Everything is made for a defined purpose anything which is not intended for further use is termed waste. In the scientific and industrial eras combined with the increasing population, the turnover of products has gone very high increasing the quantum of urban solid waste. With the increased need for health care in a changing society the role of hospitals/nursing homes comes to the forefront.
Hospital waste or types of healthcare waste should include any material generated in healthcare establishments including aqueous and other liquid waste.
Hospital waste means any solid, fluid, or liquid waste material including its container and any other intermediate product which is generated during short-term and long-term care consisting of observational, diagnostic, therapeutic, and rehabilitative services for a person suffering or suspected to be suffering from disease or injury and for parturient or during research of production and testing of biological during immunization of human being.
Types of Healthcare waste facilities are responsible for managing healthcare waste generated within their facilities, as well as waste generated through activities in the community. These facilities must undertake proper segregation, collection, in-house transportation, pre-treatment, and waste storage before handing it over to a Common Bio-medical Waste Treatment Facility (CBWTF) operator.
Therefore, proper management of healthcare waste at these facilities necessitates that all categories of staff understand and adhere to the technical requirements for waste handling as per the Biomedical Waste Management Rules, 2016.
Classifications of Waste Generated from Healthcare Sectors
1. Bio-Medical Waste
It refers to any waste produced during diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of humans or animals as well as related research activities, or during the production or testing of biologicals in health camps. This includes all waste from healthcare facilities that could potentially harm human health or the environment if improperly disposed of. Such waste is considered infectious and must be managed according to the Biomedical Waste Management Rules of 2016 to prevent adverse effects on health or the environment.
Around 10% to 15% of the total waste generated by healthcare facilities constitutes biomedical waste. This category includes materials that have come into contact with patients’ blood, secretions, infected body parts, biological fluids, chemicals, medical equipment, pharmaceutical waste, laboratory discharge, sharp objects like needles and glassware, and plastics.
According to the Biomedical Waste Management Rules of 2016, this waste is categorized into four types based on how it is segregated and color-coded. Each category includes specific types of biomedical waste, as given below:
- Yellow Category
- Red Category
- White Category
- Blue Category
These categories are divided as per the types of waste under each category as follows:
| Category | Type of Waste |
| Yellow | Human Anatomical Waste
Human tissues, organs, body parts, and fetus below the viability period (as per the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act 1971, amended from time to time). |
| Animal Anatomical Waste
Experimental animal carcasses, body parts, organs, and tissues, including the waste generated from animals used in experiments or testing in veterinary hospitals or colleges, or animal houses. |
|
| Solid Waste
Items contaminated with blood, body fluids like dressings, plaster casts, cotton swabs, and bags containing residual or discarded blood and blood components. |
|
| Discarded Medicine
Pharmaceutical waste like antibiotics, and cytotoxic drugs including all items contaminated with cytotoxic drugs along with glass or plastic ampoules, and vials. Etc. |
|
| Chemical Waste
Chemicals used in the production of biological and used or discarded disinfectants. |
|
| Chemical Liquid Waste
Liquid waste is generated due to the use of chemicals in the production of biological and used or discarded disinfectants, Silver X-ray film developing liquid, discarded Formalin, infected secretions, aspired body fluids, liquid from laboratories, and floor washings, cleaning, housekeeping and disinfecting activities, etc. |
|
| Discarded linen, mattresses, beddings contaminated with blood or body fluid, routine mask & gown. | |
| Microbiology, Biotechnology, and other clinical laboratory waste (Pre-treated) | |
| Microbiology, Biotechnology, and other clinical laboratory waste: Blood bags, laboratory cultures, stocks or specimens of microorganisms, live or attenuated vaccines, human and animal cell cultures used in research, industrial laboratories, production of biological, residual toxins, dishes, and devices used for cultures. | |
| Red | Wastes are generated from disposable items such as tubing, bottles, intravenous tubes and sets, catheters, urine bags, syringes without needles, fixed needle syringes with their needles cut, vacutainers, and gloves. |
| White | Waste Sharps Including Metals
Needles, syringes with fixed needles, needles from needle tip cutters or burners, scalpels, blades, or any other contaminated sharp object that may cause punctures and cuts. This includes both used, discarded, and contaminated metal sharps. |
| Blue | Broken or discarded and contaminated glass including medicine vials and ampoules except those contaminated with cytotoxic wastes. |
2. General Waste
General waste includes all waste other than biomedical waste that has not been in contact with hazardous waste or infectious materials, chemicals, or biological secretions, and does not include sharp objects. This type of waste typically includes:
- Newspaper, paper, and cardboard boxes
- Plastic water bottles
- Aluminum cans from soft drinks
- Packaging materials
- Food containers after removing leftover food
- Organic or biodegradable waste, mainly food waste
- Construction and demolition waste
These general wastes are classified as wet wastes and dry wastes and should be collected separately. The quantity of general waste is around 85% to 90% of the total generated from the facility.
3. Other Wastes
Other wastes include electronic devices such as batteries and radioactive materials that are not classified as biomedical waste. They must be disposed of according to specific regulations: the E-waste (Management) Rules of 2016, the Batteries ( Management & Handling) Rules of 2001, and the rules or guidelines established under the Atomic Energy Act of 1962, depending on the type of waste generated.
Guidelines for Management of Healthcare Waste Categories as per Biomedical Waste Management Rules, 2016
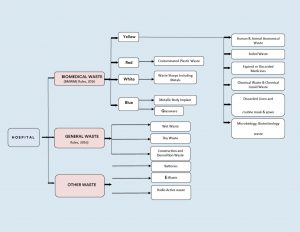

Figure 1: Categorization & Classifications of Wastes in Health Care Facilities.
Color Coding and 4 types of dustbins in hospitals used for Waste Segregation & Collection
According to Schedule I of the Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules of 2016, healthcare facilities (HCFs) must use specific color-coded dustbins and types of containers/bags for segregating and collecting biomedical waste generated within the facility.
| Category | Type of Waste | Colored Container & Type of Container | Treatment Options as per Schedule I |
| Yellow Category |
|
Yellow-colored non-chlorinated Plastic Bags.
NOTE: |
Incineration/deep burial |
| Red Category |
|
Red Colored Non-Chlorinated Plastic Bags (having thickness equal to more than 50u) and containers. | Autoclaving/microwaving/chemical treatment |
| White Category |
|
White Colored translucent puncture-proof, leak-proof, tamper-proof containers. | Autoclaving/microwaving/chemical treatment and destruction/shredding |
| Blue Category |
|
Puncture-proof, leak-proof boxes or containers with blue-colored markings. | Disposal of wastes and secured landfill |
Bio-Medical Waste Collection
Time of Collection
- Daily Collection: Ensure daily collection from each hospital ward at fixed intervals.
- Timing Adjustments: Schedule collections based on waste generation patterns throughout the day.
- Separate Collection: Avoid collecting general waste concurrently with biomedical waste.
- Visitor Waste Management: Collect general waste immediately after visiting hours to prevent accumulation.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Provide PPE to staff handling biomedical waste.
Packaging
- Filling and Sealing: Fill biomedical waste bags and sharp containers up to three-quarters full and seal them promptly.
- Sealing Methods: Use ties or plastic tags to seal bags to avoid stapling.
- Availability of Replacement: Ensure replacement bags or containers are readily available at collection points.
- Labeling Requirements: Label bags and containers with biohazard symbols, including details like date, type of waste, quantity, and sender’s and receiver’s information.
- Barcode Compliance: Affix barcoded labels on the bag as per CPCB guidelines.
Labeling
- Biohazard Symbols: Clearly label all bags, containers, and bins with biohazard or cytotoxic symbols as per BMWM Rules, 2016.




Interim Storage
- Minimization: Discourage interim storage of biomedical waste in patient care areas.
- Designated Areas: Store biomedical waste temporarily in designated, low-traffic areas if necessary.
Treatment Option for Bio-medical Waste Types
| Treatment Options | Biomedical Chemical Processes |
| Thermal Processes Low-heat Systems (93-177oC) |
|
| High-heat Systems |
|
| Mechanical Processes |
|
| Irradiation Processes |
|
| Biological Processes |
|
| Considerations for Processing Incineration |
|
| Autoclaving |
|
| Microwaving |
|
| Deep Burial |
|
| Sharp Materials Disposal |
|
| Radioactive Waste |
|
| Mercury Control |
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is clinical waste, and how is it different from infectious waste?
Ans. Clinical waste includes all waste generated from medical facilities, including non-infectious materials like packaging and expired medications, whereas infectious waste refers to waste contaminated with pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms.
Q2. What are the proper disposal techniques for biomedical waste, particularly sharps waste?
Ans. Sharp waste like needles and scalpels, must be disposed of in puncture-proof containers specifically designed for sharps disposal. These types of containers are sealed and handled carefully to prevent injuries and potential infections during disposal.
Q3. How does improper medical waste management contribute to the spread of diseases?
Ans. Improper management of biohazardous waste can lead to contamination of the environment and increase the risk of spreading infectious diseases. Pathogens present in medical waste, if not managed correctly, can infect healthcare workers, patients, and the normal public.
Q4. What is some risk associated with inadequate handling of pathological waste?
Ans. Pathological waste which includes tissues, organs, and body parts, poses significant health risks if not properly managed. Exposure to such waste can lead to infections or exposure to hazardous chemicals used in treatments.
Q5. Why is it important for medical facilities to use appropriate medical waste containers?
Ans. Medical waste containers are designed to safely store and transport various types of medical waste, including biohazardous materials and sharps. Using proper containers minimizes the risk of accidental exposure and ensures compliance with regulations for safe disposal.
DigiNerve is constantly evolving to enhance your experience while you’re on your journey to becoming a Top Doc. We are excited to bring you the latest updates with our commitment to ensure a seamless journey on the go.
Read on the July edition (Vol – 1) of our monthly newsletter to know the latest updates.
CONTENT UPDATES
PostGrad Course Updates
Dermatology MD:-
1. Chat show on ‘Discussion on Leprosy’ by Dr. Vivek Vasudev Pai, Dr. Shraddha Mahobia, and Dr. Samira Siddiqui Khatoon Mohd. Hanif has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- To learn the approach to a patient with leprosy.
- To understand the current scenario of leprosy and the National Strategic Plan for 2023-2027 for India.
- To learn the approach to patients with lepra reactions and relapse.
- To understand the management of patients with ENL reactions and relapse.
Pediatrics MD:-
1. Chat show on ‘Approach to a Child with Asthma’ by Dr. Piyush Gupta and Dr. Prawin Kumar has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Clinical presentation of asthma in children.
- How can a diagnosis of asthma in children be established?
- What is the role of the Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) in the diagnosis of asthma.
- Management of Asthma in Children.
Medicine MD:-
1. 8 new topics have been added to the following modules:
| Module | Section | Topic |
| Rheumatology | Long Case Discussions | Gout |
| Infectious Diseases | Clinical Scenarios | Amoebic Liver Abscess |
| Systemic Fungal Infections | ||
| Japanese Encephalitis | ||
| Critical Care Medicine | Decision Making | Central Venous Line |
| Intubation in Critically Ill Patients | ||
| Cardiology | Basic Sciences | Treadmill Test |
| Endocrinology and Diabetes | Long Case Discussions | Approach and Management of Hyponatremia |
Note: The topics mentioned above also include 39 new self-assessment and 16 benchmark trials.
Update Your DigiNerve App for Better Experience.
To read the updates shared in the Monthly Newsletter June (Vol-2), click here.
Embarking on the journey to secure a seat in a postgraduate medical program in India requires a deep understanding of the process of counselling for NEET PG 2024. This guide will walk you through every aspect, ensuring you are well-prepared to take the next step in your medical career and become successful medical graduates!
Why NEET PG 2024 Plays a Crucial Role?
NEET PG (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test for Postgraduate courses) is a national-level entrance exam for aspiring doctors seeking admission to MD, MS, and PG Diploma courses. This highly competitive exam evaluates candidates’ knowledge and aptitude, crucial for securing a seat in various medical institutions across India. The choices of colleges depends upon the seat allotment process, which is further dependent upon the NEET PG 2024 results and successful counselling rounds.
What are the Key Highlights of Counselling for NEET PG 2024?
NEET PG 2024 Exam Date
- It was earlier on June 23, 2024.
- At present, a crucial step has been taken. So, the admission journey of seats seem a little delayed. The new date yet to be declared.
Bodies for the Process of Counselling for NEET PG 2024
- All India Counseling: This counselling process is conducted by the Directorate General of Health Sciences (DGHS) on behalf of the National Medical Council (NMC).
- State Quota Counseling: This counselling process is managed by respective state authorities.
Seat Distribution
- All India Counseling: 50% of government seats, 100% of deemed and central university seats, ESIC, AFMC, AIIMS, and JIPMER seats.
- State Quota: 50% of government seats and 100% of private seats within the state.
What are the Types of NEET PG 2024 Counselling?
NEET PG Counselling MCC: The Centralized Counseling
Centralized counseling, conducted by MCC (Medical Counselling Committee), involves the seat allocation in government colleges across India. This counselling session ensures seats in the Govt. medical institutions. These seats are open to candidates from all states, based on their NEET PG ranks. Here, this selection process is for the Govt. based colleges.
The State Counselling
State counseling’s counselling process is managed by respective state governments/authorities, allocating seats reserved for candidates from their states. The seat allotment is based on NEET PG ranks and specific state eligibility criteria. Once the counselling schedule is out and counselling for seat allotment is done, the academic session can begin!
Who is Eligible for NEET PG Counselling 2024?
It is important for medical students to fulfil the eligibility criteria for counselling process. Availability of seats definitely are a factor in allocation of seats but before that, eligibility matters. To participate in counselling, eligibility plays a crucial role.
NEET PG 2024, Candidates Must Meet The Following Criteria
1. Educational Qualification
A recognized MBBS degree or Provisional MBBS Pass Certificate from a recognized institution is important. Also, don’t forget to keep these academic details safe for further counselling process. The counselling authorities always run after the verification of relevant documents and personal details.
2. Internship Completion
Completion of a one-year rotatory internship by a specified date is also required. A NEET PG qualified candidate must also be a successful intern!
3. NEET PG Score
Medical sciences are difficult until and unless it’s a passion. Passion is important for getting apt scores for admission. So, attain great scores!
But the eligibility says- get the minimum scores or minimum qualifying percentile in the NEET PG exam. This is just the eligibility criteria. Medical students must not lose hope to crack the medical courses with flying colours.
Summing Up Eligibility for NEET PG Counselling 2024
This year, the eligible candidates are who:
- Meet the minimum qualifying percentile.
- Have completed their MBBS degree and internship.
- Hold a valid NEET PG 2024 score.
What is the NEET PG 2024 Counseling Process? (Step-by-Step Guide for NEET PG Counselling)
The Events take place in the following order for Round 1, Round 2, and Round 3 before final step:
NEET PG 2024 Counselling Registration
⬇️
Choice Filling and Locking
⬇️
Counselling Result
⬇️
Reporting
Step 1: NEET PG 2024 Registration
If someone asks, how to apply for NEET PG counselling, just say- it’s easy and hassle-free! The first step is ‘Registration for Counselling’ on the official NEET PG 2024 counseling website (https://mcc.nic.in/). Use your NEET PG roll number and other required details to complete the online registration form. Fill in correct details, as there must be no discrepancies in application documents. Document verification is done at the later stages.
- Reach out to the official website of the Medical Counselling Committee (MCC). Counselling for admission to your own choice of colleges could begin with this.
