TNR Disorders
- Single Cell Disorder
- Specific Cytogenetic Disorders
Immunology
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Granuloma
- Complement Pathway
- Immunodeficiency Disorders
Miscellaneous
- Aging
- Marfan & Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
- Transplantation
- HIV
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Amyloidosis
Tips to Prepare Pathology in MBBS
Preparing for pathology in MBBS requires a systematic and comprehensive approach. To have an in-depth understanding of the subject, establish a strong foundation in anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry, as pathology builds upon these subjects. The MBBS curriculum caters to general pathology, hematology, systemic pathology, clinical pathology, and practicals in pathology.
To start with the pathology subject, familiarize yourself with basic medical terminologies, and then move on to the general pathology section. Understand the basics and attend regular classes. From the beginning, create a well-organized study schedule to cover all the topics systematically, and allocate sufficient time to review and consolidate your learning. Once you grasp the fundamental concepts, start with the hematology section.
Be wise while choosing the books for pathology. Opt recommended standard textbooks to clear your concepts, pathology atlases to visualize and understand various pathological conditions, and also add pathology review books to your shelves that provide concise summaries of key concepts for quick revision. Some recommendations for pathology books are Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan, Essentials in Hematology and Clinical Pathology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates Pathology by Ramadas Nayak, Rapid Review of Hematology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Review of Pathology and Genetics by Sparsh Gupta & Gobind Rai Garg, and Comprehensive Image-Based Review of Pathology by Sushant Soni.
Then, further, start emphasizing systemic pathology. Thoroughly study all the systems along with prevalent conditions and diagnostic methods. Make sure you make proper notes side by side for all the topics. They will prove quite beneficial at the time of exams for revision, be it professional exams or any competitive exams. During your studies, engage in active learning methods such as concept mapping, creating flashcards, and flowcharts, and teaching concepts to peers. Also, solve clinical case scenarios to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. Create mind maps and diagrams to visualize complex pathways and relationships between different pathological conditions.
Remember ‘P for Pathology and P for Practicals’. The subject is better understood when you conduct experiments and practicals simultaneously. It is highly advised to attend pathology practical classes to enhance your understanding of histopathology and diagnostic techniques. Also, during your lab sessions, practice identifying microscopic slides and understanding the correlation between pathology and clinical presentations. Consider shadowing or observing clinical cases in pathology labs. Correlate clinical features with pathological findings to strengthen your understanding of clinical pathology. Becoming capable of finding the clinical relevance of pathological conditions and relating pathology to signs, symptoms, and diagnostic methods is an assertive sign that you are becoming well-versed in pathology concepts.
Along with learning pathology and attending practical sessions, solve practice questions for all the topics for self-evaluation and better understanding. Also, solve past exam papers and mock papers for the exams you are determined to score high. Solving them will help you understand the exam pattern, improve time-management skills, identify key aspects, and focus on high-yielding topics. Along with college lectures, practical sessions, and ward postings, keep yourself updated with the recent advances and research in pathology by attending webinars, workshops, and conferences.
To reinforce your understanding of pathology concepts, you can enroll in the Pathology for UnderGrads online course by Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak, and Dr. Debasis Gochhait. The course provides access to video lectures, concise notes, and practice questions, all aligned with the CBME curriculum. The lectures comprise relevant case studies, case discussions, histological and gross images, and important questions for university exams, practical exams, and PG entrance exams. Most importantly, regularly revise topics to reinforce your memory.
Must Read: Important Topics of Microbiology
Must Read: Important Topics of Pharmacology
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- What are the important topics of pathology in MBBS?
The important topics of pathology in MBBS include Multiple Myeloma, Iron Deficiency Anemia, Sickle Cell Anemia, Lymphoma, Thalassemia, Acute Leukemia, Gene Repair Defects, Inflammation, Free Radical Injury, Fatty Liver, Ulcerative Colitis, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Peptic Ulcer Disease, Diabetic Retinopathy, Glomerular Nephritis, Nephrotic Syndrome, CNS Degenerative Disease, Meningitis, Occupational Disease, Infective Lung Disorder, Lung Abscess, Infective Endocarditis, Adrenal Gland Disorders, Breast Cancer, Tumor Suppressor Gene, Hypertension, Genital System, and Down Syndrome.
- Which are the recommended books on pathology for MBBS students?
Recommended books for pathology in MBBS include Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan, Essentials in Hematology and Clinical Pathology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates Pathology by Ramadas Nayak, Rapid Review of Hematology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Review of Pathology and Genetics by Sparsh Gupta & Gobind Rai Garg and Comprehensive Image Based Review of Pathology by Sushant Soni.
- What is the weightage of pathology in the NEET PG exam?
In the NEET-PG exam, approximately 12 questions are asked from the pathology subject.
- What is the subject weightage of pathology in INI-CET?
In INI-CET, approximately 13–16 questions are asked from the pathology subject.
- How to prepare for pathology for the NEET-PG?
Preparing for pathology in MBBS requires a systematic and comprehensive approach. Establish a strong foundation in fundamental subjects. Familiarize yourself with basic terminologies and then move on to sections. Attend regular classes and practical sessions. Take proper notes. Create a well-organized study schedule. Grasp the fundamental concepts. Opt for recommended standard textbooks, pathology atlases, and pathology review books. Thoroughly study all the systems along with prevalent conditions and diagnostic methods. Engage in active learning methods such as concept mapping, creating flashcards, flowcharts, mind maps, diagrams, and more. Also, solve clinical case scenarios to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. Solve practice questions for all the topics for self-evaluation and better understanding. Keep yourself updated with recent advances and research. Attend webinars, workshops, and conferences. Enroll in the Pathology for UnderGrads online course by Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak, and Dr. Debasis Gochhait to reinforce your learning.
Dermatology is a medical discipline concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of skin, hair, nail, and membrane conditions and disorders.
In MBBS, the curriculum of Dermatology, Venerology, and Leprosy subject includes the causative and risk factors of dermatological conditions along with detailed treatment and preventive measures. Identification, categorization, etiology, microbiology, pathogenesis, natural history, clinical features, presentations, complications, indications, and contraindications of skin, nail, and hair conditions are all included in the dermatology subject. Also, pharmacological administration and adverse reactions of pharmacotherapies are discussed.
Dermatology is a highly booming medical speciality, hence having a comprehensive knowledge of the subject paves the way to a successful career if you are aspiring to be a dermatologist.
Knowing high-yield topics, subject weightage in competitive exams, and reliable preparation tips help in gaining conceptual clarity over a subject and maximise your chances of getting good grades.
In NEET-PG, 6-8 questions are asked from the dermatology subject, and in INI-CET, the subject weightage of the dermatology subject is around 5-6 questions.
Important Topics of Dermatology in MBBS
These topics are important for MBBS prof exams as well as are high-yielding topics for NEET-PG and INI-CET.
Structure of Hair
Basics of Dermatology
Cells of Epidermis
Level of Epidermis
Drug Eruptions
Lepra Reactions
Photosensitivity
DDs of Bullous Lesions
Sexually Transmitted Viral Infections
Angioedema
Sebaceous Gland
Blistering Disorders
Chemical Peeling
Pigmentary Disorders
Structure of Sweat Glands and Related Disorders
Skin Lesions
Treatment of Acne Vulgaris
Deep Folliculitis and Cellulitis
Mucocutaneous Manifestations of SLE
Histopathological Findings
Basement Membrane Zone
Dermis and Subcutaneous Layer
Bacterial Infections
Fungal Infections
Mycobacterial Infections
Viral Infections
Structure of Epidermis and Dermis
Patch Test
Histopathology of PV
Oral Retinoids in Acne
List of Important Dermatological Conditions
Erythema Multiforme
Kaposi Sarcoma
Lichen Planus
Tinea Infections
STDs
Papulosquamous Disorders
Skin Tumors
Secondary Syphilis
Hepatic Fibrosis
Skin Lesions in Systemic Diseases
Allergic Dermatitis
Chikungunya Pigmentation
Ulcers
Vesicollous Disorders
Scleroderma
Urticaria
Alopecia
Clear Fluid Lesions
Secondary Skin Lesions
Nikolsky Sign
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Tzanck Smear
Bullous Pemphigoid
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Syphilis
Anogenital Warts
Chancroid
Donovanosis
Lymphogranuloma Venereum
Telogen Effluvium
Nail Psoriasis
Stratum Corneum
Genital Herpes Simplex
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
Psoriasis and its Treatment
Scabies
Atopic Eczema
Pityriasis Rosea
Kerion
Sporotrichosis aka Rose Gardener’s Disease
Chromoblastomycosis
Lupus Vulgaris
Scrofuloderma
Papulonecrotic Tuberculid
Hansen’s Disease
Mid-Borderline Leprosy
Verruca Vulgaris
HPV Infections
Molluscum Contagiosum
Melasma
Mongolian Spot
Nevus of Ota
Piebaldism
Segmental Vitiligo
Phrynoderma
Pellagra
Malignant Melanoma
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Acanthosis Nigricans
GI Adenocarcinoma
Glucagonoma
CA Lung
Discoid LE
Carpet Tack Sign
Dermatomyositis
Must Read: Important Topics of Medicine in MBBS
Must Read: Important Topics of Surgery in MBBS
Tips to Study Dermatology in MBBS
Dermatology is challenging but also a rewarding experience, opening doors to the fascinating field of medicine.
For a comprehensive study of dermatology, follow the described study pattern and reliable tips.
According to the new curriculum, the Dermatology subject is now included in the Medicine subject but is a diverse field of study in itself. It is highly fascinating if you learn in a structured way with images.
To start with the study, firstly get the syllabus and list of dermatological conditions included in the curriculum. Start with the fundamentals of dermatology and understand every basic terminology. Then go on to learn the concepts and dermatology topics. Categorise the types of dermatology diseases, disorders, and conditions. Further, learn the basic history taking, and understand common dermatology procedures, and techniques. After understanding all the concepts and procedures, refer to the syllabus and list of conditions and disorders included. Understand and learn them one by one.
Remember to study from the standard textbooks and dermatology atlases and that too, the latest edition.
Dermatology concepts are very well understood with high-quality images that aid in visualizing various skin conditions, hence, learn using images, spotters, and flashcards.
Practice IBQs and image-based clinical cases as much as possible after reading a concept. This will enhance your understanding of the topic and you will be able to memorise it for a long time.
Make sure to take proper notes with tables, flowcharts, mnemonics, flashcards, and more. Notes prove highly beneficial for revision and at the time of exams, may it be prof exams or any competitive exams, they serve as a ready reckoner.
Another thing to keep in mind while studying is to read the following for all the dermatological conditions and make a note of it: etiology, causative agents, risk factors, types, pathogenesis, clinical features, indications, contraindications, treatment, pharmacology, and preventive measures.
Try to categorise and learn accordingly to ease the learning process and improve retention. This also avoids confusion at times.
As the dermatology branch is being highly explored, don’t miss to read about the latest treatment modalities and cosmetic dermatology procedures being introduced.
You can’t ignore the importance of hands-on experience for recognizing and diagnosing skin conditions hence, actively participate in clinical sessions and rotations. Observe and practice. Try to correlate theoretical knowledge with real-life cases, and discuss with your fellows and professors.
To ease your learning process, you can complement your textbooks with online resources. Subscribing to a good online course would be of great help. You will learn from top faculty along with getting access to illustrative lectures, notes, and a lot more.
Quick Tips:
- Attend lectures and take proper notes.
- Actively participate in clinical sessions.
- Invest in best-selling titles.
- Refer to dermatology atlases.
- Complement your textbook learning with online resources.
- Actively engage in clinical rotations and postings.
- Attend conferences, seminars, and workshops.
- Practice questions and clinical cases.
- Use flashcards, mnemonics, and other memory aids.
- Stay organized.
- Stay updated on clinical guidelines for the management of dermatological conditions.
- Solve previous year’s questions.
Remember, consistency and dedication are key when studying dermatology or any medical specialty.
Best Books for Dermatology
Review of Dermatology by Saurabh Jindal is one of the best-selling dermatology books for MBBS students. The book is full of coloured images, mnemonics, memory aids, and conceptual diagrams. This exam-oriented book also includes a short review section at the end of each chapter.
IADVL’s Concise Textbook of Dermatology by Lalit Kumar Gupta is among the preferred books by MBBS students. The book is written in a lucid manner and the latest edition of it is comprehensively updated. The content is complemented with tables, flowcharts, figures, illustrations, and clinical photographs. The best part is that each chapter begins with a learning objective and the text follows a structured pattern, including MCQs and IBQs.
Fitzpatrick’s Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology is a bestselling, concise, and quick reference book for medical students, residents, and physicians. The authors of the book are Arturo P. Saavedra, Ellen K. Roh, and Anar Mikailov. The latest edition is revised and expanded. The book includes over 1000 full-colour images and a color-coded 4-part organisation. It covers the most essential content along with detailed information on diagnosis and treatment.
Neena Khanna’s Dermatology book, Illustrated Synopsis of Dermatology & Sexually Transmitted Diseases, is a highly recommended book for studying the medical, surgical, and cosmetic aspects of STDs in depth. Each topic is easy to understand and organised with concise examples facilitated by real-life scenarios and cases.
Must Read: Best books for MBBS 4th year
Must Read: Psychiatry: Important Topics and Preparation Tips
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the subject weightage of dermatology in NEET-PG?
Ans. Dermatology is a medical discipline concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of skin, hair, nail, and membrane conditions and disorders. In NEET-PG, 6-8 questions are asked from the dermatology subject.
Q2. What is the subject weightage of dermatology in INI-CET?
Ans. Dermatology is a medical discipline concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of skin, hair, nail, and membrane conditions and disorders. In INI-CET, the subject-weightage of dermatology subject is around 5-6 questions.
Q3. What are the important topics in dermatology in MBBS?
Ans. The important topics in dermatology in MBBS include structure of hair, basics of dermatology, level of epidermis, drug eruptions, blistering disorders, skin lesions, acne vulgaris, bacterial infections, fungal infections, mycobacterial infections, erythema multiforme, lichen planus, STDs, papulosquamous disorders, skin tumors, syphilis, dermatitis, ulcers, urticaria, alopecia, nail psoriasis, genital herpes simplex, and scabies.
Q4. How to prepare dermatology for NEET-PG?
Ans. Here are some tips to prepare for dermatology subject for NEET-PG:
- Attend lectures and take proper notes.
- Actively participate in clinical sessions.
- Invest in best-selling textbook titles.
- Refer to dermatology atlases.
- Complement your textbook learning with online resources.
- Actively engage in clinical rotations and dermatology clinics.
- Attend conferences, seminars, and workshops.
- Practice questions and clinical cases as many as you can.
- Use flashcards, mnemonics, and other memory aids.
- Stay organized.
- Stay updated on clinical guidelines for the management of dermatological conditions.
- Solve previous year’s questions.
The recent change in the NEET-PG exam date has left a mixed impact on the aspirants with a blend of feelings. While some aspirants view it as an opportunity to strengthen their preparation, others find it disruptive and challenging. Aspirants need to adapt their strategies, manage their emotions effectively, and utilize the additional time productively to maximize their chances of success.
Remember to optimise your time and maximise your score!
The new NEET-PG exam date is 7th July’24 and about 5 months are left for the exam. The clock is ticking! Cracking NEET-PG in just 5 months with a good rank is indeed challenging, but not impossible with the right strategy and consistent efforts. Dedicate your time and efforts to crack the exam by hook or crook.
We’ve come up with a reliable 5-month revision strategy or say, preparation plan to help you prepare effectively and excel in the NEET-PG exam with a good rank.
Month 1: Revise Foundation Subjects
Dedicate the first month of revision to the foundation subjects. In weeks 1-2, revise the Anatomy subject. Focus on important and high-yielding topics and solve previous year’s question papers. In weeks 3-4, cover all the important systems in detail given in the Physiology subject. Do prepare from the notes to cover the systems within time. In weeks 4-5, emphasize on metabolic pathways and molecular biology provided in the Biochemistry subject. Assess your weak areas and ensure you don’t miss out on any high-yielding topic.
As all the MBBS subjects are well integrated, the hold over foundational subjects will lead to a better understanding and clarity of the para-clinical and clinical subjects.
Month 2: Start with Para-Clinical Subjects
Dedicate the second month for the revision of para-clinical subjects. Focus on covering general and systemic pathology thoroughly in week 1. Then, in week 2, target and cover all the essential drugs with their mechanism of action included in the Pharmacology subject. Also, practice drug classification and side effects. As there are lot many drugs and their classes, so try to revise your notes and devote much time to the high-yielding ones. In week 3, concentrate on high-yielding topics of microbiology and important organisms, infections, and vaccinations. You must solve previous year’s papers related to infectious diseases. In the last week of the month, i.e., week 4, cover the Forensic Medicine and Toxicology subject. Stress on important topics and medical laws.
Important: Don’t forget to practice image-based questions for the Pathology, Pharmacology, and Microbiology subjects.
Month 3: Go on with MBBS Subjects
In the first week of the third month, complete the revision of the Community Medicine subject. Don’t miss out on reading various health schemes and initiatives, and pandemic modules. Then, dedicate the next one and a half weeks to revising the pediatric concepts. Make sure you read about common pediatric illnesses, neonatal care levels, and pediatric sub-speciality modules. Solve case-based questions to integrate knowledge. In the left-over weeks of the month, concentrate on both Obstetrics and Gynecology. Read the clinical cases pertaining to common OBGYN disorders. Also, learn the diagnostic procedures in detail.
Month 4: Cover Clinical Subjects
Focus on the very major part of the MBBS curriculum in the fourth month, the core clinical specialties with their allied subjects. Emphasize on General Medicine concepts in the first week of the month. In the second week, cover the medicine allied subjects. Focus on the high-yielding topics of Psychiatry and Dermatology. Cover common psychiatric disorders and treatments. Focus on frequently asked and prevalent dermatological conditions. In the third and fourth weeks, cover the high-yielding topics of Surgery subject. In the fifth week, focus on the surgery-allied subjects. Cover the Ophthalmology and ENT concepts. It becomes a huge task to complete the revision of clinical subjects in such a short time and hence it is advised to go through your notes or other learning aids that serve as your ready reckoner for quick revision. Prefer integrated learning when it comes to clinical subjects.
Month 5: Time for Final Revision.
In the first two weeks of the month, complete the subject-wise revision. In the first week, cover the Orthopaedics subject and in the second week, complete the revision of Radiodiagnosis and Anaesthesiology subject. Review common diagnostic imaging findings as well.
Now after completing the revision of individual subjects, it’s time for final revision and solving questions as much as possible. Solve mock papers and previous year’s papers. Analyse your performance and manage time efficiently. Take mock tests under timed conditions. In the last week before the exam, do a quick revision of key concepts. Get adequate rest, stay calm, and manage stress.
Remember to adapt this plan based on your strengths, weaknesses, and learning style. It’s crucial to regularly assess your progress and modify the plan accordingly.
It is highly advised to enroll in the online preparation courses for NEET-PG. Considering the competition, a single answer can make a drastic difference in your NEET-PG rank. Opt for the DigiNerve MBBS courses as they provide comprehensive video lectures that will help you learn all the concepts at your pace so that you don’t miss any topic. The courses include highly illustrative video lectures by eminent faculty and subject experts, along with concise notes that serve as ready reckoners for revision. It also includes practice questions, clinical cases, benchmark trials, and much more.
Here are some additional tips to create an effective NEET-PG study timetable and score high:
Keep the syllabus, high-yielding topics, and subject weightage pasted on your study desk.
Keep the books, notes, and other preparation materials handy with you to avoid arranging at the last minute.
Supplement your preparation with the best NEET-PG video lectures online.
Remain updated with any changes in the NEET-PG exam pattern or syllabus.
Master the art of learning. Don’t passively read; actively engage with the material. Take notes, underline key points, draw diagrams, and create flashcards.
Go with the spaced repetition method. Regularly revise what you’ve learned to solidify memory and boost recall.
You have time, so focus on understanding concepts rather than rote memorization. This will help you apply your knowledge to various scenarios and solve problems effectively.
Set achievable goals, celebrate your progress, and surround yourself with positive people who support you.
Break down your study sessions into manageable chunks and don’t try to study for hours on end.
It is completely normal to feel overwhelmed sometimes, just take a break and restart your studies. Don’t give up on your dreams.
Practice solving clinical case-based questions, especially for the clinical subjects.
Solve MCQs after each chapter to reinforce your understanding.
Exercise and meditate regularly for physical and mental well-being.
Keep a positive mindset. Practice meditation, deep breathing, or other stress management techniques to stay calm during the preparation and the exam.
Develop good eating habits and get enough sleep to stay focused and energised.
Avoid burnout and stay motivated throughout your preparation journey.
Maintain a consistent study schedule and avoid distractions.
Focus on question-solving techniques and time management.
Join study groups and seek guidance from mentors, especially if you have doubts or need clarification.
Whenever you feel like giving up, just remember, that you have come this far, and now it’s time to achieve your dream. Just have faith in your abilities, be persistent, and never give up on your dream. Most importantly, remain consistent, focused, and determined to pass the exam with flying colours.
Must Read: NEET PG 2024: Syllabus, Exam Pattern, Preparation Tips, and More
If you are an aspiring medical student or belong to Delhi, then you must have heard about one of the most prestigious medical institutions, Maulana Azad Medical College. Established in 1959, MAMC is named after Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the first education minister of independent India. The college is located in the capital city and is affiliated with the Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Delhi.
Undoubtedly, it is ranked among the top medical colleges in India and all its courses are recognized by the Medical Council of India (MCI). MAMC is renowned for its high standards of medical education and research. The college provides students with exposure to the diverse healthcare challenges prevalent in the city.
MAMC is associated with four top medical institutions and hospitals in Delhi, named GB Pant Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research, Maulana Azad Institute of Dental Sciences, Lok Nayak Hospital, and Guru Nanak Eye Center. These hospitals serve as the primary training grounds for medical students studying at MAMC and offer a diverse range of clinical experiences. The associated hospitals have a daily patient count of thousands providing outstanding practical learning exposure to students and hence, is among the preferred choices for medical studies.
MAMC offers various undergraduate, postgraduate, and super speciality courses in various medical specialities. The college is known for its rigorous and comprehensive medical curriculum with a prestigious list of alumni who have made significant contributions to the field of medicine, both in India and internationally. Actively involved in medical research, the college with its faculty and students contributes significantly to scientific publications and advancements in the medical field.
Besides top-notch quality education, MAMC has special centres for Child Development, Clinical Skills, Genetics, ART, Hemophilia Day Care, and IVF. The college is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities, including modern laboratories, libraries, and lecture halls.
Read on to know the complete details about admission to MAMC, Delhi. The blog includes the list of courses available at MAMC, their admission procedure, list of specialities, number of seats, registration fee, course fee structure, surety bond amount, and other details.
MBBS Course at MAMC
Admission Procedure
Admission to the MBBS program at MAMC Delhi is done based on the marks scored in the NEET-UG entrance examination. The rank under state quota and All India Quota along with category determines your chances of admission into the college. Once, you get a competitive required cut-off score, you can fill out the counselling form available on the www.fmsc.ac.in website. Then, go through the counselling process and admission formalities, once admitted.
Number of Seats
There are a total of 250 MBBS seats at MAMC, Delhi. The MBBS seat distribution is as follows:
| Seats Under | Total Seats | Unreserved (UR) | OBC | SC | ST |
| 15% All India Quota (AIQ) | 37 | 18 | 10 | 6 | 3 |
| 85% State Quota | 207 | 104
(94- GEN, 5 GEN-CW, and 5 GEN-PH) |
56
(50 OBC, 03 OBC-CW, and 03 OBC-PH) |
31
(29 SC, 01 SC-CW, and 01 SC-PH) |
16
(14 ST, 01 ST-CW, and 01 ST-PH) |
Also, there are 06 seats under the Central Pool Reserved Seat.
MBBS Fee Structure
The fee for the MBBS at MAMC is around Rs. 2500. Apart from this, there is a refundable deposit of Rs. 2000.
MAMC Cut-off Score for MBBS (Expected)
| Category | Cut-off percentile | Expected Cut-off Score | Expected All India Rank |
| General (UR) | 50 | 710 | 91 |
| OBC | 40 | 706 | 323 |
| EWS | 45 | 695 | 346 |
| SC | 40 | 670 | 1225 |
| ST | 40 | 665 | 3115 |
The difficulty level of the exam, total number of candidates, total number of seats and rank and marks secured in the exam are some of the factors that determine the NEET cut-off score for MBBS at MAMC.
Counselling Process
Once you get the required score in the NEET-UG exam, you need to register online at www.mcc.nic.in to participate in the UG counselling under Delhi Quota and All India Quota.
Process after Successful Seat Allocation
After you have successfully allotted a seat in the University of Delhi affiliated medical colleges, you have to register on the online admission portal of the Faculty of Medical Sciences, Delhi University. Then, upload your documents, photographs, and signatures, and pay the registration fee to get admission into MBBS/BDS for 85% Delhi Quota and 15% All India Quota.
Go to the home page of the website (www.fmsc.ac.in) then click ‘Go to courses’ and then ‘UG courses’. Further, click on ‘MBBS/BDS admission’ and then on the online link under ‘Course updates UG (MBBS/MDS)’.
College Registration Fee
The online registration fee is Rs. 1500 whereas for SC, ST, PwBD, the registration fee is Rs.1000 only.
Required Documents for MAMC Registration
The following mentioned documents are to be uploaded while registering for MAMC MBBS admission after seat allocation:
- Passport-size photograph of the applicant
- Scanned signature of the applicant
- Self-attested copy of NEET-UG admit card
- Self-attested copy of NEET-UG scorecard
- Self-attested copy of Aadhar card
- Self-attested copy of matriculation certificate for verification of DOB
- Self-attested copy of 11th and 12th mark sheet
- Self-attested copy of 10+2 certificate
- Domicile certificate (if applicable)
- Certificate from the School Principal on the prescribed proforma available on the website
- Certificate from the controlling authority of Patrachar Vidyalaya/NIOS (if required)
- Self-attested copy of character certificate
- Category and PwBD certificate (if required)
- Self-attested copy of OCI card (if required)
- Allotment letter issued by MCI
Surety Bond Money
At the time of provisional admission, you are required to execute a bond of three lakh rupees with two sureties to the college.
Click here to get conceptual clarity over MBBS subjects.
MD/MS Courses at MAMC
Admission Procedure
Admission to various MD and MS specialities is done based on the NEET-PG score. It is the only way to get admission to MAMC to pursue an MD/MS degree. A highly competitive score is required to choose a medical speciality of your choice during the counselling process.
Number of Seats
There are a total of 245 PG seats at MAMC. The following table mentions the list of PG specialisation along with the number of seats:
MD Seats
| MD Specialisation | Number of Seats | |
| 50% DUQ | 50% AIQ | |
| Anatomy | 4 | 3 |
| Anaesthesia | 14 | 14 |
| Biochemistry | 5 | 5 |
| Community Medicine | 5 | 5 |
| Dermatology | 2 | 1 |
| Forensic Medicine and Toxicology | 3 | 4 |
| General Medicine | 11 | 11 |
| Microbiology | 5 | 5 |
| Pathology | 4 | 5 |
| Pediatrics | 11 | 12 |
| Pharmacology | 3 | 2 |
| Physiology | 3 | 3 |
| Psychiatry | 2 | 1 |
| Radiodiagnosis | 10 | 10 |
| Radiotherapy | 3 | 3 |
MS Seats
| MS Specialisation | Number of Seats | |
| 50% DUQ | 50% AIQ | |
| ENT | 4 | 4 |
| Orthopaedics | 7 | 8 |
| Ophthalmology | 8 | 9 |
| General Surgery | 8 | 8 |
| Obstetrics and Gynecology | 10 | 10 |
Required Documents for MAMC Registration
These documents are to be uploaded while registering for MAMC MD/MS admission after seat allocation:
- Passport-size photograph of the applicant
- Scanned signature of the applicant
- Self-attested copy of matriculation certificate for verification of DOB
- Self-attested copy of 11th and 12th mark sheet
- Self-attested copy of certificate of MBBS qualification
- Self-attested copy of detailed marks certificate of qualifying exams: I, II, and final prof exams of MBBS and year-wise detailed marks certificate of qualifying UG degree
- Self-attested copy of MBBS examination attempt certificate
- Self-attested copy of compulsory rotatory internship certificate
- Self-attested copy of registration certificate from Delhi Medical Council/State Medical Council/NMC
- Domicile certificate (if applicable)
- Category and PwBD certificate (if required)
- Self-attested copy of employer’s certificate/NOC, if employed
- Self-attested copy of NEET-PG admit card
- Self-attested copy of NEET-PG scorecard
- Self-attested copy of Aadhar card
- Allotment letter issued by MCI
College Registration Fee for MS/MD
The registration fee for MS/MD admission is Rs. 3,000 per course except for SC/ST/PwBD category applicants. For SC/ST/PwBD applicants, the registration fee is Rs. 2000 per course.
MD/MS Fee Structure
The University’s Annual Fee is Rs. 15,900. The breakdown of the MD/MS fees at MAMC, Delhi:
| Particulars (Annual basis) | Amount (in Rs.) |
| Tuition Fees | 13,000 |
| Library Fees | 500 |
| Athletic Fees | 10 |
| Cultural Council Fees | 5 |
| NSS Fees | 20 |
| University Development Fund | 900 |
| Faculty Management Fees | 1,465 |
| Total Fees | 15,900 |
Security Deposit
You have to pay a refundable amount of Rs.10,000 as a security deposit, which will be refunded at the time of completion/leaving the course.
Surety Bond
At the time of admission, you are required to submit a surety bond of Rs. 10 lakhs with two sureties to the college.
DM/M.Ch. Courses at MAMC
Admission Procedure
Admission to three-year super speciality courses at MAMC (DM/M.Ch.) is done based on NEET-SS score. MAMC offers admission to 12 super specialty courses. The seat distribution to the super speciality courses is done under 100% Delhi University Quota (DUQ).
List of DM and M.Ch. courses at MAMC
- M. Cardiology
- M. Cardiac Anaesthesia
- M. Medical Gastroenterology
- M. Neonatology
- M. Neurology
- M. Pulmonary Medicine
- M. Endocrinology
- M. Neuro Anaesthesia
- Ch. CVTS
- Ch. Neurosurgery
- Ch. Pediatric Surgery
- Ch. Surgical Gastroenterology
Required Documents for MAMC Registration
The following documents are to be uploaded while registering for MAMC DM/M.Ch. admission after seat allocation:
- Passport-size photograph of the applicant
- Scanned signature of the applicant
- Self-attested copy of matriculation certificate for verification of DOB
- Self-attested copy of 11th and 12th mark sheet
- Self-attested copy of MBBS degree
- Self-attested copy of detailed marks certificate of qualifying exams: I, II, and final prof exams of MBBS
- Self-attested copy of MD/MS/DNB certificate
- Self-attested copy of MD/MS/DNB examination attempt certificate
- Self-attested copy of registration certificate from Delhi Medical Council/State Medical Council/NMC
- Proof of writing a thesis, if pursued DNB
- Domicile certificate (if applicable)
- Category and PwBD Certificate (if required)
- Self-attested copy of employer’s certificate or NOC, if employed
- Self-attested copy of NEET-SS admit card
- Self-attested copy of NEET-SS scorecard
- Self-attested copy of Aadhar card
- Allotment letter issued by MCI
DM/M.Ch. Fee Structure
The registration fee for college is Rs. 5,000 and the annual fee for super speciality courses is Rs. 25,900. The breakdown of the DM/MCh fee at MAMC, Delhi is:
| Particulars (Annual basis) | Amount (in Rs.) |
| Tuition Fees | 23,000 |
| Library Fees | 500 |
| Athletic Fees | 10 |
| Cultural Council Fees | 5 |
| NSS Fees | 20 |
| University Development Fund | 900 |
| Faculty Management Fees | 1,465 |
| Total Fees | 25,900.00 |
Security Deposit
You have to pay a refundable amount of Rs.10,000 as a security deposit, which will refunded at the time of completion/leaving the course.
Surety Bond
At the time of admission, you are required to submit a surety bond of Rs. 10 lakhs with two sureties to the college.
Apart from the undergraduate, postgraduate, and super speciality courses, MAMC offers admission to various PG Diploma courses and Ph.D. programs in the medical discipline.
The PG Diploma courses include Anaesthesia (D.A.), Obstetrics and Gynecology (D.G.O.), Ophthalmology (D.O.), ENT (D.L.O.), Pediatrics (D.C.H.), Radiodiagnosis (D.M.R.D.) and Dermatology, Venerology & Leprosy (D.D.V.L.)
The Ph.D. degree is offered in three subjects, biochemistry, community medicine, and microbiology with a seat intake of 4, 4, and 2 respectively.
Must Read: AIIMS, Delhi: Courses, Eligibility Qualification, Stipend, Fee Structure & More
Confused about choosing the best medical college? Want to pursue surgery as your PG specialisation?
Choosing the right college for your MS in Surgery can be a daunting task, but it’s an important decision that will impact your future career. We’ve sought out the list of some of the top MS in Surgery colleges in India based on various factors such as ranking, faculty, infrastructure, patient count, and placements. Here’s the description of the top colleges for pursuing MS Surgery and the number of seats in each college for MS Surgery:
Undoubtedly, the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi is a top choice for all medical aspirants. AIIMS is a prestigious institution known for its high academic standards and cutting-edge research in the field of medicine. It has consistently maintained its reputation as a premier medical institution since its founding in 1956, and its MS in Surgery program is no exception. The program is highly competitive, with only a handful of students admitted each year in the surgery specialty. However, those who are fortunate enough to be admitted can anticipate receiving top-notch instruction from some of the nation’s top doctors. The MS in Surgery program at AIIMS is highly sought-after and coveted, attracting the best medical talents from across the country. AIIMS, New Delhi, stands as a beacon of excellence in medical education and research in India. The faculty at AIIMS comprises distinguished experts in various surgical specialties, providing students with exposure to a diverse range of surgical cases. The state-of-the-art facilities and a strong emphasis on practical training contribute to shaping skilled and competent surgeons.
Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh is another top-ranked medical institution in India, and its MS in Surgery program is also highly regarded. Founded in 1962, PGIMER has consistently been at the forefront of medical education in India. The program is known for its strong emphasis on research, and postgraduates of the program often go on to successful careers in academic surgery. PGIMER is renowned for its emphasis on medical research and advanced clinical training. The PGIMER’s MS in Surgery program is known for its experienced faculty and comprehensive curriculum that covers both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. The university actively encourages students to participate in clinical and translational research by promoting a research-oriented strategy. The state-of-the-art labs and collaboration opportunities with other research institutes augment the entire educational experience.
Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore is a well-known private medical college and hospital with a stellar reputation. The MS in Surgery program at CMC Vellore is one of the best in the country, and graduates of the program are in high demand. CMC, Vellore, was founded in 1900 and has earned a reputation for providing high-quality medical education and healthcare services. The MS in Surgery program at CMC is distinguished by its emphasis on ethical medical practices and holistic patient care. The ethical values are integrated into the curriculum, fostering a sense of social responsibility among students. With a focus on both clinical expertise and compassionate patient care, CMC produces surgeons with a strong foundation in both the art and science of surgery.
JIPMER, Pondicherry is a public medical college that is known for providing high-quality education. Not only is JIPMER’s MS in Surgery program among the most affordable in the nation, but it is also one of the most competitive. JIPMER, located in Puducherry, is an autonomous institute known for its high academic standards and research contributions. Established in 1823, JIPMER has consistently been acknowledged as a center of excellence in medical education and healthcare. The MS in Surgery program at JIPMER focuses on advanced surgical training and research. Students have the opportunity to participate in cutting-edge research and stay up-to-date with breakthroughs in the field thanks to the institution’s well-equipped laboratories, research centers, and partnerships with national and international universities.
Banaras Hindu University (BHU), Varanasi is a large and prestigious university that offers a wide range of academic programs, including medical sciences. The MS in Surgery program at BHU is one of the oldest and most respected in the country. The MS in Surgery program at IMS-BHU places a strong emphasis on academic and clinical achievement. Located in Varanasi, the college is renowned for its extensive history and contributions to medical research and teaching Since its founding in 1960, the school has continuously upheld its excellent standards in academia. The MS in Surgery program at IMS-BHU blends practical clinical training with a solid theoretical base. The faculty, comprised of experienced surgeons, actively engages in research, further enriching the learning experience for students. The institution’s focus on academic excellence and ethical medical practices positions it as a sought-after destination for aspiring surgeons.
King George’s Medical University (KGMU), Lucknow is a government-run medical university that is one of the largest and most respected in the country. Offering a broad range of medical and surgical programs, KGMU, located in Lucknow, is a leading medical institution in northern India. The MS in Surgery program at KGMU focuses on both theoretical knowledge and practical surgical skills. Established in 1911, it has evolved into a center of excellence for medical education, research, and patient care. The MS in Surgery program at KGMU is renowned for its extensive curriculum, which includes practical clinical training in addition to academic instruction in surgery. The institution’s commitment to producing well-rounded surgeons is reflected in its emphasis on research, leadership skills, and ethical medical practices.
Armed Forces Medical College (AFMC), Pune was established in 1948 and has consistently produced skilled medical professionals, including surgeons. AFMC, Pune, holds a unique position as a premier institution that primarily caters to the education and training of medical professionals for the armed forces. The MS in Surgery program at AFMC is designed to produce surgeons for military medical services. In order to better prepare graduates for the unique challenges of serving in the armed services, the program incorporates military training with medical ethics and standards.
Maulana Azad Medical College (MAMC), New Delhi is affiliated with the University of Delhi and stands as one of the oldest and most prestigious medical colleges in India. Since 1959, MAMC has made a substantial contribution to medical education and healthcare. The MS in Surgery program at MAMC provides a solid foundation in surgical skills and clinical knowledge. The MS in Surgery program at MAMC is characterized by a robust curriculum and experienced faculty members. The institution’s location in the heart of the capital provides students with exposure to a diverse patient population and a wide range of clinical cases.
Established in 1926, Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai has a legacy of producing skilled healthcare professionals. SGSMC is affiliated with the King Edward Memorial (KEM) Hospital, offering comprehensive medical education. The MS in Surgery program at SGSMC provides students with a strong foundation in surgical principles and techniques. It is one of the largest teaching hospitals in Mumbai, ensuring that students receive exposure to a diverse range of surgical cases and hands-on experience. KEM Hospital is a government-run hospital that is affiliated with the Seth GS Medical College.
Apart from the above-mentioned colleges, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Jodhpur, Kasturba Medical College (KMC), Manipal, and Madras Medical College (MMC), Chennai are also known for their excellent academic programs and facilities.
These are just a few of the many top MS in Surgery colleges in India. When choosing a college, it is important to consider your individual needs and preferences. Some factors to consider include the college’s ranking, faculty, infrastructure, location, and cost.
Read on to know the number of seats available in the respective colleges for MS Surgery.
| College Name | MS Surgery Total Number of Seats |
| All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi | 17 |
| Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh | 19 |
| Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore | 10 |
| JIPMER, Pondicherry | 13 |
| Banaras Hindu University (BHU), Varanasi | 10 |
| King George’s Medical University (KGMU), Lucknow | 24 |
| Armed Forces Medical College (AFMC), Pune | 21 |
| Maulana Azad Medical College (MAMC), New Delhi | 16 |
| Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai | 24 |
| All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Jodhpur | 4 |
| Kasturba Medical College (KMC), Manipal | 21 |
| Madras Medical College (MMC), Chennai | 20 |
In conclusion, the top medical colleges in India offering MS in Surgery programs have a significant influence on shaping the future of surgical healthcare in the country. Each institution brings its unique strengths, be it a focus on research, a commitment to ethical medical practices, or a strong emphasis on practical training. Aspiring surgeons can choose from these esteemed institutions based on their individual preferences, career goals, and the values they prioritize in their medical education. Prospective students need to stay updated on admission criteria, faculty profiles, and program details by referring to the official websites of these institutions or getting in touch with their admission offices.
Must Read: Top Medical Colleges in India: NIRF Ranking
Psychiatry is a specialized medical field that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illnesses along with emotional and behavioral disorders. Studying psychiatry during your MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery) can be both challenging and rewarding.
The curriculum of the Psychiatry speciality in MBBS includes Doctor-patient relationship, Mental health, Introduction to psychiatry, Psychotic disorders, Depression, Bipolar disorders, Anxiety and stress-related disorders, Somatoform and Psychosomatic disorders, Personality disorders, Psychiatric disorders and emergencies, Mental retardation, and Therapeutics.
Knowing high-yield topics, subject weightage in competitive exams, and reliable preparation tips maximise your chances of gaining conceptual clarity over a subject and getting good grades.
In NEET-PG, 5-6 questions are asked from the psychiatry subject, and in INI-CET, the subject weightage of the psychiatry subject is around 4-5 questions.
Important Topics of Psychiatry for NEET-PG and INI-CET
Mental Status Examination
Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Chronic Alcoholism
Antidepressant Drugs
Bipolar Disorder and its Treatment
Substance Abuse and Substance Misuse Disorder
Factitious Disorders and Malingering
Anti-Psychotic Disorders
Acute Dependence
Dissociative Disorders
Delirium
Dementia
Depression and Depressive Disorders
Acute Cocaine Intoxication and Complications
Cannabis Misuse
Sedative Misuse
Phobic Disorders
Delusional Disorder
Capgras and Fregoli Syndrome (including images)
Risk Factors for Suicide
Post Partum Depression
Differential Diagnosis of Panic Disorder
Criterion of Obsessions
Treatment of OCD
PTSD
Stages of Death and Dying
Wernicke’s Korsakoff Syndrome
Alzheimer Disease Neuropathology
Difference between Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa
Stages of Sleep
Narcolepsy
Parasomnias
Management of ADHD
Structural and Topographical Theory of Mind
Defence Mechanisms
Electroconvulsive Therapy
ICD 10, ICD 11, and DSM
Piaget Theory
Basic Terminology in Psychiatry
Organic Amnesic Syndrome
ECT (Electroconvulsive Therapy)
Personality Disorder
Ganser Syndrome
Organic Mental Disorders
Eating Disorders
Sleep Disorders
Sexual Disorders
Schizophrenia Spectrum and Other Psychotic Disorders
Neurotic Stress-Related and Somatoform Disorders
Child Psychiatry
Psychoanalysis
Mental Health Care Act 2017
Must Read: Important Topics of Medicine in MBBS
Must Read: Important Topics of Surgery in MBBS
Tips to Study Psychiatry in MBBS
Studying psychiatry during MBBS can be a rewarding experience, opening doors to a fascinating and impactful field. Here are some tips to help you succeed in studying psychiatry:
Understand the syllabus: Familiarize yourself with the specific topics covered in your MBBS psychiatry curriculum. This will help you prioritize your study efforts and ensure you’re covering all the essential areas.
Grasp the fundamentals: A good understanding of the nervous system and mental processes is crucial for comprehending psychiatric disorders. Ensure a firm grasp of the fundamental medical disciplines, as these lay the groundwork for comprehending mental illnesses.
Practice mental state examination (MSE): Mastering MSE is fundamental for accurately assessing psychiatric patients. Attend clinical postings and practice taking detailed histories, including presenting complaints, past medical history, family history, and psychosocial factors.
Hone your communication skills: In psychiatry, building rapport and communicating with patients successfully are critical skills. Engage in open-ended inquiry, attentive listening, and concise description of diagnosis and available treatments.
Develop clinical skills: Actively seek clinical exposure. Spend time in psychiatric wards and clinics to observe and interact with patients. Practical experience is crucial in psychiatry.
Shadow experienced psychiatrists: Observing experienced professionals can provide invaluable insights into clinical practice. During your rotations, try to observe psychiatrists or seek mentorship opportunities. They can guide you, provide valuable insights, and support your career development.
Utilize effective resources: Read a variety of psychiatric literature, including textbooks, journals, and case studies. This will deepen your understanding of different disorders and treatment modalities.
Use technology: Utilize online resources and technology for self-assessment, e-learning, and staying connected with the latest advancements.
Practice questions: Solving MCQs and mock exams can help you solidify your understanding of key concepts and prepare for future exams.
Case discussions: Participate in case discussions with your peers and seniors. Sharing experiences and perspectives enhances your learning and problem-solving skills.
Embrace a holistic approach: Understanding patients’ perspectives and respecting their cultural backgrounds is essential for providing effective care and sensitive care to a wide range of patients.
Practice self-care: Studying psychiatry can be emotionally demanding. Make sure to prioritize your mental and physical well-being through regular exercise, relaxation techniques, and social support.
Stay curious and engaged: Psychiatry is an ever-evolving discipline, so keep your curiosity and involvement high. To increase your expertise, stay up to date on the most recent research findings and attend conferences, webinars, and workshops.
Stay updated with DSM criteria: Familiarize yourself with the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) criteria. The DSM is a standard classification of mental disorders and is essential for diagnosis.
Stay open-minded: Keep an open mind and avoid stigmatising attitudes towards mental health. Psychiatry often involves dealing with complex and subjective issues.
Remember that studying psychiatry is not just about acquiring knowledge but also developing the skills and attitudes necessary for compassionate and effective patient care. Balancing theoretical knowledge with practical experience is key to becoming a proficient psychiatrist.
Best Books for Psychiatry
Review of Psychiatry by Praveen Tripathi: It is among the best-selling books on Psychiatry. The latest edition of the book has been updated with DMS criteria, ICD-11, and Mental Health Care Act. This book has been developed keeping in mind the demands of students preparing for different postgraduate entrance examinations and MCI screening tests.
Textbook of Psychiatry by B.K. Puri and I. H. Treasaden: The book is written in a lucid manner and is rich in pedagogic features, such as summary boxes, and clinical cases. It includes many illustrations, self-assessment material, patient management advice, and much more.
Kaplan & Sadock’s Synopsis of Psychiatry: Behavioral Sciences/Clinical Psychiatry by Benjamin James Sadock and Virginia Alcott Sadock: The latest edition of the book is a comprehensive, succinct summary of the entire field of psychiatry and is a favorite among a wide spectrum of medical students and professionals.
Oxford Handbook of Psychiatry by David Semple and Roger Symth: The latest edition of the book covers almost all major psychiatric conditions and sub-specialities along with comprehensive and practical guidelines. It further includes psychiatric assessment, psychopathology, evidence-based practice, DSM-IV index, ICD, and much more.
Must Read: Best books for MBBS 4th year
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the subject weightage of psychiatry in NEET-PG?
Ans. Psychiatry is a specialized medical field that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illnesses along with emotional and behavioral disorders. In NEET-PG, 5-6 questions are asked from the psychiatry subject.
Q2. What is the subject weightage of psychiatry in INI-CET?
Ans. Psychiatry is a medical speciality that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illnesses along with emotional and behavioral disorders. In INI-CET, the subject-weightage of psychiatry subject is around 4-5 questions.
Q3. What are the important topics in psychiatry in MBBS?
Ans. The important topics in psychiatry in MBBS include mental status examination, antidepressant drugs, bipolar disorder and its treatment, substance abuse and substance misuse disorder, schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders, delirium, dementia, depression, phobic disorders, suicide, panic disorder, treatment of OCD, PTSD, wernicke’s korsakoff syndrome, stages of sleep, management of ADHD, ICD, and DSM criteria, ECT, sleep disorders, somatoform disorders and mental health care act.
Q4. How to prepare psychiatry for NEET-PG?
Ans. Here are some tips to prepare for psychiatry subject for NEET-PG:
- Understand the syllabus
- Grasp the fundamentals
- Practice mental state examination (MSE)
- Develop clinical skills
- Utilize effective resources
- Enroll in e-learning platforms
- Practice questions
- Case discussions
- Stay updated with DSM criteria
- Manage time efficiently
A new list of recognised medical courses has been released by NMC in the Post Graduate Medical Education Regulations dated 04.01.24. It is highly advised that the students go through the list of recognised degrees and qualifications before enrolling in any medical program.
The blog provides you with a list of recognised degree and diploma programs in the medical field along with the specialities and sub-specialities available in them. It also includes the list of qualifications and duration of the course.
It includes a list of:
• Recognised Post-Graduate Broad Speciality Qualifications (M.D./M.S.)
• Recognised Post-Graduate Super Speciality Qualifications (D.M./M.Ch.)
• Recognised Post-Graduate Diploma Qualifications
• Recognised Post-Doctoral Certificate Courses (PDCC) Qualification
• D.M. and M.Ch. Courses of Six Years Duration
• Feeder Broad Speciality Qualifications for Super Speciality Courses
List of Qualifications and Course Duration
| S. No. | Name of Qualification | Duration of Course (including examination period) |
| 1 | Post-Graduate Broad-Speciality Qualifications | 3 Years/2 years*(for those who have done two-year post-graduate diploma course in the same course) |
| 2 | Post-Graduate Super-Speciality Courses | 3 Years |
| 3 | Post-Graduate Diploma Courses | 2 Years |
| 4 | Post-Doctoral Certificate Courses (PDCC) | 1 Year |
| 5 | Post-Doctoral Fellowship (PDF) Courses | 2 Years |
| 6 | D.M./M.Ch. (6 years Course) | 6 Years |
A. List of Recognised Post-Graduate Broad Speciality Qualifications (M.D./M.S.)
M.D. (Doctor of Medicine)
1. M.D. (Aerospace Medicine)
2. M.D. (Anatomy)
3. M.D. (Anaesthesiology)
4. M.D. (Biochemistry)
5. M.D. (Biophysics)
6. M.D. (Community Medicine)
7. M.D. (Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy)
8. M.D. (Emergency Medicine)
9. M.D. (Family Medicine)
10. M.D. (Forensic Medicine and Toxicology)
11. M.D. (General Medicine)
12. M.D. (Geriatrics)
13. M.D. (Health Administration)
14. M.D. (Hospital Administration)
15. M.D. (Immuno Haematology and Blood Transfusion)
16. M.D. (Laboratory Medicine)
17. M.D. (Marine Medicine)
18. M.D. [Master of Public Health (Epidemiology)]
19. M.D. (Microbiology)
20. M.D. (Nuclear Medicine)
21. M.D. (Pediatrics)
22. M.D. (Palliative Medicine)
23. M.D. (Pathology)
24. M.D. (Pharmacology)
25. M.D. (Physical Medicine Rehabilitation)
26. M.D. (Physiology)
27. M.D. (Psychiatry)
28. M.D. (Radiation Oncology)
29. M.D. (Radio-diagnosis)
30. M.D. (Respiratory Medicine)
31. M.D. (Sports Medicine)
32. M.D. (Tropical Medicine)
M.S. (Master of Surgery)
1. M.S. (General Surgery)
2. M.S. (Obstetrics and Gynecology)
3. M.S. (Ophthalmology)
4. M.S. (Orthopaedics)
5. M.S. (Otorhinolaryngology)
6. M.S. (Traumatology and Surgery)
B. List of Recognised Post-Graduate Super Speciality Qualifications (D.M./M.Ch.)
D.M. (Doctorate of Medicine)
1. D.M. (Cardiac Anaesthesia)
2. D.M. (Cardiology)
3. D.M. (Child and Adolescent Psychiatry)
4. D.M. (Clinical Haematology)
5. D.M. (Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology)
6. D.M. (Clinical Pharmacology)
7. D.M. (Critical Care Medicine)
8. D.M. (Endocrinology)
9. D.M. (Geriatric Mental Health)
10. D.M. (Hepatology)
11. D.M. (Infectious Disease)
12. D.M. (Interventional Radiology)
13. D.M. (Medical Gastroenterology)
14. D.M. (Medical Genetics)
15. D.M. (Medical Oncology)
16. D.M. (Neonatology)
17. D.M. (Nephrology)
18. D.M. (Neuro-Anaesthesia)
19. D.M. (Neurology)
20. D.M. (Neuro-Radiology)
21. D.M. (Onco-Pathology)
22. D.M. (Organ Transplant Anaesthesia and Critical Care)
23. D.M. (Pediatric and Neonatal Anaesthesia)
24. D.M. (Pediatric Cardiology)
25. D.M. (Pediatric Critical Care)
26. D.M. (Pediatric Gastroenterology)
27. D.M. (Pediatric Hepatology)
28. D.M. (Pediatric Nephrology)
29. D.M. (Pediatric Neurology)
30. D.M. (Pediatric Oncology)
31. D.M. (Pulmonary Medicine)
32. D.M. (Virology)
M.Ch. (Master of Chirurgie)
1. M.Ch. (Endocrine Surgery)
2. M.Ch. (Gynecological Oncology)
3. M.Ch. (Hand Surgery)
4. M.Ch. (Head and Neck Surgery)
5. M.Ch. (Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary-Surgery)
6. M.Ch. (Neurosurgery)
7. M.Ch. (Pediatric Cardio Thoracic Vascular Surgery)
8. MCh. (Pediatric Orthopaedics)
9. M.Ch. (Pediatric Surgery)
10. M.Ch. (Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery)
11. M.Ch. (Reproductive Medicine and Surgery)
12. M.Ch. (Surgical Gastroenterology)
13. M.Ch. (Surgical Oncology)
14. M.Ch. (Urology)
15. M.Ch. (Vascular Surgery)
16. M.Ch. (Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery)
C. List of Recognised Post-Graduate Diploma Qualifications
1. Allergy and Clinical Immunology
2. Anaesthesiology (D.A.)
3. Clinical Pathology (D.C.P.)
4. Community Medicine (D.C.M.)/ Public Health (D.P.H.)
5. Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy (D.D.V.L.)
6. Forensic Medicine (D.F.M.)
7. Health Education (D.H.E.)
8. Health Administration (D.H.A.)
9. Immuno-Haematology and Blood Transfusion (D.I.H.B.T.)
10. Marine Medicine (Dip. M.M.)
11. Microbiology (D. Micro)
12. Nutrition (D.N.)
13. Obstetrics and Gynecology (D.G.O.)
14. Occupational Health (D.O.H.)
15. Ophthalmology (D.O.)
16. Orthopaedics (D. Ortho.)
17. Otorhinolaryngology (D.L.O.)
18. Pediatrics (D.C.H.)
19. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation (D. Phy. Med. and R.)
20. Psychiatry (D.P.M.)
21. Radiation Medicine (D.R.M.)
22. Radiodiagnosis (D.M.R.D.)
23. Radio-therapy (D.M.R.T.)
24. Radiological Physics (D.R.P.)
25. Sport Medicine (D.S.M.)
26. Tropical Medicine and Health (D.T.M. and H.)
27. Tuberculosis and Chest Diseases (D.T.C.D.)
28. Virology (D. Vir.)
D. List of Recognised Post-Doctoral Certificate Courses (PDCC) Qualification
1. PDCC in Organ Transplant Anaesthesia
2. PDCC in Pediatric Endocrinology
3. PDCC in Laboratory Immunology
4. PDCC in Nuclear Nephrology
5. PDCC in Renal Pathology
6. PDCC in Gastro-Radiology
7. PDCC in Aphaeresis Technology and Blood Component Therapy
8. PDCC in Pain Management
9. PDCC in Haemato-Oncology
10. PDCC in Pediatric Endocrinology
11. PDCC in Pediatric ENT
12. PDCC in Spine Surgery
E. List of D.M. and M.Ch. Courses of Six Years Duration
1. D.M. Neurology
2. M.Ch. Neurosurgery
Feeder Broad Speciality Qualifications for Super Speciality Courses
D.M. (Doctorate of Medicine)
| S.No. | Area of Specialisation | Feeder Broad Speciality Qualification(s) |
| 1 | D.M. (Cardiac Anaesthesia) | M.D./DNB (Anaesthesia) |
| 2 | D.M. (Cardiology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) M.D./DNB (Respiratory Medicine) |
| 3 | D.M. (Child and Adolescent Psychiatry) | M.D./DNB (Psychiatry) |
| 4 | D.M. (Clinical Haematology) | M.D./DNB (Biochemistry) M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) M.D./DNB (Pathology) |
| 5 | D.M. (Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 6 | D.M. (Clinical Pharmacology) | M.D./DNB (Pharmacology) |
| 7 | D.M. (Critical Care Medicine) | M.D./DNB (Anaesthesia) M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) M.D./DNB (Respiratory Medicine) M.D./DNB (Emergency Medicine) |
| 8 | D.M. (Endocrinology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 9 | D.M. (Geriatric Mental Health) | M.D./DNB (Psychiatry) |
| 10 | D.M. (Hepatology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 11 | D.M. (Infectious Disease) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) M.D./DNB (Microbiology) M.D./DNB (Respiratory Medicine) M.D./DNB (Tropical Medicine) |
| 12 | D.M. (Interventional Radiology) | M.D./DNB (Radio-diagnosis) |
| 13 | D.M. (Medical Gastroenterology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) |
| 14 | D.M. (Medical Genetics) | M.D./M.S./DNB in any subject |
| 15 | D.M. (Medical Oncology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) M.D./DNB (Radiation Oncology) |
| 16 | D.M. (Neonatology) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 17 | D.M. (Nephrology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 18 | D.M. (Neuro- Anaesthesia) | M.D./DNB (Anaesthesia) |
| 19 | D.M. (Neurology) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 20 | D.M. (Neuro-Radiology) | M.D./DNB (Radio-diagnosis) |
| 21 | D.M. (Onco-Pathology) | M.D./DNB (Pathology) |
| 22 | D.M. (Organ Transplant Anaesthesia and Critical Care) | M.D./DNB (Anaesthesia) |
| 23 | D.M. (Pediatric and Neonatal Anaesthesia) | M.D./DNB (Anaesthesia) |
| 24 | D.M. (Pediatric Cardiology) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 25 | D.M. (Pediatric Critical Care) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 26 | D.M. (Pediatric Gastroenterology) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 27 | D.M. (Pediatric Hepatology) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 28 | D.M. (Pediatric Nephrology) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 29 | D.M. (Pediatric Neurology) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 30 | D.M. (Pediatric Oncology) | M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 31 | D.M. (Pulmonary Medicine) | M.D./DNB (General Medicine) M.D./DNB (Respiratory Medicine) M.D./DNB (Pediatrics) |
| 32 | D.M. (Virology) | M.D./DNB (Microbiology) |
M.Ch. (Master of Chirurgie)
| S.No. | Area of Specialisation | Feeder Broad Speciality Qualification(s) |
| 1 | M.Ch. (Endocrine Surgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 2 | M.Ch. (Gynecological Oncology) | M.D./M.S./DNB (Obstetrics and Gynecology) |
| 3 | M.Ch. (Hand Surgery) | M.S./DNB (Orthopaedics) |
| 4 | M.Ch. (Head and Neck Surgery) | M.S./DNB (Otorhinolaryngology) M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 5 | M.Ch. (Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary-Surgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 6 | M.Ch. (Neurosurgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery)
M.S./DNB (Otorhinolaryngology) |
| 7 | M.Ch. (Pediatric Cardio Thoracic Vascular Surgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 8 | M.Ch. (Pediatric Orthopaedics) | M.S./DNB (Orthopaedics) |
| 9 | M.Ch. (Pediatric Surgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 10 | M.Ch. (Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery)
M.S./DNB (Otorhinolaryngology) |
| 11 | M.Ch. (Reproductive Medicine and Surgery) | M.D./M.S./DNB (Obstetrics and Gynecology) |
| 12 | M.Ch. (Surgical Gastroenterology) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 13 | M.Ch. (Surgical Oncology) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery)
M.S./DNB (Otorhinolaryngology) M.S./DNB (Orthopaedics) |
| 14 | M.Ch. (Urology) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 15 | M.Ch. (Vascular Surgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
| 16 | M.Ch. (Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery) | M.S./DNB (General Surgery) |
Dr. Aswath Kumar Raghu, the Chief Editor of OBGYN MD has crafted the course along with 98 eminent faculty. He is one of the leading practitioners and faculty affiliated with Jubilee Mission Medical College and Research Institute. He is also famous for his book – “Exploring New Horizons in Obstetrics and Gynecology” (What to do next after MD in Obstetrics and Gynecology?).
OBGYN MD course has been conceptualized based on the NMC Curriculum and the last 20 years’ question papers across various universities to aid PG students while preparing for university examinations. This course is one of the best postgraduate courses in OBGYN for students who are aiming for a master’s in gynecology / master’s in obstetrics. It encourages concept-based and approach-based learning to cater to all the learning needs of the students. It encompasses important topics in obstetrics and gynecology along with case discussions on frequently encountered as well as atypical cases in clinical practice. All the topics in the course have been thoughtfully selected keeping in mind the pain areas of the postgraduate students for which they struggle to find sufficient information as well as frequently asked topics.
The case presentations have been done as an open discussion between the concerned faculty and the students who are pursuing PG in gynecology and obstetrics. There is special emphasis on the correct format of case and history taking and eliciting the correct clinical findings. The faculty and student discussion has been done in a way to help the viewers to approach a case with appropriate differential diagnosis and work up a way to correct diagnosis. Recent evidence-based recommendations have been included for the management of various conditions to acquaint the viewers with recent advancements in the field.
A special section has been dedicated to the demonstration of Minimum Invasive Surgeries like hysteroscopy, diagnostic/operative laparoscopy. This will provide a practical orientation to the study of the subject. Students will be thrilled with the lecture on Robotic laparoscopic surgery focusing on its relevance, application, and implications in the field of obstetrics and gynecology and how it is a boon from a future perspective. The in-video demonstration of the various surgeries being performed will give a whole new dimension to the understanding of the concepts.
Lectures on the management of labor, abnormal labor, abnormal presentations, and medical disorders in pregnancy will enrich the practical application of concepts for the students as well as provide them a roadmap on how to manage these conditions effectively. The important diagnostic procedures/techniques have been covered in detail like ultrasound in the antenatal examination as well as its utility in gynecology. A detailed drug chart has been provided for quick reference by the students with a special focus on drugs dosages and their indications/contraindications in pregnancy and labor.
The lectures are richly illustrated with clinical and radiological images along with flowcharts, tables, and boxes, wherever necessary to aid students in developing a thorough overview of each topic, which will also fulfill their examination needs.
The Course Includes:
-
- Video Lectures: 145+ hours of video lecture supported with benchmark/evidence-based studies.
- Lecture Notes: This course includes well-illustrated 190+ lecture notes which will act as a ready reckoner for students.
- Clinical Case-Based Discussion: Ample case discussions have been included to provide a clinical orientation to the students.
- Self-Assessment Questions: 1750+ MCQs have been included for self-assessment.
- Interactive Drug Formulary: Detailed drug formulary including safety during pregnancy and lactation.
- OSCEs: 150+ OSCEs provide a standardized and objective method of assessing a postgrad’s clinical skills and competencies.
- DxTx: A unique tool comprising 145+ topics for quick consultation. This unique feature allows you to explore critical information in a click. You can learn about the various diseases with clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, recent advances and clinical trials in a structured format.
- Engagement Activities: Regular Chat Shows and Journal Clubs for discussion of important topics with a panel of eminent faculty.
- Dr. Wise (AI Chatbot): The chatbot clarifies theoretical as well as practical concepts with the help of AI. It is a comprehensive and interactive solution provider integrated with authentic published resources like books, journals, notes, and videos to offer apt explanations of concepts, treatment modes and more.
-
- Printed Notes: Concise notes are designed to save time by providing exam-focused, crisp details along with visual learning at an affordable price. The notes also comprise previous years’ questions and ensure comprehensive coverage in minimum time. Existing users can purchase the printed notes @3,499 from here.
3 Days Money Back Guarantee available T&Cs apply.
Anaesthesiology is a medical speciality that deals with the perioperative care of patients before, after, and during surgery. It is a dynamic field with evolving practices.
Anaesthesiology subject in MBBS requires a combination of theoretical understanding, practical application, and critical thinking. Regular, focused, and integrated study approaches will contribute to your success in understanding and applying anaesthesia concepts to real-life cases.
Knowing high-yield topics, exam pattern, subject weightage in competitive exams, and reliable preparation tips maximise your chances of gaining conceptual clarity over a subject and getting good grades.
Subject Weightage of Anaesthesiology in Competitive Entrance Exams
The Anaesthesiology speciality is grouped with Orthopaedics, ENT, Ophthalmology, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, and Radiodiagnosis in the General Surgery subject, as per the new MBBS academic pattern.
In NEET-PG, the weightage of the surgery subject is around 45 questions from which the average number of questions asked from the anaesthesiology specialty is around 5-8 questions.
In INI-CET, approximately 35 questions are asked from the General Surgery subject in the INI-CET, out of which anaesthesiology holds a weightage of around 5-7 questions.
Important Topics of Anaesthesiology for NEET-PG and INI-CET
Types of Anaesthesia
Difference between GA and LA
Spinal Anaesthesia
Epidural Anaesthesia
Intravenous GA
- Thiopentone
- Methohexital
- Propofol
- Etomidate
- Ketamine
- BZD
Inhalational GA
- N2O
- Halothane
- Enflurane
- Isoflurane
- Desflurane
- Sevoflurane
Skeletal Muscle Relaxants (Including Neuromuscular Blockers)
- Pancuronium
- Vecuronium
- Rocuronium
- Gantacurium
- Succinylcholine
- Atracurium
- Cis-atracurium
- Dantrolene
- Mivacurium
Local Anaesthesia
- Bupivacaine
- Lignocaine
- Cocaine
- MOA
- Ropivacaine
LA Toxicity
Monitoring
- ECG
- BP
- Pulse oximeter
- Capnography
- Temperature
- Arterial blood gas analysis
- Bispectral index (BIS)
- Neuromuscular monitoring
- Monitoring Anaesthesia Care
- Mandatory Monitoring
Equipments and Anaesthesia Machine
- Cylinders- pin index and colours
- Breathing circuits
- Vaporizers
- Colo
- r coding of knobs
- Endotracheal tubes (types- IBQ)
- Laryngeal mask airway
- Airway devices
- Difficult Airway
- Ventilators – Names of modes of ventilation
- Critical care
- Mapleson Circuits
IV Fluids
- Crystalloid
- Colloids
Blood Transfusion
Oxygen Therapy
Endotracheal Intubation Indications
Caudal Block
Preparation of Patient for Anaesthesia
Brain Death
Stages of Anaesthesia
Resuscitation Protocol
Tips to Study Anaesthesiology in MBBS
Wondering how to prepare a strategy to score high in Anaesthesia? Thinking of some effective Anaesthesia preparation tips?
Studying anaesthesia in MBBS can be both challenging and rewarding. Here are some tips to help you effectively study anaesthesia:
- Develop a strong foundation in basic sciences. Anaesthesia relies heavily on a good understanding of 1st and 2nd year MBBS subjects. Start by establishing a solid foundation in fundamental medical science subjects with a focus on pharmacology and physiology. Comprehending the fundamental concepts of these subjects is essential to understanding anesthesia.
- Avoid cramming and focus on understanding concepts. Since anaesthesia is a complex subject, it’s important to understand the underlying principles behind the practice. Strive to comprehend how and why things work the way rather than merely memorizing facts.
- Use a variety of learning resources. There are many different resources available to help you learn anaesthesia, including textbooks, journal articles, and online courses. Choose a variety of tools that suit your needs, and don’t be scared to explore new things. For a thorough understanding of the topic, refer to standard anesthesia textbooks.
- Get involved in extracurricular activities and case discussions. You can learn more about anesthesia through a variety of extracurricular activities, such as attending conferences, workshops, and webinars. These activities help you develop your clinical skills. Discussing complex topics with others can provide different perspectives and improve your understanding. Engage in case discussions with your peers and instructors to enhance your problem-solving skills and anaesthesia management.
- Practice, practice, practice. The best way to learn anaesthesia is to practice. The more you practice, the more confident you will be. Practice questions and cases pertaining to anaesthesia scenarios. This could involve calculating drug dosages, understanding physiological responses, and managing complications. You can also practice and enhance your clinical skills by shadowing an anaesthetist, working in a simulation lab, or participating in clinical rotations. Observing real-life scenarios will deepen your understanding and help you apply theoretical knowledge.
Some additional tips to study anaesthesia:
- Set realistic goals and focus on achieving one at a time.
- Take breaks avoid burnout and stay focused.
- Reward yourself and stay motivated.
- Don’t be afraid to seek guidance; it can make a big difference in your success.
- Attend lectures regularly and take detailed notes.
- Stay updated on the latest research, guidelines, and advancements to enhance your knowledge.
- Create mnemonics and flowcharts to help remember key concepts and their sequences.
- Use flashcards to reinforce your memory of key concepts, drug doses, and important facts.
- Prioritize High-Yield Topics.
- Pay attention to common procedures, complications, and management strategies.
- Practice time management and avoid procrastination.
- Take mock exams to identify your weak areas and refine your exam-taking strategies.
Best Books for Anaesthesiology
- Anaesthesia Essence by Pritesh Singh & Usica Chandan: A must-have book for competitive entrance examinations and a comprehensive guide with thoroughly updated and revised content. It includes exam pattern questions, important annexures, and image-based questions for better understanding and comprehension.
- Short Textbook of Anaesthesia by Ajay Yadav: One of the preferred books for medical graduates and postgraduate students. It serves as a ready reckoner. The key points are highlighted in italics with a tabular overview. Recent advancements are also included.
- Objective Anaesthesia Review: A Comprehensive Textbook for the Examinees by Atul Prabhakar Kulkarni: It is a preferred resource for examinations and equips students and practitioners to practice safe anaesthesia.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the subject weightage of anaesthesia in NEET-PG?
Ans. In NEET-PG, the weightage of the surgery subject is around 45 questions, from which the average number of questions asked from the anaesthesiology specialty is 5-8 questions.
Q2. What is the subject weightage of anaesthesia in INI-CET?
Ans. Approximately 35 questions are asked from the General Surgery subject in the INI-CET, out of which anaesthesiology holds a weightage of around 5-7 questions.
Q3. What are the important topics in anaesthesiology in MBBS?
Ans. The important topics in Anaesthesiology in MBBS are spinal anaesthesia, epidural anaesthesia, intravenous GA, inhalational GA, skeletal muscle relaxants, neuromuscular blockers, local anaesthesia, LA toxicity, bispectral index (BIS), neuromuscular monitoring, monitoring anaesthesia care, cylinders- pin index and colours, breathing circuits, modes of ventilation, IV fluids, blood transfusion, oxygen therapy, brain death, stages of anaesthesia and resuscitation protocol.
Q4. How to prepare anaesthesia for NEET-PG?
Ans. Follow some reliable tips to prepare for NEET-PG, such as establishing a solid foundation in fundamental medical sciences, focusing on understanding concepts, not just memorizing facts, using a variety of learning resources including textbooks, journal articles, and online courses, getting involved in extracurricular activities and case discussions, attending conferences, workshops, and webinars, developing clinical skills, and observing real-life scenarios. Also, the more you practice, the more confident you will become in your skills.
Intercollegiate MRCS Part B is an Objective Structured Clinical Exam (OSCE) and is a part of the Membership of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons (MRCS) qualification. It is a challenging exam designed to assess the clinical knowledge and skills of candidates who have successfully completed MRCS Part A.
Getting awarded with the Membership of the Royal College of Surgeons is a prime reason for taking the MRCS examination. Additionally, passing the MRCS Part B exam is an important step in your surgical career. It will allow you to apply for higher levels of surgical training, such as specialist registrar training. It will also give you a competitive advantage when applying for surgical jobs.
MRCS Exam Eligibility
The prime eligibility criterion to sit in the MRCS exam is a medical degree. Also, the degree must be acceptable to the UK General Medical Council (GMC) or the Medical Council in Ireland for full or provisional registration.
If you are a first-time applicant, then you are required to submit your original certificate of a medical degree acceptable to the councils of the four colleges to get registered with GMC or Medical Council (Ireland).
You can go for MRCS Part B only after passing the MRCS Part A exam.
Exam Format
MRCS Part B is an objective structured clinical exam that comprises 18 examined stations, each of 9 minutes duration. OSCEs involve a series of stations where candidates are presented with clinical scenarios and are required to demonstrate their examination, communication, and decision-making skills. Viva examinations involve verbal questioning on various aspects of surgery.
The main content areas assessed at these stations are:
Applied Knowledge: It includes anatomy, surgical pathology, applied surgical science, and critical care.
Applied Skills: It include communication skills in giving and receiving information, history taking, and clinical & procedural skills.
The ‘Knowledge’ and ‘Skills’ sections of the OSCE must be passed in a single sitting. You will have to re-sit for part B if you fail in any of the two sections.
How OSCE is Conducted?
The OSCE consists of a series of stations in a circuit that you need to rotate around.
You must complete a task that has been specifically stated at each station.
MRCS OCSE may include doing a focused history or clinical examination, analyzing an X-ray, or performing a practical procedure in a simulated setting.
One minute is given to move from one station to another and 8 minutes to complete a task. This also facilitates the completion of your mark sheets by the examiners and helps the patient or simulated patient get ready for the next candidate.
You will be given explicit instructions at each station that include a brief description of the situation and the task that needs to be performed.
Make sure you introduce yourself at each station, state the objective of the task, verify the patient’s identity, and obtain their consent before doing any necessary tasks.
You should always wash your hands both before and after dealing with patients with the supplied alcohol-based hand gel.
Exam Dates
You can only apply to one Royal College of Surgeons at a time.
| MRCS Exam | Examination Slot Dates | Application Closing Date | Fee | Exam Location |
|
UK and Ireland Exams |
03 Feb 2024 to 18 Feb 2024 | 16 Nov 2023 | £1047.00
|
London, UK
Glasgow, UK |
| 04 May 2024 to 19 May 2024 | 29 Feb 2024 | £1047.00
|
Sheffield, UK
London, UK Glasgow, UK |
|
| International Exams | 28 Feb 2024 to 08 March 2024 | 07 Dec 2023 | £1047.00
|
Cairo, Egypt |
Note: The MRCS Part 2 exam at the Cairo and New Delhi centres will be conducted in the hybrid mode, i.e., at some stations, you will be examined by an examiner on a video call.
Steps to Book an MRCS Part B Exam
To book an MRCS Part B exam, you are required to visit the official website of the Royal College of Surgeons or the website of the particular RCS college you need to book an exam. Then, go to the Intercollegiate MRCS Part B exam and click on the ‘Book Online’ option provided with the exam date and details. After that, you must sign in with your login credentials. Fill in all the required details and upload documents, wherever required. At last, pay the fee as per your exam country and centre.