- Choose ‘PG Medical Counselling’
- A fresh application process needs to be done. Exam registration would not count here.
- Pen down the login credentials and keep them safe.
- Next process involves logging in and filling in the application form
- Next, a candidate needs to enter the details, personal and academic both.
- Cross check the application form before submission and fee payment.
- Then finalise the application fee, and you are good to go!
Step 2: Payment of NEET PG Counselling Fees
After registering, candidates must pay the prescribed NEET PG counselling fees. The fee structure for NEET PG counseling is mentioned on the MCC website clearly.
Step 3: Choice Filling and Locking
Candidates must fill in their preferences for choice for college and choices of courses based on their ranks and eligibility. College authorities give seats in government colleges after students also fill up their preferences. Ensure you lock your choices before the deadline, as changes cannot be made afterwards.
Step 4: Seat Allotment
Counselling for seat allotment is a rigorous process. After that, when actual time of allotment of seats comes, students eagerly wait for that moment. Seat allotment lists are based on NEET PG ranks, preferences, and seat availability. The NEET PG counselling result is published on the official website.
What a dedicated process! Surely, medical field isn’t easy to crack. But with discipline and preparation strategy, medical professionals can always remain in the merit list!
Step 5: Reporting to Allotted Medical College
Candidates through with the counselling process and having name in the seat allotment list must report to the respective college within the stipulated time frame. Ensure you carry all necessary documents for verification process. Everything is planned and aligned by the authorities usually. However, with whatever happened recently, students must be prepared for everything. Usually there isn’t a delay but you may expect delays during verification for unavoidable reasons.
What are the Documents required for NEET PG 2024 Counseling?
- Valid ID Proof
- Birth Certificate
- NEET PG 2024 Admit Card Caste Certificate (if applicable)
- MBBS Marksheet & Degree Certificate
- NEET PG 2024 Admit Card
- NEET PG 2024 Score Card
- Internship Completion Certificate
- Disability Certificate (if applicable)
- Non-creamy layer certificate (if applicable)
What is the NEET PG 2024 Counseling Cut-off?
Only candidates who meet the NEET PG 2024 cut-off are eligible for counseling. Carry all your documents during scheduled counselling dates to avoid issues during counselling. The cut-off percentile is announced along with the NEET PG result.
For reference, the NEET PG 2023 cut-off was:
- Unreserved (UR): 50th percentile, 291 marks
- SC/ST/OBC: 40th percentile, 257 marks
- UR PWD: 45th percentile, 274 marks
What is the NEET PG Counseling Registration and Fees?
To participate, candidates must register online and pay the counseling fees as specified. The registration process involves filling out an application form and submitting preferences for colleges and courses.
Open States for NEET PG 2024 Counseling
Certain states allow candidates from other states to participate in their counseling process. Check the specific guidelines of each state to understand the eligibility and application procedures.
NEET PG Counseling Result
The result of the NEET PG counseling, including seat allotment, is released in multiple rounds. Candidates can check their allotment status on the official MCC website.
Conclusion
Navigating the NEET PG 2024 counseling process is critical for securing a postgraduate medical seat in India. By understanding the steps involved, eligibility criteria, and essential documents required, candidates can ensure a smooth and successful journey toward their MD or MS degree. With careful planning and timely action, achieving your dream of advanced medical education is well within reach.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the rounds in Counselling Process called?
Ans. There are total 4 rounds for All India Quota NEET PG 2024:
- Round One
- Round Two
- Mop-up Round
- and Stray Vacancy Round
There is no return of seats to respective states post round two.
Q2. What is the exam pattern of NEET PG 2024?
Ans. NEET PG has a 200 multiple-choice questions/ MCQs based exam pattern. It’s a computer based exam, some stating it an online mode paper, while calling it a ‘Digital Computer Based Exam’ is a much better thing to say.
The exam consists of 3.5 hours, where wrong answers get negative marking. Each correct answer gets four marks, and wrong answers get minus one mark each.
Q3. How to prepare to get seats for counselling for NEET PG 2024?
Ans. The preparation tips include staying up to date with the dates and schedule from the official website or official resources. Apart from this, it is all with knowledge. Study hard and excel in the exam.
Also, one must follow these to stay prepared:
- Always stay updated with info related to entrance exam, specific documents required on the exam day, info on the dates of counselling and tentative data of availability of seats, cut-off percentage, etc.
- Don’t forget to attempt NEET PG with the best of your efforts. Don’t get scared from the question paper. Be prepared for the exam hall challenges and stay relaxed while attempting the exam.
- Last, but not the least, after getting the desired score in NEET PG 2024 , while registering for counseling process, don’t forget to fill the application form correctly. Keep your documents like Aadhar card, marksheets, and other details handy. Always cross-check the details while registrations.
- Do not forget to be on time. Arrange your accommodation/travel beforehand. It’s a once in a lifetime chance.
Q4. What are the dates for NEET PG 2024 Counselling?
Ans. With the changes in schedule of examinations, the tentative calendar for NEET PG 2024 Exam seems to be as follows:
- Results of NEET PG are expected to be released in July, 2024
- From August 5th, 2024, the counseling process is expected to start
- Round 2 results and choice filling for round 3 are expected in the month of September, 2024.
- The online stray vacancy round result is expected to go on floors by October, 2024.
The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) UG is one of the most necessary exams for students to get admission in the medical colleges of India. The NEET UG 2024 medical entrance exam has been particularly eventful, with various incidents and developments that have kept candidates on their toes. Here’s everything you need to know about the NEET UG 2024 exam, including key dates, incidents, and what to expect next.
When was NEET UG Exam Date 2024 Scheduled?
The NEET UG 2024 exam was earlier scheduled and taken on May 5, 2024. Students in the examination hall would have never thought of the future. Due to disruptions at some places where the exam was held, a retest was scheduled for later.
When was the Retest?
The retest took place on June 23, 2024, in six cities across India for 1,563 candidates who experienced issues during the initial exam at the examination centre. Entrance examinations facing issues have become highlighted news in the country. NEET UG being one of those!
However, this National eligibility cum entrance test ‘retest’ was taken again for specific candidates who faced issues, and not all.
These specific candidates were granted grace marks due to the loss of time at their exam centres on May 5. The admit cards for this retest were released on June 20, 2024. Now, the results are expected to be declared on June 30, 2024.
What Was The NEET 2024 Paper Leak Controversy?
NEET UG was in news all around due to an alleged paper leak. The case is now with the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), assigned by the Ministry of Education.
This controversy intensified the demand for a re-exam for all 24 lakh NEET UG aspirants. However, as per authorities conducting a retest for everyone was not feasible as it would disrupt the genuine candidates’ candidature and schedule.
How Did Candidates Register For NEET UG?
Before the exam leak, when students had no clue of what would happen, they worked hard to seamlessly register themselves and get through the application form with no stress!
However, the registration process, and keeping registration credentials and documents safe is really challenging. Thankfully, it did not go waste for all. Only some specific students who got grace marks re-appeared for the NTA NEET UG Exam.
How Did Students Register For NEET UG?
Students went through rigorous application form filling. The National Testing Agency has an aligned application process. Candidates went through the same.
Amid digital and online modes, uploading documents, waiting for correction window, staying tuned to wrap up before application window closes, and keeping a close eye on the future admission process requirements, students really worked hard. Candidates kept the registration credentials safe, perfected the time management skills while application, and kept their hall tickets safe too.
What Next To Expect After NEET UG Exam Date 2024?
Followed by NEET UG exam is the counselling. So, candidates need to prepare themselves for counselling after results.
What is the NEET UG 2024 Counselling Schedule?
Despite the controversies, the NEET UG 2024 counselling will proceed as scheduled. At the time of admission, while students stand at the medical colleges, it will all be in their memories. Such a roller coaster!
NEET UG Counseling is expected to commence from July 6, 2024. The counselling process will be based on NEET 2024 scores and will be conducted for admissions to various quotas seats, including the 15% All India Quota (AIQ), 85% state quota, deemed/central universities, private colleges, AFMS/ESIC institutes, and AIIMS and JIPMER campuses. The National Testing Agency announced the NEET result for over 24 lakh students on June 4, 2024. All of these students are ready to get into the medical colleges of their choice. For sure, taking up medical courses isn’t a cakewalk.
Eligibility for NEET UG Counselling Process 2024
To participate in NEET UG Counselling 2024, candidates must meet the following eligibility criteria:
- Qualified in NEET UG 2024: Candidates must have qualified in the NEET UG 2024 exam by securing the minimum marks/ percentile score required.
- Minimum Age Requirement: Candidates must be at least 17 years old as of December 31, 2024.
- Educational Qualification: Candidates must have passed 10+2 with Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English as core subjects from a recognized board.
- Nationality: Indian citizens, Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and Foreign Nationals are eligible.
- State Eligibility: For state quota seats, candidates must meet the domicile requirements specified by the respective state authorities. Category candidates can attach their proofs also while process is on.
Steps for NEET UG Counselling 2024
1. Filling Registration Form for NEET UG Counselling 2024
- Visit the official website of the Medical Counselling Committee (MCC) or the respective state counselling authority.
- Start the application process by registering as a new candidate.
- Enter required details and registration credentials like NEET roll number, registration number, name, mother’s name, date of birth, mobile number, and email ID.
- Create a password and complete the registration process.
2. Payment of NEET UG Counselling Fee
- Pay the counselling application fee online using Net Banking, Credit Card, or Debit Card.
- The application fee structure will be specified on the official website. The application process, (separate) for counseling is incomplete without payment.
3. The Choice Filling and Locking
- Log in using the registration credentials created during registration process. It is all via online modes so try to be digitally equipped.
- Fill in the choices of medical colleges and medical courses in order of preference.
- Lock the choices before the deadline. If your medical colleges’ and courses’ choices are not locked, the system will automatically lock them.
4. Seat Allotment In NEET UG Counselling
- The MCC/state counselling authority will conduct the seat allotment process based on the choices filled, NEET UG rank, reservation criteria/quota seats, and seat availability.
- The seat allotment result will be published on the official website.
5. Reporting to Allotted Medical College
- Download the seat allotment letter from the official website.
- Report to the allotted college within the specified time frame.
- Carry all required documents for verification. It’s an offline mode process. Just like online application form, here in physical documents verification, a candidate has to be very careful.
6. Document Verification
Candidates must present original documents and their photocopies for verification.
Documents required typically include:
- NEET UG 2024 Admit Card (You can’t skip this one!)
- NEET UG 2024 Rank Card (After all the hard-work, forgetting scorecard would be an issue!)
- Class 10 and 12 Mark Sheets and Certificates (Forget not to show your pro levels of English subjects, Physics, Chemistry and Biology)
- Birth Certificate (It’s an important proof)
- Category Certificate (if applicable)
- Domicile Certificate (if applicable)
- ID Proof (Aadhar Card, Passport, etc.)
- Passport-sized Photographs
7. Admission Confirmation
- After successful document verification, candidates must confirm their admission process by paying the required fee at the allotted medical college.
- Obtain the admission confirmation letter from the college. Time of admission is crucial. Stay motivated. You already have the score for admission! Now you need only some positivity.
8. Reporting for Further Rounds
- If candidates wish to participate in further counselling rounds for better choices, they need to follow the instructions provided by the counselling authority.
9. Mop-Up Round (if applicable)
- If seats remain vacant after the first few rounds, a mop-up round will be conducted.
- Candidates who did not get a seat or want to upgrade their allotted seat can participate in this round. From day one in that exam hall to this mop-round of counseling process, it’s a rigorous journey. But faith helps a candidate sail through!
- Not to forget, for specific details and updates, regularly check the official websites of MCC and state counselling authorities.
What was the NEET 2024 Exam Pattern and Cutoff?
The cutoff scores for NEET UG 2024 are as follows:
- General Category: 720-164
- SC/ST/OBC Category: 163-129
- General-PwD Category: 163-146
- SC/ST/OBC-PwD Category: 145-129
The pattern is as follows:
- 200 Questions Format: The NEET UG 2024 exam pattern consisted of 200 questions, out of which candidates had to answer 180.
- Three Subjects: The questions covered Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.
- Marking Scheme: The marking scheme awarded four marks for each correct answer, deducted one mark for each incorrect answer, and gave no marks for unanswered questions.
- Candidates who qualify for the test will be eligible to participate in the NEET 2024 counselling process.
What are NTA’s Preparations for the Future of NEET UG EXAM?
The NTA has clarified that despite reports of a question paper leak at one examination center, the integrity of the NEET exam remains intact. The incident at the Sawai Madhopur center in Rajasthan, where students took question papers away against their will, did not affect other centers. The NTA also clarified that all question papers were accounted for and that strict security protocols were in place, including CCTV surveillance and restricted access once the exam began.
How Many Candidates Had Registered For NEET UG EXAM DATE 2024?
NEET UG 2024 saw a record-high number of registrations, with 20+ lakh students, including 10 lakh + male students and 13 lakh+ female students. It could happen because many smaller cities were included in the list of exam centers especially in the Northeast, Puducherry, Jammu and Kashmir, and other states.
What Must Be Guidance For NEET Aspirants in Future?
For aspirants preparing for future NEET exams, resources like online courses can be highly helpful. With multiple courses meticulously designed here, students can prepare really well for future exams.
Conclusion
The NEET UG 2024 has been a rollercoaster for many candidates, with its fair share of controversies and challenges. However, with the retest completed and the counselling process set to begin, students can finally see a clearer path forward. It’s essential for candidates to stay focused and not be swayed by rumours or misinformation. As the results and counselling processes unfold, aspirants should stay updated with official announcements and prepare for the next steps in their medical careers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is NEET UG Exam Date 2024 Scheduled?
Ans. Yes. NEET UG Exam was done on May 5th, 2024. But due to issues in the exam hall and specific centers, some candidates appeared for the re-test. This exam for admission was held again on June 23, 2024.
Q2. What will happen next after NEET exam 2024?
Ans. Rounds of counselling are scheduled further. The counselling process will begin as decided previously. It will most probably begin from July 6, 2024.
Q3. What is the eligibility for Counselling process?
Ans. Having qualified NEET UG exam is the first priority. To clear this exam, it is advisable to practice hard with mock tests, participate in mock competitive exams, practice questions from various sources, and analyse the previous year questions and answer key.
Over a lakh candidates participate in the exam every time. Those who get qualifying marks can participate further in the application process of NEET UG counseling process. Not to forget, the candidate must be at least seventeen years of age to be eligible for the same. For more details, refer to the blog above.
Q4: What should be the study schedule for NEET UG/PG Exams?
Ans. With so much going on in the news, it is advisable to stay calm. Do not worry about getting a minimum score, instead worry about exam preparation effectively and efficiently. Go through exam syllabus in detail, study in online modes to save time, perform mock tests, practice as per exam pattern and analyse previous year question papers to understand difficulty level.
Q5. What is the exam pattern of NEET UG exam? Would it continue in the future?
Ans. For qualifying examination, the question types are not many! It’s only an MCQ format. The NEET UG exam consists of 200 multiple-choice questions. For incorrect answers, there’s negative marking. One wrong answer snatches one mark from the candidate. While, one correct answer would fetch four marks. There is no mark given for unattempted response. As of now, the exam pattern, exam preparation, and exam syllabus seems to be same for future, inclusive of Physics, Chemistry, Biology as core subjects for the exam prep. However, it is advisable to keep a close check on the National Testing Agency and other official websites for any change, if happens.
Q6. What sources to trust for further updates?
Ans. Only official websites of National Testing Agency must be trusted. With multiple news circulating all over, there must only be websites from official sources to clarify things. For future reference, the website is: https://www.nta.ac.in/
DigiNerve is constantly evolving to enhance the user experience while you’re on their journey to becoming a Top Doc. We are excited to bring the latest updates with our commitment to ensure a seamless journey on the go.
Read our monthly newsletter’s June edition (Vol – 2) for the latest updates.
CONTENT UPDATES
PostGrad Course Updates
OBGYN MD:-
1. 5 new topics have been added to the following modules:
| Section | Module | Topic |
| Gynecology | Menstrual Abnormalities | Menopause Hormonal Therapy |
| Obstetrics | Procedural Videos | Caesarean Section |
| Third Stage of Labour and its Complications | Postpartum Psychiatric Illness | |
| Medical Disorders in Pregnancy | Case Discussion: Pregnancy Induced Hypertension | |
| Labour (Normal and Abnormal) | Management of Abnormal Labour |
Note: The topics mentioned above also include 25 new MCQs and 10 benchmark trials.
2. Chat show on ‘Primary Amenorrhea’ by Dr. Aswath Kumar and Dr. Lilly Varghese has been added to the course:
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Different etiologies of primary amenorrhea
- Important subtypes: Clinical features
- Investigations
- Management: Hormonal and surgical treatment
Surgery MS:-
1. Chat show on ‘Management of Head Injury’ by Prof. (Dr.) Nilay Mandal and Dr. Arjun Dasgupta has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Initial assessment of a head injury patient
- Prevention of secondary injury and management of raised ICP
- Types of head injury and their radiological findings
Professional Course Updates
MRCOG Part 2:-
1. Webinar on ‘Discussion of Important Questions and Doubt Clearance (MRCOG-2 EMQs)’ by Dr. Richa Saxena has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the webinar were:
- To discuss important questions of MRCOG part 2 exam.
- To prepare for exam with the help of carefully curated questions with detailed explanations, images and flowcharts.
- To ease the journey of clearing MRCOG exam.
- To understand latest patterns of questions as per RCOG curriculum (EMQs).
Technology Updates
1. Inclusion of HYQs
A new section of High Yield Questions has been included in the courses- Cracking MRCOG- PART 1 and Part 2. It comprises HYQs from the year 2016-2022.
2. Free Access to Dr. Wise
An additional benefit of 10 queries for non-subscribers.
3. Customised Question Bank Generator
- A new feature of Customised Question Bank Generator has been added, under the course of Cracking MRCOG Part-1.
- Beneath the ‘Test’ section, users can generate questions in the ‘Practice’ or ‘Test Mode’ as per the choice of difficulty level and as per the number of questions required.
Update Your DigiNerve App for Better Experience.
To read the updates shared in the Monthly Newsletter July (Vol-1), click here.
The NEET PG 2024 examination is one of the most crucial milestones for medical students in India aiming for postgraduate education. It has recently seen a dramatic turn of events. This blog will cover all the important details and the complete NEET PG exam schedule. So, if you’re wondering what is the new NEET PG exam date 2024, read ahead to get some clarity over the same.
What is NEET PG 2024? An Overview
NEET PG (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test for Postgraduates) is an important examination for medical graduates aspiring to pursue postgraduate courses of MD (Doctor of Medicine), MS (Master of Surgery), and other diploma courses in India. The exam is conducted by the National Board of Examinations (NBE).
Why has NEET PG 2024 Postponed? Latest Updates
Read below to figure out why NEET PG 2024 has been postponed!
What is the Ministry’s Announcement on NEET PG Exam Date 2024?
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) turned the tables for many. It recently announced the postponement of the NEET PG 2024 exam, which was originally scheduled for June 23, 2024. Students have reacted with dissatisfaction. How many times Neet PG is conducted in a year? It happens once! While students wait for NEET PG exam time, this news has sparked discontent among candidates.
What are the Reasons to Postpone NEET PG Exam Time?
The postponement of the NEET PG exam schedule was announced just a day before the official scheduled exam date, causing stress among the candidates. The Ministry has strong reasons for “precautionary measures” and aims to ensure fairness and transparency. Post incidents linked to NEET UG, UGC NET, and CSIR NET, this decision has been taken to ensure a thorough assessment of the examination process.
What is the Revised NEET PG Exam Date 2024?
As of now, there is no information regarding revised NEET PG exam schedule. The NEET PG 2024 seems to be on hold till the further official announcement. Presently, candidates are highly advised to keep an eye on the official website and notifications from the Ministry for the latest updates. At the same time, students must not take stress, rather stay calm and confident of their preparation.
What was the Original NEET PG 2024 Schedule?
Before the postponement, the NEET PG 2024 exam was supposed to follow a well-defined schedule. The details of previous schedule are as follows:
- Registration Start Date: April 16, 2024
- Last Date to Submit Application: May 6, 2024
- Last Date to Modify Incorrect Images: June 10, 2024
- Admit Card Release Date: June 18, 2024
- NEET PG Exam Date: June 23, 2024
- Result Date: July 15, 2024
What Preparation is Needed for NEET PG 2024 Exam?
There are preps required before the exam and after the exam. Now that the exam has been delayed, students have a chance to utilise the time for better preparation.
“Dear Candidates,
NEET PG 2024 Exam has been delayed not to cause you stress but to ignite the fire of ‘last-moment preparation.’ Now that you have a chance, how about giving your final preparation an edge, rather than stressing over things?
Let the authorities do their work. As an aspiring candidate, you do your work! Your work of- Staying focused, not getting impacted by external factors, and preparing till the last moment without anxiety.”
How Can Candidates Prepare before NEET PG 2024 Exam?
Before the NEET PG exam time, there’s a lot that students need to be prepared for.
- Documents Prep: Admit Card must be downloaded in advance. Registration login credentials must be kept safe during the registration process. Be careful while filling basic details. It stays till the last. Also, whenever NEET PG exam time is scheduled, reach before time to avoid the hassle of exhaustive verification process.
- Study Prep: It must include all sorts of mock tests and guidance from the industry experts in the form of webinars, videos, or online courses. This NEET PG is the way out to reach your dream medical college. So, before beginning the ultimate academic session, be 100% prepared.
- Psychological Prep: With meditation and focus exercises, the mind must be prepared for all sorts of challenges. The latest news is an example of how things can impact.
What are the ‘After NEET PG Exam Preps’?
After the exam is done, the results would be available in a PDF format on the official website of NBE. Here, login credentials would be required again to download the scorecards. The procedure is:
- Go to the NBE website
- Login via credentials (ID & Password)
- Download the scorecard
- Don’t forget to cross-verify the details (Name, Roll Number, Rank, etc.)
- What to do when NEET PG 2024 Exam results are out?
Post-Result Processes
After the results are announced, qualified candidates would be able to download their scorecards and take part in the counselling process further.
- First Download Scorecard: In PDF format, download the scorecard from the official website.
- Check the Merit List: Those who become eligible for counselling, their merit list will be published.
- March ahead for Counselling: The qualified candidates can then register for counselling sessions to ensure their seats in the postgraduate medical courses.
But What is the NEET PG 2024 Counselling Process?
- Post declaration of NEET PG exam results, first and foremost, get registered for the Counselling Process.
- Next, fees need to be submitted online.
- Next, Candidates need to choose the colleges and list of courses from the list and lock it.
- Then candidates can look forward to a PDF list of seat allotment.
- Post seat allotment, log in to MCC website and download the seat allotment letter. Don’t forget to reach on time for the counselling.
- Next comes the documents verification.
- Then you have NEET PG Merit List, where candidates are allotted seats.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, the news of postponement of the NEET PG 2024 exam has shaken the students. However, it is advisable to students to stay updated with the news from a trustworthy source or official websites of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the National Board of Examinations. The real victory lies in winning over such unpredictable situations. So, dear candidates, all the very best. Stay focused amid unexpected changes. Set right your schedule for neet pg preparation and go ahead!!!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How to download the NEET PG 2024 Exam Admit Card?
Ans. The admit cards for NEET PG 2024 were available on 18, June ,2024 itself. Students had downloaded it using their login credentials from the official website. It is highly important for the candidates to keep their login credentials safe, considering the crucial present times. While registration for the NEET PG Exam, login credentials are given. Those are to be kept safe to download the admit card details later.
Q2. What is the NEET PG 2024 Exam pattern?
Ans. The NEET PG 2024 exam will consist of 200 multiple-choice questions. The exam is computer-based, requiring candidates to be familiar with digital mediums.
Q3. What is the NEET PG exam time duration?
Ans. Candidates will be given 3.5 hours to complete the test. Since it is a time-based test, candidates need to wrap up accordingly. Therefore, it is highly advised to the students to get familiar with time-based mock tests beforehand for real-time simulation.
Q4. What should be the schedule for neet pg preparation?
Ans. It depends from candidate to candidate. However, it is recommended to add mock tests in the schedule for neet pg preparation. These give real-time simulation. Video lectures from experts also form a great basis of prep.
Q5. What is the application process of NEET PG exam?
Ans. The application process is via online mode. Once the application dates are out, medical students need to register themselves. Post registration, there is a time for candidates to wrap up the details within edit window. Before correction window closes, the application form needs to be absolutely correct.
During registrations, candidates are forwarded with credentials inclusive of ID and password that is used till then end to view results, download scorecard, and so on. The NEET PG exam is in computer-based mode. So, from filling application form i.e online registrations to getting details of exam center , and from counselling schedule to seat allotment process, it is all digital.
Q6. What is the NEET PG Exam marking scheme?
Ans. Students undergo a lot of pressure while thinking about type of questions, unattempted questions, negative marking, and minimum cutoff. However, medical students must not take the stress. The marking scheme of NEET PG is simple to understand. This NEET PG exam for students possesses 200 questions in the question paper. It is of 800 marks in total. For every correct response, the student gets four marks, while for every incorrect response, one mark will be deducted. So, correct answer fetches a mark and incorrect answer indicates towards negative marking. There would be no mark given for any unattempted or reviewed question. Therefore, it is advisable to take mock tests beforehand and review answer key during the practice sessions.
Q7. How to check NEET PG exam results?
Ans. NEET PG exam is yet to happen. Surely one of the most important exams in the medical field. Once it is done, students wait for the results eagerly. The steps to check results are as follows:
- Reach out to the official website of NBE.
- Login via credentials
- Download the scorecard and save in PDF format
- Verify the details and save it
- Keep hardcopy safe for counselling process
Q8. Who all are the eligible candidates to take part in the NEET PG exam?
Ans. The eligibility criteria is to have an MBBS degree or a provisional MBBS passing certification that is recognised by the MCI. Moreover, it is highly important to have one year of completion of internship.
Apart from this, proper registration must have been done. Students need to wrap up application fees, check details for a correct registration form, double check registration credentials, cross-verify application details, and keep a track of dates to avoid any miss-communication. All of it together contributes to eligibility.
Q9. What must be done now when the NEET PG schedule is not released?
Ans. Earlier the application form for NEET PG was out and candidates had to finish registration process till MAY 6, 2024. With release of Admit Cards on June 18, 2024, the candidates are now waiting for the NEET PG exam date. While it was scheduled for June 23, 2024, it is yet to be scheduled now. At this moment, when students are waiting for the date, this time must be used to stay calm. Keep a close check on the official websites to get the updates.
NEET UG 2024 results are in the news these days. The NEET UG results are out and there’s a lot that you need to know. Headlines have been talking a lot about medical students, grace marks, negative marking, exam paper chaos, compensatory marks, and suspicious qualifying marks. To clarify the confusion and update you about the NEET UG results, read the blog ahead.
What is NEET UG 2024 Examination?
The National Eligibility-cum-Entrance Test (Undergraduate), commonly known as NEET UG, is a crucial exam for students aspiring to pursue undergraduate medical courses in India. It is one of the prestigious medical entrance exams that is long awaited by the medical students. To gain that perfect score in the exam, students work hard day and night.
What is National Testing Agency?
Conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA), NEET UG serves as a gateway to prestigious medical colleges across the country. Respective colleges provide admission via NEET UG. Before the application window closes, students register for the exam and streamline their application process. From exam date announcement to exam centre information, medical students aim not to miss any single piece of information.
- National Testing Agency officially announces NEET UG Exam date, NEET UG Results, and counselling process dates too.
- A medical student must rely on the official communication from the side of National Testing Agency. After all, NTA NEET UG exam and results is a serious topic. No viral news or info must be believed.
- There are several other official websites and YouTube channels that give timely updates regarding registration process, information of fee and eligibility for category candidates, information on quota seats, the overall eligibility criteria, category-wise cutoff score, full-fledged application process and shutting down of application correction window.
- To help students prepare, timely content including informing about exam pattern, minimum marks, maximum marks, NEET 2024 tie-breaking criteria if any, difficulty level, exam syllabus, mock tests, etc. must be consumed.
What is the Significance of NEET UG 2024 in Medical Education?
NEET UG has a significant role in the Indian education system. It serves as the sole entrance test for undergraduate medical programs since the enactment of the National Medical Commission (NMC) Act in 2019. This act consolidated multiple entrance exams into a single, standardized test, streamlining the admission process to institutions such as the All India Institutes of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) and Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research (JIPMER). National Testing Agency conducts the exam. Fate of more than lakh students is decided post they appear for this exam for admission in the medical colleges of their choice. Similar to many competitive exams, this exam also results in excitement and stress at the same time. Students are worried of correct answer attempts, incorrect answer attempts, marking scheme, a great percentile score, getting through the cutoff score. All of the worry is gone if students are well-informed, prepare for the best, attempt the best, and wait for NEET UG results patiently.
What was NEET UG 2024 Results Schedule?
| Registration Held | 9 February – 10 April, 2024 |
| Admit Card Availability | 1 – 5 May, 2024 |
| Exam | 5 May, 2024 |
| Re-exam | 23 June, 2024 |
| NEET UG Results | 4 June, 2024 |
| Re-NEET UG Results | 30 June, 2024 |
Are NEET UG 2024 Results Out ? What is the Confusion?
Yes, the NEET UG 2024 results are out. The NEET UG 2024 was conducted on May 5, 2024, and this year’s examination was a notable event with several key aspects worth discussing. With involvement of Supreme Court and tons of aspiring candidates, it has become a topic of discussion.
What is the News of NEET UG?
This year’s NEET UG was not without its challenges. Following the exam, reports emerged about incidents such as wrong question paper medium distribution, question paper leaks, faulty examination centres with and proxy exam takers. These issues led to significant unrest among the candidates and stakeholders, resulting in demands for a retest. In response to these concerns, National Testing Agency formed a Grievance Redressal Committee to review and address the complaints.
Would NEET UG 2024 Results be Released Again?
Yes! Atleast for those who are appearing again. A notable decision was made regarding 1,563 candidates who were initially given grace marks due to the reported anomalies. Following a Supreme Court hearing on June 13, 2024, it was decided that the scores of these candidates would be canceled, and they were given the option to reappear for the exam on June 23, 2024. The results for this retest are scheduled to be declared on June 30, 2024.
How to Prepare for NEET UG 2024 Results?
Good results come from good hard work! Everyone would say, ”If you wish to get good NEET UG 2024 results, prepare wisely for the medical courses of your choice.” There’s no doubt in this-
‘A good exam attempted with no loss of time, no wrong answer, management of difficulty level, and strategic correct answers will always fetch good NEET UG results.’
So, let’s prepare for the exam to prepare our ears and eyes for the announcement of NEET UG results. Those who have attempted can take note of it for the next time. Re-takers can benefit from the tips here.