Number of Attempts
You have a chance to attempt the MRCS exam Part B four times, i.e., you have four attempts to qualify for Part B MRCS exam. There is a possibility that one additional attempt may be granted under the Additional Attempt Policy.
GMC recommends to complete the MRCS exam process within a time period of 7 years.
Syllabus
The content of the MRCS exam is based on the Intercollegiate Surgical Curriculum Programme (ISCP) syllabus. It is important to be familiar with the syllabus to ensure comprehensive preparation. The MRCS Part 2 syllabus involves four major content areas and four domains which cover the knowledge, competencies, skills, and professional traits of a surgeon.
Four major content areas are:
- Anatomy and surgical pathology
- Applied surgical science and critical care
- Clinical and procedural skills
- Communication skills
Four main domains are:
Domain 1: Knowledge skills and performance
Domain 2: Safety and Quality
Domain 3: Communication partnership and teamwork
Domain 4: Maintaining trust
MRCS Exam Result and Candidate Feedback Form
To pass the MRCS Part B exam, you need to demonstrate a solid understanding of surgical principles, effective clinical skills, and the ability to apply your knowledge in a practical setting. Examiners fill out the ‘Candidate Feedback Form’ which is basically an evaluation sheet. Examiners are guided in allocating marks by generic descriptors, which are used to identify and award a mark for each domain using a standardized mark sheet.
The candidate feedback form has four tables,
Table 1: Overall OSCE result (marked as PASS or FAIL).
Table 2: OSCE Marks
Table 3: Content Areas
Table 4: Domains
Every single station is evaluated in two different ways.
- a mark is awarded for each station and assessed domain.
- an overall judgement is given as pass, borderline, or fail.
As a result of the evaluation, the candidates will receive an overall performance rating and a grade out of 20 for each station. Then, using a recognized technique called ‘Borderline Regression Methodology’, the marks and global ratings are used to create the overall pass mark for each station. Although, there are no overall pass marks as a whole.
Tips for Preparing for the MRCS Part B Exam
The following are some of the reliable MRCS preparation tips:
Revision resources: Enrolling in good online revision resources will provide an edge to your MRCS preparation and also cover the entire syllabus of the exam.
Practice OSCEs: Practice OSCE questions as much as possible and solve mock exams that can help you get used to the format of the actual exam.
Self-study: There are several textbooks and resources that you can use to study for the exam.
Start preparing early: The MRCS Part B is a challenging exam, so it is important to give yourself plenty of time to prepare.
Make a study plan: Break down the syllabus into manageable chunks and create a study plan that will help you cover all the study material and syllabus.
Practice, practice, practice: The best way to prepare for the MRCS Part B exam is to practice, practice, and practice. There are a number of different platforms that offer practice OSCEs, so find one that is right for you.
Get support: Preparing for the MRCS Part B exam can be stressful, so it is important to get support from your friends, family, and colleagues.
Prioritize health: Take a good diet and a proper sleep. It is crucial to take care of your health so that you can focus on preparation and create a work-life balance.
Membership of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons (MRCS) is an intercollegiate exam conducted to assess the clinical competency, knowledge, and experience that trainees should have by the completion of their basic surgical training. The exam is designed to evaluate prospective surgeons across a wide range of surgical problems, not simply the specialty they intend to pursue.
The most important benefit of passing the MRCS Exam is that a passing score on the MRCS test allows a student enrolled in the Intercollegiate Surgical Curriculum Programme (ISCP) to advance to further specialised training, as well as membership in one of the four Surgical Royal Colleges in the UK and Ireland.
The four Surgical Royal Colleges in the UK and Ireland jointly oversee the intercollegiate MRCS and DO-HNS exams. On behalf of the colleges, the Intercollegiate Committee for Basic Surgical Examinations (ICBSE) creates, updates, and verifies MRCS and DO-HNS.
The four Royal Colleges are:
- The Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh
- The Royal College of Surgeons of England
- The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow
- The Royal College of Surgeons of Ireland
The MRCS exam has two parts:
Part A: Written Exam
Part B: Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE)
Let’s delve into the details of the MRCS Part A exam.
Intercollegiate MRCS Part A Examination
The intercollegiate MRCS Part A is a written examination and is a first step towards your journey of getting membership of the Royal College of Surgeons. Part A comprises two papers.
Eligibility
The following are the eligibility criteria for taking the MRCS Part A exam:
- You must have completed your General Medical Qualification or equivalent degree from a recognized college or university.
- You must have the UK General Medical Council or Medical Council in Ireland accepted medical degree for full or provisional registration.
- First-time applicants must email their general medical degree original certificate acceptable to the councils of four colleges to get the registration number. You can email at SurgicalEligibility@rcseng.ac.uk.
- If you are a first-time MRCS applicant, then you are required to provide your valid GMC UK or Medical Council (Ireland) registration number as a part of the booking process.
- If you have already taken an MRCS exam for any of the four colleges, you need not register with the GMC UK or Medical Council (Ireland) again.
- You can only go to Part B after passing the Part A exam.
Exam Format
The Intercollegiate MRCS Part A comprises two papers of five-hour duration in total. The papers include the fundamental information required in each of the nine specializations as well as applied and general surgical sciences knowledge.
MRCS Part A is a computer-based exam with objective-type questions. There will be five possible answers from which you have to choose one single best answer. The exam comprises both Single best answers (SBAs) and Extended matching MCQs (EMQs). Both parts of the examination will be conducted in English. The standard used for setting the exam paper is the An off method.
MRCS Part A Exam Scheme:
Paper 1:
- The duration of the AM exam is three hours.
- It comprises MCQs on Applied Basic Sciences.
- The total number of questions is 180 questions.
Paper 2:
- The duration of the PM exam is two hours.
- It comprises MCQs from Principles of Surgery in General.
- The total number of questions is 120 questions.
The best thing is that there is no negative marking and there will be a break between both papers.
Exam Date
You can only apply to one Royal College of Surgeons at a time. You will not be reimbursed for the cost of each subsequent application if you book exams at more than one of the four colleges in the same sitting.
The upcoming MRCS PART A exam is scheduled for 9th January 2024.
The table below mentions the MRCS Part A 2024 exam date and details:
| Exam Date | Fee | Application Closing Date | Result Release Date (Tentative) |
| 9 January 2024 | £578 | 19 October 2023 | 9 February 2024 |
| 7 May 2024 | £578 | 15 February 2024 | 7 May 2024 |
Steps to Book an MRCS Exam
The following are the steps to book an MRCS exam Part A:
Step 1:Visit the official website of the Royal College of Surgeons (https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/).
Step 2:In the ‘Education & Exam’ section, go to the browse ‘Surgical Exam Option’ and then choose ‘Intercollegiate MRCS Part A’.
Step 3:Go to the ‘Booking Options’ in the Education & Exam section.
Step 4:In the booking options, you will come across upcoming exam dates with other details (both for UK and Ireland exam centres and International Centres). To book acentre in India, you need to select International Exam in Asia region.
Step 5:Click on the ‘Book Online’ option available alongside the exam date.
Step 6:Then, continue to the booking option and sign up by filling in your details.
Step 7:Your online account with ID and password will be created.
Step 8:Fill out the complete application form. Then pay according to the country and Pearson VUE exam centre chosen.
Apart from the above-mentioned steps, you can also book the MRCS exam by taking the following steps:
Step 1:Go to the website of the particular Royal College of Surgeons you wish to book an MRCS exam for.
Step 2: Register and create your online account of the respective college by filling in your details.
Step 3:Your ID and password will be generated.
Step 4:After registration, the schedule for the booking window will be shared with you by email.
Step 5:You will get an opportunity to schedule, reschedule, or cancel your test centre seat during the available booking slot.
Step 6:Remember that seat and centre allocation is done on a first come first serve basis.
Step 7:Fill out the complete application form and pay the exam fee according to the selected country and Pearson VUE exam centre.
Number of Attempts
You have a chance to attempt the MRCS exam Part A six times. There is a possibility that one additional attempt may be granted under the Additional Attempt Policy.
Syllabus
The MRCS Part A syllabus is categorised into 10 modules:
| Module Number | Module |
| 1 | Basic science knowledge relevant to surgical practice |
| 2 | Common surgical conditions |
| 3 | Basic surgical skills |
| 4 | Assessment and management of the surgical patient |
| 5 | Perioperative care of the surgical patient |
| 6 | Assessment and early treatment of the patient with trauma |
| 7 | Surgical care of the pediatric patient |
| 8 | Management of the dying patient |
| 9 | Organ and tissue transplantation |
| 10 | Professional behaviour and leadership skills |
Blueprint of MRCS Part A Exam
Paper 1: Applied Basic Sciences (180 Questions)
| Topics | Number of Questions |
| Applied Surgical Anatomy | |
| Regional Anatomy | |
| Thorax | 6 |
| Abdomen | 15 |
| Pelvis | 4 |
| Perineum | 2 |
| Limbs | 15 |
| Spine | 3 |
| Head &neck | 10 |
| Brain | 6 |
| Autonomic nervous system | 2 |
| Surgically related embryology and development (Thorax, perineum, head &neck) | 8 |
| Surface and imaging anatomy (Head and neck) | 4 |
| Applied Surgical Physiology | |
| General physiological principles | 15 |
| Cardiovascular system | 5 |
| Respiratory system | 5 |
| Gastrointestinal system | 5 |
| Urinary system | 5 |
| Endocrine system | 5 |
| Neurological system | 5 |
| Applied Surgical Pathology | |
| General pathological principles | 9 |
| Surgical immunology | 2 |
| Surgical haematology | 2 |
| Surgical clinical chemistry | 2 |
| Principles of neoplasia & oncology | 2 |
| Cardiovascular system | 2 |
| Respiratory system | 2 |
| Digestive system | 2 |
| Genitourinary system | 2 |
| Central and peripheral neurological systems | 2 |
| Skin cancer | 2 |
| Lymphoreticular system | 2 |
| Musculoskeletal system | 2 |
| Pathology of the breast | 2 |
| Pathology of the endocrine glands | 2 |
| Pharmacology as applied to surgical practice | 8 |
| Microbiology as applied to surgical practice | 7 |
| Imaging | 5 |
| Data interpretation and audit | 3 |
Paper 2: Principles of Surgery in General (120 Questions)
| Topics | Number of Questions |
| Common congenital and acquired surgical conditions | |
| Gastrointestinal disease | 7 |
| Breast disease | 3 |
| Vascular disease | 4 |
| Cardiovascular & pulmonary disease | 4 |
| Genitourinary disease | 4 |
| Orthopaedic conditions | 7 |
| Diseases of skin, head & neck | 4 |
| Neurology and Neurosurgery | 2 |
| Endocrine disease | 4 |
| Lymphoreticular system | 2 |
| Principles of cancer therapy and palliative care | 2 |
| Acute emergencies | 2 |
| Perioperative management | |
| Perioperative assessment & management | 7 |
| Intraoperative care | 5 |
| Perioperative care | 2 |
| Postoperative care | 8 |
| Nutrition management | 2 |
| Haemostasis & blood products | 3 |
| Coagulation, deep vein thrombosis & embolism | 3 |
| Metabolic & endocrine disorders | 5 |
| Assessment and management of patients with trauma (including multiple injured patients) | |
| General | 4 |
| Shock | 2 |
| Wounds & soft tissue injuries | 4 |
| Burns | 2 |
| Fractures & dislocations | 8 |
| Organ-specific trauma | 10 |
| Surgical care of children | 7 |
| Medico-legal aspects of surgical practice | 3 |
Things to Remember for Exam Day
Make sure you reach 30 minutes before the scheduled examination time.
Make sure to carry the following to get admitted into the exam centre:
- One original (no photocopies) and valid (unexpired) ID that includes your name, photograph, and signature (name must exactly match with the name on the ID brought on test day).
- Valid passport from your country of citizenship, or an alternative qualifying photographic ID from the country in which you are going to take a Pearson VUE exam.
Result
The results will be accessible around a month after the examination date. You will also get a ‘Candidate Feedback Form’ after the completion of the exam. The results are published on the ‘My Account’ page of the official website. You just need to log into your ‘my account’ with your username (your email address) and password to check your results.
Enroll in the Surgery MS Online Course to Learn about Surgical Conditions and Management Procedures.
DigiNerve’s e-learning course, Surgery MS, is painstakingly created for postgraduate students aspiring to become excellent surgeons. The course is meticulously crafted under the guidance of the esteemed Chief Editor, Prof. Dr. Nilay Mandal, in collaboration with 26 subject experts and eminent surgeons across India. Working with the faculties, Dr. Mandal has also shared his valuable expertise, steering the route with his superb guidance.
This Surgery MS online course employs a case-based approach to solve the challenges faced by postgraduate students in comprehending clinical settings, especially for the ones with little exposure to actual surgeries. The course enables aspiring surgeons to effectively manage patients and apply theoretical knowledge to real-world surgical settings. In addition to preparing postgraduate students for their Master of Surgery final exams, the course strives to instill in them a strong desire to become excellent surgeons who will stop at nothing to ensure the best possible care for their patients.
Course Inclusions
- Video Lectures
- Lecture Notes
- Surgical Tips
- Benchmark Trials
- Self-Assessment Questions
- OSCEs
- DxTx
- SxTools
- Engagement Activities such as Regular Chat Shows
- Wise AI Chatbot
- Printed Notes
The following is the description of Surgery MS online course inclusion and features:
Highly Illustrative Video Lectures: The surgery video lectures for medical students include long and short-case discussions, surgical techniques, and surgical management decisions. The case-based lectures cover differential diagnosis, management techniques, surgical strategies, surgical procedures, complications, preventive patient care, and more. Each segment has been thoughtfully chosen to correspond with the curriculum for the MS exams.
Short and Long Case Discussions: A compilation of carefully chosen short and long case discussion topics covering a wide range of medical super-specialties, designed to help with thorough MS exam preparation.
Lecture Notes: Well-illustrated notes are provided with the lectures that serve as a ready reckoner for learners.
Evidence-based Research: At the end of each lecture, evidence-based research studies are provided to complement the notes and lectures.
Clinical Methods: MS General Surgery postgraduate students can learn about clinical skills by watching the video lectures, which cover pre- and post-operative assessments.
Surgical Procedures: To help students grasp surgical skills, actual surgical procedures are featured in the surgery video lectures with MCQs and notes.
Self-Assessment Questions: Practice questions are incorporated strategically after each video to enhance comprehension in addition to serving as a valuable practice assessment. This helps in self-evaluation helping the learners to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
OSCEs: Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) are an essential tool for evaluating clinical abilities, competencies, and rapid revision. This course feature has an assessment in the flashcard format for self-evaluation, just like the actual exam.
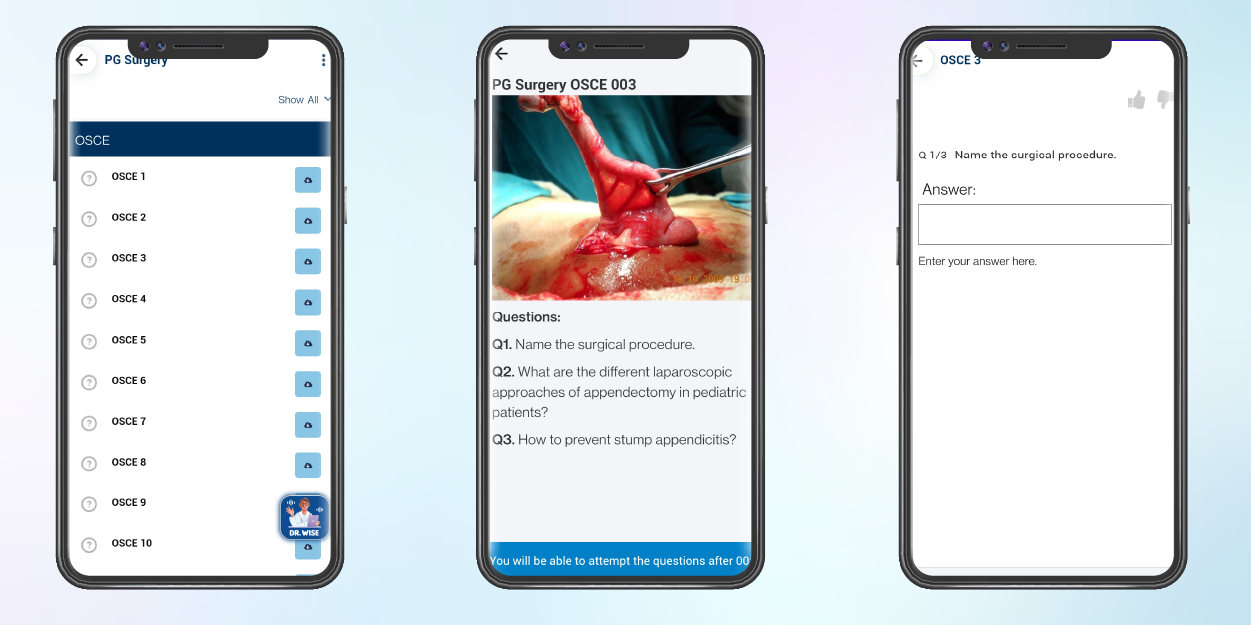

Surgical Tips: This section includes Master of Surgery tips, dos and don’ts of surgical procedures guiding to make informed decisions both before and during surgical procedures. This will help students make the right choices while performing surgery.
DxTx: This special feature is a unique tool for rapid reference, aligned with the NMC curriculum. In this feature, a human model is presented that allows you to explore various diseases and health conditions of body systems with just a click. It includes information about various medical conditions and surgical procedures in a clear and organized manner, including clinical features, diagnosis, pathophysiology, treatment, clinical trial information, and recent advances.
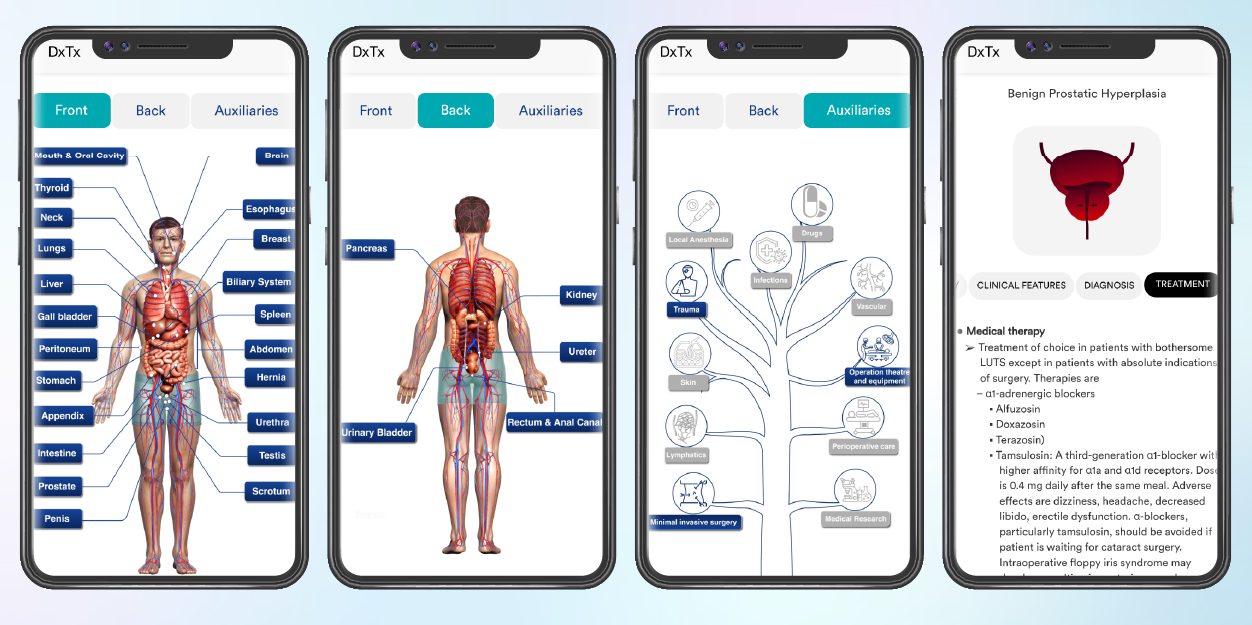

Benchmark Trials: Postgraduates can now stay up to date on the latest developments in the discipline with the addition of evidence-based studies.
SxTools: This is an amazing feature of the course for MS Surgery exam preparation wherein there are flashcards with thorough explanations of surgical instruments.
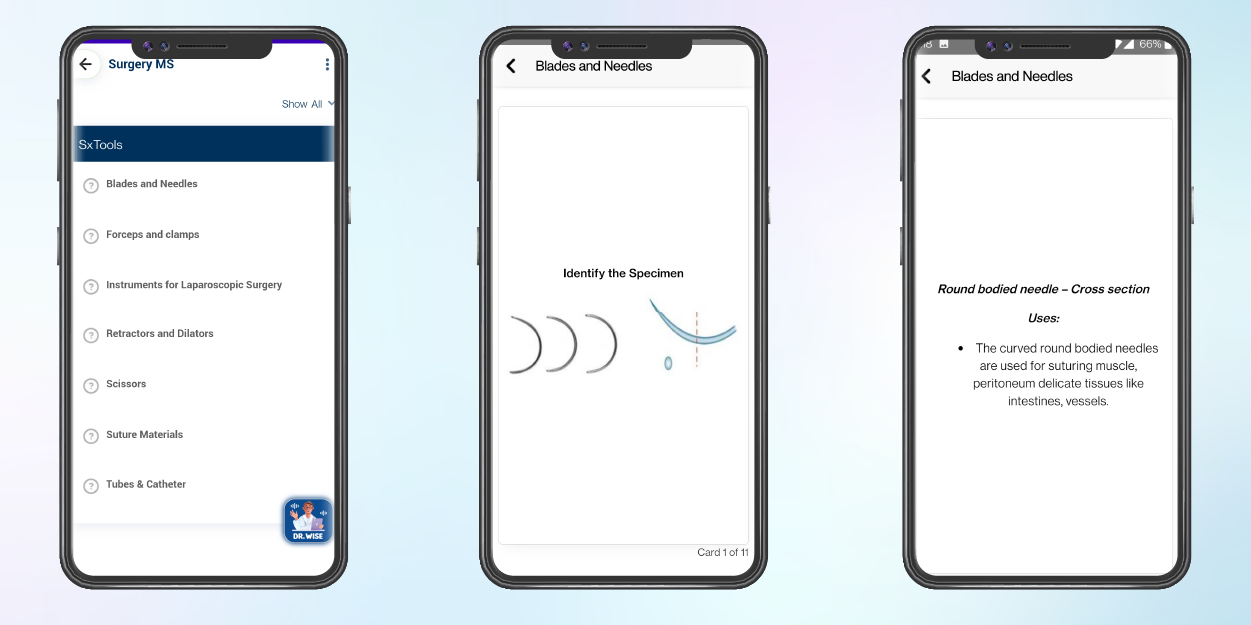

Engagement Activities: This includes Journal clubs and chat shows where you directly get to learn from the faculty and other eminent surgeons and medical practitioners.
Dr. Wise AI chatbot: It is a comprehensive and interactive solution provider coupled with real published resources including books, journals, notes, and videos to provide appropriate explanations of topics, treatment techniques, and more.
Printed Notes: Brief notes are designed to save your time by providing exam-focused, crisp details with visual learning at an affordable price.
Key Features of Surgery MS Online Course
Surgery MS adopts a case-based approach towards a comprehensive range of medical super specialties, equipping postgraduates with essential clinical skills. The key features are as follows:
- Case-based systemic approach as per NMC curriculum
- Surgical tips comprising dos &don’ts to follow during procedures
- Instrumentation is made easy with flashcards through the SxTools feature
- Critical DxTx information provided through the human model
- OSCEs to prepare and assess one’s skills
- Wise AI chatbot for comprehensive &interactive solutions
Benefits of Enrolling in Surgery MS Course
Pursuing an MS in Surgery can bring a multitude of benefits to your career and personal growth. Online Master of Surgery (MS) courses are becoming increasingly popular because of their flexibility and accessibility. They offer a unique opportunity for medical professionals to gain advanced surgical knowledge and skills without interrupting their careers or relocating. While traditional on-campus programs remain valuable, online MS in Surgery courses present several distinct benefits:
- Flexibility and Convenience.
- Reduced geographical limitations.
- Opportunity to learn from world-class surgeons.
- Master surgical techniques through visual learning.
- Potential Cost and Time Saving.
- Tailored curriculum as per NMC.
- Keeps you abreast of the most recent developments.
- Deepen your understanding of the subject.
- Refine your critical thinking and decision-making skills.
- Greater income potential.
- Enhances professional recognition and reputation.
- Enhances your interpersonal and communication skills.
- Greater sense of accomplishment and satisfaction.
- Enhances networking opportunities.
- Robust research base.
Surgery MS Table of Content
Surgical Skills
Abdominal Wall and Retroperitoneum
- Management of Open Abdomen
- Abdominal Compartment Syndrome and Its Management
- Abdominal compartment syndrome
- Abdominal Compartment Syndrome and its Management
- Abdominal compartment syndrome and Its Management
- Urethral Dilatation
Intestinal Stoma and its Management
Urology
- Uroflowmetry
- Urethral Catheterization
- Understanding Suprapubic Catheterization
- Urethral Injury
- Suprapubic Catheterization
- Urethral Injury
- Urethral Dilation
- Urethral Injury
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
- Principles of Suturing Technique
- Instruments and Suture Handling
- Suturing Techniques Models, Foams and Bars
- Skin Incision, Scalpel, and Blades
Vascular Disorders
- Acute Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
- Venesection
- Interpretation of TEG and ROTEM
- Thromboelastography and Rotational Thromboelastometry
Principles of Anesthesia and Pain Management
- Regional Anesthesia Digital Block
- Regional Anesthesia Hernia Block
- Regional Anesthesia Penile Block
Basics of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Basic Principles of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Basics of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
Trauma
- Interpretation of Trauma Chest X-ray the Advance Trauma Life Support Protocol
- FAST and eFAST
- Needle Decompression, Finger Thoracostomy, and ICD Placement: Chest Decompression
- Helmet removal in a Trauma patient
- Management of Unstable pelvic fracture and Application of Pelvic Binder
- Application of Cervical Collar and Ruling out C-Spine Injury
- Understanding Triage
- General Approach to a Patient with Thoracic Trauma
- Trauma CT Scan
- Venous Access in a Hemodynamically Unstable Trauma Patient and Intravascular Device Placement
- FAST and eFAST
- Helmet Removal in a Trauma Patient
- Management of Unstable Pelvic Fracture and Application of Pelvic Binder
- Application of Cervical Collar and Ruling out C-Spine Injury
- Trauma-Induced Coagulopathy and Interpretation of TEG /ROTEM
- General Approach to Abdomen Trauma
- Trauma CT Scan
- Management of Retroperitoneal Trauma
- Trauma CT Scan
- Helmet Removal in a Trauma Patient
- Damage Control Surgery
- Trauma-Induced Coagulopathy and Importance of Viscoelastic Assays
- Vascular Access in Trauma
- Application of cervical collar and ruling out C-Spine Injury
- Interpretation of Trauma Chest X-ray: The Advance Trauma Life Support Protocol
- Retroperitoneal Trauma
- Principles of Damage Control Surgery
- General Approach to Abdominal Trauma
Wound Healing
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Basic Surgical Skills
- Study of Tracheostomy
- Basic Life Support
- Central Venous Pressure Monitoring Technique
- Endotracheal Intubation
- GI Staplers
- Nasogastric Tube
- Suture Material
- Basics of Blood Transfusion
- Head and Neck Cancer- Punch Biopsy
- Understanding Transfusion Reactions
- Drains in surgery
- GI staplers
- Basics of Blood Transfusion
- Incision and Drainage
- Skin Incision, Scalpel, and Blades
- Use of Different Types of Drains
- Intralesional Injection of Keloid
- Use of Different Types of Scissors Cutting and Dissection
- Drains in Surgery
- Central Venous Pressure Monitoring
- Transfusion Reactions
- Tracheostomy
- Incision and Drainage
- Principles of Seldinger Technique
- Tracheostomy
- Drains in Surgery
- Endotracheal Intubation
- Needle Holder
- Different types of Retractors
- Understanding Transfusion reactions
- Vascular Anastomosis
- Punch Biopsy
- Use of Scissors for Cutting, Dissection
Common Surgical Procedures
- Splenectomy
- Excision of a Scalp Swelling
- Neck Dissection
- Excision of a Scalp Swelling
- Common Surgical Procedures
- Understanding Harmonic Device
- Basic things about harmonic Device and Vessel Sealer (Harmonic Scalpel)
OT Design Technologies
- Patient Positioning in Operation Theatre Table
- Patient Positioning in Operation Theatre Table
Testis, Scrotum and Penis
- Understanding Fournier’s Gangrene
- Evaluation and management of Paraphimosis
- Evaluation and Management of Varicocele Part II
- Penile Fracture
- High inguinal orchidectomy
- Methodology of Prostate Biopsy
- Varicocele Part I
- Mechanism and Management of Zipper Injury
- TRUS Guided Prostate Biopsy
- Management of Zipper Injury
- Evaluation and Management of Fournier’s Gangrene
- Penile Fracture
- Hypospadias
- Phimosis and Circumcision
- Evaluation and Management of Paraphimosis
- Principle of Partial, Total, and Radial Penectomy
- Evaluation and Management of Acute Scrotum
- Orchidopexy
- Phimosis
- Evaluation and Management of Paraphimosis
- Principle of partial/total penectomy
- Management of testicular trauma
- Hydrocele
- Management of Testicular trauma
Clinical Examination
- Examination of Oral Cavity
- Examination of Salivary Neoplasms
- Examination of Hernia
- Examination of Scrotum and Male External Genitalia
- Clinical Examination of Swelling
- Clinical Examination of Ulcer
- Clinical Examination in Arterial Disease
- Clinical Examination in Vascular Disease
- Examination of Varicose Veins
- Examination of Lymph Nodes
- Clinical Examination
Short Cases
- Cleft Lip and Palate
- Neck Swelling
- Breast
- Spleen
- Urology
- Testis, Scrotum and Penis
- Diabetic Foot
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
- Vascular Disorders
- Basics of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Wound Healing
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma
- Principles of Oncology
- Hernia
Long Cases
- Thyroid
- Breast
- Stomach and Duodenum
- Small Intestine
- Hernia
- Vascular Disorders
Management Decisions
- Liver
- Spleen
- Testis, Scrotum, and Penis
- Hernia
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue
- Trauma
- Principles of Anaesthesia and Pain Management
- Cleft Lip and Palate
- Abdominal Wall and Retroperitoneum
- Urology
- Vascular Disorders
- Principles of Oncology
Radiology for Surgical Residents
Surgical Tips
OSCEs
DxTx
Link to the TOC: https://www.diginerve.com/course/surgery-ms/
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve, which is vital for good vision. It is among the leading causes of vision impairment and blindness globally. It is referred to as a silent threat.
In this blog, we’ll read about this vision impairment condition, including its anatomy and physiology, risk factors, types, diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, and recent advancements. Let’s start with the most important and majorly asked question, why is glaucoma called a silent threat to vision?
Why is glaucoma called a silent threat to vision?
In contrast to certain eye disorders that could result in pain, redness, or other evident discomfort, glaucoma can progress silently, and without any clear warning indications. It can cause blindness and irreversible vision loss if it is not treated timely.
Here are a few reasons why glaucoma is considered a silent threat:
- Lack of Early Symptoms: People frequently do not exhibit any symptoms at all in the early stages of glaucoma. The gradual loss of peripheral vision may go unnoticed since the early stages of the condition mostly spare the central vision, which is necessary for tasks like reading and driving.
- Painless Progression: Optic nerve damage from glaucoma usually occurs without discomfort. People might delay seeking medical assistance until the disease has progressed which contributes to delayed discovery.
- Peripheral Vision Loss: Peripheral vision is frequently the first impacted area by glaucoma, however the affected person may not notice this right away. The continued functioning of central vision during the early stages of this condition can lead to a delusion of security as it is responsible for tasks requiring concentrated attention.
- Gradual Vision Changes: Glaucoma-related visual loss typically worsens gradually over time. People can adapt to their visual limits as a result of the progressive alterations, not realizing the full degree of the damage until it has progressed to an advanced level.
- Importance of Regular Eye Exams: For early glaucoma detection, routine eye exams are essential. In order to identify any indications of peripheral vision loss, eye care specialists can monitor intraocular pressure, evaluate the condition of the optic nerve, and conduct visual field tests during an examination of the eyes. On the other hand, glaucoma may go undiagnosed until it results in significant symptoms or irreparable vision loss if people do not get routine eye exams.
The phrase “silent threat” highlights the value of preventative eye care and routine examinations, particularly for people with risk factors like age and family history. Early identification and care of the condition with the right medications can significantly slow the progression of glaucoma and help preserve vision.
Overview of Glaucoma
Understanding the details of glaucoma, including its types, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, is essential for both individuals at risk and healthcare professionals to effectively manage and prevent vision loss associated with this condition. Regular eye check-ups remain a cornerstone in the early detection and management of glaucoma.
Characterisation
Glaucoma is characterized by:
- Optic Nerve: The optic nerve transmits visual information from the retina to the brain and hence, is crucial for vision. Glaucoma is characterised by optic nerve damage leading to vision loss.
- Intraocular Pressure (IOP): The eye maintains a delicate balance of fluid production and drainage. Increased intraocular pressure can result in an imbalance, contributing to optic nerve damage.
Risk Factors
- Elevated IOP: Elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor as it damages the optic nerve.
- Age: The risk of glaucoma rises with age, and it is more common in the elderly.
- Family History: A family history of glaucoma increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Ethnicity: People from specific ethnic backgrounds, such as Asians, Hispanics, and African Americans, are more vulnerable.
- Medical Conditions: Glaucoma risk can be elevated by conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular illnesses. Additionally, prolonged corticosteroid use may turn out to be a risk factor.
- Eye Conditions: Certain anatomical anomalies of the eyes and high myopia (nearsightedness) can increase the risk of glaucoma.
Types of Glaucoma
There are several types of glaucoma, each with its characteristics and causes. Here’s an overview of these types:
1. Open-Angle Glaucoma: This is the most common form. The drainage angle between the iris and cornea is open, but the trabecular meshwork does not function properly, leading to increased intraocular pressure.
-
- Chronic Open-Angle Glaucoma: A steady, gradual rise in intraocular pressure. This kind of open-angle glaucoma is the most prevalent. It happens when the trabecular meshwork, which drains the aqueous humor (fluid in the eye), is not functioning properly, even though the drainage angle between the iris and cornea is open. This causes the intraocular pressure to gradually rise over time, eventually damaging the optic nerve.
- Normal-Tension Glaucoma: This particular subtype of open-angle glaucoma results in damage to the optic nerve, even when the intraocular pressure stays within the normal range. Although the precise explanation is not entirely known, this shows that forces other than pressure might be involved.
2. Closed-Angle Glaucoma: In this type, the drainage angle is blocked, causing a sudden increase in intraocular pressure and is considered a medical emergency.
-
- Acute Closed-Angle Glaucoma: This condition arises when the drainage angle is blocked by the iris pushing forward. A sharp rise in intraocular pressure brought on by this unexpected blockage results in symptoms including excruciating eye discomfort, headaches, nausea, and blurred vision. Although this is less frequent, you must get medical help right away to relieve the strain and prevent vision loss.
- Chronic Closed-Angle Glaucoma: Slower drainage angle closure results in a progressive rise in intraocular pressure. The drainage angle closes more slowly, and symptoms might not be as obvious. Vision loss may occur gradually over time as a result of chronic closed-angle glaucoma.
3. Secondary Glaucoma:
-
- Pseudoexfoliative Glaucoma: This kind is linked to an abnormal build-up of material on the eye’s lens, which raises intraocular pressure.
- Secondary Angle-Closure Glaucoma: This can occur due to various conditions, such as cataracts or tumors, which physically block the drainage angle.
4. Congenital Glaucoma:
-
- Primary Congenital Glaucoma: This rare type of glaucoma is usually brought on by anomalies in the drainage systems of the eye and is present from birth. It can cause damage to the optic nerve and elevated intraocular pressure if left untreated.
Symptoms
- Early Stages: Often asymptomatic.
- Advanced Stages: Peripheral vision loss, tunnel vision, difficulty adjusting to low light, and, in some cases, complete blindness.
Prognosis
- Early Detection: Crucial for managing and slowing the progression of glaucoma.
- Treatment: Focuses on lowering intraocular pressure and preserving vision.
- Regular Monitoring: Necessary for ongoing management.
Diagnosis
- Tonometry: Measures intraocular pressure.
- Ophthalmoscopy: Examines the optic nerve.
- Visual Field Testing: Assesses peripheral vision.
- Gonioscopy: Evaluate the drainage angle.
Treatment
The choice of treatment for glaucoma depends on the type and severity of glaucoma.
- Medications: Eye drops or oral medications are given to lower intraocular pressure. Prescription medications include prostaglandins, beta blockers, alpha-adrenergic agonists, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and Rho kinase inhibitors.
- Laser Therapy: Procedures like laser trabeculoplasty, cyclodiode laser, or iridotomy to improve drainage.
- Surgery: Trabeculectomy, Viscocanalostomy, Deep sclerectomy, trabecular stent bypass, drainage tubes, or other surgical interventions to create a new drainage channel.
No treatment till now has been proven for a complete cure for glaucoma but yes, these treatment methods are quite beneficial for preventing further damage and vision loss.
Prevention
- Regular Eye Exams: Highly crucial preventive step, especially for individuals at higher risk.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and not smoking may contribute to overall eye health.
It is imperative to take proactive measures to maintain their eye health, particularly those who are more vulnerable. Glaucoma management and vision preservation depend heavily on routine eye exams, knowledge of risk factors, and prompt intervention.
Glaucoma: Recent Advances
Here are some general trends and potential advancements that were being explored concerning glaucoma:
- Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery (MIGS) procedures have gained popularity as they offer a less invasive alternative to traditional glaucoma surgeries. These procedures are intended to lower intraocular pressure by enhancing the eye’s natural drainage pathways. Trabecular micro-bypass stents and the usage of micro-incisions are two examples.
- Researchers are exploring neuroprotective agents that could potentially protect the optic nerve from damage, slowing down the progression of glaucoma.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a revolutionizing advancement in Diagnosis and Monitoring. AI technologies are being developed for more accurate and efficient diagnosis of glaucoma. AI algorithms analyze imaging data to detect early signs of the disease and monitor its progression.
- Advances in telemedicine allow remote monitoring of glaucoma patients. This eliminates the need for frequent in-person visits by allowing medical professionals to monitor intraocular pressure and other pertinent factors.
- Sustained-release drug delivery systems, such as implantable devices or injections, are also being explored to provide a continuous release of glaucoma medications, reducing the need for daily eye drops. Ongoing research also focuses on the development of novel drug classes with improved efficacy and reduced side effects.
- Some investigations are underway to explore the potential of gene therapy for glaucoma. Gene therapy aims to modify or replace defective genes associated with the disease.
It’s essential to note that the field of medicine, including ophthalmology, is dynamic, and new advancements occur regularly. For the latest information on advancements in glaucoma treatment, it’s recommended to consult recent medical literature, and clinical trial updates, join webinars, or enroll in online courses by top ophthalmologists who can provide the most up-to-date information on available treatments and emerging therapies.
Checklist for an Ophthalmology student to have a comprehensive understanding of the condition:
- Introduction to Glaucoma
- Epidemiology
- Risk Factors
- Pathophysiology
- Glaucoma Types
- Clinical Presentation
- Diagnostic Tools and Methods
- Treatment Options
- Advancements and Emerging Trends
- Patient Management and Education
- Research Opportunities
- Case Studies
- Clinical Experience
Remember to stay updated with the latest literature and attend relevant conferences or seminars to enhance your knowledge. Glaucoma is a complex and evolving field, and staying informed will contribute to your effectiveness as a future healthcare professional.
Must Read: Basic Toolkit for Glaucoma- Dr. Parul Ichhpujani
Click here to learn more about glaucoma from top faculty and ophthalmologists.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. Why is glaucoma called a silent threat to vision?
Ans. The reason glaucoma is called a “silent threat to vision” is that it usually advances slowly and without any obvious symptoms in its early stages. In contrast to certain eye disorders that could result in pain, redness, or other evident discomfort, glaucoma can progress silently, and without any clear warning indications. It can cause blindness and irreversible vision loss if treatment is not treated timely.
Q2. What are the major risk factors for glaucoma?
Ans. While elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor, other factors include age, family history, ethnicity (African Americans, Hispanics, and Asians are at higher risk), and certain medical conditions like diabetes. Additionally, individuals with high myopia (nearsightedness) may also be at an increased risk.
Q3. Which are the recommended online courses for aspiring ophthalmologists?
Ans. The recommended online courses for aspiring Ophthalmologists include Ophthalmology for UnderGrads by Dr. Parul Ichhpujani and Dr. Talvir Sidhu and Ophthalmology MD online course by Dr N. Venkatesh Prajna.
Orthopaedics subject in MBBS deals with the study of the musculoskeletal system of the human body. The subject includes topics such as Fracture and Dislocation – General Principle and Management, Disease of Bones and Joints – Infections, Tumour of the Bones and Joints, Congenital disorder of the Bones and Joints, Disorder of the Growing Skeleton, Disorder of Muscle Tendons and Ligaments,Hand and the Foot, Spine, Vertebral Column and Spinal Cord, Metabolic Diseases of the Bones, and Nerves and Nerve Injuries.
Subject Weightage of Orthopaedics in Competitive Entrance Exams
According to the new MBBS academic pattern, the Orthopaedics specialty is combined in the General Surgery subject along with Anaesthesiology, ENT, Ophthalmology, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, and Radiodiagnosis.
In NEET-PG,the weightage of the surgery subject is around 45 questions from which the average number of questions to be asked from Orthopaedics is around 5-8 questions.
In INI-CET, a total of around 30 questions are asked from the General Surgery section. Out of the total number of questions, the orthopaedics subject holds a weightage of about 5-7 questions.
Important Topics of Orthopaedics
Here’s a list of high-yielding topics for Orthopaedics for NEET-PG, INI-CET, and MBBS Prof exams.
- Management of Traumatic Paraplegia
- Osteomyelitis and Bone tumors
- Pott’s Spine
- B. Knee and Hip
- Diagnosis of Benign tumor
- Management of Malignant Tumors
- Bone Cyst
- Cruciate Ligaments and Meniscal Injuries
- Congenital Dislocation of Hip Joint
- Compartment Syndrome
- Crush Injury
- Fat Embolism
- Myositis Ossification
- Shoulder and Elbow Dislocation
- Fractures: Clavicle, Humerus, Lateral condyle Humerus, Supracondylar Humerus, Colles
- Carpo Metacarpal Injuries
- Fractures: Hip Femur Shaft, Patella, Tibia and Calcaneum, Scaphoid, Jefferson’s, Hangman’s
- Investigation forStress Fracture
- Radiological Features
- Cervical Spine Injuries
- Hip and Knee Dislocations
- Ankle Sprain
- Polio
- Amputation
- Salter and Haris, Rang Classification
- Disc Prolapsed
- DupuytrensContracture
- Rickets and Osteomalacia
- Paget’s Disease
- Osteoporosis
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Osteoarthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Gout
- Erb’s Palsy
- Ulnar, Median and Radial Nerve Injury
- CDH
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
- Osteoclastoma
- Osteopontin
- Osteocalcin
- Carpel Tunnel Syndrome
- Genu Varum
- DDH
- Knuckle Bender Splint
- Fibrous Dysplasia
- Volkmann’s Ischemia
- Sudeck’s Osteodystrophy
- Management of Open Fractures
- Treatment of Congenital Dislocation of Hip Joint
- Clinical Features in 6 months Old Paraplegia
- Compartment Syndrome and its Presentation, Diagnosis, &Treatment
- Structure of Bone with Diagram
- Clinical Features, Pathological Anatomy, and Treatment of Recurrent Dislocation of Shoulder
- Ewing’s Sarcoma
- Myositis Ossificans
- Etiopathogenesis of Necrotizing Fasciitis.
- Management of Case of Necrotizing Fasciitis of Lower Limb
- Classification of Epiphyseal Injuries and Complications
- Classify Nerve Injuries and Treatment
- Management of CTEV- Congenital Talipes Equinovarus aka Club Foot
- Management of GCT- Giant Cell Tumor of Bone
- Structure of Growth Plate with diagram. How does it help in endochondral ossification?
- Clinical Features, Etiology, Pathology, and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Thomas Splint
- Intracapsular Fracture of Neck of Femur. Anatomical Classification of Fracture Neck Femur
- Etiopathogenesis, C/F, and Management of Pyogenic Osteomyelitis of Distal end of Femur
- Mechanism of Injury, C/F, and Management of Supracondylar Fracture of Humerus and Complication
- Frozen Shoulder
- Causes of Low Lack Pain
- Enumerate Complications of Fracture
- Tuberculosis Knee Joint
- Volkmann Ischemic Contracture
- Principle in Management of Extremity Fracture
- Open Fracture and Complications
- Guillotine Amputation
- Bone Biopsy
- Rickets Orthopaedics Manifestations
- Cubitus Deformity
- Post-hip Dislocation
- Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis of proximal end of tibia in 5 years old
- Wrist Drop
- B Splint
- ABC in Polytrauma
- Sodeck’sOsteodystrophy
- Pott’s Paraplegia
- Painful Heel
- GenuValgum
- Classify Bone Tumors. Clinical Features, Management of Ewing Sarcoma
- Mandible Fracture – First Aid Management
- Dietary Rickets
- Fractured Pelvis – Mechanism, Diagnosis &Treatment
Click here to get conceptual clarity on the Orthopaedics topics in detail.
Skills Required to Excel in Orthopaedics in MBBS
To excel in Orthopaedics, aspiring ophthalmologists must be skilled in the following:
- Diagnose sprains and strains, as well as other soft tissue ailments.
- Look for common fractures in the limbs.
- Apply first aid for common sprains and fractures.
- Give patients with polytrauma immediate care.
- Handle simple fractures of the forearm, clavicle, phalanges, etc.
- Apply splinting procedures, such as the thomas splint, slabs of plaster and castings, paralysis due to skin tractions, etc.
- Learn indications for fracture internal and external fixations, as well as closed and open reductions.
- Handle frequent bone infections; get knowledgeable about sequestration, amputation, and bone deformity correction protocols.
- Advice and counsel patients undergoing post-traumatic stress disorder, poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, or amputation recovery.
- Possess a precise set of orthopaedic abilities and give wise counsel on skeletal and associated problems at the primary or secondary level of healthcare.
Must Read: Important Topics of Surgery in MBBS
Introducing Surgery MS: Suturing your Clinical Gaps
The meticulously crafted Surgery MS is an E-learning course by DigiNerve. The course follows a case-based approach that focuses on pain areas of postgraduate students who get limited exposure to actual surgeries, leading to difficulties in understanding the clinical context. The course helps them in becoming competent in patient management, and practical application of theoretical concepts in surgical settings. It provides surgical videos aiming to address the potential impact of limited exposure to actual surgeries on students’ confidence levels. The course not only aims to prepare postgrads for their MS final examinations; its mission is to ignite a passion in them to emerge as exceptional surgeons, determined in their commitment to prioritize the well-being of their patients above all else. The course has been expertly designed under the profound guidance of the esteemed Chief Editor, Prof. Dr. Nilay Mandal. He has steered the course with exemplary direction by providing quality & valuable knowledge in collaboration with 26 experts in the field.
The course includes a comprehensive coverage of basic surgical skills, trauma and various surgical super-specialities including urology, oncology, plastic and reconstructive surgery, etc. Each super-specialty is further divided into 4 modules (long cases, short cases, management decisions and surgical skills), offering a structured learning experience. Some of the unique features that set this course apart are mentioned below:
- Case-based approach: The course follows a case-based approach wherein the various lectures focus on case discussions (inclusive of both long and short cases). The case-based lectures address several concepts such as differential diagnoses, management strategies, surgical strategies, surgical pathways, complications, prevention, patient care messages, etc., all while incorporating global and Indian recommendations. Long and short case discussions in various sections are carefully curated to align with the MS examination curriculum.
- Clinical Methods: Pre and post-operative assessments covered in the videos would help postgraduate students get acquainted with clinical skills.
- Surgical Procedures: Real surgical procedures are covered in the video lectures to enable students to understand surgical skills.
- Interactive learning Experience: After each video lecture, self-assessment questions will help students to test their understanding and retention.
- OSCEs: Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) are vital in assessing clinical skills. These assessments are provided in flashcard formats, enabling rapid revision and self-evaluation, just like in the real exam.
- Surgical Tips: This part of the course will guide students to make appropriate decisions before and during the surgical procedures.
- DxTx: A tool for quick reference, this unique feature is represented by a human model that allows you to explore critical information with a click. You can learn about the various medical conditions and surgical procedures including clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, recent advances, and clinical trials in a crisp and structured format. Furthermore, intricate etiopathological concepts are skillfully clarified using flowcharts, whenever necessary. This tool is aligned with the NMC curriculum.
The course includes:
- Video Lectures: 110+ hours of video lecture series, encompassing basic sciences, in-depth long and short case discussions, surgical skills, and management decisions in surgery.
- Long Case Discussion Videos: Collection of 11 meticulously chosen long case discussion videos spanning important surgical super-specialties, designed to aid in comprehensive preparation for the MS examination.
- Short Case Discussion Videos: Compilation of 35 carefully curated topics of short case discussions spanning diverse surgical super-specialties, aimed at seamless preparation of MS-level examinations.
- Lecture Notes: This course includes well-illustrated 205+ topics in notes which will act as a ready reckoner for students. They are supplemented with evidence-based research studies mentioned at the end of each topic.
- Surgical Tips: 450+ tips comprising dos and don’ts before and during the surgical procedures are explained in this section. This will guide students to make appropriate decisions in their surgical practices.
- Benchmark Trials: 400+ Evidence-based studies have been added for postgrads to remain updated with recent advances in the field.
- Self-Assessment Questions: 1100+ MCQs serve both as valuable practice assessments and as a strategic integration within each video to improve comprehension.
- OSCEs: 200+ flashcards provide a standardized and objective method of assessing a candidate’s clinical skills and competencies.
- DxTx: A unique tool comprising 250+ topics aligned with the NMC curriculum across various super-specialties for quick reference.
- SxTools: Instruments used in surgery are well-explained through 100+ flashcards.
- Engagement Activities: Regular chat shows, journal clubs, and recent updates are included as engagement activities.
- Dr. Wise (AI Chatbot): The chatbot clarifies theoretical as well as practical concepts with the help of AI. It is a comprehensive and interactive solution provider integrated with authentic published resources like books, journals, notes, and videos to offer apt explanations of concepts, treatment modes and more.
- Printed Notes: Concise notes are designed to save time by providing exam-focused, crisp details along with visual learning at an affordable price. The notes also comprise previous years’ questions and ensure comprehensive coverage in minimum time. Existing users can purchase the printed notes @4,995 form here.
3 Days Money Back Guarantee available T&Cs apply.
Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (IGIMS) is a government medical institution located in Patna, Bihar. IGIMS offers MBBS, MD, MS, and other programs in various medical specialties. It also conducts cutting-edge research in areas like cancer, cardiology, and neuroscience. IGIMS was established as an autonomous organisation on the pattern of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi with an objective to provide super specialty medical facilities in Bihar. IGIMS, Patna is recognized by the University Grants Commission(UGC),Medical Council of India (MCI), and Association of Indian Universities (AIU).
IGIMS has a sprawling campus and is well-equipped with modern infrastructure, including lecture halls, laboratories, and hostels. IGIMS boasts a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors, researchers, and medical professionals. The college is associated with the 1000+ bedded IGIMS hospital with advanced medical facilities and caters to a wide range of specialties. It is a major healthcare provider for the people of Bihar and beyond.
IGIMS, Patna: Course Details
MBBS Course
Course Duration: MBBS is a five and a half yearundergraduate medical degree that essential for pursuing a medical career in India. The degree also includes one year of compulsory rotational internship. The college MBBS degree program is strictly aligned according to the CBME pattern.
Number of MBBS Seats: There are a total of 120 MBBS seats at IGIMS, Patna.
Admission Procedure: The admission to IGIMS for MBBS program is done based on the merit ofthe NEET-UG entrance examination. NEET-UG is a highly competitive exam but is the only pathway to get admission into an MBBS degree in India. Aspirants must start early preparation with a proper plan and the best resources to score high in this competitive exam.
Fee Structure: The fee structure for the MBBS course at IGIMS, Patna is as follows:
| Particulars | Fees |
| Admission Fee | Rs. 10,000 (One time) for Gen/OBC/ERC candidates
Rs.5,000 (One time) for SC/ST candidates |
| Registration Fee | Rs. 10,000 (One time) for Gen/OBC/ERC candidates
Rs.5,000 (One time) for SC/ST candidates |
| Caution Money | Rs. 10,000 (Refundable) |
| Miscellaneous | Rs. 10,000 (One time) |
| Tuition Fee | Rs. 58,333 (for 1st Prof)
Rs. 50,000 (for 2ndProf) Rs. 54,167 (for 3rdProf Part-I) Rs. 62,500 (for 3rdProf Part-II) |
| Hostel Fee | Rs. 20,000 (Optional, if allotted) |
| Examination Fee | Rs. 4,000 (Per Regular University Exam) |
NEET-UG Minimum Cut-off Marks:
| Category | Marks Range | Cut-off Percentile |
| General/UR/EWS (Unserved/ Economically Weaker Sections) | 720-138 | 50th |
| OBC (Other Backward Classes) | 137-108 | 40th |
| SC (Scheduled Castes) | 137-108 | 40th |
| ST (Scheduled Tribes) | 137-108 | 40th |
PG Broad Specialty Courses
Course Duration: PG Broad Specialty Courses at IGIMS includean MS/MD degree, of 3 years duration.
Admission Procedure: Admission to MD/MS courses is done based on the marks scored in theNEET-PG entrance examination.
PG Broad Specialities: The following is a list of PG Broad Specialities available at IGIMS, Patna:
- Pathology
- General Medicine
- Anatomy
- Forensic Medicine
- Biochemistry
- Radio Diagnosis
- Physiology
- Psychiatry
- Microbiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Pediatrics
- Obstetrics &Gynecology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Orthopaedics
- Ophthalmology
- Pharmacology
- Community Medicine
- General Surgery
- Anaesthesiology
Number of Seats: The IGIMS has a total of 88 MD/MS seats. The following table mentions the number of PG seats in each specialty:
| Specialty/Subject | Number of Seats |
| Pathology | 05 |
| General Medicine | 08 |
| Anatomy | 02 |
| Forensic Medicine | 01 |
| Biochemistry | 03 |
| Radio Diagnosis | 05 |
| Physiology | 01 |
| Psychiatry | 03 |
| Microbiology | 07 |
| Radiation Oncology | 04 |
| Pediatrics | 03 |
| Obstetrics &Gynecology | 04 |
| Otorhinolaryngology | 03 |
| Orthopaedics | 03 |
| Ophthalmology | 04 |
| Pharmacology | 01 |
| Community Medicine | 04 |
| General Surgery | 08 |
| Anaesthesiology | 17 |
NEET-PG Minimum Cut-off Marks:
| Category | Qualifying Percentage | NEET-PG Cut-off Score |
| General/EWS | 50th Percentile | 291 |
| General PwD | 45th Percentile | 274 |
| OBC/SC/ST | 40th Percentile | 257 |
Super Specialty Courses (DM/MCh)
Course Duration: TheSuper specialisationdegree program (DM/M.Ch.) is of 3 years duration.
Admission Procedure: The admission to DM and M.Ch. courses are donebased on marks scored in the NEET-SS entrance examination.
Super specialties: The following is a list of Super specialties available at IGIMS, Patna:
- Nephrology
- Cardiology
- Neurology
- Gastroenterology
- Pediatric Surgery
- Urology
- Surgical Gastroenterology
- Neurosurgery
Number of Seats: The IGIMS has a total of 21 DM/M.Ch. seats from which it has 10 seats for DM and 11 seats for M.Ch. course. The following table mentions the number of DM/M.Ch. seats in each specialty:
| Specialty/Subject | Number of Seats |
| Nephrology | 03 |
| Cardiology | 03 |
| Neurology | 02 |
| Gastroenterology | 02 |
| Pediatric Surgery | 02 |
| Urology | 04 |
| Surgical Gastroenterology | 03 |
| Neurosurgery | 02 |
List of Para Medical Courses/Diploma Courses at IGIMS, Patna
Nursing Courses
B.Sc. Nursing
M.Sc. Nursing
Other Undergraduate courses
B.Sc. Ophthalmic Techniques
B.Sc. (Hons.) Medical X-ray Technology (BMXRT)
Diploma Courses
General Nursing & Midwifery (GNM)
Diploma in Medical Laboratory Technology (DMLT)
Diploma in Medical Record Technology (DMRT)
Diploma in Urological Technology (DUT)
Diploma in Neuro Technology (DNT)
Diploma in O.T. Assistant Technology (DOT
Diploma in Cardiac Technology (DCT)
Diploma in Dialysis Technology (DDT)
Diploma in Anaesthesia Technology (DAT)
Diploma in Endoscopy Technology (DET)
Diploma in Medical Radiotherapy Technology (DMRT)
Aspiring doctors can enroll in online medical courses to excel in the medical journey. DigiNerve provides you with an opportunity to learn from the best faculty in India and delivers premium medical content to enhance conceptual clarity, clinical skills, and trial excellence. The platforms offer courses inUG, PG, Exam Prep, and Professional medical categories, such as Microbiology by Dr. Apurba S Sastry, Pathology by Prof Harsh Mohan,Medicine by Dr. Archith Boloor,Surgery by Dr.Sriram Bhat,OBGYN MD by Dr. Aswath Kumar,Ophthalmology MD by Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna, and the list goes on.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the ranking of IGIMS colleges in India?
Ans. According to NIRF Ranking 2023, IGIMS was ranked at 151st position in India and 3rd position in Bihar. IGIMS is a government medical institution located in Patna, Bihar, and offers MBBS, MD, MS, and other programs in various medical specialties.
Q2. What is the total fee for MBBS at IGIMS Patna?
Ans. The total fee for MBBS at IGIMS, Patna is around 2.5 lakhs.The tuition fee for MBBS is as follows:
Rs. 58,333 (for 1st Prof)
Rs. 50,000 (for 2nd Prof)
Rs. 54,167 (for 3rd Prof Part-I)
Rs. 62,500 (for 3rd Prof Part-II)
Q3. Which is the top 1 government hospital in India?
Ans. All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Delhi is a top government medical college in India. Also, according to NIRF, it is ranked No. 1 in the medical college category.
Q4. Is the Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences a government or private organization?
Ans. Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences is a government medical institute located in Patna, Bihar. IGIMS was established as an autonomous organisation on the pattern of All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi with an objective to provide super specialty medical facilities in Bihar.
Q5. Which PG specialisations are available at IGIMS, Patna?
Ans. The following PG Specialisations are available at IGIMS, Patna:
- Pathology
- General Medicine
- Anatomy
- Forensic Medicine
- Biochemistry
- Radio Diagnosis
- Physiology
- Psychiatry
- Microbiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Pediatrics
- Obstetrics &Gynecology
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Orthopaedics
- Ophthalmology
- Pharmacology
- Community Medicine
- General Surgery
- Anaesthesiology
Q6. How many MBBS seats are there in IGIMS Patna?
Ans. There area total of 120 MBBS seats at IGIMS, Patna. IGIMS has a sprawling campus located in Sheikhpura, Patna. It’s well-equipped with modern infrastructure, including lecture halls, laboratories, and hostels. IGIMS boasts a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors, researchers, and medical professionals.
Q7. Is IGIMS, Patna MCI-recognised?
Ans. Yes, Indira Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (IGIMS), Patna is MCI-recognized.The Medical Council of India (MCI) is a statutory body that establishes and maintains high standards of medical education in India.
In recent years, telemedicine has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, revolutionizing the way medical services are delivered and received. This technological evolution has significantly impacted pediatric practice, offering a spectrum of benefits while presenting unique challenges that require thoughtful consideration. Technological developments, legal frameworks, and healthcare delivery models are always striving to optimize telemedicine in pediatric practice to improve child accessibility and quality of care, despite several advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding the benefits and challenges, or the pros and cons, of telemedicine in pediatric practice is essential for healthcare providers, parents, and policymakers as they navigate the evolving landscape of virtual pediatric care. In navigating the benefits and challenges of telemedicine in pediatric practice, a balanced approach is essential. Addressing technological disparities, ensuring privacy and security, and maintaining a complementary balance with in-person care are crucial considerations. In this article, we’ll read about the benefits and challenges of telemedicine in pediatric practice in detail.
Benefits of Telemedicine in Pediatric Practice
Geographical Accessibility
Telemedicine allows children in rural or remote areas to access pediatric care without the need to travel long distances. Telemedicine breaks down geographic barriers, ensuring that children, regardless of their location, have access to quality pediatric care. This is especially important in underdeveloped or rural areas where pediatricians are scarce and might cause delays or deficiencies in healthcare. Pediatricians can reach a wider audience by using telemedicine to consult and provide medical advice from a distance.
Remote Monitoring and Timely Consultation
Parents don’t have to wait for long for appointments to seek medical advice for their kids. Remote monitoring of children is made possible by telemedicine, which facilitates proactive management and lessens the need for frequent in-person visits. A child’s progress can be tracked by pediatricians, who can easily modify treatment programs as necessary. In the management of chronic pediatric illnesses, telemedicine is essential. In order to make better decisions, healthcare professionals can track a child’s health parameters and child development in real-time by using remote monitoring systems. Remote monitoring of children is made possible by telemedicine, which facilitates proactive management and lessens the need for frequent in-person visits.
Convenience for family and patients
Travel time has decreased, and flexibility has increased as a result of telemedicine practice. By reducing the need to go to healthcare facilities, families can save money and time. Working parents find it easier to schedule appointments without compromising the child’s health. Families benefit greatly from telemedicine’s convenience, particularly those with hectic schedules or little money. Especially after the child’s birth, a lot of questions arise in the minds of parents regarding early childhood development, which can easily be answered by a pediatrician during an online consultation.
Preventive Care and Education
Healthcare professionals can advise parents on preventive care and provide information on child health and wellness through telemedicine. Early detection and intervention for behavioral or developmental difficulties might be facilitated by prompt virtual consultations. Enhancing preventive treatment and health education is one of the main benefits of telemedicine in pediatric practice. Through virtual consultations, pediatricians can advise parents on immunizations, diet, and general child wellness. In addition to encouraging better lifestyles and the early identification of possible problems, this proactive approach gives parents the power to make decisions regarding their child’s well-being.
Reduced Exposure to Infections
Infection risk is reduced with the use of telemedicine, particularly in the event of pandemics or disease outbreaks. It is crucial to limit exposure to pathogens, especially during health emergencies. In this sense, telemedicine plays a vital role in facilitating remote consultations. Telemedicine supports public health initiatives by minimizing the need for in-person visits to medical facilities, protecting both patients and healthcare professionals. In pandemics and outbreaks, telemedicine reduces the need for in-person hospital visits, thereby limiting the number of people exposed to illnesses.
Efficient Use of Resources
Telemedicine makes the most of healthcare resources, enabling pediatricians to better manage their time and potentially reducing wait times for appointments. With the increasing technology, all three main telemedicine components, be it teleconsultation, telementoring, and telemonitoring, are flourishing. Telemedicine resources also offer opportunities for better communication and collaboration between pediatricians and other specialists for the enhanced treatment of patients to achieve developmental milestones.
Enhanced Follow-Up Care
Pediatricians can more easily take follow-up consultations through virtual visits, guaranteeing continuity of care and tracking development. Another noteworthy advantage is the efficiency of follow-up care. Telemedicine can frequently be used to carry out routine examinations, medication management, and chronic illness monitoring efficiently. In addition to saving time for families and healthcare professionals, this also reduces the chance of infection exposure, which is crucial given current global health issues like the COVID-19 pandemic. Telemedicine thus positively affects a child’s growth and development, disease management, and other treatment modalities leading to enhanced follow-up care.
Challenges of Telemedicine in Pediatric Practice
Technology Barriers
Undoubtedly, one of the biggest obstacles to telemedicine is limited access to reliable network connectivity, smartphones, and other communication methods. Some families might not have access to the required technology to engage in telemedicine appointments, such as smartphones or dependable internet. Despite the quick advancement of technology, not every family has equal access to the necessary pediatric healthcare tools. Access to healthcare can differ depending on one’s ability to use telepathic resources. To guarantee that telemedicine helps all socioeconomic groups, it is imperative to close this digital gap.
Lack of Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination might not be possible in remote consultations, which could make it more difficult to diagnose and schedule treatments. One of the main problems with telemedicine is that it does not include physical examinations, which are essential to pediatric diagnosis. Lack of competence to perform in-person examinations and developmental assessments may result in the overlooking of some medical disorders and subtleties. Maintaining a healthy balance between virtual consultations and sporadic in-person visits becomes essential to providing children with complete treatment. For several pediatric illnesses, the lack of physical inspections during virtual consultations may make it more difficult to accurately diagnose and plan treatments.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Although it can be difficult, it is essential to protect the confidentiality and privacy of pediatric health information when conducting virtual consultations. Concern over safeguarding patient data online is growing. Strong security requirements must be followed by telemedicine systems to protect sensitive pediatric health information and data. Ensuring privacy and confidentiality is a legal and ethical responsibility that calls for continuous improvements in secure telehealth infrastructure.
Communication Challenges
In virtual encounters, non-verbal cues—which are vital for figuring out a child’s condition—may be weakened. Healthcare Some parents could be less comfortable using telemedicine technology or properly communicating information about their child’s health. In pediatric treatment, effective communication is essential, and telemedicine creates additional communication difficulties. Healthcare professionals must come up with ways to get around these restrictions, such as using video calls to have more sophisticated conversations. For telemedicine to be used successfully, parents must feel at ease and be proficient in using digital platforms. To improve parental proficiency in telehealth encounters, pediatricians ought to think about providing assistance, materials, and training. Aspiring pediatricians can gain insights into telemedicine practices through the best online pediatrics courses.
Reimbursement and Regulation
The financial viability of pediatric practices may be impacted by difficulties with payment procedures for telemedicine services. Healthcare providers may face difficulties due to the constantly changing legislation and licensing requirements for telehealth services. The reimbursement policies in pediatric practice have a significant impact on the financial sustainability of telemedicine. To ensure that telemedicine efforts are sustained, policymakers and healthcare organizations must collaborate to create transparent policies and fair reimbursement schemes. Also, families in rural areas might not have proper knowledge about online payments or access to digital payment methods, making it difficult to consult a pediatrician online.
Emergency Situations
When an emergency calls for quick medical attention, telemedicine might not be the best option. Even though telemedicine works well for normal consultations, it might not be the best option in an emergency where prompt medical attention is needed. Clear procedures for recognizing emergencies during virtual visits and advising parents on when to seek urgent in-person care must be established by pediatric practices. Telemedicine might not be appropriate in situations where prompt physical intervention is needed.
Possibility of Overuse or Misuse
Parents may rely on virtual consultations for small concerns that could be handled in a different way if telemedicine is used excessively or inappropriately. Also, relying only on telephonic consultations can lead to communication barriers, which can have a bad impact on the health of the patient.
Technological Glitches and Professional Burnout
Poor internet connectivity or platform failures can cause virtual consultations to be disrupted, which can have an impact on the standard of service and patient experience. The rising demand for virtual consultations may cause burnout among healthcare professionals, which could have an impact on pediatricians’ general well-being.
Conclusion
To conclude, telemedicine in pediatrics has great potential to transform the way chronic illnesses are managed, increase access to healthcare, and improve preventative care. To reach its full potential, though, resolving issues with technology, privacy, communication, and legal frameworks is essential. Legislators, medical experts, and software developers must constantly collaborate to create a telemedicine environment that prioritizes the well-being of children and families. Future efforts to enhance and improve telemedicine practices in pediatric care will be crucial in determining how children’s healthcare is delivered, as long as technology and healthcare systems keep evolving. Even as we celebrate the advancements made in the first year of telemedicine integration into pediatric care, we must keep improving these standards for the sake of future generations.
Click here to master the concepts of MD Pediatrics.
INI-CET is a combined national-level entrance examination for admission to the medical postgraduate courses – MD, MS, DM (6 yrs), MCh (6 yrs), and MDS at INI institutes (Institute of National Importance). The INI-CET exam is around the corner. Getting admission to INI institutes is highly challenging and a dream for MBBS students. This is a highly competitive task to secure a seat in the renowned medical colleges in India.
Remember, Perseverance is the key.
The INI-CET exam will be held on 5th Nov 2023 for admission to the AIIMS INI-CET January session 2024.
Here’s the final seat position (Category-wise) for admission to various MS/MD/DM (6 years)/MCh (6 years)/MDS courses at AIIMS, New Delhi, and other AIIMS located pan India through the INI-CET entrance examination for the January 2024 session.
Table 1: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, New Delhi:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats
|
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD Seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 14 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 7 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Biophysics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 11 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Lab. Medicine | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Medicine | 10 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 18 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Palliative Medicine | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 12 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis & Interventional Radiology | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Surgery | 16 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxofacial Surgery | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Orthodontics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatrics & Preventive Dentistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Prosthodontics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Neuro Surgery MCh (Direct 6 year Course) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DM | Infectious Diseases DM (Direct 6 year Course) | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 189 | 82 | 49 | 27 | 13 | 18 | 9 | |
Table 2: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bhopal:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 8 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 71 | 29 | 19 | 11 | 5 | 7 | 4 | |
Table 3: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bhubaneswar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 9 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 7 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obst. & Gynecology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MDS | Orthodontics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 95 | 35 | 26 | 17 | 10 | 7 | 5 | |
Table 4: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Jodhpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology & Critical Care | 10 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 |
1
|
0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology, Venerology & Leprology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Family Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiology | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 71 | 28 | 19 | 11 | 6 | 7 | 4 | |
Table 5: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Patna:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 10 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | FMT (Forensic Medicine & Toxicology) | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG (Obstetrics &Gynecology) | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Pediatrics Surgery (6 yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery (6 yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Surgical Gastroenterology (6 yrs) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Trauma Surgery & Critical Care (6 yrs) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 86 | 40 | 22 | 12 | 5 | 7 | 4 | |
Table 6: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Raipur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery (6yrs) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 82 | 31 | 21 | 14 | 5 | 11 | 3 | |
Table 7: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Rishikesh:
| Course | Subject/Specialisation | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Respiratory Medicine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Periodontology (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCH 6 Years | Pediatric Surgery (MCH 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Plastic, Reconstructive & Burns Surgery (M.CH. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Trauma Surgery& Critical Care (MCH 6yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Urology (6yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 96 | 43 | 24 | 13 | 7 | 9 | 5 | |
Table 8: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Nagpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | Number of PwBD seats | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservation Dentistry & Endodontics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 73 | 30 | 20 | 11 | 5 | 7 | 4 | |
Table 9: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bibinagar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Numberof Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | CFM | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | ENT | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | FMT | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | OBGYN | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radio Diagnosis | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 53 | 20 | 16 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 3 | |
Table 10: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bathinda:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | Number of PwBD seats | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesia | 10 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Anatomy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Periodontics (Dental) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pulmonary Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 60 | 24 | 16 | 9 | 5 | 6 | 3 | |
Table 11: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Deoghar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesia | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatrics& Preventive Dentistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Pediatric Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 20 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
Table 12: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Mangalagiri:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 42 | 17 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 3 | |
Table 13: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Raebareli:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
|
UR |
OBC |
SC |
ST |
EWS |
||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 39 | 15 | 11 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 2 | |
Table 14: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Kalyani:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
|
UR |
OBC |
SC |
ST |
EWS |
||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venereology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MDS | Orthodontics & Dentofacial Orthopaedics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 67 | 27 | 18 | 10 | 5 | 7 | 3 | |
Table 15: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bilaspur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venereology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxilofacial Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 35 | 15 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 2 | |
Table 16: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Gorakhpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venereology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 44 | 18 | 12 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 2 | |
Table 17: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Guwahati:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 33 | 15 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 2 | |
Table 18: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Rajkot:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats |
Number of PwBD seats |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 27 | 11 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 2 | |
Table 19: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at PGIMER, Chandigarh:
| Course | Subject | Total Number of Seats |
Number of PwBD seats |
Rural Area Seats |
|||||
| Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||||
| MD | Anaesthesiology & Intensive Care | 16 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology, Venereology & Leprology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Medicine | 16 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 17 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis and Imaging | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 17 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Obstetrics and Gynecology | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics Surgery | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 120 | 59 | 31 | 21 | 9 | 0 | 6 | 6 | |
Table 20: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at JIPMER, Puducherry:
| Course | Subject | Total Number of Seats |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 11 |
| MD | Anatomy | 3 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 3 |
| MD | Dermatology, Venereology & Leprology | 4 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 4 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 |
| MD | General Medicine | 13 |
| MD | Immuno Hematology & Blood Transfusion | 2 |
| MD | Microbiology | 5 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 10 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 4 |
| MD | Physiology | 4 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 |
| MD | Pulmonary Medicine | 4 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 6 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 5 |
| MS | General Surgery | 13 |
| MS | Obstetrics and Gynecology | 11 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 6 |
| MS | Orthopaedics Surgery | 4 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 4 |
| MCh | Neurosurgery | 1 |
| MCh | Pediatric Surgery | 1 |
| MDS | Orthodontics & Dentofacial Orthopaedics | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxofacial Surgery | 0 |
| TOTAL | 132 | |
*Roaster Point Allocation for Counselling (Dynamic)
Table 21: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at NIMHANS, Bengaluru:
| Course | Subject | Number of Seats | Number of PwBD seats | |||||
| Total | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 13 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry (Karnataka Domicile Category) | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry (North-Eastern Domicile) | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DM (6yrs) | Neurology | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh (6yrs) | Neurosurgery | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 22 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
Table 22: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at SCTIMST Trivandrum:
| Course | Specialty | Number of Seats | Number of PwBD seats | |||||
| Total | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Must Know: INI-CET 2024: Schedule of Online Seat Allocation
To get conceptual clarity on the MBBS subjects online, click here
Medicine MD is an e-learning course curated to cater to all the learning needs of medicine postgraduate students. The course is meticulously crafted and conceptualised under the guidance of the eminent Chief Editors, Dr. Jyotirmoy Pal and Dr. Shashank R Joshi; Advisory Editors, Dr. Girish Mathur and Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander; and Associate Editors, Dr. Nandini Chatterjee, Dr. Jimit Vadgama, and Dr. Priyanka Shah.