Preparation Tips for NEET UG
Given the competitive nature of NEET UG, thorough preparation is essential. Candidates are advised to focus on a balanced study plan that covers all three subjects—Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. Regular practice of previous years’ question papers and taking mock tests can help in understanding the exam pattern and improving time management skills. Additionally, staying updated with any official announcements from National Testing Agency is crucial for a seamless exam experience. So, the Prep Tips are:
- Keeping in mind loss of time, prepare with mock tests to get real time exam simulation.
- Go through colleges, programs & specializations beforehand to start preparation accordingly. Get exhaustive info days in advance, from official websites.
- Having no mental stress is very important for qualifying examination . So, your prep schedule must include ‘A NO STRESS MANTRA.’
- Increasing percentile score should be the goal. So, during mock tests, try that you grasp the maximum out of it. However, always introspect and mention your short term and long term goals. Attempt the exam accordingly.
- Start by creating a study schedule that allows you to allocate enough time for each subject. Make sure to cover all the important topics and concepts within the given time frame.
- To understand the exam pattern better, it is crucial to solve previous years’ question papers. This will not only give you a clear idea about the type of questions asked but also help you identify your strengths and weaknesses.
- Take mock tests regularly to gauge your preparation level. Mock tests simulate the actual exam environment and help you improve your time management skills. Analyze your performance after each mock test to identify areas that need improvement.
- Don’t just focus on memorizing facts, but also try to understand the concepts behind them. This will help you in applying your knowledge to different scenarios and solving complex problems.
- Form study groups with like-minded individuals who are also preparing for NEET UG. Discussing difficult topics and solving problems together can enhance your understanding of the subjects.
- Answer key is not always required. Sometimes, incorrect answer teach you better. Imagine one wrong answer while you appear in mock test. It will give you a lesson of life!
What are the Basic Preps Before NEET UG 2024 Results?
- Stay updated with any official announcements from the National Testing Agency. This will ensure that you have the latest information regarding the exam date announcement, changes in the exam syllabus, and any other important updates.
- Also, align with National Testing Agency again for exam pattern, tips to overcome difficulty level, eligibility criteria, registration process, admission process, counselling process, etc.
- Do not forget to keep your registration credentials safe. When NEET test results will be out, it will help you.
- ‘How to check NEET UG result’ will become a popular search. So, ensure you are aware of the tech errors that occur when the entire world is buy checking NEET UG results.
What are the Key Points to Remember when NEET UG Results are Out?
Tech-Related Preparation
As the NEET UG 2024 results are approaching, it’s important to ensure that you have no issues with your PCs or laptops, Candidates must be technically prepared to access NEET UG 2024 results and subsequent information from counselling authorities smoothly:
- Stable Internet Connection: While checking your NEET US results link or registering for counseling rounds, there must not be any buffering.
- Updated Browser: An updated web browser to access the official National Testing Agency and MCC websites is always better. It is advisable for compatibility and security when downloading your scorecard.
- Bookmark Official Sites: Save the official NTA NEET website and MCC counseling portal for ease.
Preparation of Credentials
Before the NEET UG results are announced, keep the necessary credentials and documents handy to streamline the process:
- Admit Card: Keep your NEET UG 2024 admit card readily available as it contains essential registration credentials and other details required to check your results.
- Registration Credentials: Ensure you know have your registration number and password. It is provided to the candidate at -UG registrations and then required for logging into the result portal. Also, do not share your OTPS or security pin in case required anywhere.
- Valid Contact Details: The email ID and phone number must be registered with NEET. Ensure they are active and accessible.
- Document Folder: A physical folder of academic certificates, ID proof, and other relevant documents will help at the time of admission. This will be useful for both checking results and the counseling process.
When NEET UG Result be Declared?
These qualifying marks of some students became questionable to many. People are figuring out if there is any imbalance of minimum marks or maximum marks. Following a Supreme Court hearing on June 13, 2024, it was decided that the scores of these candidates would be omitted. The NEET UG results for this retake are expected to be declared on June 30, 2024.
When will NEET UG 2024 Counseling Process Results be Out?
Once the NEET UG results are out, the counseling process begins, which is crucial for candidates to secure their seats in medical colleges. After overcoming all the negative markings and obtaining those qualifying marks, NEET UG counselling process starts. the eligibility criteria calls for passing the exam.
What is NEET UG Counselling?
The counseling for NEET UG 2024 is traditionally conducted in four rounds:
- Round 1
- Round 2
- Mop-Up Round
- Stray Vacancy Round
If there are still vacant seats after the Stray Vacancy Round, an additional seat allocation round may be conducted. The Medical Counselling Committee (MCC) oversees the first three rounds in an online mode for All India Quota (AIQ) seats. To participate, students must register on the official MCC website. For state quota seats, registration must be done on the respective state NEET websites.
Final Words
NEET UG exam result date is now JUNE 30th, 2024, post re-test.
In the confusion between a correct answer and an incorrect answer, a candidate may lose its confidence while attempting the exam. So, it’s advisable to stay confident. Getting a minimum score in NEET UG can close doors for that one golden opportunity. So, be calm and prepare nicely. Be it Government medical college or a private one, whatever you get, study hard. Hopefully NEET UG results would write a new destiny for all the future doctors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How to check NEET UG result?
Ans. NEET results are available on the official website on the National Testing Agency. After the official notice of ‘NEET UG 2024 Results are OUT’, candidates can reach them out to check, via their registration credentials.
Q2. How many counselling rounds exist after NEET UG 2024?
Ans. Counselling authorities have four rounds for it. It has been mentioned above, in the blog. And to mention, NEET UG is the only way out to get through qualifying status for counselling.
Q3. What is application correction facility?
Ans. Post registration process, the application can be corrected till a specific date. It is to help the concerned omit errors during the application process.
Q4. What is the official cutoff?
Ans. A source over the internet confirms the cut off as 720 to 137 for the general category and 136 to 107 for quota seats/OBC/SC/ST for previous year. This time, it hasn’t released.
Q5. Why is NEET UG in news?
Ans. For some medical students, the current marking system, and certain methods of taking up the exam did not go well with the aspiring doctors.
Q6. How to study at a NEET UG coaching centre?
Ans. Your offline or online coaching institute must help you streamline your prep for the dream medical colleges. Ask them what’s raw score? Do you help in admission process? Do we get extra marks? or How to master the core subjects? All these questions would help you stay aware and updated. Study the entire syllabi, with hard work.
The skeleton is the framework of bones, it is a type of connective tissue, reinforced with bone cells and calcium. Bones include a yielded core known as bone marrow, it is a spongy soft tissue that fills the cavities in bones and holds cells that create red and white blood cells.
Bones are responsible for protecting organs from potential damage and help support our body enabling movement.
In various types of bone fractures, the severity of the fracture depends upon the strength and direction of the force, with the bone involved.
What are the Different Types of Bone Fractures?
| Common Types of Bone Fracture | Description |
| Close (Simple Fracture) | Bone breaks without piercing the skin. |
| Open (Compound Fracture) | Bone breaks through the skin’s surface, causing an open wound. |
| Greenstick Fracture | Incomplete fracture is where the bone bends and cracks but doesn’t completely break. |
| Hairline Fracture | Minor crack in the bone’s surface without full separation. Most common form of stress fracture. |
| Complicated Fracture | Bone breaks and causes damage to surrounding tissues and organs |
| Avulsion Fracture | The tendon or ligament pulls off a fragment of bone. |
| Compression Fracture | Bone collapse due to pressure, often in the vertebrae. |
| Transverse Fracture | The fracture line is horizontal across the bone shaft. |
| Oblique Fracture | The fracture line is diagonal across the bone shaft. |
| Spiral Fracture | Fracture lines spiral around the bone, often caused by a twisting force. |
Fractures can occur not only in limbs such as arms and legs but also in critical areas like the head, chest, spine, or pelvis.
Injuries to bones like skull or ribs are the regions that can be particularly challenging due to the complex structures they protect.
Managing fractures in these areas often requires more than basic first-aid techniques and may involve complex medical interventions. These kinds of fractures represent life-threatening injuries that require emergency assistance.
Let’s dive into these complex fractures:
1. Compression Fracture: It typically occurs in vertebrae (bones of the spine), where the affected bone is compressed or collapses. It can result from trauma, such as falls or road traffic accidents, or from conditions like osteoporosis, which is the most common cause of compression fractures.
2. Skull Fracture: It occurs when one or more bones that make up the skull are broken, these fractures can vary in severity depending on the force and direction of the impact. It may also called a traumatic brain injury or TBI. Mild breaks cause few problems and heal over time and severe fractures can lead to bleeding around the brain, leaking of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), infection, brain damage, and seizures. The role of different skull bones, including the temporal, parietal, and occipital bones is crucial in understanding the potential consequences of a fracture:
- Temporal Bone: Bone is found on the sides and base of the skull. It is relatively thin, typically around 4mm thick. The temporal bones include important structures like the middle and inner ear, as well as some blood vessels.
- Parietal Bones: These bones form the sides and top of the skull. They are thicker than temporal bone, ranging from 5 to 10 mm thick.
- Occipital Bone: Located at the back and base of the skull, the occipital bone is the thickest among these three, typically measuring around 15 mm in thickness.
Skull Fractures are Classified into Various Types of Fracture Based on their Location
| Type of Skull Fracture | Description | Mechanism of Injury |
| Linear Fracture | Also known as a fissured fracture that is often thin and may be missed on X-rays, making it more detectable during MRI or CT-scan. It typically occurs due to a heavy blunt blow to the head, resulting in a linear break in the skull’s continuity. | Direct Impact or blunt trauma to the skull. |
| Basilar Skull Fracture | Occurs at the base of the skull, involving bones such as the temporal, occipital, and sphenoid bones. | Associated with head trauma it can lead to leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose or ears. |
| Diastatic Fracture | Fracture involves separation along sutures, which is common in young adults. A frequent site is the sagittal suture, where widening or separation occurs due to significant trauma. | Sudden force causing separation of sutures. |
| Depressed Fracture | Known as a signature or ala fracture, results from a small, focused impact such as from a hammer. It causes inward indentation of the skull’s surface, often damaging both outer and inner layers of bone. |
Direct blow from a heavy weapon or object with a small striking surface. |
| Pond/ Indented Fracture | Commonly seen in infants, this fracture leaves a visible dent or indentation on the skull’s surface. It’s also referred to as ping pong ball fracture and is caused using obstetric forceps during childbirth. |
Obstetric forceps apply pressure during delivery. |
| Gutter Fracture | Occurs on the outer surface of the skull due to the tangential impact of an oblique bullet, resulting in a groove-like depression along the bone. It’s characteristic of glancing bullet wounds. |
Trajectory of an oblique bullet causing an outer surface fracture. |
| Comminuted Fracture | Multiple bone fragments caused by a heavy blunt blow, this fracture pattern resembles a spider web with intersecting lines and fragments displaced from the impact site. | Severe blunt force trauma leading to shattered bone fragments. |
| Ring/ Foramen Fracture | Bones may be broken around the foramen magnum, the hole in the base of the skull through which the brain stem exits and becomes the spinal cord. This may result in injury to the blood vessels and nerves exiting the foramen magnum. | Impact involves the base of the skull, such as falls or specific blows to the head. |
| Motorcyclist Fracture | Common among motorcyclists, these fractures occur at the skull base, typically from lateral impacts. They are classified into Type 1 (Hinge), Type 2(Frontal to contralateral), and Type 3 (Anterior) based on specific patterns of fracture propagation. |
Lateral force transmitted across the skull, typical in motorcycle accidents. |
| Bow Out Fracture | Involves fractures of the orbital wall (median, posterior, or floor) caused by blunt trauma, resulting in an outward blowing or displacement of bone. It commonly occurs due to forceful impact on the eye area. | Blunt force trauma causes fractures of the orbital bones. |
What are Some Common Causes of Bone Fracture?
Bone fractures can result from various causes, including:
- Trauma: Falls, sports, injuries, motor vehicle accidents, and direct blows to the body result in traumatic bone fractures.
- Osteoporosis: In this condition, bones become weak due to loss of bone density. In this condition, even minor stresses and falls can cause a fracture.
- Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Repetitive motions can strain bones over time which leads to stress fractures. These fractures develop gradually with small cracks and repetitive impact, which is common in athletes.
- Pathological Conditions: Diseases that weaken bones, such as bone cancer (resulting in pathological fractures), osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease), or infections like osteomyelitis, can make bones more susceptible to fractures.
What are Some Common Symptoms of Fracture?
- Bone fractures cause pain due to inflamed nerve endings in the bone lining (periosteum) and muscle spasms around the fracture site.
- Fractured bones bleed, which leads to swelling and seepage of blood into surrounding tissues, which adds to the pain.
- Bruising around the fracture site may appear as dark red or purple marks due to blood leakage.
- Due to muscle and tendon integrity, movement of the injured limb still be possible, so mobility alone does not rule out a fracture.
- Arteries damage can result in a cool, pale area distal to the injury, while nerve damage may cause numbness in the same area.
What is the Treatment Plan for the Bone Fracture?
Treatment for bone fracture depends upon the complication and level of severity to make sure the bone pieces are lined up accurately through surgical procedures or surgical traction.
Types of Treatment Based on Fracture Location and Site Include
- Braces: provide support to the bone
- Splints: to stop the movement of the fractured limb
- Plaster Cast: provide rigid support and immobilization
- Traction: for complex fractures to align and stabilize
- Surgically inserted Metal Rods or Plates: In severe cases of fracture that do not heal properly with other methods, metal implants such as metal rods, screws, or metal plates are surgically placed to hold bone fragments.
Few Surgical Treatments Depending on the Location and Severity of the Fracture
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): It is the procedure of realigning the fracture bone fragments ( open reduction) and stabilizing them with internal fixation devices such as metal plates, screws, or metal rods.
- External Fixation: In these types of cases fractures open like a bone protruding through the skin or severely unstable, external fixation may be used. It involves placing metal pins, and screws into the bone above and below the fracture, which are connected to external fragments. Commonly used for fractures of the long bones in the arms and legs.
- Intramedullary Rodding: This procedure includes a metal rod inserted into the hollow center (Medullary canal) of the long bone to stabilize and align the broken bone fragments.
- Joint Replacement: Also known as arthroplasty, becomes necessary in some cases in which fractures severely affect the upper portion of the femur bone, a crucial component of the hip joint, or the humerus bone, integral to the shoulder joint.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between a closed fracture and an open fracture?
Ans. A closed fracture occurs when the bone breaks but does not penetrate the skin. It is typically less complicated and carries a lower risk of infection compared to an open fracture, in which bone breaks through the skin. An open fracture requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications such as infection.
Q2. How are head injuries diagnosed and treated?
Ans. Head injuries can vary from mild concussions to severe traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). This diagnosis involves a thorough physical exam and imaging tests like CT scans to assess the extent of the damage.
Treatment options depending on the severity include rest, medication for pain and swelling, with recommended physical therapy which restores range of motion and strength.
Q3. What can do to keep bones strong and reduce the risk of fractures?
Ans. To maintain strong bones and reduce the risk of fractures, it’s important to engage in regular weight-bearing exercises, consume a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Following medical advice and gradually returning to normal activity and daily activities can support bone healing and restore mobility.
Medical students must burn the midnight oil to get through medical colleges. An academic session in a medical college is loaded with struggles and experiences. Above all, clearing NEET PG Examination is a breathtaking journey. First the exam, and then with NEET PG 2024 results around the corner, the heartbeats of students would be fastened. To make it a little easy for them, we have a complete guide here. Read ahead in the blog ‘NEET PG 2024 Results: How to Check and What to Expect?’ to get answers to all your queries.
What is the NEET PG Result Date?
From appearing for NEET PG to waiting to be in the merit list is the dream of medical students. Post all the struggles, they wait for just one thing and that’s RESULTS! This year, NEET PG results are to be announced on July 15, 2024.
What is the NEET PG 2024 Schedule?
You can download NEET PG schedule information from the official website. To update you here, this medical examination of NEET PG is scheduled on 23rd June 2024. Post 15-20 days, NEET PG results can be expected. For your information, National Board of Examinations had created the following schedule:
| Registration process had started on | April 16, 2024 |
| Last day to submit application form was | May 6, 2024 |
| Last day to modify incorrect images was | June 10, 2024 |
| Admit card will be released on | June 18, 2024 |
| NEET PG exam on | June 23, 2024 |
| NEET PG result date is | July 15, 2024 |
We understand the anticipation for the results could be overwhelming. But take it in a way that it would be worth the wait. Think how this big day would open doors for long-awaited opportunities.
How to Prepare for NEET PG Results’ Announcement?
Ensure that you have your credentials ready. It is because the NEET PG results are announced in online mode. So, it is advisable to pen down passwords, roll numbers, and other basic details during the registration process. Remember:
- Post successfully filling the online application form, generally complete login details are received. Keep those ready.
- Do not forget to be vigilant during the entire application process.
- Last but not the least, do not delay things. Before the announcement of NEET PG results, keep it all handy to view results seamlessly.
- Also, we must always be mentally prepared for tech errors and websites taking time in loading.
What is the Mental State of Students while Appearing for NEET PG?
Students who appear for the NEET PG exam undergo stress at various levels. Students have stress of mentally preparing themselves for a great academic session ahead. Next is the stress of fitting into the shoes of eligibility criteria. The completion of internships is another stress. Then is the major stress of the exam and finally passing it with flying colours.
Details from National Board of Examinations and information regarding exam center, seat allotment process, exam schedule, application dates, fee structure, and mode of application will be what, are to be known beforehand. All of it gives a huge stress. Remember:
- Note down all the details on digital notes or a piece of paper to avoid skipping.
- Make note of Application details, exam pattern, aggregate marks calculation, counselling for seat allotment, issues during counselling, etc. beforehand. This will limit the stress on the spot.
- Ensure there are no discrepancies in application documents.
- Keep a record of previous answer key, information of minimum scores or cutoff score, college authorities’ previous decision-making policies, previous toppers list, etc. to stay 100% prepared.
We understand, from application fee or the exam fee to downloading the admit card is altogether another exercise. Finally entering the examination hall doesn’t put an end to the anxiety. Then emerges a series of questions like ‘What if I attempt an incorrect answer in the NEET PG exam?’ ‘What if I am unable to decode the exam pattern?’ ‘What if I write correct answers but get confused to make it wrong again?’ ‘What if I make silly mistakes by entering personal details wrong?’
Put an end to all of it! It’s high time to stay calm and be confident about your exam preparation. This eligibility cum entrance examination is going to be a fabulous experience. Just soak in this thought and go ahead!
What is the NEET PG Results Process?
NEET PG Exam is the entrance test for doctors to pursue post-graduation ahead. To study Doctor of Medicine (MD), Master of Surgery (MS), Diplomate of National Board (DNB), Doctorate of National Board, and diploma courses, it is the pathway to move ahead towards a noble profession. Since it’s a big opportunity, make sure to master the art of preparation throughout.
Pre NEET-PG Results Procedure
Pre procedure is almost done. Registrations are closed. Now the admit cards would be available on June 18th, 2024. Students can then enter the exam hall with their hall ticket and take up the exam. It’s a computer-based exam so it requires attention and focus, especially for those who do not like digital mediums much. This medical entrance exam plays a crucial role. So, staying positive is the most important.
Make sure to reach beforehand because the photo identification and checking takes time. It’s an elaborative verification process so do not get exhausted or tensed. All exam centres in all the exam cities must follow this rigorous process. Therefore, it’s better to reach before time and not lose your calm.
Post NEET PG Results Process
Post evaluation of the exam, NEET PG results 2024 would be available in the form of PDF. It is important to have login credentials at this moment. Those medical students who qualify for the exam will have the option to download the scorecard. Once the merit list is released, registration for counselling can be completed.
NEET PG RESULTS 2024
⬇️
DOWNLOAD SCORECARD
⬇️
RELEASE OF MERIT LIST
⬇️
REGISTER FOR COUNSELLING
How To Check NEET PG 2024 Results?
It’s an easy process involving four steps.
Step 1: Visiting the Official Website
Reach out to NBE’s official website for the results.
Step 2: Login
Insert credentials to login to your account. ID and passwords are to be kept safe for this step.
Step 3: Downloading the Scorecard
The scorecard can be downloaded in PDF format.
Step 4: Verify and Save
Verify and carefully go through details such as Name, Roll Number, Marks Scored, Rank, etc. Post thorough monitoring, save it. A hard copy must be kept for further counselling rounds.
Conclusion
The NEET PG 2024 results day is an important milestone for every aspiring postgraduate medical student. In the medical field, it holds a great importance. Whether you’re from the aspiring candidate’s group, eligible candidates’ group or qualified candidates group, the anxiousness lasts till the end. Now that you have clarity over timelines for NEET PG results and information on evaluation of NEET-PG scores, academic details, application process, eligibility criteria, counselling sessions, and other details, you are good to go!
We wish you all the luck. So, get, set, and go!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the NEET PG 2024?
Ans. It is required for the candidates to have an MBBS degree or a provisional MBBS pass certificate, accepted by the Medical Council of India (MCI). Also, it is necessary to have completed the internship deadline.
Q2. What is the exam pattern of NEET PG 2024?
Ans. It is a computer system-based entrance exam, known as Computer Based Test (CBT). With 200 multiple-choice questions, it is a test that covers the entire syllabus from 19 subjects of MBBS. With reference to previous year’s NEET PG test question papers, individual analysis/evaluation can be done with regards to weightage of subjects and their questions.
Q3. What are the criteria for evaluating NEET PG results?
Ans. Each right answer gets four marks. With each wrong answer, the candidate is supposed to witness a deduction of one mark. Via scores, candidates are ranked further while declaring NEET PG results.
Q4. What is the counselling process called?
Ans. Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS) conduct the counselling sessions for admission of candidates to various places.
Q5. When is NEET PG held?
Ans. NEET PG is conducted once a year. It is the most crucial exam in the medical field. So, students eagerly wait for that. Also, the exam timing is for 3.5 hours.
The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test for Post-Graduation is a qualifying and ranking test in India for candidates interested in doing MD, MS, or PG Diploma. This year’s NEET PG Exam is scheduled for 23rd June’24.
Let’s go into the eligibility, Application fee updates, marking scheme, and other details.
NEET PG 2024 Eligibility Criteria:
- According to the Indian Medical Council Act 1956, the candidates are required to have an MBBS degree or a Provisional MBBS Pass Certificate.
- Candidates must have a permanent or provisional MCI or SMC-issued MBBS qualification registration.
- The candidates must have completed a year of internship before applying.
Application and Fees:
As per the NEET PG 2024 fees have been reduced, and the General and OBC applicants must pay Rs. 3,500 to fill out the NEET PG application form, while SC/ST/PWD candidates must pay Rs. 2,500.
Duration:
The exam will be 3.5 hours long.
Exam Format:
The exam will be computer-based and administered at the designated locations.
Test Pattern & Marks:
14 subjects are classified under 3 parts in the paper:
Part A – Pre-clinical subjects
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Biochemistry
Part B – Para-clinical subjects
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Forensic medicine
- Social & preventive medicine
Part C – Clinical subjects
- General medicine including
- Dermatology & venereology
- Psychiatry
- General surgery including
- Orthopedics, anaesthesia & radiodiagnosis
- Obstetrics & gynecology
- Pediatrics
- ENT
- Ophthalmology
Marking scheme:
Incorrect answers will incur a penalty of 25% through negative marking. No deductions will be made for questions left unanswered.
- +4 marks for correct response
- -1 for incorrect response
- No marks for unattempted question
Important Dates: NBEMS has published the official exam calendar having dates of NEET PG 2024.
| Events | Dates |
| NEET PG 2024 Application form release | 16-April-2024 |
| Last Date to submit an application | 6-May-2024 |
| Cut-off Release | 15-Aug-2024 |
| NEET PG 2024, Exam Date | 23-June-2024 |
| Result Declaration | 15-July-2024 |
Note: Candidates should be aware that admit cards will not be provided to those who are found ineligible before the examination.
How to prepare for NEET PG 2024?
It’s time for you to make the most of the preparation period. Revise as much as you can. Whatever you’ve studied to date, it’s now time to test yourself and prepare for the bigger one. Always keep in mind that your perspective defines your reality.
Here are the 7 Tips to crack NEET PG 2024:
- Create and Stick by a Plan: Decide for the next day before you go to bed and stick to it no matter what. Wake up and stick to your plan so you’re prepared and don’t waste time deciding what to study.
- Prioritize the subjects where you need conceptual clarity: Focus on conceptual clarity with the help of trusted content only. Finding the right content can be a hassle so choose DigiNerve, an app by Jaypee Brothers who have published most of your textbooks. This online app provides video lectures by India’s top faculty which include your textbook authors.
- Revision and MCQs: The more you revise, the better; devote the first two months to clarifying concepts of the topics you’re having trouble with, and the last month to solving MCQs.
- Question papers from previous years: This will assist you in comprehending the NEET PG Exam structure and identifying essential topics that may appear in the exam.
- Notes: You probably have read everything, and you have the knowledge so now the only thing left is to go through your notes, it will help you recall important points.
- ITD method: Memorize with the help of the ITD Method- Importance of the topic, Time consumption, and Detailing.
- Enroll for Mock Tests: Attending mock tests will help you assess your knowledge. This will help you know the subjects where you need clarity. On its official website, the NBE publishes practice tests. One of the most important components of the exam preparation approach is the mock test. You must conduct mock tests after concluding their revision to assess their preparation. You will get to learn what else must be done to increase a particular topic’s score. To access the sample test, you must first log in to the NBE’s official website. Before beginning the online mock test, candidates should carefully read all the instructions. Recalibrate your strategy by taking a mock test and weighing your results.
To prepare for NEET PG 2024, subscribe to DigiNerve’s courses by India’s top faculty today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. When will NEET PG be in 2024?
Ans. The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test-Postgraduate (NEET PG 2024) will now be held on June 23, 2024.
Q2. Is PG necessary after MBBS?
Ans. For doctors to be successful in their specialties, they must have a postgraduate degree in medicine.
Q3. How do I pay the fees for NEET PG 2024?
Ans. Fees can be paid using a debit/credit card or a net banking service. Candidates should print the confirmation page after successfully paying the application fees.
Pathology is a comprehensive subject, included in the 2nd year of the MBBS curriculum. It covers various aspects of disease processes, their causes, and the resulting changes in the structure and function of the body. The subject serves as the bridge between the basic sciences and clinical medicine, helping medical professionals understand the underlying processes of diseases.
Medical students must have a sound knowledge of the pathology subject, as it provides a foundation for understanding disease processes, making accurate diagnoses, and formulating appropriate treatment plans. The subject also plays a crucial role in research and contributes significantly to medical knowledge and patient care advancements.
The Pathology course curriculum in MBBS includes an introduction to pathology, cellular pathology, hematology, general pathology, systemic pathology, common pathogens and their mechanisms, histopathology, clinical pathology, autopsy, and forensic pathology.
Subject Weightage of Pathology in Competitive Exams
Approximately 12 questions are asked in the NEET-PG exam, and in the INI-CET, approximately, 13-16 questions are asked from the Pathology subject.
The competitive exams mainly assess the understanding of the aspirant regarding disease processes, diagnostic principles, and the application of pathology in clinical scenarios.
Getting familiar with the subject weightage of subjects in exams, exam patterns, high-yield topics, and reliable preparation tips multiplies the chances of gaining conceptual clarity over a subject and scoring high in the exams.
Important Topics of Pathology in MBBS
Hematology
- Coagulation Pathway
- Hemophilia
- Blood Bank
- Megaloblastic Anemia
- Multiple Myeloma
- Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Hemolytic Anemia
- Lymphoma
- Hypercoagulability
- Thalassemia
- Acute Leukemia (AML/ALL)
- CML & MDS
- Waldenstrom’s Disease and Heavy Chain Disorders
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
- Stain
Cell Biology
- Cell Injury Concept
- Cellular Adaption
- Irreversible Injury 1 and 2
- Free Radical Injury
- Pigmentation
- Necrosis
GIT
- Jaundice
- Fatty Liver
- Hepatitis
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Celiac Disease
- Whipple Disease
- GI Polyps
- Liver disorders
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Peptic Ulcer Disease
- Acute and Chronic Gastritis
- GIT Tumor
- Congenital GIT Anomalies
- Mesothelioma
Renal
- PSGN
- Diabetic Retinopathy
- ADPKD
- Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Glomerular Nephritis
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Alport Syndrome
- Renal Spotters
- Renal Stones
CNS
- Malformations of Brain
- CSF Analysis
- Prion Disease
- Medulloblastoma
- Meningioma
- CNS Degenerative Disease
- Meningitis
- CNS Tumor
- Neuroblastoma
Lung
- ARDS
- Emphysema
- TB Lung Lesions
- Adenocarcinoma
- Occupational Disease
- Obstructive Lung Disorders
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Infective Lung Disorders
- Lung Abscess
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Lung Cancer
- COPD
- Asbestosis
CVS
- Myocardial Infarction
- DCM & HCM
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Rheumatic Heart Disease
- Vasculitis
- Infective Endocarditis
- Vascular Sclerosis
- Bleeding Disorders
- Clotting Factor Disorders
- Blood Transfusion and Blood Grouping
- Platelets Disorders
Breast
- Fibroadenoma
- Breast Oncogenesis
- Breast Cancer
- TNM Staging
Endocrine
- Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
- Follicular Carcinoma
- Pheochromocytoma
- Parathyroid and Thyroid Disorders
- Adrenal Gland Disorders
Inflammation
- Plasma Chemical Mediators
- Coagulation Cascade
- Chronic Inflammation
- Neutrophil Extracellular Trap
- Inflammatory Markers
Malignancy
- Tumor Marker
- Tumor Suppressor Gene
- Molecular Hallmark of Cancer
- Bone Tumors
- Melanoma
- Hodgkin & Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Seminoma
Genetics
- Gene Repair Defects
- Inheritance Pattern
- Down Syndrome
- Turner Syndrome
- TNR Disorders
- Single Cell Disorder
- Specific Cytogenetic Disorders
Immunology
- Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Granuloma
- Complement Pathway
- Immunodeficiency Disorders
Miscellaneous
- Aging
- Marfan & Ehlers Danlos Syndrome
- Transplantation
- HIV
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Amyloidosis
Tips to Prepare Pathology in MBBS
Preparing for pathology in MBBS requires a systematic and comprehensive approach. To have an in-depth understanding of the subject, establish a strong foundation in anatomy, physiology, and biochemistry, as pathology builds upon these subjects. The MBBS curriculum caters to general pathology, hematology, systemic pathology, clinical pathology, and practicals in pathology.