The Medicine MD online course brings together the intelligence and clinical experience of more than 200 eminent experts in the field. The course not only serves as a complete guide to excel in final MD examinations but also accelerates your journey to becoming a skilled physician. It also provides you with the proper guidance to enhance your clinical expertise.
A wide number of medical disciplines are covered in this online medicine MD course, including rheumatology, neurology, cardiology, gastroenterology, hepatology, pulmonary and chest medicine, and many more. The course provides an organised learning environment that covers decision-making, long cases, short instances, and the fundamental sciences.
Course Inclusions
The Medicine MDonline course is meticulously crafted to provide youwith the following:
- Video Lectures
- Long Case Discussions
- Short Case Discussions
- Lecture Notes
- Self-Assessment Questions
- OSCEs
- DxTx
- Animated Videos
- Interactive Drug Formulary
- Regular Chat Shows
- Benchmark Trials
- Wise AI bot
- Printed Notes
Key features
The following are the unique features that make our course one of the bestMedicine MDonline courses for PG students and residents:
- To enhance the decision-making ability of the PG students/residents during their clinical practice, the course focuses on differential diagnosis and clinical methods.
- The course has a few sections dedicated to history-taking and clinical methods, investigations in medicine, procedures in medicine, pharmacotherapeutics, and research methodologies.
- To enhance the clinical skills of the learners, the course follows a case-based approach. The case-based lectures are highly illustrative and include differential diagnosis, management strategies, laboratory algorithms, treatment pathways, complications, prevention, patient care messages, and global and Indian recommendations.
- Questions provided after each video lecture are strategically integrated for self-assessment which enhances comprehension and engagement. This also helps in better retention of the concept.
- The integration of the 2D animations in the video lectures is visually appealing and hence helps understand the complex proceduresmuch more easily.
- Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs)are an essential tool for evaluating clinical competencies. These tests are available in video and flashcard forms throughout the course, allowing for quick review and self-evaluation in a manner similar to the actual exam.It is a standardised and impartial way to evaluate a candidate’s clinical abilities and competencies.
- The Pharmacotherapeutics section provides information on medicine drugs and their mechanism through videos and a drug formulary. You may expedite your decision-making process by using the drug formulary to search for drugs based on indications, drug names, and pharmacological categorization. These medications are divided into three risk categories: high, moderate, and low using colour coding.A comprehensive, color-coded drug formulary with common brand names, doses, essential indications, and much more aids in quick revision and retention and helps a lot during residency.
- DxTx,a special feature, a tool for rapid consultation, is represented by a human model that enables you to study important information with a single click. In an organised manner, you will get to learn about various bodily diseases along with their clinical features, pathophysiology, characteristics, diagnosis, treatment, indications, contraindications, and clinical trials. Moreover, complex etiopathological ideas are expertly explained using flowcharts when needed. This DxTx tool is in line with the NMC curriculum to help you excel in MD exams as well as competitive examinations.
- Highly illustrative Medicine MD video lecturescover a wide range of topics, including fundamental sciences, long and short cases, and clinical decision-making.
- To help you out with the MD exam preparation, the course follows a clinical and differential approachandprovide you with the compilation of long case discussions and short case discussion covering major medical topics and concepts.
- The Medicine MD course provides well-illustrated lecture notes that will serve as a handy reference for students. Research papers that provide evidence are included after each topic to complement them.
- Regular chat shows are conducted by India’s top medical faculty and subject experts.
- To stay current with recent developments in the area, evidence-based papers, and benchmark trials have been included.
- Wise AI chatbotis has a super amazing featured tool to give appropriate explanations of topics, treatment techniques, and more.It is a complete and interactive solution provider coupled with real published resources including books, journals, notes, and videos.
- Printed Notesare designed to save your time by offering clear, exam-focused facts and visual learning at a reasonable cost.
Benefits of Enrolling in Medicine MD Course
The following are some benefits of enrolling inan online MD medicine course:
Flexibility: Online MD programs frequently allow you to study at your own pace and location. For medical professionals who could have erratic schedules or must juggle their academics and clinical duties, this flexibility is invaluable.
Accessibility: Students no longer have to relocate or commute to a certain place in order to enrollin the courses, which provide them with high-quality medical education.
Self-paced Learning: Students can advance at their own pace. This is very helpful for people who wish to learn more quickly or who require more time to understand complicated medical concepts.
Diverse Learning Materials: Online courses can include a large array of learning materials, such as video lectures, digital notes,printed notes, practice questions, and drug charts. These resources can accommodate various learning preferences and styles.
Cost-Effective: Since online MD programs do not need travel, lodging, or other related costs, they may be less expensive than on-site programs.
Networking Opportunities: Students enrolled in online MD programs frequently get to know to learn from eminent professors and peers across the nation. This may result in beneficial networking chances and exposure to other viewpoints inside the medical industry.
Since the area of medicine is everchanging, online programs more readily update their content to take into account the most recent findings and recommended practises.
Table of Content
The following is a list of modules included in the Medicine MD online course:
History Taking and Clinical Methods
Neurology
Cardiology
Gastroenterology
Nutrition
Hepatology
Procedures in Medicine
Endocrinology and Diabetes
Pulmonary and Chest Medicine
Infectious Diseases
Rheumatology
Hematology
Nephrology
Geriatrics
Dermatology
Critical Care Medicine
Envenomation and Poisoning
Allergy and Immunology
Genetics
Diagnostics
Pharmacotherapeutics
Research Methodology and Publications
OSCEs
Link to the complete TOC:Evidence-Based Medical Learning Now At Your Fingertips
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1. Can medical courses be done online?
Ans. Of course, yes, you cantake medical courses online. Online medical courses by DigiNerveprovide you with this opportunity to learn medical courses online from India’s top faculty and subject experts. These online courses supplement your college studies and clinical training to a great extent.
Q2. Can I complete my MD in 2 years?
Ans. No, you cannot complete MD in 2 years in India. MD (Doctor of Medicine) is a three-year full-time postgraduate program.
Q3. Can I do an MD immediately after MBBS?
Ans. Yes, you can do MD directly after MBBS but you need to fulfill the general eligibility criteria and crack the PG entrance examination, such as NEET-PG and INI-CET.
The curriculum of MBBS is vast and the MBBS final year comprises the most difficult subjects and modules. At this stage of your MBBS journey, you are well equipped with studies along with ward postings and competitive exam preparations.
Undoubtedly, the life of a medical student can be stressful and exhausting due to the demanding schedule of studies and clinical postings. Despite the numerous benefits of being a doctor, you must acknowledge the depth of the profession. As an aspiring doctor, you must be ready to work under extreme pressure and in life-or-death scenarios while doing your duties flawlessly to ensure that patients are treated effectively, and lives are saved.
Here are some effective and reliable tips to study Medicine in MBBS.
Medicine is an interlinked subject, and hence, you need to have a foundational knowledge of all the other subjects. For instance, if you are studying Bronchitis, an infection in which the bronchial tubes become inflamed and swollen and fill with mucus. You need to first know the anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system, and then for the diagnostic result interpretation, you need to understand pathology and radiology and to understand the treatment and drugs, you need to have a sound knowledge of pharmacology and biochemistry. Thus, you must learn a concept or a disease in an inter-related manner for better understanding and retention.
Although reading and understanding the concepts is important and remains the first step but retention and retrieval are the other crucial aspects of studying. Understanding the subject will ease the learning process but only focusing on learning new and new topics will end up with a question of memory! Learning new topics is equally important as remembering the old ones. Hence, make sure to prepare a study plan that focuses on both learning and retention. Otherwise, after a certain period, our memory starts to fade which makes us difficult to recall and interlink the concepts. Medicine is a clinical subject, that finds its application in the real world where your memory or retention power has to be very solid. Spaced practice is quite helpful in this case. This is an amazing tip for MBBS final year preparation. You must stay curious to learn more. Try fascinating examples, mnemonics, storylines, and cases to retain the information for a long time.
Students have different learning styles, so stress your strengths and weaknesses while creating a study plan. Also, prioritizing time management is highly crucial. Always consider your personal preference while setting up your study area while considering your environment. Whether you are an AM or a PM person, consider this point while your study plan to multifolds the benefits of your preparation. These prove effective study strategies for medical students.
Once you are done with learning a concept or about a disease, say Diabetes Mellitus, then don’t go to the next topic without practicing questions on diabetes mellitus. Practicing questions will help you evaluate your understanding of the topic and improve your performance. Solve the questions from all the topics of the given module or disease, such as disease mechanism, pathophysiology, differential diagnosis, and the first line of treatment. This practice will enhance your understanding of the subject leading to better retention and let you know which topic you are well-versed in, and which topic needs to be re-studied.
Must Read: Important Topics of Medicine in MBBS
Another effective study technique for medicine is solving clinical cases. Suppose you are learning about Diabetes Mellitus, you can either learn via clinical case or practice a case after understanding a concept. But don’t miss it. Your actual test will be a practical case in a hospital; the clinical case is your helping hand for that practice. While solving a clinical case, you will have to answer all the questions in a single go. What are the symptoms a patient is suffering? What is the probable diagnosis? What is the disease mechanism and source of infection? What is the pathophysiology of a disease? How to relate to the patient history? What are the treatment methods possible? How to figure out the best possible treatment for a particular patient? What is the best first-line treatment? What medications to prescribe and determine the effect of the route of administration with dosage? Which surgery is to be carried out and how? What are pre- and post-operative requirements? How to determine the treatment efficacy? And so on.
You are also required to learn effective patient communication. The best way to practice this is during ward postings. It connects you to a real-life scenario along with deepening your learning. Try to see a case from different angles to reach the utmost conclusion.
Medicine is a vast subject and there can be topics where one or the other thing is similar and while memorizing the concept or answering a question or especially while learning symptoms and drugs, you might get confused. This feels so bad that you put in so much effort in understanding and learning but ultimately get confused. Whenever you are learning a similar concept, try to add different cues, learn with different examples, and learn in a different manner with a different example. Try and keep the information separate with new cues, flashcards, or mnemonics and try to learn concepts in an inter-related manner, wherever feasible.
Always remember, treat your body well and everything will fall into place. If you are physically or mentally fatigued, you won’t be able to learn effectively, and the chances of human error increase. Be well-rested to focus on your studies. Take sound sleep, proper rest, and feed yourself healthy. Avoid stress. Studying medicine and having a work-life balance can be exhausting and stressful at times. To avoid such situations and challenges, take breaks, get enough sleep, exercise, do leisure activities, and eat well. Talk with your loved ones and figure out solutions rather than stressing about problems. Listen to good music and try the things you love doing.
Try to incorporate these MBBS Medicine final year study tips in your study schedule to excel. To get expert guidance, you can enroll in Dr. Archith Boloor’s video lectures for medicine on the DigiNerve app. The DigiNerve’s Medicine for UnderGrads course not only includes online medicine course video lectures but also self-assessment questions, and worthy notes. This online medicine course helps you understand the topics along with developing practical and clinical skills. You get to learn in a case-based format aligned with the CBME curriculum. Along with excelling in medicine prof exams, this course also helps you with NEET-PG medicine exam preparation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. Which book to study for medicine final year MBBS?
Ans. An Insider’s Guide to Clinical Medicine by Archith Boloor & Anudeep Padakanti, Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates: Medicine by Archith Boloor & Ramadas Nayak, Self-Assessment & Review Medicine (Part A & B) by Mudit Khanna, and Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine are some of the recommended books to study medicine in MBBS.
Q2. How many months is the final year of MBBS?
Ans.The duration of the final year MBBS is of 18 months.
Q3. What is the best way to study MBBS?
Ans. Students have different learning styles, so stress your strengths and weaknesses while creating a study plan. Also, prioritizing time management is highly crucial. Always consider your personal preference while setting up your study area and consider your environment. You are an AM or a PM person, and considering this point will enhance your preparation to a greater extent.
The three-part MRCOG (Member of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists) exam is acknowledged as the gold standard qualification in O&G on a global scale.
The fundamental and applied sciences pertinent to OBGYN clinical practise are covered in the MRCOG Part 1 exam. Exams with multiple-choice questions (MCQs) are administered four times a year at Pearson VUE testing locations across the globe.
Steps to Book the MRCOG Part 1 Exam
The MRCOG Part 1 exam is a first step towards achieving the gold standard qualification in the obstetrics and gynecology specialty. Before proceeding to book an MRCOG exam, you must be well-versed with all the steps of the MRCOG Part 1 exam registration process so that you don’t miss any to avoid application rejection.
The following are the steps for the MRCOG Part 1 exam application procedure:
1. Create an RCOG account.
First and foremost, you should create an RCOG account. Go to the MRCOG official website and click on the ‘Register’ button at the top of your screen. If you already have booked or taken an RCOG exam earlier, you are required to book this time with the same credentials.
2. Get Your Eligibility Checked.
If you are booking an exam for the first time, then you are required to submit the eligibility form and get it approved. Make sure you stick to the timeline. If you have previously booked an exam, then you need not submit the eligibility form again as you will already be considered eligible.
In the MRCOG Part 1 eligibility form, you need to fill in the following details:
- RCOG College Account Number
- Personal Details (Includes First name, Last name, Gender, and Date of Birth)
- Medical Qualification (Includes Medical registration country, Medical registration number, Primary medical qualification, Country and University of PMQ)
- Ethnicity (Includes mentioning Nationality and disability or long-time illnesses or health conditions, if any)
How to Submit Your Eligibility Application?
- You are required to compose an email with “Part 1 Eligibility Assessment Application [insert your College number]” as the subject line.
- You must attach the completed application form to the email.
- Then attach either your original photo/scanned primary medical degree certificate or photo/scanned medical registration certificate.
- Also, attach the scanned copy of your government-issued ID. You are required to use this ID for all further examination procedures.
- Now send this email with the attachments to part1eligibility@rcog.org.uk.
- You will receive an automated response regarding the further steps to be taken.
You can expect a revert regarding your eligibility status confirmation within four weeks after the closing date of the Part 1 Eligibility application.
3. Submit Expression of Interest Form.
The following are the steps to submit an Expression of Interest Form:
- You are required to submit an Expression of Interest Form within the stipulated time to proceed with exam booking.
- You must submit a new form every time you take an MRCOG exam.
- The Expression of Interest Form comprises the RCOG College Account Number, Email address, First name, and last name.
- You will get this form on the RCOG official website in the MRCOG Part 1 section.
- Fill in all the required details correctly and then provide your consent for submission.
- After the form submission, a screen with confirmation will appear. Don’t forget to take a screenshot of the same.
Upon commencement of the application window, eligible candidates who have successfully submitted the Expression of Interest form will receive an email. The email will have instructions for booking an exam at the available Pearson VUE test centres.
Check the exam calendar for exam dates and fees before booking an exam.
First-time applicants may submit their Expression of Interest form at any time without waiting for a response back on their MRCOG Part 1 eligibility application. They will only be able to reserve a spot, though, once the booking window opens, provided their MRCOG Part 1 eligibility application form has been accepted and submitted by the deadline.
4. Check the Exam Calendar.
You must check the exam calendar and MRCOG Part 1 exam booking details for the upcoming dates and fees before booking an exam. Make sure you book an exam when you are confident enough about your MRCOG Part 1 exam preparation. You can also enroll in the MRCOG Part 1 preparation courses online to ace the exam.
Click here to get the access to MRCOG Part 1 Mock Exam.
MRCOG Part 1 Exam Calendar
The MRCOG Exam is conducted twice a year. The MRCOG Part 1 dates for the 2024 session are 16 January 2024 and 2 July 2024.
For the January exam, the booking window application has been started from 14 November 2023 and will close by 14 December 2023. The MRCOG Part 1 exam date is 16 January 2024 and the MRCOG Part 1 result date is 13 February 2024.
MRCOG Part 1 Fees
The table below mentions the fees for MRCOG Part 1 exam registration:
| Band | Fees for 2024 Session |
| UK and Republic of Ireland | £534 |
| Band A | £644 |
| Band B | £555 (India falls under this category) |
| Band C | £443 |
5. Book available Pearson VUE test centre and slot.
After the successful submission of the Expression of Interest Form, book your Pearson VUE test once the booking window opens. To proceed with booking, check the exam centres available in the respective country you wish to book an exam.
Available MRCOG Part 1 Exam Centres in India
- Brilliant Computer Education, Ongole
- Achievers Online Academy, Rajahmundry (Rajamahendravaram)
- Coreglobal, Vijayawada
- Computer.in IT and Ecom Service, Vijayawada
- Itechnoplus Education and Solution Pvt. Ltd, Patna
- Chandigarh Networks Academy, Chandigarh
- Secure Net Technologies, Chandigarh
- Pearson Professional Centers, New Delhi
- Agilitics Edutech Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi
- Goldman Consulting Private Limited, New Delhi
- National Industrial Training Centre, New Delhi
- Positive Solutions, New Delhi
- The Guest Institute, Goa Velha
- Pearson Professional Centers, Ahmedabad
- Indo-American Education Society, Ahmedabad
- Siddhi Techsoft and Management Pvt Ltd, Ahmedabad
- Charotar University Science of Technology, Changa
- Pearson Professional Centers, Surat
- Baroda Institute of Technology, Vadodara
- Intudo Consulting, Gurgaon
- Pearson Professional Centers, Gurugram
- Mindful Immigration Services, Panipat
- Sircl Tech Pvt. Ltd, Sirsa
- Secure Net Technologies, Solan
- Tantray Online Services Pvt Ltd, Jammu
- Pearson Professional Centers-Bangalore
- Acharya Education Services Pvt Ltd, Bangalore
- Global Marketing and Commercial Services Company, Bangalore
- Honeydewz Software Technologies, Bangalore
- iDomains Technologies, Bangalore
- Parkus Technologies Pvt. Ltd, Bangalore
- Tvaksa Technologies Pvt. Ltd, Bangalore
- Ally Tech Services, Bengaluru
- Consulace Business Solutions Private Limited, Bengaluru
- Linux Academy, Mysuru
- Nuaxil, Ernakulam
- Blastline Institute, Kochi
- Nyeste Venture Technologies, Kochi
- R-3 Info Solution, Kottayam
- GlobalTrack Technologies Pvt Ltd, Thiruvananthapuram
- MIGORB, Trichur
- Networkz Systems, Trivandrum
- iTrainu Technologies, Indore
- Orlando Academy, Indore
- Rockford Softsol-Computer Academy &Training Center, Jabalpur
- IFuture Technologies Private Limited, Kalyan
- Pearson Professional Centers, Mumbai
- GIIT Computer Institute, Mumbai
- iFuture Technologies Private Limited – Additional, Mumbai
- Span Labs, Mumbai
- The English Advantage, Mumbai
- Learn Well Technocraft, Nagpur
- Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering, Nagpur
- Tech-Act, Navi Mumbai
- Pearson Professional Centers, Pune
- Forte Webasha Technologies Pvt. Ltd, Pune
- Learn Well Technocraft, Pune
- The Symbiosis Medical College for Women, Pune
- Vinsys It Services (I) Pvt. Ltd, Pune
- LIT INDIA, Bhubaneshwar
- Technohub LLP, Bhubaneswar
- Micireds Network Technologies, Pondicherry
- Pearson Professional Centers, Amritsar
- Pearson Professional Centers, Amritsar
- Pearson Professional Centers, Chandigarh
- Pearson Professional Centers, Jalandhar
- Munjal BCU Centre of Innovation & Entrepreneurship, Ludhiana
- Chandigarh University, Mohali
- Him Technology Private Limited, Mohali
- GNA University, Phagwara
- Naveen Model Senior Secondary School, Punjab
- Akashdeep PG Girls College, Jaipur
- Evalult Digital Private Limited, Jaipur
- Tech Solutions, Sri Ganganagar, Rajasthan
- HINT, Udaipur
- Eastern Online Test Centre, Gangtok
- Pearson Professional Centers-Chennai
- AATRALZ (Additional Site), Chennai
- Bloom Cloud IT Services Private Limited, Chennai
- Rajaji Institute of Technology, Salem
- I Tech Academy, Tirunelveli
- Pearson Professional Centers-Hyderabad
- Coreglobal- Additional Site, Hyderabad
- Dolphin, Hyderabad
- Edguru Overseas Education Consultants, Hyderabad
- Gusto Techno Solutions, Hyderabad
- Vast Technologies, Hyderabad
- Easy Dots Technologies, Agra
- Myinfotech, Bijnor
- Meritorious Academy Pvt Ltd- Additional Site, Ghaziabad
- P.C.C, Lucknow
- Polishsys Technologies Pvt Ltd, Lucknow
- Thirumala Education Academy, Lucknow
- Pearson Professional Centers-Noida
- Agilitics Edutech Pvt. Ltd, Noida Center
- Advita Innovations, Dehradun
- VGRASSP Services, Dehradun
- Sheel Institute, Haridwar
- ATA Infotech Ventures Pvt. Ltd, Kolkata
- Readybell Software Services Pvt. Ltd, Kolkata
- ISOEH, Siliguri
Steps to Book Pearson VUE test Centres:
- Log in to your RCOG account using your email ID and password.
- You will be redirected to the RCOG Exam Candidate Portal.
- On the portal, search for the exam centres feasible for you.
- You can search the nearest test centres to your registered address by using the default option.
- The availability and seat booking are completely done on a first come first serve basis.
Must Read: MRCOG Part 1: Eligibility, Exam Pattern, Timetable & Fee Structure
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. Where to register for the MRCOG Part 1 exam?
Ans. Once you open the RCOG official website on the browser, click on the ‘Register’ option at the top left of the screen to register to book an MRCOG Part 1 exam.
Q2. Which documents are required for the MRCOG Part 1 exam booking?
Ans. The documents required for MRCOG Part 1 exam booking are an original photo/scanned copy of your primary medical degree certificate, or a photo/scanned copy of your medical registration certificate, and a scanned copy of your government-issued ID.
Q3. When will I get the confirmation of the MRCOG test centre booking?
Ans. After completing your test centre booking, Pearson Vue will automatically send you an email confirming the reservation and outlining the necessary identification.
Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) is a premium medical institution and is among the top 10 medical colleges in India, according to the NIRF Ranking. The college is in Trivandrum, Kerala. It is recognized as an Institution of National Importance with the status of a University under the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India. The college focuses on advanced superspecialty postgraduate training programs in medical specialties and health research. The major branches SCTIMST targets are:
- Interventional radiology
- Interventional stroke care
- Cardiac electrophysiology
- Advanced cardiothoracic and vascular surgery
- Surgery for epilepsy
- Micro neurosurgery
- Deep brain stimulation for movement disorders
- Development of new biomedical devices and products
- Evaluation of medical devices to global specifications
SCTIMST offers admission to various Postgraduate courses, Post Doctoral Fellowship courses, Post Doctoral Certificate courses, PG Diplomas, Diplomas, Specialty Nursing Diploma programs, Advanced Certificate Programs, and Ph.D. programs. It further conducts new academic programs and health science research and training for medical professionals.
MEDICAL COURSES AT SCTIMST, TRIVANDRUM
POSTGRADUATE PROGRAMS
MD Transfusion Medicine
Course Duration: 3 years
General Eligibility: For the January batch, the candidates must have completed the necessary education, training, and employment by January 31, 2024; for the July batch, the deadline is July 31, 2024.
Registration with the Kerala State Medical Council (KSMC)/Travancore Cochin Medical Council (TCMC) is mandatory, and at the time of admission, submission of a registration certificate to the Division of Academic Affairs is necessary.
Upper Age Limit: 40 years (till 1st January 2024 for the January session and 1st July 2024 for the July session). Five-year age relaxation is given for SC/ST candidates, sponsored candidates, and qualified ex-service personnel with a service of not less than five years.
Mode of Selection: INI-CET (Institutes of National Importance-Common Entrance Test)
Stipend: The stipend (per month in INR) for MD candidates (except for sponsored category candidates) is Rs. 61,300 for all three years. Other HRA, NPA, DA, and DA on TA are applicable as per Institute rules.
Table: List of PG courses along with number of seats and eligibility qualification
| Course | Number of Seats | Eligibility Qualification (NMC-recognised) | |
| General Quota | Sponsored Quota | ||
| MD in Transfusion Medicine | 2 (UR) | 1 | MBBS or equivalent degree |
DOCTORAL PROGRAMS
Ph.D. Program
The institute provides PhD admission to various areas of Physical Sciences, Chemical Sciences, Biological Sciences/Biomedical Sciences, Bioengineering, Biomaterial Science and Technology, Health Sciences, and Medical Science. The admission to Ph.D. courses at SCTIMST is conducted twice a year, in June and November for July and January sessions respectively. Admission to the July session is restricted to fellowship holders and MPhil (Biomedical Technology-SCTIMST) degree holders only.
The PhD Programs are available in the following areas:
- Neurosciences
- Cardiac Sciences
- Imaging Sciences & Interventional Radiology
Eligibility Qualification: MBBS/MD/MS/DNB
In the case of an MBBS degree, a minimum of 55% marks are required along with holders of National Level fellowship from UGC/CSIR/ICMR.
Course Duration: Three to five years.
Selection Process: The selection is done via a written test followed by an interview. The JRF holders are exempted from written tests and can directly appear for an interview.
You are required to submit a Research Proposal (about 1000 words) and a Statement of Purpose for undertaking a research career (about 300 to 500 words).
Registration to Kerala State Medical Council (KSMC)/Travancore Cochin Medical Council (TCMC) is mandatory at the time of admission.
Number of Fellowships and Reservations: The institute offers a total of six institute fellowships and four ST category fellowships.
Table: List of Important Dates for PhD Admissions
| Particulars | Date |
| The deadline for applying for admission to PhD and Integrated PhD programs | 30th November 2023, 05.00 p.m. |
| Date of entrance examination | 11th December, 2023 |
| Date of interview | 12th December, 2023 |
| Mode of conduct of entrance examination | Computer Based Test (CBT) |
| Mode of conduct of interview for PhD and integrated PhD | Hybrid mode |
| Centres (State/Union Territory/City) at which the CBT will be conducted | Delhi, Jammu & Kashmir, Assam, and Thiruvananthapuram. |
Integrated Courses
There are three integrated courses available at SCTIMST, Trivandrum
- Integrated MD-PhD program
- Integrated DM-PhD program
- Integrated MCh-PhD program
Course Duration: 5 Years
Course Curriculum: The course is divided into two phases. The first phase comprises the first three years, i.e.,1st, 2nd, and 3rd years that follow the MD/DM/MCh syllabus depending on the enrolled course including clinics. The second phase comprises the last two years, i.e., the 4th and 5th years that are dedicated to research.
General Eligibility: The following are the eligibility criteria for admission to the integrated MD-PhD, DM-PhD, and MCh-PhD programs at SCTIMST, Bangalore:
- The integrated programs are only open to first-year residents accepted into SCTIMST’s standard MD/DM/MCh program.
- The resident must enroll in the integrated Ph.D. program within six months of enrolling in SCTIMST’s MD/DM/MCh program.
- Registration to Kerala State Medical Council (KSMC)/Travancore Cochin Medical Council (TCMC) is mandatory and at the time of admission, submission of a registration certificate to the Division of Academic Affairs is mandatory.
Upper Age Limit: 40 years (as of 1st January 2024 for the January session and 1st July 2024 for the July session).
Five-year age relaxation is given for SC/ST candidates, sponsored candidates, and qualified Ex-service personnel with a service of more than five years.
Mode of Selection:
For MD/DM/MCh: INI-SS entrance examination
For Integrated MD-Ph.D./DM-Ph.D./MCh-Ph.D. programs: First-year residents are required to apply along with a Research Proposal (about 1000 words) and a Statement of Purpose for undertaking a research career (about 300 to 500 words). The selection will be done through a comprehensive viva voce examination.
Number of Seats: One seat in each specialty.
Stipend/Salary: The salary for Integrated Ph.D. candidates will be the same as MD/DM/MCh candidates for the first three years and in the fourth and fifth years, the salary will be the same as the salary of the third-year senior resident. Other HRA, NPA, DA, & DA on TA are applicable as per Institute rules.
POSTDOCTORAL PROGRAMS
DM and MCh Courses
Course Duration: 3 years
General Eligibility: For the January batch, the candidates must have completed the necessary education, training, and employment by January 31, 2024; for the July batch, the deadline is July 31, 2024.
Registration to Kerala State Medical Council (KSMC)/Travancore Cochin Medical Council (TCMC) is mandatory and at the time of admission, submission of a registration certificate to the Division of Academic Affairs is mandated.
Upper Age Limit: 40 years (till 1st January 2024 for the January session and 1st July 2024 for the July session).
Five-year age relaxation is given for SC/ST candidates, sponsored candidates, and qualified Ex-service personnel with a service of more than five years.
Mode of Selection: INI-SS (Institutes of National Importance-Super Specialty)
Stipend: The stipend (per month) for DM and MCh candidates (except for sponsored category candidates) are as follows:
- Ist Year: Rs. 74,000
- IInd Year: Rs. 76,200
- IIIrd Year: Rs. 78,500
Other HRA, NPA, DA, & DA on TA are applicable as per Institute rules.
Table: List of DM courses at SCTIMST along with number of seats, and eligibility qualification
| Course | Number of Seats | Eligibility Qualification (NMC-recognised) | |
| General Quota | Sponsored Quota | ||
| DM Cardiology
|
8 | 3 | MD/DNB in General Medicine/Pediatrics /Equivalent degree |
| DM Neurology
|
6 | 3 | MD/DNB in General Medicine/Pediatrics /Equivalent degree |
| DM Neuroimaging and Interventional Neuroradiology
|
4 | 1 | MD/DNB Radiology/Radiodiagnosis/ Equivalent degree |
| DM Cardiovascular Imaging and Vascular Interventional Radiology
|
3 | 1 | MD/DNB Radiology/Radiodiagnosis/ Equivalent degree |
| DM Cardiothoracic & Vascular Anaesthesia
|
8 | 3 | MD/DNB in Anaesthesia/Equivalent degree |
| DM Neuroanaesthesia
|
7 | 2 | MD/DNB in Anaesthesia/Equivalent degree |
Table: List of MCh courses at SCTIMST along with the number of seats, and eligibility qualification
| Course | Number of Seats | Eligibility Qualification (NMC-recognised) | |
| General Quota | Sponsored Quota | ||
| M.Ch. Cardiovascular & Thoracic Surgery
|
6 | 2 | MS/DNB in General Surgery/Equivalent degree |
| M.Ch. Neurosurgery (after MS)
|
4 | 2 | MS/DNB in General Surgery/Equivalent degree |
| M.Ch. Vascular Surgery
|
1 | 0 | MS/DNB in General Surgery/Equivalent degree |
Postdoctoral Fellowship (PDF) Courses (Post DM/MCh/DNB)
Course Duration: One year
Educational Qualification: DM/MCh (3 years) or equivalent qualification
General Eligibility: Registration with KSMC/TCMC.
Admission must include biodata and a 500-word write-up on the work/ project proposal along with the submission of a Reference letter.
Upper Age Limit: 40 years (till 1st January 2024 for the January session and 1st July 2024 for the July session).
Five-year age relaxation is given for SC/ST candidates, sponsored candidates, and qualified Ex-service personnel with a service of not less than five years.
Method of Selection:
Application shortlisting is done based on the merit of a 500-word short research project proposal and letters of reference.
If there are less than 10 candidates, then the selection is done based on an open Departmental interview followed by a final interview.
If there are more than 10 candidates, the selection is done based on a written exam followed by a final interview.
Departmental interview/written exam accounts for 75% of total marks and final interview accounts for 25% of the total marks.
Salary/Stipend: The stipend (per month) for PDF candidates (except for sponsored category candidates) is Rs. 80,900 along with applicable HRA, DA, and DA on TA as per institute rules.
Table: List of PDF courses at SCTIMST available for the January 2024 session:
| Department/Subspecialty | Number of Seats | Minimum educational qualification |
| Department of Neurology | ||
| Electroencephalography | 01 | DM (3 years) or equivalent qualification |
| Epilepsy | 01 | |
| Movement Disorders | 01 | |
| Neuromuscular Disorders | 01 | |
| Stroke | 01 | |
| Department of Cardiology | ||
| Adult Cardiology and Interventions | 02 | DM (3 years) or equivalent qualification |
| Cardiac Electrophysiology | 02 | |
| Pediatric Cardiology | 02 | |
| Department of Neurosurgery | ||
| Cerebrovascular Surgery | 01 | MCh (3 years) or equivalent qualification |
| Skull Base Neurosurgery | 01 | |
| Spine Surgery | 01 | Post MCh Neurosurgery within 5 years of passing the MCh examination |
| Functional Neurosurgery | 01 | |
| Department of CVTS | ||
| Adult Cardiac Surgery | 01 | MCh (3 years) or equivalent qualification |
| Pediatric Cardiac Surgery | 01 | |
| Department of Anaesthesiology | ||
| Pediatric cardiac Anaesthesia | 02 | DM (3 years) or equivalent qualification |
| Perioperative Neuromonitoring and Neurosurgical Intensive Care | 01 | Post DM Neuroanaesthesia within 5 years of passing the DM examination |
| Adult Cardiothoracic Vascular Anaesthesia | 01 | Post DM Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anaesthesia within 5 years of passing the DM examination |
Postdoctoral Certificate Courses
Course Duration: 01 year
Upper Age Limit: 40 years (as of 1st January 2024).
Five years age relaxation is given for SC/ST candidates, sponsored candidates, and qualified Ex-service personnel with a service of not less than five years.
Method of Selection: There is a three-step evaluation process for PDCC at SCTIMST. It includes a theory examination and departmental assessment followed by a final interview.
Salary/Stipend: The salary/stipend (per month in Rupees) given during PDCC at SCTIMST is Rs. 74,000 along with applicable HRA, NPA, DA, and DA on TA as per institute rules.
Table: List of PDCC programs along with number of seats & eligibility qualification for the January 2024 session
| PDCC Program | Number of Seats | Minimum Educational Qualification |
| PDCC in Transfusion Transmitted Disease Testing | 01 | Post MD Transfusion Medicine within 5 years of passing the MD examination or equivalent qualification |
| PDCC in Hospital Infection Control | 01 | Post MD Microbiology within 5 years of passing the MD examination equivalent qualification |
| PDCC in Neuropathology | 01 | Post MD Pathology within 5 years of passing the MD examination equivalent qualification |
OTHER PROGRAMS AVAILABLE AT SCTIMST
Diploma Courses
- Diploma in Public Health (DPH)
- Diploma in Cardiovascular & Thoracic Nursing (DCTN)
- Diploma in Neuro- Nursing (DNN)
- Diploma in Advanced Medical Imaging Technology (DAMIT)
- Diploma in Operation Theatre & Anaesthesia Technology (DOTAT)
PG Diploma Courses
- PG Diploma in Cardiac Laboratory Technology (PGDCLT)
- PG Diploma in Neuro Technology (PGDNT)
- PG Diploma in Medical Records Science (PGDMRS)
- PG Diploma in Clinical Perfusion (PGDCP)
- PG Diploma in Blood Banking Technology (PGDBBT)
Advanced Certificate Program
- Advanced Certificate Program in Physiotherapy in Neurological Sciences (ACP-PN)
- Advanced Certificate Program in Physiotherapy in Cardiovascular Sciences (ACP-PC)
Joint/Affiliated Programs with IIT Madras & CMC Vellore
- Master of Technology (M Tech) in Clinical Engineering
- PhD (Biomedical Devices and Technology)
Affiliated Programs Conducted at Other Centres
- Master of Public Health [(MPH) (Epidemiology and Health Systems)] at ICMR-National Institute of Epidemiology, Chennai
- Master of Science (Bioengineering), PhD (Bioengineering/Biomedical Sciences/Health Sciences), and Master of Public Health (MPH) courses at Christian Medical College, Vellore
FEE STRUCTURE FOR COURSES AT SCTIMST, TRIVANDRUM
| Particulars | Fees (in INR) | ||||
| PDF /DM/ MCh/ PDCC/MD Courses | PhD and Integrated PhD (4th & 5th year) | MPH | DPH | PG Diploma/ Diploma | |
| Application Fee | 2000
1600 (for SC/ST) |
1500
1200 (for SC/ST) |
1500
1200 (for SC/ST) |
1500
1200 (for SC/ST) |
840
640 (for SC/ST) |
| Admission Fee | 2,000 | 2,000 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 500 |
| Tuition Fee | 63,000 (annual) | 20,000 (annual) | For Non-sponsored candidates: 1,10,000 (2 years)
For sponsored candidates: 2,00,000 (2 years) |
– | 10,000 (annual) |
| Course Fee | – | – | – | 2,00,000 | – |
| Caution Fee | 10,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 | 10,000 |
| Examination Fee | 2,000(Part 1)
10,000 (Part 2) |
– | 1,000 | – | 250 |
| Comprehensive Exam | – | 6,000 | – | – | – |
| Thesis Evaluation Fee | 1,500 | 15,000 | – | – | – |
| Identity Card | 220 | 220 | 220 | 220 | 220 |
| Library | 1,000 | 1,000 | 500 | 500 | 200 |
| Student Welfare Fund | 1,000 | 1,000 | 500 | 500 | 200 |
| Certificates | 1,000 | 1,000 | 1,000 | 500 | 200 |
| Miscellaneous | 10,000 | – | – | – | 5,000 |
Must Read: NIMHANS, Bangalore: Courses, Admission Procedure, Fees & Stipend
Click here to get conceptual clarity on medical subjects online.