To start with the pathology subject, familiarize yourself with basic medical terminologies, and then move on to the general pathology section. Understand the basics and attend regular classes. From the beginning, create a well-organized study schedule to cover all the topics systematically, and allocate sufficient time to review and consolidate your learning. Once you grasp the fundamental concepts, start with the hematology section.
Be wise while choosing the books for pathology. Opt recommended standard textbooks to clear your concepts, pathology atlases to visualize and understand various pathological conditions, and also add pathology review books to your shelves that provide concise summaries of key concepts for quick revision. Some recommendations for pathology books are Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan, Essentials in Hematology and Clinical Pathology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates Pathology by Ramadas Nayak, Rapid Review of Hematology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Review of Pathology and Genetics by Sparsh Gupta & Gobind Rai Garg, and Comprehensive Image-Based Review of Pathology by Sushant Soni.
Then, further, start emphasizing systemic pathology. Thoroughly study all the systems along with prevalent conditions and diagnostic methods. Make sure you make proper notes side by side for all the topics. They will prove quite beneficial at the time of exams for revision, be it professional exams or any competitive exams. During your studies, engage in active learning methods such as concept mapping, creating flashcards, and flowcharts, and teaching concepts to peers. Also, solve clinical case scenarios to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. Create mind maps and diagrams to visualize complex pathways and relationships between different pathological conditions.
Remember ‘P for Pathology and P for Practicals’. The subject is better understood when you conduct experiments and practicals simultaneously. It is highly advised to attend pathology practical classes to enhance your understanding of histopathology and diagnostic techniques. Also, during your lab sessions, practice identifying microscopic slides and understanding the correlation between pathology and clinical presentations. Consider shadowing or observing clinical cases in pathology labs. Correlate clinical features with pathological findings to strengthen your understanding of clinical pathology. Becoming capable of finding the clinical relevance of pathological conditions and relating pathology to signs, symptoms, and diagnostic methods is an assertive sign that you are becoming well-versed in pathology concepts.
Along with learning pathology and attending practical sessions, solve practice questions for all the topics for self-evaluation and better understanding. Also, solve past exam papers and mock papers for the exams you are determined to score high. Solving them will help you understand the exam pattern, improve time-management skills, identify key aspects, and focus on high-yielding topics. Along with college lectures, practical sessions, and ward postings, keep yourself updated with the recent advances and research in pathology by attending webinars, workshops, and conferences.
To reinforce your understanding of pathology concepts, you can enroll in the Pathology for UnderGrads online course by Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak, and Dr. Debasis Gochhait. The course provides access to video lectures, concise notes, and practice questions, all aligned with the CBME curriculum. The lectures comprise relevant case studies, case discussions, histological and gross images, and important questions for university exams, practical exams, and PG entrance exams. Most importantly, regularly revise topics to reinforce your memory.
Must Read: Important Topics of Microbiology
Must Read: Important Topics of Pharmacology
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- What are the important topics of pathology in MBBS?
The important topics of pathology in MBBS include Multiple Myeloma, Iron Deficiency Anemia, Sickle Cell Anemia, Lymphoma, Thalassemia, Acute Leukemia, Gene Repair Defects, Inflammation, Free Radical Injury, Fatty Liver, Ulcerative Colitis, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Peptic Ulcer Disease, Diabetic Retinopathy, Glomerular Nephritis, Nephrotic Syndrome, CNS Degenerative Disease, Meningitis, Occupational Disease, Infective Lung Disorder, Lung Abscess, Infective Endocarditis, Adrenal Gland Disorders, Breast Cancer, Tumor Suppressor Gene, Hypertension, Genital System, and Down Syndrome.
- Which are the recommended books on pathology for MBBS students?
Recommended books for pathology in MBBS include Textbook of Pathology by Harsh Mohan, Essentials in Hematology and Clinical Pathology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates Pathology by Ramadas Nayak, Rapid Review of Hematology by Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai, Review of Pathology and Genetics by Sparsh Gupta & Gobind Rai Garg and Comprehensive Image Based Review of Pathology by Sushant Soni.
- What is the weightage of pathology in the NEET PG exam?
In the NEET-PG exam, approximately 12 questions are asked from the pathology subject.
- What is the subject weightage of pathology in INI-CET?
In INI-CET, approximately 13–16 questions are asked from the pathology subject.
- How to prepare for pathology for the NEET-PG?
Preparing for pathology in MBBS requires a systematic and comprehensive approach. Establish a strong foundation in fundamental subjects. Familiarize yourself with basic terminologies and then move on to sections. Attend regular classes and practical sessions. Take proper notes. Create a well-organized study schedule. Grasp the fundamental concepts. Opt for recommended standard textbooks, pathology atlases, and pathology review books. Thoroughly study all the systems along with prevalent conditions and diagnostic methods. Engage in active learning methods such as concept mapping, creating flashcards, flowcharts, mind maps, diagrams, and more. Also, solve clinical case scenarios to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. Solve practice questions for all the topics for self-evaluation and better understanding. Keep yourself updated with recent advances and research. Attend webinars, workshops, and conferences. Enroll in the Pathology for UnderGrads online course by Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak, and Dr. Debasis Gochhait to reinforce your learning.
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has achieved the coveted World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) Recognition Status for a tenure of 10 years. This is a prestigious achievement for India’s medical education. This esteemed award proves NMC’s steadfast dedication to the highest standards in medical education and accreditation.
The WFME recognition will now enable Indian medical graduates to pursue postgraduate training and practice in other countries that require WFME recognition, such as Australia, USA, Canada, and New Zealand.
The World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) is a global organization dedicated to raising the standard of medical education all over the world. The WFME accreditation programme is crucial in ensuring that medical institutions uphold and adhere to the highest levels of global education and training standards.
Dr. Yogender Malik, Member of the Ethics and Medical Registration Board and Head Media Division at NMC, on this remarkable achievement, said, “WFME’s recognition underscores that the quality of medical education in India adheres to global standards. This accolade empowers our students with the opportunity to pursue their careers anywhere in the world, while also making India an attractive destination for international students due to our globally recognized standards.”
Under this accreditation, all the 706 existing medical colleges in India will be considered WFME accredited, and the new colleges being set up in the coming 10 years will also be considered as WFME accredited. This will also benefit NMC in enhancing the quality and standards of Indian medical education by aligning them with global benchmarks. This will facilitate academic collaborations and promote continuous improvement and innovation in medical education.
Now NMC being WFME accredited has opened the doors for all the medical students for ECFMG and USMLE. All Indian students will become eligible to apply for the Education Commission on Foreign Medical Graduates and United States Medical Licensing Examination.
The National Medical Council, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in a press release dated 20th September 2023 has announced this remarkable update.
Pathology is a medical specialty that deals with the causes and nature of disease. By delivering early and accurate diagnoses, which are crucial for successful treatment, pathologists play a crucial role in patient care.
A pathologist works with the causes and characteristics of illness and employs information acquired from the laboratory application of the biological, chemical, and physical sciences to aid in diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. For the diagnosis and monitoring of illness, this specialist uses data obtained from microscopic inspection of tissue samples, cells, and bodily fluids as well as from clinical laboratory testing on bodily fluids and secretions. By delivering early and accurate diagnoses, which are crucial for successful treatment, pathologists play a crucial role in patient care.
If you are good at going with a microscope as your friend than a stethoscope, then pathology is a great option to choose as a specialty. This specialty is more of working behind the scenes sitting for long hours diagnosing rather than directly dealing with the patients.
Steps for Becoming a Pathologist
- Complete your 12th standard in the Science stream with a minimum of 55% aggregate.
- Then you have two options for your undergraduate degree, either you can go with an MBBS undergraduate degree, or you can go with a B.Sc. in Pathology. The former is more into medicine side while the latter is a basic health and allied sciences degree. Depending on your preference and educational qualification, you can choose between both. To pursue an MBBS degree, you must crack the NEET-UG entrance examination with a competitive score. You can opt for a government or private college for any of the undergraduate courses as per your preference and score. Always seek proper guidance before choosing a medical college.
Must Read: Things to know before choosing a medical college.
- After completing graduation, you must complete your postgraduation in pathology. If you did an MBBS, then go with an MD in Pathology degree and if you opted for BSc then go with an MSc Pathology degree. To pursue MD Pathology, you need to score high in the NEET-PG/INI-CET and for M.Sc. Pathology, you need to follow the admission procedure of the particular college.
- Then after completing postgraduation, you need to gain experience, then you have the option to pursue fellowship courses in various pathology subspecialities. You can also opt for a Ph.D. programme.
Apart from a degree, you also have the option to pursue a Diploma in Pathology or relevant certification courses.
Top Medical Colleges to Pursue MD Pathology in India
- AIIMS, Delhi
- Christian Medical College, Vellore
- Grant Government Medical College, Mumbai
- AFMC, Pune
- JIPMER, Puducherry
- Kasturba Medical College, Manipal
- IPGME&R and SSKM Hospital, Kolkata
- KGMU, Lucknow
- St. John’s Medical College, Bangalore
- Lady Hardinge Medical College, New Delhi
- Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi
- VMMC, New Delhi
Pathologists employ a wide range of instruments and methods to investigate illness, such as:
- Microscopical analysis of tissue samples: Pathologists use microscopes to analyse tiny slices of tissue in search of anomalies that might be signs of illness.
- Testing in the laboratory: Pathologists do several tests in the lab on tissues and bodily fluids to determine the concentrations of various chemicals, including hormones, enzymes, and proteins. These examinations can support illness diagnosis, track disease development, and evaluate therapy effectiveness.
- Autopsies: Pathologists examine a deceased person’s body after death to ascertain the cause of death and learn more about any ailments they may have had.
List of Pathology Subspecialities
Pathology is a broad specialty that encompasses a variety of subspecialties, including:
- Transfusion Medicine
- Chemical Pathology
- Cytopathology
- Dermatopathology
- Histopathology
- Forensic Pathology
- Hematopathology/Hematology
- Molecular Genetic Pathology
- Neuropathology
- Pediatric Pathology
- Pulmonary Pathology
- Renal Pathology
- Surgical Pathology
- Clinical Pathology
- Molecular Pathology
Skills Required for Becoming a Pathologist
A skilled pathologist should be well-versed in the following:
Establish a diagnosis for common and difficult clinical issues using histopathology (surgical pathology) and cytopathology specimens, blood and bone marrow examinations, and different laboratory medicine tests (clinical pathology, Blood Banking (Transfusion Medicine), and clinical biochemistry.
Construct correlations between clinical and laboratory data to ensure that clinical disease symptoms can be explained.
Suggest the proper samples and tests to conduct to reach a diagnosis in a difficult case.
Compare pathology results from an autopsy with those from the clinic, the causes of disease-related deaths, and their miscorrelations (other than isolated metabolic causes).
Should be competent to instruct pathology to nursing students, postgraduates, undergraduates, and paramedical professionals, including lab staff.
Be able to work as a team, cultivate a cooperative attitude among coworkers, and communicate with patients, clinicians, and other coworkers to offer the best diagnostic or opinion.
Always uphold ethical values, maintain an appropriate demeanour in interactions with patients, family members, and other medical professionals, and respect the patient’s rights, including access to information and a second opinion.
Capable of carrying out standard procedures in a pathology lab, such as grossing specimens, processing, slicing paraffin and frozen sections, and staining.
Capable of routinely performing non-invasive outpatient procedures like venipuncture, finger pricks, fine needle aspirations of superficial lumps, and bone marrow aspirates in order to collect specimens, and to give appropriate assistance to colleagues performing invasive procedures like a biopsy or an imaging-guided biopsy.
Salary and Scope of Pathologist
Pathology is a highly promising job as no diagnosis is complete without pathology. Pathologists are in great demand, and the job outlook for them is predicted to improve over the coming ten years at a faster-than-average rate. Pathologists can find employment in a range of places, such as hospitals, clinics, research facilities, diagnostic labs, and governmental organisations. After completing your medical education and gaining experience in Pathology, you can open your diagnostic pathology centre.
Pathologists have a highly diverse range of employment options and several prospects for progression. Anatomic pathology, clinical pathology, and forensic pathology are just a few examples of the areas of pathology in which pathologists might specialise.
For those with a passion for science and medicine, attention to detail, and strong analytical abilities, pathology is a good speciality. Additionally, pathologists must be able to operate both alone and collaboratively. On average, a pathologist earns 50K to 80K per month and it varies depending on the area of employment.
The job profiles associated with pathologist include Clinical Pathologist, Professor/Lecturer, Forensic Pathologist, Clinical Researcher Associate, Medical Writer, Transfusion Medicine Specialist, and more.
Best Books for Studying Pathology
- Prof Harsh Mohan’s Textbook of Pathology
- Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates Pathology by Ramadas Nayak and Sharda Rai
- Rapid Review of Hematology by Ramadas Nayak and Sharda Rai
- Review of Pathology and Genetics by Gobind Rai Garg and Sparsh Gupta
- Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Diseases by Vinay Kumar, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster
- Fundamentals of Pathology by Husain A. Sattar
- Surgical Pathology of the GI Tract, Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas
- Cytopathology Review by Fang Fan and Ivan Danjanov
- Gray’s Diagnostic Cytopathology
- Rosai and Ackerman’s Surgical Pathology
- Atlas and Text of Haematology by Tejinder Singh
- Orell’s Atlas of Aspiration Cytology
- Lever’s Dermatopathology
By offering precise and fast diagnoses, which are necessary for efficient treatment, pathologists play a crucial role in the healthcare industry. They also strive to create innovative diagnostic methods and disease-specific therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What should I do after 12th to become a Pathologist?
Ans. After completing the 12th standard, either you can go with an MBBS undergraduate degree, or you can go with a B.Sc. in Pathology. The former is more into medicine side while the latter is a basic health and allied sciences degree. Depending on your preference, you can choose between both. To pursue an MBBS degree, you must crack the NEET-UG entrance examination with a competitive score, and for a B.Sc., you need to follow the admission procedure of the particular college. You can opt for a government or private college for any of the undergraduate courses as per your preference and entrance exam score. Always seek proper guidance before choosing a medical college.
Q2. What are the career prospects for pathologists?
Ans. Pathologists can find employment in a range of places, such as hospitals, clinics, research facilities, diagnostic labs, and governmental organisations. After completing your medical education and gaining experience in Pathology, you can open your diagnostic pathology centre. The job profiles associated with pathologist include Clinical Pathologist, Professor/Lecturer, Forensic Pathologist, Clinical Researcher Associate, Medical Writer, Transfusion Medicine Specialist, and more.
Q3. How good is pathology as a career?
Ans. Pathology is a highly promising job as no diagnosis is complete without pathology. Pathologists are in great demand, and the job outlook for them is predicted to improve over the coming ten years at a faster-than-average rate. Pathologists can find employment in a range of places, such as hospitals, clinics, research facilities, diagnostic labs, and governmental organisations. After completing your medical education and gaining experience in Pathology, you can open your diagnostic pathology centre. Pathologists have a highly diverse range of employment options and several prospects for progression. Anatomic pathology, clinical pathology, and forensic pathology are just a few examples of the areas of pathology in which pathologists might specialise.
Q4. What is the salary of an MBBS MD pathologist in India?
Ans. On average, a pathologist earns 50K to 80K per month and it varies depending on the area of employment. The job profiles associated with pathologist include Clinical Pathologist, Professor/Lecturer, Forensic Pathologist, Clinical Researcher Associate, Medical Writer, Transfusion Medicine Specialist, and more.
Click here to get conceptual clarity on MBBS subjects.