The National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS) is a multidisciplinary centre for state-of-the-art research in mental health and neurosciences, academic pursuits, and patient treatment. It is located in Bangalore, India, and is one of the premier institutes in the country for the treatment and study of mental health disorders.
The NIMHANS offers the latest modern medical advancements and is a centre of excellence. The college was founded in 1974 as an independent organisation under the jurisdiction of the Indian government’s Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. In 2012, it was designated as an Institute of National Importance. The college is highly renowned for the following:
- Academics: A range of undergraduate, graduate programs, doctoral, and postdoctoral courses in mental health and neurosciences are available at NIMHANS.
- Research: In neuroscience and mental health, NIMHANS is a premier research centre. The institution carries out research on many different subjects, including aetiology, diagnosis, and management of mental health conditions.
- Patient care: The 2,000-bed hospital at NIMHANS offers thorough treatment for mental health conditions including obsessive-compulsive disorder, schizophrenia, depression, and anxiety. The institute also features dedicated addiction, geriatric, and child and adolescent psychiatric clinics.
Here are some of NIMHANS’s most recent accomplishments:
- According to the National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2023, NIMHANS is India’s best medical facility for neuroscience and mental health, and it holds the 4th place in the Medical Sciences category in India.
- NIMHANS researchers have created a brand-new artificial intelligence-based method for diagnosing and screening depression.
- To help individuals in India’s rural and tribal areas who need mental health treatments, NIMHANS has started a telemedicine program.
Courses Available at NIMHANS
- MD courses
- Post MBBS DM (Neurology) course
- Post MBBS MCh (Neurosurgery) course
- DM (Post MD/DNB) courses
- MCh (Post MS/DNB) courses
- PhD programme
- Fellowship Courses
- Phil. Courses
- B.Sc. & M.Sc. Courses
- Postdoctoral Diploma Courses
- Postdoctoral Fellowship Courses
Admission to MD Courses
Course Duration: 3 years
Mode of Selection: INI-CET entrance examination
Age Criteria: For applicants applying under:
- General/Unreserved Category- 32 Years
- OBC Category- 35 Years
- SC/ST Category-37 Years
- Sponsored/Deputed Category- 45 Years
Emoluments/Stipend: The emoluments/stipend for the MD Students is:
- 1st year: Rs.56,100
- 2nd year: Rs.57,800
- 3rd year: Rs.59,500
Candidates chosen under the “Sponsorship Category” or the “External Fellowship Category” who get income and benefits from their employers are not qualified to receive any emoluments from the Institute.
Fee Structure: The tuition fee for the MD courses at NIMHANS, Bangalore is Rs. 73,250/-.
List of MD Courses
| MD Courses | Eligibility | Number of Seats |
| MD in Psychiatry | MBBS OR DPM | 13 seats (for each session) under All India category
4 seats (session 1) & 1 seat (session 1) under Karnataka Domicile 3 Seats (for each session) under the Northeastern category. |
| MD in Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation | MBBS | 02 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary’
01 seat under the ‘Sponsored/Deputed category’ |
Admission to DM Neurology and M.Ch. Neurosurgery Courses (Post MBBS Category)
Course Duration: 6 years Post MBBS (3 years as Junior Resident and 3 years as Senior Resident)
Eligibility Qualification: MBBS
Mode of Selection: INI-CET entrance examination
Age Criteria: 32 years
Emoluments/Stipend: The emoluments/stipend for the DM/M.Ch Students is:
- 1st year: Rs.56,100
- 2nd year: Rs.57,800
- 3rd year: Rs.59,500
- 4th year: Rs.67,700
- 5th year: Rs.69,700
- 6th year: Rs.71,800
Candidates chosen under the “Sponsorship Category” or the “External Fellowship Category” who get income and benefits from their employers are not qualified to receive any emoluments from the Institute.
Fee Structure: The tuition fee for the 6 years of DM/M.Ch (Post MBBS) courses at NIMHANS, Bangalore is Rs. 91,150/-.
List of DM/M.Ch (Post MBBS) Courses
| Courses | Number of Seats |
| DM in Neurology | 04 seats under ‘Institute Stipendiary’ (Session 1) |
| M.Ch. in Neurosurgery | 02 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ (each in both the session 1 & 2) |
Admission to DM (Post MD/DNB) & M.Ch (Post MS/DNB) Courses
Course Duration: 3 years
Eligibility Qualification: MD/DNB
Mode of Selection: INI-SS (Super Specialty) entrance examination
Age Criteria: 37 years
Emoluments/Stipend: The emoluments/stipend for the DM and MCh Students is:
1st year: Rs.67,700
2nd year: Rs.69,700
3rd year: Rs.71,800
Candidates chosen under the “Sponsorship Category” or the “External Fellowship Category” who get income and benefits from their employers are not qualified to receive any emoluments from the Institute.
Fee Structure: The tuition fee for the 3 years of DM/MCh courses at NIMHANS, Bangalore is Rs. 81,250/-.
List of DM and M.Ch Courses
| Course | Eligibility | Number of Seats |
| DM in Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | MD in Psychiatry or DNB in Psychiatry | 02 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’
02 seats under the ‘Sponsored Category’ |
| DM in Neuroanaesthesia & Neurocritical Care | MD in Anaesthesiology or DNB in Anaesthesiology | For Session 1,
04 seats are under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ 02 seats are under the ‘Sponsored Category’ For Session 2, 03 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ |
| DM in Neuroimaging and Interventional
Radiology |
MD in Radiodiagnosis or DNB in Radiodiagnosis | 04 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’
01 seat under the ‘Sponsored Category’. |
| DM in Neurology | MD in Internal (General) Medicine/Pediatrics or DNB in
Internal (General) Medicine/Pediatrics |
For Session 1,
05 seats are under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ 01 seat is under the ‘Sponsored Category’ For Session 2, 10 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary’ |
| DM in Neuropathology | MD in Pathology or DNB in Pathology | 01 seat under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’
01 seats under the ‘Sponsored Category’ |
| DM in Geriatric Psychiatry | MD in Psychiatry or DNB in Psychiatry | 02 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ |
| DM in Addiction Psychiatry | MD in Psychiatry or DNB in Psychiatry | 02 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’
02 seats under the ‘Sponsored Category’ |
| DM in Forensic Psychiatry | MD in Psychiatry or DNB in Psychiatry | 02 seats under the ‘Sponsored Category’ |
| M.Ch in Neurosurgery | MS in General Surgery or DNB in General
Surgery |
For session 1,
02 seats are under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ 01 seat is under the ‘Sponsored Category’. For Session 2, 03 seats are under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ |
Admission to Ph.D. Program
Course Duration: 3 to 5 years
Mode of Selection: NIMHANS conducts an entrance examination which contributes 70% to the final score calculation followed by an Interview which holds a 30% contribution to the final score.
Qualifying Percentage in the Entrance Examination:
- UR/SC/ST/OBC/EWS: 50%
- PwBD: 45%
Emoluments/Stipend: The stipend to Ph.D. candidates (Except for Ph.D. in Clinical Neurosciences courses) is given as follows:
- Ist Year: 31,000 per month
- IInd Year: 31,000 per month
- IIIrd Year: 35,000 per month
- IVth Year: 35,000 per month
- Contingency Grants (for all years): Rs. 20,000 per annum
Candidates chosen under the “Sponsorship Category” or the “External Fellowship Category” who get income and benefits from their employers are not qualified to receive any emoluments from the Institute.
In the case of Ph.D. in Clinical Neurosciences, the stipend to PhD candidates is given as follows:
- Ist Year (Basic Pay + Grade Pay): 18,750 + Rs. 6,600 per month
- IInd Year (Basic Pay + Grade Pay): 19,510 + Rs. 6,600 per month
- IIIrd Year (Basic Pay + Grade Pay): 20,300 + Rs. 6,600 per month
- Contingency Grants (for all years): Rs. 1,00,000 per annum
Fee Structure: The tuition fee for the PhD program at NIMHANS, Bangalore is Rs. 32,000/-.
Course Structure (Except for Ph.D. in Clinical Neurosciences): The candidate will initially be enrolled for a Ph.D. on a provisional basis. After passing the Pre-Ph.D. test, the enrollment will be verified. The applicant would get training in both the theoretical and practical components of the discipline’s curriculum. The candidate must submit the thesis for the granting of the Ph.D. degree after completing the intended work and receiving approval of the synopsis.
Course Structure (For Ph.D. in Clinical Neurosciences): The scholars must pass the Pre-Ph.D. test and finish the Ph.D. coursework within the first year. Based on their qualifying post-graduate degree, the scholars would be paired with a faculty mentor in the corresponding department for the first three months.
The scholars then work on their Ph.D. dissertations with the mentor’s assistance as well as co-guides from clinical and fundamental specialisations. Until the end of their course, they will be assigned to the appropriate clinical department of the Principal Guide, where they will serve as Senior Residents. The Ph.D. scholars are required to work on a dissertation that combines clinical and fundamental science expertise with translational research. The scholars are required to complete the preparation of their thesis protocol within 6 months of their course.
List of Ph.D. Programs
| Ph.D. Program | Eligibility | Number of Seats |
| Ph.D. in Biophysics | MBBS OR M.Phil. Biophysics/Neuroscience OR Master’s Degree in Biochemistry/Biophysics/ Bioinformatics/Biotechnology/All branches of Life Sciences/Microbiology/Physics/Physiology/ Pharmacology/Regenerative Medicine | 01 seat |
| Ph.D. in Biostatistics | Master’s Degree in Agricultural Statistics/Applied Statistics/Biostatistics/Health Statistics/Medical Statistics/Statistics OR M.Stat. (ISI) through the regular course. | 01seat |
| Ph.D. in Child & Adolescent Psychiatry | DNB in Psychiatry OR MD in Psychiatry OR M.Phil. in Clinical Psychology/Psychiatric Social Work. | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Clinical Neurosciences (Course is funded by ICMR) | MD in Psychiatry/General Medicine/Community Medicine/Pediatrics/Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation/Neurorehabilitation OR MS in General Surgery OR DM in Neurology/Child and Adolescent Psychiatry/Geriatric Psychiatry/Addiction Medicine OR M.Ch. in Neurosurgery and any other degrees as approved by appropriate statutory bodies | 08 seats, funded by ICMR |
| Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology | M.Phil. in Clinical Psychology OR M.Phil. in Mental Health and Social Psychology OR 2 years Master’s Degree in Applied Psychology/Clinical Psychology/ Counselling Psychology/Psychological Counselling/ Psychology | 03 seats |
| Ph.D. in Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neurotoxicology | MBBS OR DPM OR MD in Psychiatry/Psychological Medicine or DNB in Psychiatry or M.Pharm OR PharmD or MD in Biochemistry/Microbiology/ M.Phil./2 years M.Sc. in Biochemistry/Microbiology/ Physiology/Neurosciences/Zoology/Biotechnology/ M.Tech in Biotechnology | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Human Genetics | 2 years Master’s Degree in Zoology/Biotechnology/ Biochemistry/Applied Genetics/Human Genetics/ Molecular Biology/Biomedical Genetics OR M.Tech in Genetic Engineering/Genetic Biotechnology OR B.Tech in Biotechnology OR MBBS | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Mental Health Education | MBBS/Masters in Health Education/Media Studies/ Journalism/Mass Communication/Masters in Public Health/Masters in Social Work/Nursing/Psychology with 2 years of experience in a mental health setting or Health Journalism | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Neurochemistry | 2 Years M.Sc. Degree in Biochemistry/Biotechnology/ Neuroscience/Medical Biochemistry | 01 seat |
| Ph.D. in Neuroimaging and Interventional Radiology | BE/B.Tech/DNB in Radiodiagnosis/MBBS/MD/ Master’s Degree in Medical Subjects/M.Tech Degree. | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Neurology | MBBS OR MD OR BDS OR M.Tech with experience in Neuroscience Research OR 2 years M.Sc. in Life Sciences | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Neurological Rehabilitation | DNB in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation OR Master’s Degree in Physiotherapy (MPT)/Occupational therapy (MOT)/Orthotics & Prosthetics OR MBBS OR MD in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation OR M.Phil. in Clinical Psychology/Psychiatric Social Work/Clinical Neurosciences OR Master’s Degree in Nursing/Speech Therapy | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Neuro microbiology | MD Microbiology OR Master’s Degree in Applied Microbiology/Biomedical Genetics/Biotechnology/ Medical Microbiology/Microbiology/MLT/Molecular Biology | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Neuropathology | MBBS OR MD in Pathology OR 2 years Master’s Degree in Zoology/Neurosciences/Physiology/Biotechnology/ Biological Sciences/Cell Biology/Life Science/Anatomy /Biochemistry/Microbiology/Molecular Biology and Human Genetics/Bioinformatics/Biophysics/ Developmental Biology/Evolutionary Biology/Systems Biology | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Neurophysiology | M.Phil in Neurophysiology/Neurosciences/Yoga OR MD in Ayurveda/Physiology/Yoga OR 2 years Master’s Degree in Physiology/Anatomy/Biochemistry/ Biotechnology/Life Sciences/Cognitive Neuroscience/ Neuroscience/Zoology/Pharmacology OR MBBS OR MS (Pharm)/M.Pharm (Pharmacology OR Biotechnology) OR BE/B.Tech/ME/M.Tech in Electronics/Electricals/Computer Science/ Biotechnology | 03 seats |
| Ph.D. in Neurovirology | MBBS OR MD in Microbiology OR 2 years Master’s Degree in Biotechnology/Medical Microbiology/ Microbiology/Virology | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Nursing | Master’s Degree in Nursing | 01 seat |
| Ph.D. in Psychiatric Social Work | 2 years Master’s Degree in Social Work OR M.Phil. in Psychiatric Social Work | 01 seat |
| Ph.D. in Psychiatry | BE OR B.Tech OR MBBS OR MD OR ME OR M.Tech OR 2 years Master’s Degree in Medical Biotechnology/ Biotechnology/Biochemistry/Genetics/Microbiology/ Immunology/Physiology/Bioinformatics/Cellular Biology and Anatomical Sciences/Molecular Biology/ Biophysics/Anatomy/Neurosciences/Pharmacology /Zoology/Life Sciences/M.Pharm | Variable |
| Ph.D. in History of Psychiatry | MBBS OR 2 years Master’s Degree in Psychology/ Philosophy/History/Sociology/Social Work/Languages | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Mental Health Rehabilitation | MBBS OR M.Phil. Degree in Clinical Psychology/ Psychiatric Social Work OR 2 years Master’s Degree in Psychiatric Nursing/Psychosocial Rehabilitation/ Occupational Therapy. | 02 seats |
| Ph.D. in Speech Pathology and Audiology | Master’s Degree in Speech Pathology & Audiology/ Speech-Language Pathology/Audiology | 01 seat |
| Ph.D. in Integrative Medicine | MBBS/BAMS/BNYS/MA OR M.Sc. OR M.Phil. in Yoga/ Clinical Psychology/Neuroscience/M.Sc. in Nursing/M. Pharm OR Masters in Physiotherapy | Variable |
| Ph.D. in Psychosocial Support in Disaster Management | Master’s Degree in Social Work/Psychiatric Social Work/Applied Psychology/Clinical Psychology/ Counselling Psychology/Psychological Counselling/ Psychology OR M.Sc. in Psychiatric Nursing OR MD in Psychiatry OR DNB in Psychiatry | 02 seats
|
Admission to Master of Public Health Course
Course Duration: The duration of Master of Public Health courses at NIMHANS is 02 years.
Eligibility: MBBS OR Bachelor of Dental Sciences OR Postgraduate degree in Sociology/Statistics/Environmental Sciences/Physiotherapy/Occupational Therapy/Health Management/Social Work/Economics/Speech Pathology and Audiology/Speech Pathology/Audiology/Nursing
Mode of Selection: Entrance Test followed by Verification of Original Certificates on the day of admission
Qualifying Percentage in Entrance Test: The qualifying percentage is 50% for UR/OBC/EWS categories and 45% for SC/ST/PwBD.
Age Criteria: The age limit is 45 years.
Emoluments/Stipend: The emoluments/stipend for ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ candidates is 25,000/- per month.
Candidates chosen under the “Sponsorship Category” or the “External Fellowship Category” who get income and benefits from their employers are not qualified to receive any emoluments from the Institute.
Fee Structure: The tuition fee for the MPH course at NIMHANS, Bangalore is Rs. 96,500/-.
Number of Seats: There are 05 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ (out of which one seat is under Karnataka Domicile) and 05 seats under the ‘Sponsorship Category’.
Admissions to M.Phil. Courses
Course Duration: The duration of M. Phil courses at NIMHANS is 02 years.
Mode of selection: Entrance Test + Verification of Original Certificates on the day of admission
Qualifying percentage in Entrance Test: The qualifying percentage is 50% for UR/OBC/EWS categories and 45% for SC/ST/PwBD.
Age Criteria: The age limit is 32 years.
Emoluments/Stipend: The emoluments/stipend is 25,000 per month along with Rs. 15,000/- as Contingency Grants per annum.
Candidates chosen under the “Sponsorship Category” or the “External Fellowship Category” who get income and benefits from their employers are not qualified to receive any emoluments from the Institute.
Fee Structure: The tuition fee for M.Phil. courses at NIMHANS, Bangalore is Rs. 24,800/-.
List of M.Phil. Courses
| Courses | Eligibility | Seats |
| M.Phil. in Clinical Psychology | 2 years Master’s Degree in Applied Psychology/ Clinical Psychology/ Counselling Psychology/ Psychological Counselling/ Psychology | 23 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ (in All India Category)
06 seats under ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ (Karnataka Domicile category) 03 seats for the Foreign/Sponsored category |
| M.Phil. in Psychiatric Social Work | 2 years Master’s Degree in Social Work | 23 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ (in All India Category)
06 seats under the ‘Institute Stipendiary Category’ (Karnataka Domicile category) 03 seats for the Foreign/Sponsored category |
Other Courses at NIMHANS, Bangalore
M.Sc. Courses
- Sc. Biostatistics
- Sc. Psychiatric Nursing
- Sc. Neuroscience Nursing
- Sc. in Yoga Therapy (Mental Health & Neurosciences)
- Sc. in Neuroscience
Postgraduate Diploma Course (1 year)
- Postgraduate Diploma in Clinical Biochemistry
Click here to get conceptual clarity on MBBS subjects.
We have witnessed remarkable advancements in the ophthalmology field, which is still at a rapid pace of transformation. When it comes to embracing new technologies and incorporating cutting-edge advancements into routine clinical and surgical procedures, ophthalmology frequently leads the way. These advancements hold a bright future where eye disease may be detected and treated earlier, vision restoration becomes more effective, and the overall quality of people with ocular issues is significantly improved.
Surgical Ophthalmology Advancements
A few mentioned below are surgical ophthalmology advancement w.r.t particular vision issues or disorders:
- Surgical interventions, such as simple limbal epithelial transplantation and corneal endothelial transplantation have significantly improved the surgical management of severe ocular surface disorders (OCD).
- In the management of cataract surgery, small incision phacoemulsification cataract surgery with IOL implantation, and femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery are being widely used.
- Promising clinical treatments of glaucoma include minimally invasive glaucoma surgeries and advanced imaging techniques: Optical coherence tomography, and intraocular technology.
- Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is a non-invasive new technology to visualize vascular networks in the eye and anti-VEGF drugs have emerged for the treatment of fundus vascular disease. The benefits of these emerging treatments include reduced surgical complications, improved cure rate, minimally invasive techniques, and improved patient prognosis.
- Laser-assisted surgery is a boon in the field of ophthalmology and has been explored for a variety of conditions, such as refractive surgery techniques, and cataract surgeries.
- Retinal surgery innovations include hypersonic vitrectomy, intraoperative OCT, heads-up 3D visualization systems, and endoscopic vitrectomy.
Other emerging trends in ophthalmology include the rise of AI-based devices, bionic eye implants, synthetic cornea implants, the rise in the use of robotic surgical assistants or robotic surgery, microsurgical instruments & techniques, and more.
Advancements and Innovations in Ophthalmology
Artificial Intelligence in Ophthalmology
The AI in ophthalmology is being explored to a greater extent ranging from diagnoses to treatment of ophthalmic conditions and diseases. The conditions targeted till now include diabetic retinopathy, glaucoma, retinopathy, cataracts, age-related macular degeneration, anterior segment diseases, and retinal vein occlusion.
AI makes analyzing and managing huge data and radiological images easier ultimately helping in clinical data collection, automated image analysis, early disease detection, and interpretation, and incredible differential diagnosis. Detection and monitoring of retinal disease have become easier with AI-powered retinal imaging and screening. In the field of ophthalmic research, AI has proved quite beneficial, especially in genomics and biomarker research, and drug discovery.
AI is efficiently being used in ophthalmology to conduct a variety of tasks, but a certain degree of human intervention is crucial.
LIQD Cornea
LIQD Cornea is considered a potential alternative to Corneal transplantation. It is a biosynthetic liquid hydrogel matrix crafted from recombinant human collagen type III to regenerate the cornea and is also cell-free. It comprises short collagen-like peptides, polyethylene glycol, and fibrinogen. As there is a global donor cornea scarcity, this advancement will be greatly beneficial. It is assumed to be cost-effective along with minimizing health care costs. Further, research on corneal transplantation techniques is being done to a greater extent.
Hypersonic Vitrectomy
Hypersonic Vitrectomy (HV) is being considered a major advancement in the field of vitreoretinal surgery. This surgical technique uses ultrasound to liquefy vitreous along with removing the retained lens particles. The introduction of HV will reduce or eliminate the requirement of frequent probe change and will also shorten the surgical procedure time. It may also possibly replace the Guillotine vitrectomy probe.
The major application involves complicated cataract surgeries with intraoperative posterior capsular rupture with vitreous loss. It is mostly done in a single sitting and has minimal complications.
Refractive Surgery Techniques
The refractive surgery techniques are conducted to correct the refractive errors of the eyes. The different types of refractive surgery include LASIK, Photorefractive keratectomy (PPK), Radial keratotomy, Small Incision Lenticule Extraction (SMILE), Contoura, and more.
LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis) is most preferred nowadays to correct vision issues caused by refractive errors. This refractive surgery option is an almost pain-free flexible procedure, has the least healing period, is less time-consuming, and has quick results. Due to these many advantages, LASIK has been widely opted to reduce a person’s dependency on corrective glasses or contact lenses. LASIK has revolutionized the ophthalmology field, especially the refractive surgery discipline. It enables the precise and efficient correction of various visual impairments.
Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery (LACS)
LACS is an advanced procedure that utilizes a femtosecond laser to remove cataracts. Unlike conventional methods, Laser-assisted cataract surgery has become popular due to improved accuracy and consistency in surgical procedures. It helps in making precise incisions faster. It is a bladeless technology and is considered minimally invasive. It may reduce the risk thereby, improving the result of the cataract surgery. In this procedure, the laser is used to make the corneal incisions, execute capsulotomy, and then initiate lens fragmentation.
Nanotechnology in Ophthalmology
Nanotechnology has been potentially employed in targeted drug delivery, enhanced imaging, and tissue engineering that ultimately leads to vision enhancement. To reduce the drug dose and minimize the risk of side effects, nanocarriers, and nano-suspensions are coming into the picture. For early diagnosis, the contribution of remote monitoring of nanodevices is being explored.
Nano-sized ophthalmic medicines are found to have great benefits such as large dissolution area, fast dissolution speed, good solubility, strong biological adhesion, and strong corneal penetration. This highly improves the effectiveness of the ophthalmic treatment.
The nanotechnology/nanomedicine is being explored in visual conditions, such as Conjunctivitis, Dry kerato-conjunctivitis, Uveitis, Cataract, Glaucoma, Diabetic retinopathy, and more.
Introduction of PROSE for Complex Corneal Disease
PROSE is a Prosthetic Replacement of the Ocular Surface Ecosystem. This PROSE lens is quite innovative and completely covers the ocular surface to restore vision in patients dealing with complex corneal diseases. The lens returns the ocular surface to its natural curve while shielding and encasing it from the external environment. PROSE lens is used in conditions such as severe dry eye or lid and corneal irregularities.
AR/VR Technology in Ophthalmology
The application of AR/VR technology in Ophthalmology includes IOP checks, amblyopia management, visual field testing, educating patients, diagnosis and management, and accessibility. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality technology are a boon for medical training and education as they help refine surgical skills and enhance ophthalmic learning. The visual representation makes it easier to visualize and comprehend complex procedures and treatment options in a more engaging manner.
It also benefits planning treatment procedures and thereby, enhancing precision and reducing errors. It holds great significance in telemedicine, research, and therapeutic interventions that ultimately contribute to enhanced learning and better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
These advancements are only the tip of the iceberg. The rapid progress in ophthalmology reflects the commitment of researchers, clinicians, and technology developers to address the complex and varied needs of patients with eye care. With the developing technology, every medical professional must stay up-to-date with the recent developments to provide the best possible care to the patients.
You can enroll in an online ophthalmology course to get access to ophthalmology video lectures for medical students to learn from the basics of ophthalmology to all the new advancements in the field.
The meticulously crafted Medicine MD is an E-learning course by DigiNerve to provide a structure to the learning of postgraduate students. This course will help in addressing the gaps in clinical skills of postgraduate students and physicians. Differential diagnosis and clinical methods will help students in decision making in their clinical day-to-day practice. It aims to prepare them for their final MD examinations and transform them into exceptional physicians who excel clinically for better patient management. The course has been conceptualised under the guidance of esteemed Chief Editors, Dr. Jyotirmoy Pal and Dr. Shashank R Joshi; Advisory Editors, Dr. Girish Mathur and Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander, who have provided overall guidance and direction to the course; and Associate Editors, Dr. Nandini Chatterjee, Dr. Jimit Vadgama and Dr. Priyanka Shah in collaboration with more than 200 experts in the field.
Medicine MD course includes a comprehensive range of medical specialties, including Neurology, Cardiology, Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Pulmonary and Chest Medicine, Rheumatology, and many more. The course offers a structured learning experience that includes basic sciences, long cases, short cases, and decision-making under each speciality.
Besides the systemic coverage, a few sections are provided that cover the following important aspects of a postgraduate course:
- History-taking and Clinical Methods: Learn the art of patient interaction and examination, the fundamental skill for any physician.
- Investigations in Medicine: Arrive at the appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan with medical investigations.
- Procedures in Medicine: Understand important diagnostic procedures and techniques.
- Pharmacotherapeutics: Make informed decisions about prescription medications
- Research Methodologies: Get acquainted with the nuances of medical research.
Some unique features have been incorporated in this course which sets it apart:
- Case-based approach: The course follows a case-based approach wherein the various lectures focus on case-based discussions, equipping postgraduate students with essential clinical skills. The case-based lectures address several concepts such as differential diagnosis, management strategies, laboratory algorithms, treatment pathways, complications, prevention, patient care messages, etc., all while incorporating global and Indian recommendations. Long and short case discussions in various sections are carefully curated to align with the MD Examination curriculum. Knowledge of these cases, specifically in neurology is extremely essential to steer through the final exams.
- Interactive learning Experience: After each video lecture, self-assessment questions test your understanding and retention of the content. Multiple-choice questions are also strategically integrated into the videos, enhancing comprehension and active engagement.
- Visual learning experience: The course features 2D animations to simplify complex concepts and make learning more visual and intuitive.
- OSCEs: Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) are vital in assessing clinical skills. The course offers these assessments in video and flashcard formats, enabling rapid revision and self-assessment, just like the real exam.
- Pharmacotherapeutics: Pharmacotherapeutics is presented through videos and a drug formulary, offering insights into drug usage in medical practice. The drug formulary empowers you to search for medications based on indications, drug names and pharmacological classification, streamlining your decision-making process. Color-coding is used to classify these drugs in high-risk, moderate-risk and low-risk categories.
- DxTx: A tool for quick consultation, this unique feature is represented by a human model that allows you to explore critical information in a click. You can learn about the various diseases associated with the human body along with clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, recent advances and clinical trials in a structured format. Furthermore, intricate etiopathological concepts are skillfully clarified using flowcharts, whenever necessary. This tool is aligned with the NMC curriculum.
The Course Includes:
- Video Lectures: 215+ hours of video lecture series, encompassing fundamental basic sciences, in-depth long and short case discussions, and lectures on decision-making in medicine.
- Long Case Discussion Videos: Collection of 60+ meticulously chosen long case discussion videos spanning important medical specialties, designed to aid in comprehensive preparation for the MD examination.
- Short Case Discussion Videos: Compilation of 40+ carefully curated topics of short case discussions spanning diverse medical specialties, aimed at seamless preparation of MD level examinations.
The long and short cases are discussed with differential and clinical approach.
- Lecture Notes: This course includes well-illustrated 315+ lecture notes which will act as a ready reckoner for students. They are supplemented with evidence-based research studies mentioned at the end of each topic.
- Self-Assessment Questions: 1650+ MCQs serve both as valuable practice assessments and as a strategic integration within each video to improve comprehension.
- OSCEs: 10+ videos lectures and 125+ flashcards provide a standardized and objective method of assessing a candidate’s clinical skills and competencies.
- DxTx: A unique tool comprising 230+ topics aligned with the NMC curriculum across various specialties.
- Animation videos: 30+ animations integrated in the videos covering mainly basic sciences, to simplify complex concepts.
- Interactive Drug Formulary: Detailed color-coded drug formulary included with important indications, contraindications, dosages, and common brand names.
- Engagement Activities: Regular chat shows, journal club, and recent updates are included as engagement activities.
- Benchmark trials: 605+ evidence-based studies/benchmark trials have been added to remain updated with recent advances in the field.
- Dr. Wise AI bot: Chatbot that clarifies theoretical as well as practical concepts with the help of AI. It is a comprehensive and interactive solution provider integrated with authentic published resources like books, journals, notes, and videos to offer apt explanations of concepts, treatment modes and more.
- Printed Notes: Concise notes are designed to save time by providing exam-focused, crisp details along with visual learning at an affordable price. The notes also comprise previous years’ questions and ensure comprehensive coverage with an added highlight that provides reference for students to read more pertaining to topics. Existing users can purchase the printed notes @5,495 from here.
3 Days Money Back Guarantee available T&Cs apply.
INI-CET is a combined national-level entrance examination for admission to the medical postgraduate courses – MD, MS, DM (6 yrs), MCh (6 yrs), and MDS at INI institutes (Institute of National Importance). The INI-CET exam is around the corner. Getting admission to INI institutes is highly challenging and a dream for MBBS students. This is a highly competitive task to secure a seat in the renowned medical colleges in India.
Remember, Perseverance is the key.
The INI-CET exam will be held on 5th Nov 2023 for admission to the AIIMS INI-CET January session 2024.
Here’s the tentative seat distribution (Category-wise) for admission to various MS/MD/DM (6 years)/MCh (6 years)/MDS courses at AIIMS, New Delhi, and other AIIMS located pan India through the INI-CET entrance examination for the January 2024 session.
Table 1: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, New Delhi:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 14 | 8 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biophysics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 11 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Lab. Medicine | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Medicine | 10 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 18 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Palliative Medicine | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 11 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physiology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis & Interventional Radiology | 7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Surgery | 15 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MDS | Oral &Maxofacial Surgery | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MDS | Orthodontics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatrics& Preventive Dentistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Prosthodontics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Neuro SurgeryMCh (Direct 6 year Course) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DM | Infectious Diseases DM(Direct 6 year Course) | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 185 | 81 | 48 | 26 | 13 | 17 | |
Table 2: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bhopal:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 55 | 22 | 15 | 8 | 5 | 5 | |
Table 3: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bhubaneswar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 9 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 7 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obst. &Gynecology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MDS | Orthodontics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 90 | 35 | 24 | 15 | 9 | 7 | |
Table 4: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Jodhpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology & Critical Care | 10 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 |
1
|
0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology, Venerology & Leprology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Family Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiology | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 71 | 28 | 19 | 11 | 6 | 7 | |
Table 5: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Patna:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 10 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | FMT (Forensic Medicine & Toxicology) | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG (Obstetrics & Gynaecology) | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Pediatrics Surgery (6 yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery (6 yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Surgical Gastroenterology (6 yrs) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Trauma Surgery & Critical Care (6 yrs) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
TOTAL |
86 | 40 | 22 | 12 | 5 | 7 | |
Table 6: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Raipur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery (6yrs) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 80 | 31 | 21 | 14 | 5 | 9 | |
Table 7: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Rishikesh:
| Course | Subject/Specialisation | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 6 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Respiratory Medicine | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Periodontology (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCH 6 Years | Pediatric Surgery (MCH 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Plastic, Reconstructive & Burns Surgery (M.CH. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Cardiothoracic & Vascular Surgery (MCH 6yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Neurosurgery (MCH 6 yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Urology (6yrs) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 98 | 46 | 23 | 13 | 7 | 9 | |
Table 8: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Nagpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 73 | 30 | 20 | 11 | 5 | 7 | |
Table 9: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bibinagar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Numberof Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | ENT | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radio Diagnosis | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 10 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |
Table 10: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bathinda:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesia | 10 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Periodontics (Dental) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 5 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pulmonary Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 56 | 25 | 14 | 9 | 3 | 5 | |
Table 11: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Deoghar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesia | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MDS | Pediatrics& Preventive Dentistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Pediatric Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 20 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 2 | |
Table 12: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Mangalagiri:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats (Category-wise) | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 42 | 17 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 4 | |
Table 13: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Raebareli:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
||||
|
UR |
OBC |
SC |
ST |
EWS |
|||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 39 | 15 | 11 | 6 | 3 | 4 | |
Table 14: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Kalyani:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Number of Seats |
|||||
| Total Number of Seats |
UR |
OBC |
SC |
ST |
EWS |
||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venereology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Orthodontics & Dentofacial Orthopaedics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 67 | 27 | 18 | 10 | 5 | 7 | |
Table 15: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Bilaspur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Number of Seats (Category-wise) |
|||||
| Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venereology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxilofacial Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 35 | 15 | 9 | 5 | 2 | 4 | |
Table 16: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Gorakhpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | Number of Seats | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venereology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine& Toxicology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 40 | 16 | 11 | 7 | 2 | 4 | |
Table 17: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at AIIMS, Guwahati:
| Course | Subject/Specialty |
Total Number of Seats |
Number of Seats | ||||
| UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | |||
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics &Gynecology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| TOTAL | 33 | 15 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 3 | |
To get conceptual clarity on the MBBS courses online, click here.
INI-CET is a combined national-level entrance examination for admission to the medical postgraduate courses – MD, MS, DM (6 yrs), MCh (6 yrs), and MDS at INI institutes (Institute of National Importance). The INI-CET exam is around the corner. Getting admission to INI institutes is highly challenging and a dream for MBBS students. This is a highly competitive task to secure a seat in the renowned medical colleges in India.
Remember, Perseverance is the key.
The INI-CET exam will be held on 5th Nov 2023 for admission to the INI-CET January session 2024.
Here’s the tentative seat distribution (Category-wise) for admission to various MS/MD/DM (6 years)/MCh (6 years)/MDS courses at INI institutes through the INI-CET entrance examination for the 2024 January session.
Table 1: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at PGIMER, Chandigarh:
| Course | Subject | Total Number of Seats | |||||
| Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||
| MD | Anaesthesiology & Intensive Care | 16 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology, Venereology & Leprology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Medicine | 16 | 9 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 17 | 8 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis and Imaging | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy and Clinical Oncology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 17 | 9 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Obstetrics and Gynecology | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics Surgery | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 120 | 59 | 31 | 21 | 9 | 0 | |
Table 2: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at JIPMER, Puducherry:
| Course | Subject | Total Number of Seats |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 10 |
| MD | Anatomy | 3 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 3 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 3 |
| MD | Dermatology, Venereology & Leprology | 4 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 3 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 |
| MD | General Medicine | 12 |
| MD | Immuno Hematology & Blood Transfusion | 2 |
| MD | Microbiology | 4 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 10 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 4 |
| MD | Physiology | 4 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 |
| MD | Pulmonary Medicine | 4 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 6 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 5 |
| MS | General Surgery | 12 |
| MS | Obstetrics and Gynecology | 11 |
| MS | Ophthalmology | 6 |
| MS | Orthopaedics Surgery | 4 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 4 |
| MCh | Neurosurgery | 1 |
| MCh | Pediatric Surgery | 1 |
| MDS | Orthodontics & Dentofacial Orthopaedics | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxofacial Surgery | 0 |
| TOTAL | 126 |
*Roaster Point Allocation for Counselling (Dynamic)
Table 3: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2024 session at NIMHANS, Bengaluru:
| Course | Subject | Number of Seats | |||||
| Total | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 13 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry (Karnataka Domicile Category) | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry (North-Eastern Domicile) | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| DM (6yrs) | Neurology | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh (6yrs) | Neurosurgery | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 22 | 12 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |
Table 4: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at SCTIMST Trivandrum:
| Course | Specialty | Number of Seats | |||||
| Total | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS | ||
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Must Know: INI-CET 2024: Exam Pattern, Subject-Wise Weightage & High-Yielding Topics
To get conceptual clarity on the MBBS subjects online, click here.