Global health comprises the biological and clinical facets of diseases along with the social, economic, political, and environmental determinants of health. The ability to confine health issues inside national borders has diminished as the globe becomes more linked.
The contribution of technology to the medical sector is unparalleled. With the years passing by technology is improving at the highest pace in the medicine sector. Nowadays, the use of AI, and the development of new therapies, drugs, drug development, and surgical procedures, have made complex medical procedures less complex and paved a path to minimally invasive surgeries. Millions of individuals throughout the world are having their lives improved as a result of these developments.
Global health has improved recently despite several obstacles like poverty, pandemics, disease outbreaks, conflicts, and climate change. Maternal and child fatalities have dropped significantly and since the development of new vaccinations, infectious illness spread has also been reduced. Governments and organisations have also boosted their funding for global health concerns and also significantly invested in newer technologies. The current developments in the healthcare industry are beneficial to global health and are an area with significant potential to enhance the health of people all over the world and in the medical field. We can improve the health of people all across the world by addressing the issues and embracing the possibilities.
Medical students and professionals must keep themselves updated and knowledgeable about the recent advancements in healthcare as it is going to impact their career growth to a great extent. To escalate the growth of your medical career, it is mandated to upskill.
The recent advancements in the global healthcare and medicine field are significant for several reasons. By offering more precise diagnoses, earlier illness detection, and more individualised treatment regimens, they have the potential to:
- Improve the quality of care for patients.
- By enabling remote monitoring and care and minimising the need for in-person visits, healthcare may be made more accessible and cheaper.
- Increase the effectiveness of healthcare delivery by simplifying administrative procedures and facilitating information exchange between healthcare professionals.
- Develop novel therapies and preventative measures to lessen the impact of chronic illnesses.
- Boost public health by keeping track of and rapidly and efficiently addressing illness outbreaks.
Below mentioned are technological advancements in medicine and global healthcare:
Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
With the introduction of unprecedented tools for patient care, treatment, and diagnosis, artificial intelligence (AI) is drastically changing the healthcare industry.
For researchers interested in global health, AI-driven health interventions fall into four categories: diagnosis, patient morbidity or mortality risk assessment, disease outbreak prediction and surveillance, and health policy and planning. Machine learning, signal processing, data mining, natural language processing, and other forms of AI are applied in the healthcare sector.
Here are a few current applications of AI in healthcare:
- Diagnosis and treatment: Artificial intelligence (AI) paves the way for the screening of disease and can analyse medical images like X-rays and scans to identify illnesses early and more accurately than humans. AI may be used to create individualised treatment regimens for individuals based on their unique traits and requirements. Other applications of artificial intelligence being used in medicine include Digital chest radiographs, cervical cancer screening, estimating perinatal risk factors, and characterising and predicting the global spread of the Zika virus.
- Drug discovery: Artificial intelligence (AI) may be used to search through extensive databases of chemicals and compounds to find possible new medicines. AI may also be used to foresee how pharmaceuticals would react in the body, lowering the possibility of adverse effects.
- Personalised medicine: Artificial intelligence (AI) may be used to examine a patient’s genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle choices in order to develop a personalised treatment plan that has the highest chance of success.
- Risk assessment: AI may be used to predict the risk of disease and figure out how likely a patient is to have cancer or heart disease. Patients can utilise this knowledge to guide lifestyle adjustments that will lower their risk.
- Healthcare administration: AI may be used to automate processes like appointment scheduling, patient record management, and claim processing. This might free up medical personnel to concentrate on treating patients.
- Telemedicine: Platforms that employ AI in telemedicine can be used to offer doctor consultations via the Internet. Patients with limited access to healthcare in remote locations may particularly benefit from this.
- Robotics: Surgery, pharmaceutical dispensing, and other medical services can be carried out by AI-powered robots. This might aid in enhancing the effectiveness and precision of healthcare delivery.
- Big data analytics: Using AI, enormous databases of healthcare data may be analysed to spot trends and patterns. The diagnosis and treatment of illnesses can be made better with the use of this knowledge.
- Virtual assistants: AI-driven virtual assistants may be used to set up appointments, answer patients’ inquiries, and offer information about their conditions. The patient experience may be enhanced as a result of this.
The future of AI in healthcare is very promising. The use of AI in healthcare is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we diagnose, treat, and manage diseases. In the years to come, as AI technology advances, it is anticipated to have a more significant influence on the healthcare industry.
Advances in Gene Editing Technology
The science of gene editing is expanding quickly. The way we treat illnesses is changing as a result of gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9. These technologies can be used to fix genetic flaws that lead to disease or to add new genes that can offer disease protection.
The following are some of the developments in gene editing technologies that are being investigated for medical applications:
- CRISPR-Cas9: A protein called Cas9 is used by CRISPR-Cas9 to cut DNA at a precise spot. This enables precise gene replacement, deletion, and insertion. The most popular gene editing technology, CRISPR-Cas9, is being researched for a number of uses, including the treatment of HIV, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and hereditary illnesses.
For instance, in cancer patients, CRISPR-Cas9 is being utilised to create novel cancer medicines that can target and eliminate cancer cells. CAR T-cell treatments, a sort of immunotherapy that employs a patient’s immune cells to combat cancer, are being developed by researchers utilising CRISPR-Cas9.
- Base editing: A more recent gene editing technique, base editing allows you to alter specific DNA nucleotides without actually cutting the DNA. Compared to CRISPR-Cas9, this makes it less likely to result in unwanted side effects. For the therapy of conditions including cystic fibrosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, base editing is being researched.
- RNA editing: An approach to gene editing that can target RNA molecules rather than DNA. This can be utilised to treat conditions like certain cancers that are brought on by RNA alterations.
- Gene therapy: Gene therapy is a treatment that involves introducing genes into cells to correct a genetic defect. Numerous illnesses, including cancer, HIV, and hereditary ailments, have been treated by gene therapy.
These are only a handful of the gene editing innovations that are being investigated for medical applications. Technology’s continued advancement will probably have a significant influence on how we manage diseases in the years to come.
Development of Precision Medicine
A person’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment are all taken into consideration when developing a medical treatment plan in precision/personalised medicine. This may result in a more effective and targeted treatment with fewer adverse effects.
Personalising medicine may be done in a variety of ways. Typical strategies include:
- Genetic testing includes examining a person’s DNA to see if there are any mutations or variances that might impact their likelihood of contracting a certain disease or their reaction to a particular medication.
- Biomarkers are quantifiable indications of a biological condition or state. Biomarkers can be used to monitor a patient’s response to therapy or to spot those who are most likely to catch a particular disease.
- Environmental factors, such as pollutant exposure, food, and exercise impact how people respond to therapy as well as the development of many diseases.
Precision medicine is becoming more and more feasible as we understand more about the human genome and the part genetics plays in disease. We can create more effective and focused therapies that may result in improvement by taking into consideration a person’s particular demands.
Here are some examples of current applications of precision medicine:
- High-risk cancer patients are identified via genetic testing, and targeted medicines are created that are more efficient for those who have certain genetic alterations.
- Biomarkers are being utilised to monitor an individual’s risk of developing heart disease and to pinpoint those who will benefit from certain therapies the most.
- Scientists are examining the genetic component of Alzheimer’s disease and creating targeted treatments that might be more efficient for those who carry particular genetic abnormalities.
Some of the challenges and limitations of precision medicine include cost, accuracy, accessibility, and regulation.
Personalised medicine is a promising subject with the potential to enhance millions of people’s lives despite these difficulties. It is anticipated to become more accessible, inexpensive, and accurate as technology advances.
Development of Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare
Telemedicine and remote healthcare allow patients to receive care from a doctor or other healthcare provider without having to travel to a doctor’s office or hospital. This can help with healthcare access, particularly in remote locations. The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred telemedicine and remote healthcare development to a great extent. These services are increasingly enticing to patients and providers alike because of the requirement to maintain social distance and avoid in-person visits to healthcare institutions. There are several advantages to telemedicine and remote medical care, such as better access to healthcare, lower healthcare expenses, increased patient satisfaction, and better patient results.
Remote healthcare services and telemedicine come in a wide variety. The most popular ones are Tele-education, remote patient monitoring, and virtual doctor appointments.
Additionally, there are several drawbacks to telemedicine and remote treatment, such as security and privacy issues, a lack of financing, technical issues, and a shortage of skilled providers.
Despite these impediments, telemedicine and remote healthcare are expanding quickly and playing a bigger role in the healthcare system. These services are expected to become progressively more common and available as technology advances.
Here are some of the future trends in telemedicine and remote healthcare:
- Increasing the use of artificial intelligence (AI): AI may be applied to personalise treatment regimens, increase the precision of diagnoses, and keep track of patient’s health.
- Development of novel telehealth technology: More thorough and individualised treatment will be feasible thanks to new gadgets like wearable sensors and virtual reality headsets.
- Expansion into new areas: Telemedicine and remote healthcare will be utilised to deliver care in new areas, such as managing chronic diseases and mental health.
Application of 3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing in medicine is being used to create customised medical items including prostheses, implants, and surgical guides. This innovation might save expenditures while raising the standard of treatment. A rapidly developing technology, 3D printing has a wide range of potential uses in the healthcare sector. Among the most widespread applications of 3D printing in the medical field, some are mentioned below:
- Producing patient-specific medical devices: 3D printing may be used to produce personalised medical items like implants, prostheses, and surgical guides that are tailored to the anatomy of a single patient. In addition to lowering the risk of problems, this can enhance the device’s fit and functionality.
- Building medical models and educating healthcare professionals: 3D printing may be used to build accurate representations of the human body’s organs, tissues, and tumours. These models can be used to aid in the planning and execution of intricate treatments as well as the education of patients about their conditions. This can assist them in picking up new abilities and methods, as well as in practising approaches in a secure setting.
- Creating novel medications and treatments: Tissue scaffolds for cell culture and intricate drug delivery systems may be made using 3D printing. This can aid in the development of novel treatments and medications by researchers for a number of disorders.
- Customising care: Using 3D printing, it is possible to develop treatments and drugs that are specifically suited to the requirements of a certain patient. This might increase the therapy’s efficacy and security.
Here are some specific examples of how 3D printing is being used in healthcare today:
- A company named Materialise has created a 3D-printed breast implant that is specifically designed for women with tuberous breasts. This type of breast deformity is often difficult to treat with traditional implants, but the 3D-printed implant can provide a more natural and comfortable fit.
- A team of researchers at the University of California, San Diego has developed a 3D-printed surgical guide that can be used to remove brain tumors with greater precision and accuracy.
- A company named Organovo has developed a 3D printer that can be used to create human tissue. This tissue can be used to study diseases, develop new drugs, and create personalized medical implants.
These are some of the numerous uses for 3D printing that are now being made in the medical field. As technology advances, it will probably have a bigger influence on the healthcare sector, enhancing the standard of treatment and enhancing accessibility for all.
The use of blockchain technology to increase the security and effectiveness of healthcare data exchange is one of the significant developments being made in the world of healthcare. Smart technologies, particularly wearable sensors, are being developed to extract therapeutically significant health-related data from physical (body) indicators like heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, respiration rate, and body motion. The technology has now also come up with immersive virtual and augmented reality training and education in the medical field.
Advancements in technology, increased investment in global health, partnerships, collaborations among the government, organizations, and individuals, and innovations altogether make a significant contribution to addressing the challenges to global health and improving health outcomes. The rapid pace of technical improvement has made these developments feasible. These technologies will have a bigger influence on global healthcare as they advance.
Obstetrics and Gynecology (OBGYN) is a branch of medicine that deals with the health of women, including the reproductive system, pregnancy, and childbirth. OBGYN is a compulsory clinical subject in the MBBS curriculum. Being an MBBS student, you will get hands-on experience in OBGYN during clinical rotations. You will observe and assist doctors in delivering babies, performing surgeries, and treating gynecological conditions. OBGYN is a challenging but rewarding field of medicine.
MBBS Prof Exam Pattern
The OBGYN Prof exam comprises two theory papers of 100 marks each and a practical examination of 200 marks. The theory exam consists of short-answer questions, long-answer questions, case-based questions, and objective-type questions. The practical examination includes clinical examination and viva.
Recommended books for Obstetrics and Gynecology
The most preferred books for studying OBGYN in MBBS are DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics (Including Perinatology and Contraception), DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology, Shaw’s Textbook of Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Obstetrics, Bedside Clinics in Gynecology, and Ward Rounds in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Subject weightage in NEET-PG and INI-CET
Concentrate on early preparation for both professional exams and competitive exams, especially if you want to pursue postgraduate studies. The subject weightage of Obstetrics and Gynecology in NEET-PG is about 25–30 questions and about 15-20 questions in INI-CET. The subject weightage clearly shows the importance of the subject in both NEET-PG and INI-CET. Try not to miss any high-yielding topics in obstetrics and Gynecology.
High-yielding topics are a crucial component of a productive study plan that will improve your test-taking efficiency. You must carefully schedule your study sessions, giving priority to time management, the course’s high-yielding topics, and, most importantly, your health.
Important and High-Yielding Topics of OBGYN for MBBS Prof Exams, NEET-PG, and INI-CET
Carcinoma Cervix
Aetiology and Staging of Carcinoma Endometrium
Postmenopausal Bleeding in Diabetics and Hypertensives
Hysteroscopy
Endometrial Ablation
PCOS
Letrozole and Metformin Pharmacology
Ovulation Induction
Carcinoma Ovary Staging
Germ cell tumors, especially Dermoid and Dysgerminomas
Laparotomy
Raloxofene and Bisphosphonates
HRT Indications and Contraindications
Testicular Feminization Syndrome
Treatment of CAH
Turners Syndrome
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
Antepartum and Intrapartum Surveillance
NST and CTG
Biophysical profile and dynamics of amniotic fluid
Doppler of the Uterine Artery
Ductus venosus ‘M’ wave pattern
Malpresentation and Malposition
Placenta-accrete case
Management of PPH
Blood Component Therapy
Management of Shoulder Dystocia
Stages of labour
Ectopic Pregnancy
Molar Pregnancy
Cell-free DNA
Preterm Labour
APH
Sterilisation Surgeries
COVID Pregnancy
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Cesarean section of childbirth
Ultrasound in Pregnancy
Diabetic Mother
Pre-eclampsia
Ca Cervix
Ovarian Cancer
Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
Uterine Prolapse
Fibroid
Postmenopausal Bleeding
Contraception, especially Oral Contraceptive Pills
Endometriosis
Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases
Stress Urinary Incontinence
Important Topics in OBGYN for the Practical Examination
OBGYN is a vast but rewarding clinical subject, and hence, it is highly crucial to learn and excel in the practical curriculum as well. During MBBS, you learn about the anatomy and physiology of the female reproductive system, as well as the diagnosis of common gynecological and obstetrical conditions. You also gain experience performing pelvic exams and other diagnostic procedures. To score well in MBBS practical exams, you should be familiar with the basic principles and procedures of OBGYN and be able to perform the essential clinical skills.
Some of the important topics for the OBGYN practical exam include:
Common Surgical Instruments
Pelvic Examination
History-taking and Clinical assessment of common OBGYN conditions
Bimanual Examination
Vaginal Ultrasound
Speculum Examination
Pap Smear: Cervical Cytology
Breast Examination
Contraception
Infertility
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
Normal Labor and Delivery
Postpartum Care
Gynecological Surgery Procedures
Here are some additional tips for preparing for the MBBS practical exams in OBGYN:
- Practice performing the pelvic examination and other clinical skills on mannequins or other simulated patients.