The exam is around the corner, and it is time for final revision. MBBS subjects are quite vast and revising all at the eleventh hour is a cumbersome task. At this moment, prioritizing topics is necessary to score high in the exam. Hence, we are here with the exam pattern, subject weightage, and frequently asked topics in the INI-CET. A thorough revision of the high-weightage topics will multifold the benefit in a limited time. It is highly advised to solve mock test papers and work on time and accuracy.
INI-CET 2024: Exam Pattern
| Particulars | Description |
| Mode | Computer-based test (CBT) |
| Number of Questions | 200 |
| Duration | 3 hours (180 minutes) |
| Type of Questions | Objective-type questions (includes single correct answer and multiple correct answers) |
| Marking Scheme | +1 mark for every correct answer and (-)1/3 for every incorrect answer.
No mark is awarded for unanswered/marked for a review question |
| Total Marks | 200 |
INI-CET 2024: Minimum Percentile
All participating INIs will consider the INI-CET percentile results for admission to postgraduate seats. The following percentile cut-off will be the minimal requirement for applicants:
- For seats designated as Unreserved (UR), EWS, Overseas Citizens of India (OCI), Sponsored, and Foreign Nationals, the minimum percentile required will be 50th percentile.
- For SC, ST, PwBD, and Bhutanese Nationals (PGI-Chandigarh) seats, the minimum percentile required will be 45th percentile.
Must Read: INI-CET 2024: Application Form Details and Important Dates
INI-CET Subject-Wise Weightage/Marks Distribution
Here, we have a list of MBBS subjects along with a tentative number of questions asked in the INI-CET from the respective subject. This will help you with your INI-CET revision plan and prioritize subjects to score well.
| Subject | Number of Questions |
| Medicine | 22 |
| Surgery | 17 |
| Obstetrics and Gynecology | 16 |
| Pathology | 16 |
| Pharmacology | 15 |
| Microbiology | 14 |
| PSM | 14 |
| Anatomy | 11 |
| Physiology | 10 |
| Biochemistry | 10 |
| Pediatrics | 10 |
| Radiology | 8 |
| Ophthalmology | 6 |
| FMT | 6 |
| Orthopaedics | 6 |
| ENT | 5 |
| Anaesthesia | 5 |
| Dermatology | 5 |
| Psychiatry | 4 |
INI-CET 2024: High Yielding Topics
Don’t miss out on studying and revising the important topics and INI-CET previous year question papers. Here, we have sorted the list of important high-weightage topics for INI-CET aspirants.
Anatomy
- Cranial Nerves
- Embryology
- Head and Neck Anatomy
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Rotator Cuff
- Tonsillectomy
- Ulnar Nerve
- Skull Fractures
- Corpus Callosum
- Skull – Anatomy
Physiology
- Nerve Physiology
- Renal Physiology
- Respiratory Physiology
- Spirometry
- Oxygen Haemoglobin Dissociation Curve
- Pressure-Volume Loop
- Exercise Physiology
- Second Messengers
- Cardiac Cycle
- Hypothalamus
- Blood Pressure Regulation
Biochemistry
- Lysosomal + Glycogen Storage Diseases
- Familial Dyslipidemia
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism
- Genetics
- Vitamins
- Metabolic Cycles
- Fatty Acid Oxidation
- Fed & Fasting State
- DNA Repair and its Defects
- Cardiac Biomarkers
- Competitive and Non-Competitive Inhibition
Pharmacology
- General Pharmacology – Important formulae and graphs
- Anti-Cancer drugs
- Dementia
- COVID-19 treatment
- Route of Drug Administration
- Factors affecting drug response and drug absorption
- Warfarin
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Asthma
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Opioids
- Antiarrhythmic drugs
- Statins
- Clinical Trials
- Antipsychotics
- Zero Order and First Order Kinetics
- Half-life
- Drug Regulatory Schedules
- Morphine
- NSAIDs
- Alkylating agents
- Myasthenia Gravis
Microbiology
- Mycology
- Virology
- Stool examination
- Sterilization and Disinfection
- Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Type 4 Hypersensitivity
- Antigen-Antibody Reactions
- Inclusion Bodies
- Herpes Simplex Virus
- Yellow Fever
- Zika
- Scrub Typhus
- Vaccines
- Staining and fixation
- Hepatitis B
- Skin Lesions
- Viruses-Microscopy and Culture
Pathology
- Peripheral Smear Images
- Hematology Formulae
- Blood Products & Transfusion
- Molecular tests (FISH, Micro-array, NGS, Exon sequencing)
- TEG/ROTEM
- Hepatitis
- Glomerulonephritis
- Lewy Body Dementia
- Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Thyroid Swelling Evaluation
- Testicular Carcinoma
- Graft Rejection
- Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
- Oncogenes
Forensic Medicine and Toxicology
- IPCs
- Poisoning- C/F & Management
- Drowning
- Arsenic Poisoning
- Teeth Eruption
- Thermal Injuries
- Snake Bite
- Alcohol Intoxication
- Laceration
- Asphyxia – Hanging
- Identification – Age Estimation
Community Medicine
- Biostats
- Epidemiology
- Screening Tests
- Intussusception
- Vaccines-Types
- Biomedical Waste Management
- Standard Error
- Post Exposure Prophylaxis
- Anemia Mukt Bharat Programme
- Antenatal Care-Diet
- Maternal Mortality Ratio/MMR
- Water & Mild Contamination
- Sterilization & Disinfection
- Recent Updates
Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Cervical Cancer & Screening
- Stages of Labor
- Intrapartum Fetal Monitoring
- Contraception
- Turner’s Syndrome
- Abortion
- Oral Contraceptive Pills/OCPs – Mechanism of Action
- Urinary Tract Infections
- Teratogenic Drugs
- Postpartum Hemorrhage
- Molar Pregnancy
- PCOD/PCOS
- Bishop’s Score
- Infertility
- Postmenopausal Bleeding
- Secondary Amenorrhea
- Cord Prolapse
- Semen Analysis
Pediatrics
- Immunization
- Developmental Milestones
- Neonatology
- Growth and Development
- Neonatal Jaundice
- Severe Acute Malnutrition
- COVID 19 – Treatment
- Dehydration
- Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support
- Urinary Incontinence
- Choking
- Growth Hormone
- Kangaroo Mother Care/KMC
Surgery
- Trauma
- Burns
- Breast Carcinoma
- General Surgery
- Thyroid
- Varicose Veins
- Instruments, Lines, Tubes (Also Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology and ENT)
- Basic Life Support / BLS
- Hypothyroidism
- Sepsis/Septic Shock
- Suture Materials and Techniques
- Triage
- Skin Graft
- Psoas Abscess
- Thyroid Swelling Evaluation
- Ulcers
- Hernia
- Rectal Prolapse
- Whipple’s Procedure
- Germ Cell Tumors
- Kidney Transplantation
Orthopaedics
- Nerve Injuries
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Shoulder Dislocation
- Fractures
- Pediatric Orthopaedics
- Scoliosis
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Ulnar Nerve
- Bone Cysts
- Knee Injuries
ENT
- X-ray Special Views
- Hearing Aids and Cochlear Implant
- Pure Tone Audiometry
- Impedance Audiometry
- Larynx – Nerve Supply
- Sinusitis
- Nasal Polyps
- Laryngoscopy & Rhinoscopy
Ophthalmology
- Glaucoma – Angle Closure
- Pedigree Chart/Pattern of Inheritance
- Cataract Surgery – Procedures
- Paralytic Squint
- Tests in Ophthalmology
- SAFE Strategy
- Uveitis
- Anti-Glaucoma Drugs
- Pleomorphic Adenoma & Warthin’s Tumor
- Retinoblastoma
- Ocular & Orbital Injuries
Medicine
- Acid-base Balance
- ECG
- Electrolyte Imbalance
- Emergencies (Shock, stroke, SAH, HHK, Arrhythmia)
- Localisation of Stroke and CNS Lesions
- Wilson’s Disease
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Graves’ Disease
- Hepatitis B
- Electroencephalography
- Azole Antifungals
- Mycoplasma
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Drugs in Renal Impairment
- Nitrates
- Multiple Myeloma
- Rheumatic Fever
- Meningitis
- Fluid Resuscitation
- Ischemic Stroke
- Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Heart Failure
- Headache – Tension & Cluster
- Acute Kidney Injury
- Hypoxia
- Pulmonary Function Tests- Flow Volume Loop/Curve
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Community Acquired Pneumonia
Dermatology
- Dermatomyositis
- Herpes Zoster
- Leprosy
- Leishmaniasis
- Psoriasis
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Fixed Drug Eruption
- Skin Lesions
- Vitiligo
- Alopecia
- Chikungunya
- AcneVulgaris
Psychiatry
- ICD Criterion and timelines
- Sleep Disorders
- Defense Mechanism
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
- Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
- Bipolar Disorder
- Nicotine
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Tobacco Cessation Drugs
Anaesthesia
- ACLS, BLS
- Capnography
- Components of High-Quality CPR
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- Mechanical Ventilation
- Local Anesthetics
- Fluorinated Anesthetic Agents
- Air & Amniotic Fluid Embolism
Radiology
- Intestinal Obstruction
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Radiation Exposure & Radiation Injury
- Glasgow Coma Scale
- Barium Studies
- Important radiology images interrelated with other subjects
Click here to learn from the MBBS subject experts.
INI-CET is conducted for admission to PG courses (MD, MS, DM(6yrs), MCh (6yrs), and MDS) at various INIs, including AIIMS, JIPMER, NIMHANS, PGIMER and SCTIMST.
If you are an INI-CET aspirant, it’s crucial for you to know the important dates, eligibility criteria, application process, and other exam-related essential details. You must arrange all the required documents you need to upload beforehand.
For the July session 2024, INI-CET is going to be held on 19th May 2024 and for the same, you must be well versed with the important dates including application commencement, documents upload, admit card release, and more.
In this blog, we have mentioned all the INI-CET important dates, application fees, must-know things before filling out the application form, and the step-by-step application process.
Important Dates for INI-CET July 2024 Session
| Procedure | Start Date | Closing Date |
| Online Application for Registration and Basic Information | 18.03.2024 | 12.04.2024 (by 05:00 pm) |
| Confirmation of Status of Registration and Basic information and Last Date of Correction of Rejected Images | 13.04.2024 | 15.04.2024 (by 05:00 pm) |
| Final Status of Accepted Registration and Basic Information | 16.04.2024 (05:00 pm) | |
| Date of Uploading Notice for Seat Position of Sponsored/Foreign National Category | 05.04.2024 | |
| Generation of Examination Unique Code (EUC) [Only for Accepted Registration and Basic Information]
Completion of Application form [Only for candidates who have generated EUC code]
Editing of Completion of Application Form [Change of category will not be allowed after payment of registration fee in any circumstances]
*(Previous EUC code not valid for July 2024 session)
|
05.04.2024 | 26.04.2024 (05:00 pm) |
| Uploading of Valid Certificate/Card [SC/ST/OBC(NCL)/EWS/PwBD Certificate and OCI Card]
* The OBC(-NCL) certificates should have been issued on or between 20.05.2023 to 19.05.2024 (Date of Exam) *The EWS certificate must be valid for the financial year 2023-2024 and issued on or between 01.04.2024 to 19.05.2024 |
05.04.2024 (05:00 pm) | 19.05.2024 (05:00 pm) |
| Date(s) of Checking Status of Completion of Application Form & Last Date of Submission of Required Documents
*Status of Completion of Application will be displayed on My Page after Login |
02.05.2024 | 04.05.2024 (05:00 pm) |
| Regularization of Rejected Application | 04.05.2024 (05:00 pm) | |
| Final Status of Online Registration and Uploading of Admit Card on AIIMS website |
13.05.2024 (Monday) |
|
| Date of Examination | 19th May 2024 (Sunday) | |
| Last Date of receiving application form duly recommended & forwarded with “No Objection Certificate” from the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Govt. of India for Foreign Nationals to apply and appear in the INI-CET for PG courses –July 2024 session | 17.05.2024 (by 05:00 pm) | |
| Last Date to Upload a Scanned Copy of the Sponsored Certificate | 17.05.2024 (by 05:00 pm) | |
| Result Declaration (Tentative) | 25.05.2024 (Saturday) | |
| Online Seat Allocation | To be notified | |
| Date of Commencement of Courses | 01.07.2024 | |
| Last Date of Admission | 31.08.2024 | |
Must Read: INI-CET Participating Institutes and Eligibility criteria for January session 2024.
INI-CET 2024: Application Fee
The INI-CET application fee for the General/OBC Candidates/Foreign National/OCI applicant is Rs. 4000/- whereas for the SC/ST/EWS applicant, the application fee is Rs. 3200/-.
The PwBD candidates are exempted from paying the examination fee.
The application form is successfully submitted only after the application fee payment. It is to be paid at the last step of the application in the online mode only.
Must know Things Before Filling out the Application Form
You must check the eligibility criteria for admission to various postgraduate courses at participating INIs for the July 2024 session.
If you are already pursuing any medical PG degree in any subject, then you are not eligible for seat allocation.
Without the provisional or permanent registration of NMC/DCI, you are not eligible to apply or online register for the INI-CET examination.
You must arrange all the required documents beforehand for INI-CET and for the particular INI, you want to apply to, such as a domicile certificate.
You can’t change your category later so be very careful while filling out the form, that either you belong to the general category or EWS or any other category. You are also required to upload the particular category certification to which you have opted. If your category certificate is found invalid or not uploaded within the stipulated time, then you will be counted under the General/Unreserved category. Hence, you will not be liable for any relaxation for cut-off and counselling.
You must always recheck the details filled and the images uploaded in the application form. Fill in all the details and upload images according to the instructions otherwise your application may be rejected and if in case after appearing in the exam, your uploaded documents don’t qualify for the prescribed format or are morphed, then your candidature will be cancelled.
The Person with a Benchmark Disability must go through all the guidelines available at aiimsexams.edu.in for admission to PG courses.
INI-CET 2024: Application Process
- Registration and Basic Candidate Information
In this stage, you have to generate the Registration ID and Password. It is a one-time process for getting admission to PG courses. Then, log in to fill in all your personal details, and upload images. In the images, you need to upload a photo, signature, and left thumb impression. Only after the registration is accepted, you will get the EUC for subsequent completion of the application. Candidates who already have accepted registration for the previous PG exam need not register again and can directly proceed to the generation of the EUC step.
While filling out the form, on the registration and basic information page, you can access the ‘How to Upload Images’ tab. Follow all the instructions very carefully to avoid application rejection. The instructions will include the image format, size, pixels, background colour, ink to be used for signature and thumb impression, and more relevant information.
- Generation of Exam Unique Code (EUC)
Only after the completion of step 1, your EUC will be generated. Generation of EUC is a prerequisite for the application login zone. The generated EUC for the previous session is not acceptable.
- Completion of Application Form
After the generation of the code, log in at the applicant login zone. You will be required a valid registration ID, password, and Exam Unique Code (EUC) for the INI-CET July 2024 successful login. Fill in all the details and upload the relevant documents on or before the due date and time (as mentioned in the important dates table above). Minutely check every detail you have filled in. Make sure the phone number and email address you have filled in the application form are correct and active.
By following all the above-mentioned points, you will be able to complete your application within the stipulated time.
Click here to learn from the MBBS subject experts.
Clearing MBBS is itself a difficult task and then cracking competitive exams is another level of challenge. But you can’t skip this challenging situation if you want to the accelerating graph of your career.
Success in the MRCP Part 1 exam signifies that you have not only retained the knowledge you learned during your undergraduate studies but that it has also grown to keep up with developments that have happened since you graduated and continues to serve as a foundation for clinical decision-making.
Most important to note, MRCP is just a pass or fail exam.
Step-by-Step Study Guide for MRCP Part 1 Exam
1. Understand the Exam Pattern.
MRCP Part 1 is a single-day Computer-based exam comprising two papers. Each paper has 100 multiple-choice questions to be solved in three hours. The MCQs follow the ‘best of five’ exam format. No negative marking gives a bit of relaxation for this competitive exam.
This MRCP Part 1 overview will let you get familiar with the exam pattern and will help you plan your preparation and revision strategy with effective time management. It is crucial to distribute the time to learn each specialty depending on the vastness of the subject, subject weightage, your level of understanding of the subject, etc.
Click here to learn the subject- weightage/blueprint of the MRCP Part 1 exam.
2. Choose your Exam Date Wisely.
It is advised to give the MRCP Part 1 first attempt after 12-24 months of graduation. Once you feel confident enough to take an exam, then only register for it. Usually, competitive exams are held once or twice a year, but the MRCP Part 1 exam occurs four times a year (January/April/August/October), which provides an opportunity for you to apply as per your suitability. You don’t have to wait for another year to sit the exam if you don’t want to sit for the exam this time.
3. Start Preparing Early.
Given how difficult the MRCP Part 1 test is, it’s crucial to give yourself plenty of time to study. Give a minimum of 6-10 months for sincere preparation. Don’t get confused; talk to seniors, faculty, friends, or mentors to get the best advice for you. Early preparation saves your time and boosts your confidence. Effective planning and consistency pave the way to effective results.
4. Make a Realistic Study Plan.
Create an MRCP Part 1 study plan that describes the material you will cover each day or week after you have your study materials. Allocate the time to a particular specialty keeping the factor in mind that your level of understanding is at beginner level or intermediate. Also, consider that there is enough time left for revision and practice questions. Revision strategy is also a must so that you don’t miss out on anything at the eleventh hour. Practice the question according to the exam pattern to get more familiar with it and this will also enhance your ability to tackle a question in the exam. Review your performance and revise your strategy accordingly.
5. Stick to Reliable Study Resources.
There are several options for MRCP Part 1 study materials, including books, online MRCP 1 exam resources, and question banks. To have a thorough grasp of the subject, it’s crucial to employ a range of materials, and resource selection is recommended. The preferred books for MRCP Part 1 are “Mastering Medicine: MRCP Made Easy” by Dr. Archith Boloor, Essential Revision Notes for MRCP by Philip A. Kalra, and the Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine by R.A. Hope. For online MRCP preparation may it be video lectures or Practice questions, you can subscribe to the ‘Cracking MRCP Part 1’ course. You can attend webinars and exam discussion videos only by the eminent faculty.
6. Enroll in online MRCP part 1 preparation courses.
To ace your MRCP preparation, you can enroll in one of the best online courses for MRCP Part 1, “Cracking MRCP Part 1” by eminent faculty, Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander and Dr. Archith Boloor. The course covers modules covering all the major specialities and is devised based on The Royal College of Physicians curriculum. Every module in the Cracking MRCP Part 1 study materials includes webinars and video archives, approx. 2000 best of five MCQs/MRCP Part 1 practice questions, notes, high-yielding questions, e-chapters, and performance tracking. It additionally benefits you with the mock papers intended to give a feel of a real exam. The leaderboard ranking feature of the course enables you to track your performance and prepare accordingly. To ease the preparation and revision, the Cracking MRCP Part 1 notes are categorised into three sections: Wake-up calls, Golden signs, and Clinical gems. The Wake-up calls indicate the red flag signs pointing towards a certain disease or condition, Golden signs signify characteristic diagnostic features of a disease or condition, and Clinical gems signify recommended management or preferred drug choice for a disease or condition.
7. Don’t Miss Out on High-Weightage Topics.
A wide number of subjects are covered in the MRCP Part 1 exam; however, some are assessed more rigorously than others. The following are the high-weightage speciality/subjects:
- Cardiology
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Clinical Sciences
- Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolic Medicine
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Infectious Diseases
- Neurology
- Renal Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine
- Rheumatology
8. Practice Mock Exams and Previous Year Papers.
Practicing mock exams and previous year’s papers is an excellent method to gauge your progress and determine where you need to concentrate and revise your strategy. There are a variety of mock tests accessible, both online and in books. DigiNerve with the Cracking MRCP Part 1 online course gives access to the free mock paper. You must attempt it under the timed condition for self-evaluation. Utilising question banks for practise will give you a better understanding of the questions that are asked.
9. Be Consistent and Manage Time Effectively.
Consistency is the key. Although taking the MRCP Part 1 test might be nerve-wracking, it’s crucial to remain composed and concentrated. Be consistent with your study routines along with balancing clinical practice.
Also, time management skills are crucial because the MRCP Part 1 test is timed. Give yourself enough time to respond to each question but avoid spending too much time on a single question. Mark the question for review if you are unsure about the answer, then go on. If you have time, you can return to the marked questions later. Remind yourself that you are prepared for the exam by taking deep breaths.
10. Take Good Care of your Health.
Consume healthful meals and get adequate sleep. Good health improves concentration and memory. Don’t get stressed a lot and meditate regularly because mental health is as important as physical health. Especially on the day of the exam, it’s critical to obtain adequate sleep and consume a balanced diet. You’ll be able to focus and remain awake as a result.
MRCP Part 1 Exam Day Tips
- Get familiar with the route and location of the exam centre and reach on time on exam day.
- Don’t be late for Paper-II after the break. It is advised to be at your desk at least 15 minutes before Paper-II is about the start.
- You are not allowed to take any items, accessories, or stationary along with you in the exam.
- The required stationery items are provided in the exam hall itself.
- Don’t wear hoods for the exam.
- Keep your ID handy for entry and checking purposes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What score do you need to pass MRCP Part 1?
Ans. The pass marks for MRCP Part 1 are around 540. The Equating process based on Response theory is used to calculate the candidate’s overall result. The pass marks are calculated as the overall scaled score unlike other exams, where the overall percentage score is considered.
Q2. Is there a negative marking in MRCP Part 1?
Ans. No, there is no negative marking in the MRCP Part 1. This is a great advantage for all the candidates aiming to clear the MRCP exam.
Q3. Is MRCP difficult to pass?
Ans. Undoubtedly, the MRCP exam is difficult to pass but not impossible. With smart study, consistent efforts, proper clinical practice, and effective time management, you can crack the MRCP exam.
The UPSC CMS is an abbreviation for “Union Public Service Commission-Combined Medical Services” Examination. It is a competitive examination that the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) of India administers. The CMSE is held every year to fill various medical positions in government agencies including the Indian Railways, Central Health Service, Municipal Corporation of Delhi, and several other central government health institutions. The CMS exam allows medical professionals to join the esteemed Indian government healthcare service organizations and support the country’s healthcare system.
The difficulty level of the exam is self-explanatory by the term UPSC; UPSC CMSE is a hard nut to crack. With smart study, consistent efforts, and a lot of practice, you will pass with flying colours. Make sure to start early and stick to a realistic study plan and reliable study resources.
In this blog, you will get detailed information about the UPSC CMS exam recruitment category, eligibility criteria, exam pattern, selection procedure, and syllabus.
To be eligible to sit in the exam, a candidate must be either:
(a) an Indian citizen, or
(b) a subject of Nepal, or
(c) a subject of Bhutan, or
(d) a Tibetan refugee who came over to India before the 1st January 1962 to permanently settle in India, or
(e) a person of Indian origin who has migrated from Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka, or East African Countries of Kenya, Uganda, the United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, 6 Malawi, Zaire, and Ethiopia or Vietnam to permanently settle in India.
Provided that a certificate of eligibility has been issued by the Government of India in favour of the candidate belonging to categories (b), (c), (d), and (e) mentioned above.
UPSC CMS Recruitment Category
UPSC CMS exam is conducted for the recruitment for the following categories and positions:
Category-I:
Medical Officers Grade in General Duty Medical Officers Sub-cadre of Central Health Services
Category-II:
Assistant Divisional Medical Officer in the Railways
General Duty Medical Officer in New Delhi Municipal Council
General Duty Medical Officer Gr-II in Municipal Corporation of Delhi
There are reservations for candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, Economically Weaker Sections, and Persons with Benchmark Disability as per the vacancies by the Government.
UPSC CMS Exam Pattern
Medical graduates with an MBBS degree along with completion of internship are eligible to apply for the UPSC CMS exam. There are two parts of CMSE, one is a written examination and the other is an interview. The CMSE comprises two theory papers followed by a personality test or interview. Here’s a breakdown of the exam pattern:
Part-I: Written Examination
The written examination comprises two papers:
Paper-I: This paper includes questions from General Medicine and Pediatrics subject. The exam Pattern 2024 for UPSC CMSE Paper-I is mentioned in the below table:
| Particulars | Details |
| Duration | 2 hours |
| Type of Questions | Objective type Questions (MCQs) |
| Total Marks | 250 |
| Total Number of Questions in Paper I | 120 (96 questions from General Medicine and 24 from Pediatrics) |
| Medium of Question Paper | English |
| Negative Marking | One-third of the marks assigned to a question are deducted for each incorrect answer.
If a candidate gives more than one answer, it will be treated as a wrong answer even if one of the given answers is correct and there will be the same penalty as above for that question. If a question is left blank i.e., no answer is given by the candidate, there will be no penalty for that question. |
Paper-II: This paper includes questions from Surgery, Obstetrics & Gynecology, and Preventive and Social Medicine subjects. The Surgery subject also includes ENT, Ophthalmology, Traumatology, and Orthopaedics subjects. The table below mentions the exam scheme for UPSC CMSE Paper-II 2024:
| Particulars | Details |
| Duration | 2 hours |
| Type of Questions | Objective type Questions (MCQs) |
| Total Marks | 250 |
| Total Number of Questions in Paper II | 120 (40 questions from each subject, Surgery, OBGYN, and Community Medicine) |
| Medium of Question Paper | English |
| Negative Marking | One-third of the marks assigned to a question are deducted for each incorrect answer.
If a candidate gives more than one answer, it will be treated as a wrong answer even if one of the given answers is correct and there will be the same penalty as above for that question. If a question is left blank i.e., no answer is given by the candidate, there will be no penalty for that question. |
Part-II: Interview/Personality Test
After passing the written test, candidates are invited by the Union Public Service Commission for an interview/personality test to determine their fit for the open positions.
The personality test carries 100 marks. The interview is designed to complement the written examination for measuring the general knowledge and academic study skills of the applicants as well as to function as a personality test to evaluate the candidate’s critical thinking skills, absorption capacity, and overall capacity for social cohesiveness, sound judgment, and moral character, initiative, and leadership potential. Basically, it aims to assess the candidate’s personality, communication skills, and suitability for the posts in medical services.
Final Selection
The final selection is done based on the combined marks obtained in Paper-I, Paper-II, and the Interview/Personality test.
Recruitment of a number of candidates is based on the vacancies in the particular position. Succeeding applicants are assigned to different Group-A positions within the public health system. The particular positions and openings change every year.
It’s significant to note that the Paper-I and Paper-II syllabuses contain a broad variety of medical science-related topics. A wide range of medical topics, including clinical disciplines, general knowledge, and current events, are covered in the CMSE curriculum. To score well on the test, candidates must have a solid comprehension of these topics. It is a crucial aspect of a good preparation strategy to know and understand the syllabus of the CMS exam. It leads to effective time management.
UPSC CMS Syllabus
UPSC CMS Syllabus Paper I:
General Medicine subject includes the following topics:
- Cardiology
- Respiratory diseases
- Gastro-intestinal
- Genito-Urinary
- Neurology
- Hematology
- Endocrinology
- Metabolic disorders
- Infections/Communicable Diseases
-
- Virus
- Rickets
- Bacterial
- Spirochetal
- Protozoan
- Metazoan
- Fungus
- Nutrition/Growth
- Diseases of the skin (Dermatology)
- Musculoskeletal System
- Psychiatry
- General
- Emergency Medicine
- Common Poisoning
- Snakebite
- Tropical Medicine
- Critical Care Medicine
- Emphasis on medical procedures
- Patho physiological basis of diseases
- Vaccines-preventable diseases and Non-vaccines preventable diseases
- Vitamin deficiency diseases
- In psychiatry – Depression, psychosis, anxiety, bipolar diseases, and Schizophrenia
Pediatrics subject includes the following topics:
- Common childhood emergencies
- Basic newborn care
- Normal developmental milestones
- Accidents and poisonings in children
- Birth defects and counselling including autism
- Immunization in children
- Recognizing and managing children with special needs
- National programmes related to child health
UPSC CMS Syllabus Paper II:
Surgery subject includes the following topics:
- General Surgery
- Wounds
- Infections
- Tumours
- Lymphatic
- Blood vessels
- Cysts/sinuses
- Head and neck
- Breast
- Alimentary tract
-
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Intestines
- Anus
- Developmental
-
- Liver, Bile, Pancreas
- Spleen
- Peritoneum
- Abdominal wall
- Abdominal injuries
- Urological Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Otorhinolaryngology/E.N.T.
- Thoracic surgery
- Orthopaedic surgery
- Ophthalmology
- Anaesthesiology
- Traumatology
- Diagnosis and management of common surgical ailments
- Pre-operative and post-operative care of surgical patients
- Medico-legal and ethical issues of surgery
- Wound healing
- Fluid and electrolyte management in surgery
- Shock pathophysiology and management
Obstetrics and Gynecology subject includes the following topics:
- Questions on applied anatomy
- Questions on applied physiology of menstruation and fertilization
- Questions on infections in the genital tract
- Questions on neoplasm in the genital tract
- Questions on displacement of the uterus
- Normal delivery and safe delivery practices
- High-risk pregnancy and management
- Abortions
- Intra Uterine growth retardation
- Medicolegal examination in OBGYN including the rape
Family Planning subject includes the following topics:
- Conventional contraceptives
- D. and oral pills
- Operative procedure, sterilization, and organization of programmes in the urban and rural surroundings
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy
Preventive Social & Community Medicine subject include the following topics:
- Social and Community Medicine
- Concept of Health, Disease and Preventive Medicine
- Health Administration and Planning
- General Epidemiology
- Demography and Health Statistics
- Communicable Diseases
- Environmental Health
- Nutrition and Health
- Non-communicable Diseases
- Occupational Health
- Genetics and Health
- International Health
- Medical Sociology and Health Education
- Maternal and Child Health
- National Programmes
- Management of common health problems
- Ability to monitor national health programmes
- Knowledge of maternal and child wellness
- Ability to recognize, investigate, report, plan, and manage community health problems including malnutrition and emergencies.
You can also enroll in online MBBS courses to get conceptual clarity over MBBS subjects by the top medical faculty of India. You have the opportunity to learn and get your concepts clear in Surgery by Dr. Sriram Bhat M, Microbiology by Dr. Apurba S Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat and Dr. Deepashree R, Medicine by Dr. Archith Boloor, Pathology by Prof Harsh Mohan, Prof Ramadas Nayak, and Dr. Debasis Gochhait, and similarly other MBBS subjects by subject’s eminent faculty. The comprehensive knowledge of MBBS subjects and problem-solving capabilities will directly impact your CMS exam.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. Is UPSC CMS conducted every year?
Ans. Yes, the UPSC CMS exam is conducted every year and the recruitment is based on the number of vacancies for a particular post in various government health organizations.
Q2. What is a career after CMS?
Ans. UPSC CMSE is conducted for the recruitment of the Medical Officers Grade in General Duty Medical Officers Sub-cadre of Central Health Services, Assistant Divisional Medical Officer in the Railways, General Duty Medical Officer in New Delhi Municipal Council, and General Duty Medical Officer Gr-II in Municipal Corporation of Delhi
Q3. Who conducts the CMS exam?
Ans. The CMS exam is a competitive examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) of India.
Q4. What is the pattern of UPSC CMS exam?
Ans. There are two parts of CMSE in which part-I is a written examination and the part-II is an interview. The CMSE comprises two theory papers followed by a personality test or interview.
The Part-I written examination comprises two papers: Paper-I and Paper-II.
A critical care specialist, also known as an intensivist or critical care physician, plays a crucial role in the management of critically ill patients. Their main duty is to offer specialised medical attention to patients with grave injuries or life-threatening illnesses. The majority of the time, critical care specialists operate in intensive care units (ICUs) in hospitals, while they may sometimes be called upon to provide care while being transported or in specialised facilities for the treatment of the critically ill. In complex medical circumstances, their knowledge is essential for enhancing patient outcomes and preserving life. They closely monitor and treat patients with urgent medical needs. They closely watch over trauma victims and treat major infections with multiple organ failure. Critical care specialists treat a wide range of conditions, including:
- Heart failure
- Stroke
- Renal failure
- Respiratory failure
- Severe infections
- Multiple organ failure
- Trauma
- Burns
- Poisoning
- Postoperative complications, etc.
Critical care medicine is a multidisciplinary and multi-professional field of medicine. Considering the unavoidable need for a full-time critical care specialist, NMC has mandated the establishment of a critical care medicine department in all healthcare facilities and medical colleges to provide the timely utmost treatment of emergency cases.
Specialists in critical care are crucial to the healthcare system. They are skilled in employing technology for life support and managing complicated medical issues. To give their patients comprehensive treatment, they also collaborate closely with other healthcare specialists including nurses, respiratory therapists, clinical pharmacologists, occupational therapists, and others.
Specific Role and Responsibilities of a Critical Care Specialist
- Extensive Patient Assessment: Critical care professionals are educated to assess a patient’s status rapidly and precisely. They must have a comprehensive knowledge and approach to deal with all kinds of specialties emergencies to an extent. They offer seriously ill individuals extensive medical care. They use clinical expertise, medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic procedures to ascertain the gravity of the sickness or damage. This entails handling a variety of medical conditions, including organ failure, infections, trauma, respiratory failure, heart problems, and more. They are responsible for obtaining and interpreting orders for imaging investigations, laboratory testing, and managing and prescribing drugs.
A critical care specialist is expected to master the procedures and fundamental aspects of treating a critically ill patient including:
- Airway management
- Oxygen and Inhalation therapy
- Mechanical Ventilation
- Invasive and non-invasive hemodynamic monitoring
- Use of cardiac pacemakers
- Performance and interpretation of ECG
- Use of defibrillators/external pacemakers
- Diagnosis of brain death
- Lumbar Puncture
- Support of an organ donor
- Insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter
- Management of peritoneal dialysis
- Insertion of hemodialysis catheters
- Safe transport
- Interpretation of routine radiology; computerized tomography; ultrasonography; MRI and EEG/EMG.
- Bronchoscopy
- Ultrasound-guided procedures
- External ventricular drain insertion
- Intracranial Pressure measurement
- Decision-Making and Quick Response Attitude: They make decisions that are crucial to the patient’s treatment plan, including whether to utilise medicine, ventilator support, and other life-saving measures. Critical care specialists decide on the start and modification of treatment regimens. They carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of various treatments and drugs. They must take into account the patient’s general health as well as the possible drawbacks and advantages of various treatment alternatives. Mental alertness and a quick response attitude are must-haves for a critical care expert. Keeping a check on all the equipment and basic required tools for treating the critically ill at all times is highly crucial to avoid unnecessary chaotic situations at times of emergency.
- Monitoring and Diagnostic Expertise: Critical care professionals keep a tight eye on a patient’s vital signs, test data, organ performance, and other condition markers. They track changes in real-time using sophisticated monitoring equipment and modify therapy as necessary. They are skilled in interpreting a variety of diagnostic procedures, including laboratory results, radiographic studies, and monitoring data, to establish precise diagnoses and treatment choices.
- Ventilator Management: To assist their breathing, many critically sick patients need mechanical ventilation. To ensure that patients receive the proper settings and modifications for their ventilators, intensivists are knowledgeable in this area. They keep a check on the functioning of life-support systems like ventilators and dialysis units.
- Excellent Communication and Patient Advocacy: Critical care experts constantly interact with the families of their patients to address concerns, discuss treatment choices, and provide updates on their health. In times of crisis, effective communication is essential. Critical care specialist doctors need to possess the requisite abilities in addition to the necessary knowledge to handle crises and difficult situations when a patient’s life is in danger. Because of this, an intensivist must constantly monitor the patient’s status and, in the event of any issues, act rapidly to resolve them so that the patient is no longer in danger and may proceed with his or her recovery.They act as a voice for their patients, ensuring that they get the finest treatment possible and that their moral and medical requirements are addressed. In addition, an intensivist serve as a crucial conduit between the patient and his family. Not just the sufferer, but also his or her family, who are perpetually frightened and concerned require emotional support through difficult times.
- Interdisciplinary teamwork and Care Coordination: To deliver comprehensive and coordinated treatment to critically ill patients, they collaborate closely with a diverse team of healthcare professionals, including nurses, respiratory therapists, clinical pharmacologists, occupational therapists, and others. They collaborate with members of a multidisciplinary team to avoid any lapses in the treatment. To give critically sick patients thorough treatment, cooperation is necessary.
- Procedures: They have received training in a variety of critical care procedures for patient stabilisation, including intubation, central line installation, administration of mechanical ventilation, invasive monitoring procedures, renal support, and bedside treatments to deal with urgent medical conditions. They could carry out a range of operations, including maintaining sophisticated medical equipment and placing chest tubes, arterial lines, and central lines. Of course, a specialist working in an ICU or trauma unit should be knowledgeable about technology and skilled in the clinical management of critical care.
- Resuscitation and Quality Improvement: Intensivists are frequently called upon to direct resuscitation efforts during emergencies, including cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), emergency medicine, advanced life support procedures, or advanced medical procedures. They actively take part in efforts to enhance patient outcomes engage in quality improvement initiatives within the ICU and improve overall quality of life.
- End-of-Life Care: When a patient’s condition is terminal or when aggressive treatment is not in their best interests, they are adept at delivering compassionate end-of-life care. Talking about hospice or palliative care services may be part of this.
- Research and Education: Clinical research and medical education are two areas in which many experts in critical care are active. They may instruct medical students, residents, and fellows, keeping abreast of the most recent developments in critical care medicine.
Learning from the Critical Care Medicine Course
The objective of the Critical Care Medicine Course is to make the medical professional skilled at the following modules:
- Basic Medical Sciences related to Critical Care Medicine
- Clinical – Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of acute life-threatening medical and surgical diseases related to Critical Care Medicine
- Clinical – Procedures, interventions, professionalism, ethics, and research methods related to Critical Care Medicine
- Recent Advances in the field of Critical Care Medicine
The topics included in the critical care medicine curriculum for academically and clinically competent critical care specialists:
- Resuscitation and Initial Management of Acutely Ill Patients
- Diagnosis: Assessment, Investigation, Monitoring, and Data: Interpretation of the Acutely-Ill Patients
- Disease Management
- Organ System Failure
- Therapeutic Interventions/Organ System Support in Single or Multiple Organ Failure
- Peri-operative Care
- Critical Care of Children
- Transportation
- Physical & Clinical Measurement
- Research Methods (Includes Data Collection and Statistics)
- Breaking the Bad News
- Applied Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry & Pharmacology of the Human Body
- Quality and Patient Care
- Ethics/End-of-Life Care
- Medico-Legal Knowledge
- Organ Donation Procedure
Requirements for Becoming a Critical Care Medicine Expert
A skilled Critical Care Expert must be competent in the following:
- Critical care’s general and specialised attributes, including service management.
- Supervising long-term cooperative management strategies for more patients.
- Team leadership for the Intensive care unit (ICU).
- Mentoring and supervising younger coworkers.
- Information integration.
- Efficient operation of critical care services in a multi-specialty case.
- Capacity to schedule professional development in a way that contributes to the overall development of a specialty involving medical treatment, instruction, and research.
- Gain experience in diagnosis and treatment of acute, serious, and life-threatening medical and surgical diseases.
- Always conduct medical procedures and treat patients considering medical ethics.
- Effective communication skills and empathy in dealing with all situations.
Our Critical Care Simplified course is among the best online critical care courses for medical professionals. It provides comprehensive online critical care education. In addition to concentrating on certain organ systems throughout the course, learners will study a variety of critical care topics including resuscitation, trauma treatment, hemodynamic instability, neurological crises, and sepsis management. They will learn about the most recent developments in monitoring methods, infection control regimens, and critical care treatments. The training also emphasises the value of good inter-disciplinary critical care team communication and collaboration.
In conclusion, a critical care specialist’s duties include providing critically ill patients with specialised medical care and expertise, coordinating their care, making life-saving choices, and ensuring the best results for these patients. Their work is difficult and demands a high level of clinical proficiency, medical knowledge, and the capacity to deal with stressful circumstances.
Must Read: Benefits of Enrolling in a Critical Care Simplified Course
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has achieved the coveted World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) Recognition Status for a tenure of 10 years. This is a prestigious achievement for India’s medical education. This esteemed award proves NMC’s steadfast dedication to the highest standards in medical education and accreditation.
The WFME recognition will now enable Indian medical graduates to pursue postgraduate training and practice in other countries that require WFME recognition, such as Australia, USA, Canada, and New Zealand.
The World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) is a global organization dedicated to raising the standard of medical education all over the world. The WFME accreditation programme is crucial in ensuring that medical institutions uphold and adhere to the highest levels of global education and training standards.
Dr. Yogender Malik, Member of the Ethics and Medical Registration Board and Head Media Division at NMC, on this remarkable achievement, said, “WFME’s recognition underscores that the quality of medical education in India adheres to global standards. This accolade empowers our students with the opportunity to pursue their careers anywhere in the world, while also making India an attractive destination for international students due to our globally recognized standards.”
Under this accreditation, all the 706 existing medical colleges in India will be considered WFME accredited, and the new colleges being set up in the coming 10 years will also be considered as WFME accredited. This will also benefit NMC in enhancing the quality and standards of Indian medical education by aligning them with global benchmarks. This will facilitate academic collaborations and promote continuous improvement and innovation in medical education.
Now NMC being WFME accredited has opened the doors for all the medical students for ECFMG and USMLE. All Indian students will become eligible to apply for the Education Commission on Foreign Medical Graduates and United States Medical Licensing Examination.
The National Medical Council, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in a press release dated 20th September 2023 has announced this remarkable update.
Pathology is a medical specialty that deals with the causes and nature of disease. By delivering early and accurate diagnoses, which are crucial for successful treatment, pathologists play a crucial role in patient care.
A pathologist works with the causes and characteristics of illness and employs information acquired from the laboratory application of the biological, chemical, and physical sciences to aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. For the diagnosis and monitoring of illness, this specialist uses data obtained from microscopic inspection of tissue samples, cells, and bodily fluids as well as from clinical laboratory testing on bodily fluids and secretions. By delivering early and accurate diagnoses, which are crucial for successful treatment, pathologists play a crucial role in patient care.
If you are good at going with a microscope as your friend than a stethoscope, then pathology is a great option to choose as a specialty. This specialty is more of working behind the scenes sitting for long hours diagnosing rather than directly dealing with the patients.
Steps for Becoming a Pathologist
- Complete your 12th standard in the Science stream with a minimum of 55% aggregate.
- Then you have two options for your undergraduate degree, either you can go with an MBBS undergraduate degree, or you can go with a B.Sc. in Pathology. The former is more into medicine side while the latter is a basic health and allied sciences degree. Depending on your preference and educational qualification, you can choose between both. To pursue an MBBS degree, you must crack the NEET-UG entrance examination with a competitive score. You can opt for a government or private college for any of the undergraduate courses as per your preference and score. Always seek proper guidance before choosing a medical college.
Must Read: Things to know before choosing a medical college.
- After completing graduation, you must complete your postgraduation in pathology. If you did an MBBS, then go with an MD in Pathology degree and if you opted for BSc then go with an MSc Pathology degree. To pursue MD Pathology, you need to score high in the NEET-PG/INI-CET and for M.Sc. Pathology, you need to follow the admission procedure of the particular college.
- Then after completing postgraduation, you need to gain experience, then you have the option to pursue fellowship courses in various pathology subspecialities. You can also opt for a Ph.D. programme.
Apart from a degree, you also have the option to pursue a Diploma in Pathology or relevant certification courses.
Top Medical Colleges to Pursue MD Pathology in India
- AIIMS, Delhi
- Christian Medical College, Vellore
- Grant Government Medical College, Mumbai
- AFMC, Pune
- JIPMER, Puducherry
- Kasturba Medical College, Manipal
- IPGME&R and SSKM Hospital, Kolkata
- KGMU, Lucknow
- St. John’s Medical College, Bangalore
- Lady Hardinge Medical College, New Delhi
- Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi
- VMMC, New Delhi
Pathologists employ a wide range of instruments and methods to investigate illness, such as:
- Microscopical analysis of tissue samples: Pathologists use microscopes to analyse tiny slices of tissue in search of anomalies that might be signs of illness.
- Testing in the laboratory: Pathologists do several tests in the lab on tissues and bodily fluids to determine the concentrations of various chemicals, including hormones, enzymes, and proteins. These examinations can support illness diagnosis, track disease development, and evaluate therapy effectiveness.
- Autopsies: Pathologists examine a deceased person’s body after death to ascertain the cause of death and learn more about any ailments they may have had.
List of Pathology Subspecialities
Pathology is a broad specialty that encompasses a variety of subspecialties, including:
- Transfusion Medicine
- Chemical Pathology
- Cytopathology
- Dermatopathology
- Histopathology
- Forensic Pathology
- Hematopathology/Hematology
- Molecular Genetic Pathology
- Neuropathology
- Pediatric Pathology
- Pulmonary Pathology
- Renal Pathology
- Surgical Pathology
- Clinical Pathology
- Molecular Pathology
Skills Required for Becoming a Pathologist
A skilled pathologist should be well-versed in the following:
Establish a diagnosis for common and difficult clinical issues using histopathology (surgical pathology) and cytopathology specimens, blood and bone marrow examinations, and different laboratory medicine tests (clinical pathology, Blood Banking (Transfusion Medicine), and clinical biochemistry.
Construct correlations between clinical and laboratory data to ensure that clinical disease symptoms can be explained.
Suggest the proper samples and tests to conduct to reach a diagnosis in a difficult case.
Compare pathology results from an autopsy with those from the clinic, the causes of disease-related deaths, and their miscorrelations (other than isolated metabolic causes).
Should be competent to instruct pathology to nursing students, postgraduates, undergraduates, and paramedical professionals, including lab staff.
Be able to work as a team, cultivate a cooperative attitude among coworkers, and communicate with patients, clinicians, and other coworkers to offer the best diagnostic or opinion.
Always uphold ethical values, maintain an appropriate demeanour in interactions with patients, family members, and other medical professionals, and respect the patient’s rights, including access to information and a second opinion.
Capable of carrying out standard procedures in a pathology lab, such as grossing specimens, processing, slicing paraffin and frozen sections, and staining.
Capable of routinely performing non-invasive outpatient procedures like venipuncture, finger pricks, fine needle aspirations of superficial lumps, and bone marrow aspirates in order to collect specimens, and to give appropriate assistance to colleagues performing invasive procedures like a biopsy or an imaging-guided biopsy.
Salary and Scope of Pathologist
Pathology is a highly promising job as no diagnosis is complete without pathology. Pathologists are in great demand, and the job outlook for them is predicted to improve over the coming ten years at a faster-than-average rate. Pathologists can find employment in a range of places, such as hospitals, clinics, research facilities, diagnostic labs, and governmental organisations. After completing your medical education and gaining experience in Pathology, you can open your diagnostic pathology centre.
Pathologists have a highly diverse range of employment options and several prospects for progression. Anatomic pathology, clinical pathology, and forensic pathology are just a few examples of the areas of pathology in which pathologists might specialise.
For those with a passion for science and medicine, attention to detail, and strong analytical abilities, pathology is a good speciality. Additionally, pathologists must be able to operate both alone and collaboratively. On average, a pathologist earns 50K to 80K per month and it varies depending on the area of employment.
The job profiles associated with pathologist include Clinical Pathologist, Professor/Lecturer, Forensic Pathologist, Clinical Researcher Associate, Medical Writer, Transfusion Medicine Specialist, and more.
Best Books for Studying Pathology
- Prof Harsh Mohan’s Textbook of Pathology
- Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates Pathology by Ramadas Nayak and Sharda Rai
- Rapid Review of Hematology by Ramadas Nayak and Sharda Rai
- Review of Pathology and Genetics by Gobind Rai Garg and Sparsh Gupta
- Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Diseases by Vinay Kumar, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster
- Fundamentals of Pathology by Husain A. Sattar
- Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas
- Cytopathology Review by Fang Fan and Ivan Danjanov
- Gray’s Diagnostic Cytopathology
- Rosai and Ackerman’s Surgical Pathology
- Atlas and Text of Haematology by Tejinder Singh
- Orell’s Atlas of Aspiration Cytology
- Lever’s Dermatopathology
By offering precise and fast diagnoses, which are necessary for efficient treatment, pathologists play a crucial role in the healthcare industry. They also strive to create innovative diagnostic methods and disease-specific therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What should I do after 12th to become a Pathologist?
Ans. After completing the 12th standard, either you can go with an MBBS undergraduate degree, or you can go with a B.Sc. in Pathology. The former is more into medicine side while the latter is a basic health and allied sciences degree. Depending on your preference, you can choose between both. To pursue an MBBS degree, you must crack the NEET-UG entrance examination with a competitive score, and for a B.Sc., you need to follow the admission procedure of the particular college. You can opt for a government or private college for any of the undergraduate courses as per your preference and entrance exam score. Always seek proper guidance before choosing a medical college.
Q2. What are the career prospects for pathologists?
Ans. Pathologists can find employment in a range of places, such as hospitals, clinics, research facilities, diagnostic labs, and governmental organisations. After completing your medical education and gaining experience in Pathology, you can open your diagnostic pathology centre. The job profiles associated with pathologist include Clinical Pathologist, Professor/Lecturer, Forensic Pathologist, Clinical Researcher Associate, Medical Writer, Transfusion Medicine Specialist, and more.
Q3. How good is pathology as a career?
Ans. Pathology is a highly promising job as no diagnosis is complete without pathology. Pathologists are in great demand, and the job outlook for them is predicted to improve over the coming ten years at a faster-than-average rate. Pathologists can find employment in a range of places, such as hospitals, clinics, research facilities, diagnostic labs, and governmental organisations. After completing your medical education and gaining experience in Pathology, you can open your diagnostic pathology centre. Pathologists have a highly diverse range of employment options and several prospects for progression. Anatomic pathology, clinical pathology, and forensic pathology are just a few examples of the areas of pathology in which pathologists might specialise.
Q4. What is the salary of an MBBS MD pathologist in India?
Ans. On average, a pathologist earns 50K to 80K per month and it varies depending on the area of employment. The job profiles associated with pathologist include Clinical Pathologist, Professor/Lecturer, Forensic Pathologist, Clinical Researcher Associate, Medical Writer, Transfusion Medicine Specialist, and more.
Click here to get conceptual clarity on MBBS subjects.
Global health comprises the biological and clinical facets of diseases along with the social, economic, political, and environmental determinants of health. The ability to confine health issues inside national borders has diminished as the globe becomes more linked.
The contribution of technology to the medical sector is unparalleled. With the years passing by technology is improving at the highest pace in the medicine sector. Nowadays, the use of AI, and the development of new therapies, drugs, drug development, and surgical procedures, have made complex medical procedures less complex and paved a path to minimally invasive surgeries. Millions of individuals throughout the world are having their lives improved as a result of these developments.
Global health has improved recently despite several obstacles like poverty, pandemics, disease outbreaks, conflicts, and climate change. Maternal and child fatalities have dropped significantly and since the development of new vaccinations, infectious illness spread has also been reduced. Governments and organisations have also boosted their funding for global health concerns and also significantly invested in newer technologies. The current developments in the healthcare industry are beneficial to global health and are an area with significant potential to enhance the health of people all over the world and in the medical field. We can improve the health of people all across the world by addressing the issues and embracing the possibilities.
Medical students and professionals must keep themselves updated and knowledgeable about the recent advancements in healthcare as it is going to impact their career growth to a great extent. To escalate the growth of your medical career, it is mandated to upskill.
The recent advancements in the global healthcare and medicine field are significant for several reasons. By offering more precise diagnoses, earlier illness detection, and more individualised treatment regimens, they have the potential to:
- Improve the quality of care for patients.
- By enabling remote monitoring and care and minimising the need for in-person visits, healthcare may be made more accessible and cheaper.
- Increase the effectiveness of healthcare delivery by simplifying administrative procedures and facilitating information exchange between healthcare professionals.
- Develop novel therapies and preventative measures to lessen the impact of chronic illnesses.
- Boost public health by keeping track of and rapidly and efficiently addressing illness outbreaks.
Below mentioned are technological advancements in medicine and global healthcare:
Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
With the introduction of unprecedented tools for patient care, treatment, and diagnosis, artificial intelligence (AI) is drastically changing the healthcare industry.
For researchers interested in global health, AI-driven health interventions fall into four categories: diagnosis, patient morbidity or mortality risk assessment, disease outbreak prediction and surveillance, and health policy and planning. Machine learning, signal processing, data mining, natural language processing, and other forms of AI are applied in the healthcare sector.
Here are a few current applications of AI in healthcare:
- Diagnosis and treatment: Artificial intelligence (AI) paves the way for the screening of disease and can analyse medical images like X-rays and scans to identify illnesses early and more accurately than humans. AI may be used to create individualised treatment regimens for individuals based on their unique traits and requirements. Other applications of artificial intelligence being used in medicine include Digital chest radiographs, cervical cancer screening, estimating perinatal risk factors, and characterising and predicting the global spread of the Zika virus.
- Drug discovery: Artificial intelligence (AI) may be used to search through extensive databases of chemicals and compounds to find possible new medicines. AI may also be used to foresee how pharmaceuticals would react in the body, lowering the possibility of adverse effects.
- Personalised medicine: Artificial intelligence (AI) may be used to examine a patient’s genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle choices in order to develop a personalised treatment plan that has the highest chance of success.
- Risk assessment: AI may be used to predict the risk of disease and figure out how likely a patient is to have cancer or heart disease. Patients can utilise this knowledge to guide lifestyle adjustments that will lower their risk.
- Healthcare administration: AI may be used to automate processes like appointment scheduling, patient record management, and claim processing. This might free up medical personnel to concentrate on treating patients.
- Telemedicine: Platforms that employ AI in telemedicine can be used to offer doctor consultations via the Internet. Patients with limited access to healthcare in remote locations may particularly benefit from this.
- Robotics: Surgery, pharmaceutical dispensing, and other medical services can be carried out by AI-powered robots. This might aid in enhancing the effectiveness and precision of healthcare delivery.
- Big data analytics: Using AI, enormous databases of healthcare data may be analysed to spot trends and patterns. The diagnosis and treatment of illnesses can be made better with the use of this knowledge.
- Virtual assistants: AI-driven virtual assistants may be used to set up appointments, answer patients’ inquiries, and offer information about their conditions. The patient experience may be enhanced as a result of this.
The future of AI in healthcare is very promising. The use of AI in healthcare is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we diagnose, treat, and manage diseases. In the years to come, as AI technology advances, it is anticipated to have a more significant influence on the healthcare industry.
Advances in Gene Editing Technology
The science of gene editing is expanding quickly. The way we treat illnesses is changing as a result of gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9. These technologies can be used to fix genetic flaws that lead to disease or to add new genes that can offer disease protection.
The following are some of the developments in gene editing technologies that are being investigated for medical applications:
- CRISPR-Cas9: A protein called Cas9 is used by CRISPR-Cas9 to cut DNA at a precise spot. This enables precise gene replacement, deletion, and insertion. The most popular gene editing technology, CRISPR-Cas9, is being researched for a number of uses, including the treatment of HIV, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and hereditary illnesses.
For instance, in cancer patients, CRISPR-Cas9 is being utilised to create novel cancer medicines that can target and eliminate cancer cells. CAR T-cell treatments, a sort of immunotherapy that employs a patient’s immune cells to combat cancer, are being developed by researchers utilising CRISPR-Cas9.
- Base editing: A more recent gene editing technique, base editing allows you to alter specific DNA nucleotides without actually cutting the DNA. Compared to CRISPR-Cas9, this makes it less likely to result in unwanted side effects. For the therapy of conditions including cystic fibrosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, base editing is being researched.
- RNA editing: An approach to gene editing that can target RNA molecules rather than DNA. This can be utilised to treat conditions like certain cancers that are brought on by RNA alterations.
- Gene therapy: Gene therapy is a treatment that involves introducing genes into cells to correct a genetic defect. Numerous illnesses, including cancer, HIV, and hereditary ailments, have been treated by gene therapy.
These are only a handful of the gene editing innovations that are being investigated for medical applications. Technology’s continued advancement will probably have a significant influence on how we manage diseases in the years to come.
Development of Precision Medicine
A person’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment are all taken into consideration when developing a medical treatment plan in precision/personalised medicine. This may result in a more effective and targeted treatment with fewer adverse effects.
Personalising medicine may be done in a variety of ways. Typical strategies include:
- Genetic testing includes examining a person’s DNA to see if there are any mutations or variances that might impact their likelihood of contracting a certain disease or their reaction to a particular medication.
- Biomarkers are quantifiable indications of a biological condition or state. Biomarkers can be used to monitor a patient’s response to therapy or to spot those who are most likely to catch a particular disease.
- Environmental factors, such as pollutant exposure, food, and exercise impact how people respond to therapy as well as the development of many diseases.
Precision medicine is becoming more and more feasible as we understand more about the human genome and the part genetics plays in disease. We can create more effective and focused therapies that may result in improvement by taking into consideration a person’s particular demands.
Here are some examples of current applications of precision medicine:
- High-risk cancer patients are identified via genetic testing, and targeted medicines are created that are more efficient for those who have certain genetic alterations.
- Biomarkers are being utilised to monitor an individual’s risk of developing heart disease and to pinpoint those who will benefit from certain therapies the most.
- Scientists are examining the genetic component of Alzheimer’s disease and creating targeted treatments that might be more efficient for those who carry particular genetic abnormalities.
Some of the challenges and limitations of precision medicine include cost, accuracy, accessibility, and regulation.
Personalised medicine is a promising subject with the potential to enhance millions of people’s lives despite these difficulties. It is anticipated to become more accessible, inexpensive, and accurate as technology advances.
Development of Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare
Telemedicine and remote healthcare allow patients to receive care from a doctor or other healthcare provider without having to travel to a doctor’s office or hospital. This can help with healthcare access, particularly in remote locations. The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred telemedicine and remote healthcare development to a great extent. These services are increasingly enticing to patients and providers alike because of the requirement to maintain social distance and avoid in-person visits to healthcare institutions. There are several advantages to telemedicine and remote medical care, such as better access to healthcare, lower healthcare expenses, increased patient satisfaction, and better patient results.
Remote healthcare services and telemedicine come in a wide variety. The most popular ones are Tele-education, remote patient monitoring, and virtual doctor appointments.
Additionally, there are several drawbacks to telemedicine and remote treatment, such as security and privacy issues, a lack of financing, technical issues, and a shortage of skilled providers.
Despite these impediments, telemedicine and remote healthcare are expanding quickly and playing a bigger role in the healthcare system. These services are expected to become progressively more common and available as technology advances.
Here are some of the future trends in telemedicine and remote healthcare:
- Increasing the use of artificial intelligence (AI): AI may be applied to personalise treatment regimens, increase the precision of diagnoses, and keep track of patient’s health.
- Development of novel telehealth technology: More thorough and individualised treatment will be feasible thanks to new gadgets like wearable sensors and virtual reality headsets.
- Expansion into new areas: Telemedicine and remote healthcare will be utilised to deliver care in new areas, such as managing chronic diseases and mental health.
Application of 3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing in medicine is being used to create customised medical items including prostheses, implants, and surgical guides. This innovation might save expenditures while raising the standard of treatment. A rapidly developing technology, 3D printing has a wide range of potential uses in the healthcare sector. Among the most widespread applications of 3D printing in the medical field, some are mentioned below:
- Producing patient-specific medical devices: 3D printing may be used to produce personalised medical items like implants, prostheses, and surgical guides that are tailored to the anatomy of a single patient. In addition to lowering the risk of problems, this can enhance the device’s fit and functionality.
- Building medical models and educating healthcare professionals: 3D printing may be used to build accurate representations of the human body’s organs, tissues, and tumours. These models can be used to aid in the planning and execution of intricate treatments as well as the education of patients about their conditions. This can assist them in picking up new abilities and methods, as well as in practising approaches in a secure setting.
- Creating novel medications and treatments: Tissue scaffolds for cell culture and intricate drug delivery systems may be made using 3D printing. This can aid in the development of novel treatments and medications by researchers for a number of disorders.
- Customising care: Using 3D printing, it is possible to develop treatments and drugs that are specifically suited to the requirements of a certain patient. This might increase the therapy’s efficacy and security.
Here are some specific examples of how 3D printing is being used in healthcare today:
- A company named Materialise has created a 3D-printed breast implant that is specifically designed for women with tuberous breasts. This type of breast deformity is often difficult to treat with traditional implants, but the 3D-printed implant can provide a more natural and comfortable fit.
- A team of researchers at the University of California, San Diego has developed a 3D-printed surgical guide that can be used to remove brain tumors with greater precision and accuracy.
- A company named Organovo has developed a 3D printer that can be used to create human tissue. This tissue can be used to study diseases, develop new drugs, and create personalized medical implants.
These are some of the numerous uses for 3D printing that are now being made in the medical field. As technology advances, it will probably have a bigger influence on the healthcare sector, enhancing the standard of treatment and enhancing accessibility for all.
The use of blockchain technology to increase the security and effectiveness of healthcare data exchange is one of the significant developments being made in the world of healthcare. Smart technologies, particularly wearable sensors, are being developed to extract therapeutically significant health-related data from physical (body) indicators like heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, respiration rate, and body motion. The technology has now also come up with immersive virtual and augmented reality training and education in the medical field.
Advancements in technology, increased investment in global health, partnerships, collaborations among the government, organizations, and individuals, and innovations altogether make a significant contribution to addressing the challenges to global health and improving health outcomes. The rapid pace of technical improvement has made these developments feasible. These technologies will have a bigger influence on global healthcare as they advance.
The goal of the PG in Obstetrics and Gynecology programme is to standardise the teaching of obstetrics and gynecology at the postgraduate level to benefit from achieving consistency in undergraduate instruction and, ultimately, produce competent obstetricians and gynecologists with the necessary expertise.
Here’s a list of important topics in Obstetrics and Gynecology:
Obstetrics:
- Antepartum Hemorrhage
- Rh-Negative Pregnancy
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Definition, Types of RPL, Causes, Evaluation
- Recurrent Pregnancy Loss: Definition and Causes of RPL, Evaluation, Evidence-Based Management of RPL
- Twin Pregnancy
- Fetal Growth Restriction
- Hypertension in Pregnancy
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Anemia in Pregnancy
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Cephalopelvic Disproportion
- Previous Cesarean Section
- Breech Presentation
- Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Gynecology:
- Primary Amenorrhea
- Secondary Amenorrhea
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
- Fibroid Uterus
- Pelvic Organ Prolapse
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
- Infertility
- Carcinoma Cervix
- Endometrial Carcinoma
- Carcinoma Ovary
These are only a few of the crucial topics covered in MD/MS OBGYN. The specific important topics will change based on the patient’s requirements and the practise setting.
The following are the procedures and operations that an OBGYN student must observe and do during their PG training programme:
1. Obstetrics:
- Venesection
- Culdocentesis
- Conduct normal deliveries
- Episiotomy and its repair
- Application of forceps and ventouse
- Carry out caesarean section delivery
- Manual removal of placenta
- Management of genital tract obstetrical injuries
- Postpartum sterilization/Minilap tubal ligation
- Medical termination of pregnancy-various methods
2. Gynecology:
- Endometrial/Cervical biopsy
- Dilatation and Curettage
- Culdocentesis
- Colpotomy
- Opening and closing of the abdomen
- Operations for pelvic organ prolapse
- Ovarian cyst operation
- Operation for ectopic pregnancy
- Vaginal and abdominal hysterectomy
- Cervical cancer screening
MD/MS OBGYNs need to be knowledgeable in these subjects in addition to the fundamentals of physiology, pharmacology, and anatomy. Additionally, they must be competent to conduct a physical exam and interpret diagnostic testing.
MD/MS OBGYNs are essential to women’s and families’ health. Women receive treatment from them at all stages of life, including adolescence and after the menopause. MD/MS OBGYNs may give their patients the finest treatment possible by staying updated on the most recent medical advancements.
Before the completion of the postgraduation in Obstetrics and Gynecology, MD/MS OBGYN students and residents must be well-versed in the following skills:
- Able to perform normal or abnormal pregnancy and manage labour.
- Proper diagnosis and treatment of gynecological conditions in non-pregnant females.
- Provide quality care to the community in the diagnosis and management of normal and abnormal pregnancy at all stages, may it be Pre-natal care, Intra-natal, and Post-natal.
- Able to provide adequate care to the normal or high-risk neonate.
- Examine and effectively manage all obstetric complications and gynecological emergencies.
- Conduct a thorough assessment of infertile couples and possess a thorough understanding of assisted reproductive techniques/infertility techniques, such as ovulation induction, in-vitro fertilisation, intracytoplasmic sperm injection, gamete donation, surrogacy, related gynecological surgeries, and the moral and legal ramifications of these practises.
- Offering advice for reproductive health and delivering fertility control techniques such as emergency contraception options, reversible and irreversible contraception, etc.
- Provide women who are aborting naturally or who are seeking medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) quality treatment and handle any difficulties that may arise.
- Should understand the principles and legal issues and follow medical ethics.
- Aware of the relevant procedures and strategies to ensure confidentiality.
- Able to interpret X-rays, sonographic pictures, and fetal surveillance methods.
- Clinical quality management and improvement, the performance, interpretation, and implementation of clinical audit cycles, and the creation and utilisation of clinical standards, guidelines, and procedures.
- The MTP Act, sterilisation, preconception, and P.N.D.T. Acts, in particular, should be known and properly used while practising obstetrics and gynecology.
To learn PG OBGYN at your own pace and supplement your college learning, you can subscribe to the OBGYN MD online course. The course is crafted by Dr. Aswath Kumar along with 98 eminent faculty. Dr. Kumar is a renowned practitioner, faculty, and author of the bestselling title – “Exploring New Horizons in Obstetrics and Gynecology” (What to do next after MD in Obstetrics and Gynecology?). In order to meet all of the students’ learning requirements, it promotes concept- and approach-based learning. Along with case discussions on common as well as rare patients in clinical practice, it covers significant obstetrics and gynecology topics.
The OBGYN MD course has been designed based on the past 20 years of question papers from various institutions around the nation, which PG students will find very beneficial as they get ready for their university exams. For students pursuing a master’s degree in obstetrics or gynecology, this course is among the best Obstetrics and Gynecology online courses.
The following are the course features of OBGYN MD:
- OBGYN MCQs & Video Lectures
- Lecture Notes
- Clinical Case-Based Discussion
- Benchmark Studies
- Interactive Drug Formulary
- Regular Chat Shows
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the salary of an Obstetrician and Gynecologist in India?
Ans. During the initial years, the average salary of an Obstetrician and Gynecologist in India is around 12-15 lakhs annually. However, the salary increases with experience, and other factors also influence the salary package such as employment sector, geographical area, area of expertise, and more.
Q2. What are the job profiles associated with the OBGYN specialty?
Ans. The job profiles associated with the OBGYN specialty are Obstetrician, Gynecologist, Family Planning Consultant, Reproductive Medicine Specialist, Reproductive Endocrinologist, Gynecologist-Oncologist Specialist, Professor/Lecturer, Critical Care Expert, etc.
Q3. Which are the most recommended books for MD/MS OBGYN?
Ans. The recommended books for MD/MS OBGYN are FOGSI’s Postgraduate Obstetrics Textbook and FOGSI’s Postgraduate Gynecology Textbook, William Obstetrics, William’s Gynecology, DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics, DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology, Bedside Clinics in Gynecology, and Case Discussions in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Q4. What is the difference between a gynecologist and an obstetrician?
Ans. In OBGYN, OB refers to Obstetrics or Obstetrician, a doctor who specializes in the care of women and their babies during pregnancy and childbirth. GYN stands for Gynecology or Gynecologist, a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of female reproductive disorders.
Q5. What are key areas to focus on for OBGYN residents?
Ans. The key areas to focus on for OBGYN residents are Antepartum Hemorrhage, Rh-Negative Pregnancy, Recurrent Pregnancy Loss, Twin Pregnancy, Fetal Growth Restriction, Hypertension in Pregnancy, Ectopic Pregnancy, Anemia in Pregnancy, Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Primary Amenorrhea, Secondary Amenorrhea, Abnormal Uterine Bleeding, Fibroid Uterus, and Pelvic Organ Prolapse.
Obstetrics and Gynecology (OBGYN) is a branch of medicine that deals with the health of women, including the reproductive system, pregnancy, and childbirth. OBGYN is a compulsory clinical subject in the MBBS curriculum. Being an MBBS student, you will get hands-on experience in OBGYN during clinical rotations. You will observe and assist doctors in delivering babies, performing surgeries, and treating gynecological conditions. OBGYN is a challenging but rewarding field of medicine.
MBBS Prof Exam Pattern
The OBGYN Prof exam comprises two theory papers of 100 marks each and a practical examination of 200 marks. The theory exam consists of short-answer questions, long-answer questions, case-based questions, and objective-type questions. The practical examination includes clinical examination and viva.
Recommended books for Obstetrics and Gynecology
The most preferred books for studying OBGYN in MBBS are DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics (Including Perinatology and Contraception), DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology, Shaw’s Textbook of Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Obstetrics, Bedside Clinics in Gynecology, and Ward Rounds in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Subject weightage in NEET-PG and INI-CET
Concentrate on early preparation for both professional exams and competitive exams, especially if you want to pursue postgraduate studies. The subject weightage of Obstetrics and Gynecology in NEET-PG is about 25–30 questions and about 15-20 questions in INI-CET. The subject weightage clearly shows the importance of the subject in both NEET-PG and INI-CET. Try not to miss any high-yielding topics in obstetrics and Gynecology.
High-yielding topics are a crucial component of a productive study plan that will improve your test-taking efficiency. You must carefully schedule your study sessions, giving priority to time management, the course’s high-yielding topics, and, most importantly, your health.
Important and High-Yielding Topics of OBGYN for MBBS Prof Exams, NEET-PG, and INI-CET
Carcinoma Cervix
Aetiology and Staging of Carcinoma Endometrium
Postmenopausal Bleeding in Diabetics and Hypertensives
Hysteroscopy
Endometrial Ablation
PCOS
Letrozole and Metformin Pharmacology
Ovulation Induction
Carcinoma Ovary Staging
Germ cell tumors, especially Dermoid and Dysgerminomas
Laparotomy
Raloxofene and Bisphosphonates
HRT Indications and Contraindications
Testicular Feminization Syndrome
Treatment of CAH
Turners Syndrome
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
Antepartum and Intrapartum Surveillance
NST and CTG
Biophysical profile and dynamics of amniotic fluid
Doppler of the Uterine Artery
Ductus venosus ‘M’ wave pattern
Malpresentation and Malposition
Placenta-accrete case
Management of PPH
Blood Component Therapy
Management of Shoulder Dystocia
Stages of labour
Ectopic Pregnancy
Molar Pregnancy
Cell-free DNA
Preterm Labour
APH
Sterilisation Surgeries
COVID Pregnancy
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Cesarean section of childbirth
Ultrasound in Pregnancy
Diabetic Mother
Pre-eclampsia
Ca Cervix
Ovarian Cancer
Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
Uterine Prolapse
Fibroid
Postmenopausal Bleeding
Contraception, especially Oral Contraceptive Pills
Endometriosis
Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases
Stress Urinary Incontinence
Important Topics in OBGYN for the Practical Examination
OBGYN is a vast but rewarding clinical subject, and hence, it is highly crucial to learn and excel in the practical curriculum as well. During MBBS, you learn about the anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive system, as well as the diagnosis of common gynecological and obstetrical conditions. You also gain experience performing pelvic exams and other diagnostic procedures. To score well in MBBS practical exams, you should be familiar with the basic principles and procedures of OBGYN and be able to perform the essential clinical skills.
Some of the important topics for the OBGYN practical exam include:
Common Surgical Instruments
Pelvic Examination
History-taking and Clinical assessment of common OBGYN conditions
Bimanual Examination
Vaginal Ultrasound
Speculum Examination
Pap Smear: Cervical Cytology
Breast Examination
Contraception
Infertility
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Normal Labor and Delivery
Postpartum Care
Gynecological Surgery Procedures
Here are some additional tips for preparing for the MBBS practical exams in OBGYN:
- Practice performing the pelvic examination and other clinical skills on mannequins or other simulated patients.
- Read textbooks, review articles, and case studies on OBGYN.
- Attend lectures and tutorials on OBGYN procedures and examinations.
- Shadow an OBGYN physician to get hands-on experience.
- Take practice exams to assess your knowledge and skills.
By following these tips, you can be well-prepared for the MBBS practical exams in OBGYN.
To ace your examinations and escalate your learning, you can enroll in the OBGYN for Undergrads course by Dr. K. Srinivas. The content and video lectures in the course are aligned with the CBME curriculum and also incorporate knowledge from the various standard textbooks. This comprehensive course is well integrated with knowledge of clinical obstetrics and gynecological examinations, case discussions, and highly illustrative clinical and radiological images. This course by the eminent faculty provides access to video lectures, notes, self-assessment questions, and clinical cases.
Case discussions and Qbanks of Obstetrics and Gynecology acquaint the students with the commonly asked questions during the practical exam and viva voce. Hence, this course is ideal for OBGYN students to excel in Obstetrics and Gynecology subject and to eventually score high in MBBS theory exams, practical exams, viva voce, and competitive entrance exams.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the difference between a gynecologist and an obstetrician?
Ans. An obstetrician is a doctor who specializes in the care of women and their babies during pregnancy and childbirth whereas a Gynecologist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of female reproductive disorders.
Q2. What are the high-yield topics in obstetrics and gynecology?
Ans. The high-yield topics in obstetrics and gynecology are Endometriosis, Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases, Stress Urinary Incontinence,
Postmenopausal bleeding in diabetics and hypertensives, Hysteroscopy, Endometrial Ablation, PCOS, Letrozole and metformin pharmacology, Antepartum and intrapartum surveillance, Malpresentation and malposition, Management of PPH, Blood component therapy, Management of Shoulder Dystocia and more.
Q3. Which book is best for OBG MBBS?
Ans. The most preferred books for studying OBGYN in MBBS are DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics (Including Perinatology and Contraception), DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology, Shaw’s Textbook of Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Obstetrics, Bedside Clinics in Gynecology, and Ward Rounds in Obstetrics and Gynecology.