- Read textbooks, review articles, and case studies on OBGYN.
- Attend lectures and tutorials on OBGYN procedures and examinations.
- Shadow an OBGYN physician to get hands-on experience.
- Take practice exams to assess your knowledge and skills.
By following these tips, you can be well-prepared for the MBBS practical exams in OBGYN.
To ace your examinations and escalate your learning, you can enroll in the OBGYN for Undergrads course by Dr. K. Srinivas. The content and video lectures in the course are aligned with the CBME curriculum and also incorporate knowledge from the various standard textbooks. This comprehensive course is well integrated with knowledge of clinical obstetrics and gynecological examinations, case discussions, and highly illustrative clinical and radiological images. This course by the eminent faculty provides access to video lectures, notes, self-assessment questions, and clinical cases.
Case discussions and Qbanks of Obstetrics and Gynecology acquaint the students with the commonly asked questions during the practical exam and viva voce. Hence, this course is ideal for OBGYN students to excel in Obstetrics and Gynecology subject and to eventually score high in MBBS theory exams, practical exams, viva voce, and competitive entrance exams.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the difference between a gynecologist and an obstetrician?
Ans. An obstetrician is a doctor who specializes in the care of women and their babies during pregnancy and childbirth whereas a Gynecologist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of female reproductive disorders.
Q2. What are the high-yield topics in obstetrics and gynecology?
Ans. The high-yield topics in obstetrics and gynecology are Endometriosis, Pelvic Inflammatory Diseases, Stress Urinary Incontinence,
Postmenopausal bleeding in diabetics and hypertensives, Hysteroscopy, Endometrial Ablation, PCOS, Letrozole and metformin pharmacology, Antepartum and intrapartum surveillance, Malpresentation and malposition, Management of PPH, Blood component therapy, Management of Shoulder Dystocia and more.
Q3. Which book is best for OBG MBBS?
Ans. The most preferred books for studying OBGYN in MBBS are DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics (Including Perinatology and Contraception), DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology, Shaw’s Textbook of Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Gynecology, Self-Assessment and Review Obstetrics, Bedside Clinics in Gynecology, and Ward Rounds in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Forensic Medicine and Toxicology subject is included in the third prof of the MBBS curriculum. The main objective of teaching forensic medicine to undergraduate students is to create a doctor who is knowledgeable about medico-legal duty while practicing medicine. You will also be able to make observations and draw conclusions using logical inquiries into criminal situations and related medicolegal issues in the proper direction. You learn about applying law to medical practice, and adherence to medical ethics regulations.
MBBS Prof Exam Pattern
According to the CBME curriculum, the MBBS prof exam of the Forensic Medicine and Toxicology subject comprises one theory exam of 100 marks, and the practical examination (Practical/Clinical + Viva) of 100 marks. The theoretical exam has a variety of question types, such as structured essays (long answer questions, or LAQ), short response questions, and objective questions (MCQs and IBQs).
Recommended Books of FMT
Recommended books for FMT in MBBS include Review of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology and Recent Advances in Forensic Medicine and Toxicology (Volume-1 and 2) by Gautam Biswas, The Essentials of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology by KS Narayan Reddy and OP Murty, Forensic Medicine by J Magendran, and The Synopsis of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology by KS Narayan Reddy.
Subject Weightage of FMT in NEET-PG and INI-CET
Concentrate on early preparation for both professional exams and competitive entrance exams, especially when you want to pursue postgraduate study. The two main entrance examinations in India are NEET-PG/NExT and INI-CET to get admission into PG courses. The subject weightage of the FMT subject is about 10 questions in NEET-PG and 8 questions in the INI-CET entrance examination.
Important Topics of FMT for MBBS Prof Exams, NEET-PG, and INI-CET Entrance Examination
High-yielding topics are a crucial component of a productive study plan that will improve your test-taking efficiency. You must carefully schedule your study sessions, giving priority to time management, the course’s high-yielding themes, and, most importantly, your health. FMT in MBBS is a multidisciplinary subject and is among the high-scoring subjects. The subject requires frequent revision for better retention.
Here’s a list of high-yielding topics of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology for NEET-PG, INI-CET, and MBBS Prof exams:
Medical Jurisprudence and Ethics
Functions of MCI
Functions of SMC
Professional Misconduct and Penal Erasure
Difference between Professional Negligence and Infamous Misconduct
Consent: Types, Exceptions, Age of Consent, Inform Consent, False Consent
Difference between Civil and Criminal Negligence
Res Ipsa Loquitur
Defenses against negligence
Acts Related to Medical Practice
Transplantation of Human Organ Act, 1994
Consumer Protection Act, 1986
Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act, 1971
Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012
The Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
Legal Procedure
Inquest
Courts of Law
Difference between Dying Declaration and Dying Deposition
Exceptions to Oral Evidence
Duties of a doctor in the witness box
Capital Punishment
Type of Evidence and Witness
Homicide
Identification
Cephalic index
Intersex
Age determination by dentition, x-rays, and mandible
Gustafson’s method
MLI of age
MLI of scar, tattoo marks
Dactylography
Fingerprint Identification
Difference between antemortem and PM clot
Autopsy
Exhumation
Forensic Psychiatry
Delusion
Hallucination
Impulse
Difference between psychosis and neurosis
Lucid interval
Schizophrenia
Testamentary capacity
Section 84 IPC
Somnambulism
Erectile Dysfunction and Sterility
Impotence, Sterility, Frigidity, Quod
Vaginismus
Artificial Insemination
Surrogate mother
Causes of erectile dysfunction and sterility in males
Causes of impotence and sterility in females
Virginity, pregnancy, and delivery
Hymen
Difference between true virgin and false virgin
Presumptive, probable, and positive signs of pregnancy
Superfecundation and superfetation and their MLI
Difference between nulliparous and parous uterus
Sexual Offences
Classification of sexual offences
Section 375 IPC
Punishment of rape 376 IPC
Examination of rape victim/survivor
Locard’s exchange principle
Sodomy/Buggery
Tribadism/Lesbianism
Sexual paraphilias types
Exhibitonism, frotteurism/toucherism
Seminal strains test
Injuries
Grievous hurt, section 320 IPC
Joule burn
Classification of thermal injuries
Heat hyperpyrexia/Heat stroke
Burns
Difference between pugilistic attitude and rigor mortis
Skull fractures
Extradural/Epidural hematoma
Bullet types
Components of gun powder
Abrasion
Contusion
Laceration
Ectopic/Migratory bruise
Fabricated/forged wounds
Intracranial hemorrhages
Cold injuries- frostbite
Would ballistics
Asphyxia
Causes/Classification of asphyxia deaths
Lynching
Difference between hanging and strangulation
Cafe coronary syndrome
Post-mortem examination of a drowning case
Diatom test
Sexual asphyxia
Death/Thanatology
Rigor mortis/Stiffness of death
Cadaveric spasm
Heat stiffening
Order of putrefaction
Mummification
Brain stem death
Cause, manner, and mode of death
Sudden death
Tache noire
Infanticide and Child Abuse
Hydrostatic test
Cause of infant death
Shaken baby syndrome or infantile whiplash syndrome
Difference between live born, dead born, and stillborn fetus
Hydrostatic test
Toxicology
Section 284 IPC
Classification of poison
Organophosphorus compounds poisoning
Alphos poisoning
Vitriolage
Chronic arsenic poisoning
Hydragyrism
Phossy jaw/Lucifer’s jaw/Glass jaw
Sui
Difference between true and artificial bruise
Signs and symptoms of Ophitoxemia
Snake poisoning
Section 85 IPC
Widmark’s formula
LSD
Date rape drugs
Others
Poat-mortem artefacts
Transportation injuries
Confirmatory tests for blood
Medico-legal application of blood groups
Precipitin methods
To get conceptual clarity in the FMT modules and learn in a simplified manner, subscribe to DigiNerve’s online FMT course. The Forensic Medicine and Toxicology for UnderGrads course is well conceptualized by eminent faculty, Dr. Gautam Biswas according to the CBME curriculum. Application-based learning has been given top priority, and even the test question format is created to gauge students’ clinical expertise. The training is designed for medical students to help them be ready for both their university examinations and the NEET PG/NExT Exam. The lectures for the course cover every relevant topic in an interesting manner. In order to help students comprehend ideas better, the course includes flowcharts, animations, brief films, diagrams, and well-integrated MCQs.
Click here to know the right way to approach FMT in MBBS.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What are the important topics of FMT in MBBS?
Ans. The important topics of FMT in MBBS include Legal Procedure, Identification, Thanatology, Asphyxia, Injuries, Rape, General toxicology, OPC poisoning, Snakebite, Medicinal poisoning, Autopsy, fingerprint identification, Burns, Skull fracture, and more.
Q2. Which are the recommended books of Anatomy for MBBS students?
Ans. Recommended books for FMT in MBBS include Review of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology and Recent Advances in Forensic Medicine and Toxicology (Volume-1 and 2) by Gautam Biswas, The Essentials of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology by KS Narayan Reddy and OP Murty, Forensic Medicine by J Magendran, and The Synopsis of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology by KS Narayan Reddy.
Q3. What is the weightage of FMT in the NEET PG exam?
Ans. The weightage of FMT in NEET PG is approximately 10 questions.
Q4. Where can I find an affordable yet comprehensive online course for forensic medicine?
The best forensic medicine online course 2023 is Forensic Medicine and Toxicology for UnderGrads by Dr. Gautam Biswas. The course is comprehensive, clinically up-to-date, and quite affordable.
National Medical Commission (Undergraduate Medical Education Board) on the notification dated 1st August 2023 released Competency Based Medical Education Curriculum (CBME) regulations 2023 for the MBBS programme. The latest CBME pattern elaborates on the subject competencies, broad subject-specific objectives, skills, and integration. The CBME regulations further include an academic calendar, schedule, training, new teaching/learning elements, phases of the MBBS curriculum, electives, clinical postings, and more.
Subjects Included in the MBBS Curriculum
| Professional Year | Subjects |
| 1st |
|
| 2nd |
|
| 3rd (Part I) |
|
| 3rd (Part II) |
|
New Teaching/Learning Elements
- Foundation Course
- Early Clinical Exposure
- Electives
- Professional Development including Attitude, Ethics, and Communication Module (AETCOM)
- Learner-doctor method of clinical training (Clinical Clerkship)
- Assessment
The Latest CBME Curriculum for MBBS Programme Includes
1. Training Period and Time Distribution
The first professional year must commence through the Foundation Course by the 1st August of each year from the academic year 2024-25. The foundation course aims to orient medical students to the undergraduate MBBS programme and provide them with the requisite knowledge, communication (including electronic), and technical and language skills.
There shall be no admission of students in respect of any academic session beyond 30th August from the academic year 2024-25.
The duration of the MBBS course shall be the same, i.e., four and a half years divided into four professional years from the date of commencement of the course to the date of completion of the examination followed by one year of compulsory rotating internship.
There will be at least 39 teaching weeks in each academic year, with each day of work requiring no less than eight hours, including one for lunch.
Didactic lectures are allowed to make up no more than one-third of the timetable; the other two-thirds must include interactive sessions, practicals, clinicals, or group discussions.
For greater student comprehension, teaching and learning must be vertically and horizontally linked and integrated across specializations.
Early clinical exposure, problem-oriented learning, case studies, community-oriented learning, self-directed, experiential learning, and electives should all be included in a learner-centered curriculum.
University exams will be conducted at the end of every professional year.
There will be supplementary examinations in case the students fail to clear the university exam and the supplementary exam result shall be processed within 3-6 weeks from the declaration date of the main exam results.
There will be no supplementary batches and hence, if any candidates fail the supplementary exams will have to join the next/subsequent academic year batch.
Partial attendance in an examination shall be counted as an attempt.
2. MBBS Phase-wise Curriculum
| Phase & Year of MBBS Training | Duration | Main Subjects | Additional Curriculum | University Examination |
| I | 12 Months (including the foundation course of one week and university exams) | Anatomy
Physiology Biochemistry |
Foundation Course
Introduction to Community Medicine, Humanities, Professional development including Attitude, Ethics & Communication (AETCOM) module. Family adoption programme through village outreach where-in each student shall adopt a minimum of three (03) families and preferably at least five (05) families and Pandemic module. Early clinical exposure, ensuring alignment & all types of integration and simulation-based learning. |
1st Professional |
| II | 12 Months | Pathology
Pharmacology Microbiology |
Family visit for FAP
Professional development including the AETCOM module. Introduction to clinical subjects ensuring both alignment & all types of integration and simulation-based learning. A part of training during clinical postings should take place at the primary level of health care. |
2nd Professional |
| III | 30 Months | |||
| III (Part 1) | 12 Months (including university exams and a 1-month elective course) | Forensic Medicine and Toxicology
Community Medicine It also includes one month for Electives. |
The curriculum includes Medicine & allied Surgery & allied, Pediatrics, and Obstetric & Gynecology foundational knowledge.
AETCOM Pandemic module Clinical Postings Family Visits under FAP Clinical teaching in General Medicine, General Surgery, Obstetrics & Gynecology, Pediatrics, Orthopedics, Dermatology, Community Medicine, Psychiatry, Respiratory Medicine, Radio-diagnosis (& Radiotherapy), and Anesthesiology & Professional development. Electives will be in 2 blocks of l5 days each in Final first; 1st block after the annual exam of III MBBS part I and 2nd block after the end of 1st elective |
Final Professional – Part I |
| III (Part 2) | 18 Months (including the university exam) | Medicine and allied specialties (General Medicine, Psychiatry, Dermatology, Venereology and Leprosy (DVL), Respiratory Medicine including Tuberculosis)
Surgery and allied specialties (General Surgery, Otorhinolaryngology, Ophthalmology, Orthopedics, Dentistry, Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Anesthesiology, and Radiodiagnosis) Obstetrics and Gynecology (including Family Welfare) Pediatrics |
AETCOM Module
Clinical Postings |
Final Professional Part – II |
3. Foundation Course
The time duration of the foundation course is one week and additionally spread over 6 months at the discretion of the college.
| Subjects/Contents | Teaching Hours |
| Orientation | 30 |
| Skills Module | 34 |
| Field Visit to Community Health Center | 08 |
| Introduction to Professional Development & AETCOM Module | 40 |
| Sports, Yoga, and Extra-Curricular Activities | 16 |
| Enhancement of Language/Computer Skills | 32 |
| Total | 160 |
4. Phase-wise Distribution of Teaching Hours
a. Teaching hours of First, Second, and Third Professional Part-1:
Time allotted: 12 months (approx. 52 weeks)
Time available: Approx. 39 weeks (excluding 13 weeks) (39 hours/week)
Prelim/University Exam & Results: 9 weeks
Vacation: 2 weeks
Public Holidays: 2 weeks
Time distribution in weeks: 39 weeks x 39 hours = 1521 hours for Teaching-Learning
b. Teaching Hours of Final MBBS Part-2:
Time allotted: 18 months (approx. 78 weeks)
Time available: Approx. 62 weeks (excluding 16 weeks) (39 hours/ week)
Prelim / University Exam & Results: 10 weeks Vacation: 3 weeks
Public Holidays: 3 weeks
Time distribution in weeks: 62 x 39 hrs = 2418 hrs available for Teaching- Learning
5. Clinical Posting
The Clinical Postings shall start from the II phases of the MBBS programme.
The duration of the Clinical Postings shall be 15 hours per week.
Clinical Posting Schedule in Weeks
| Subjects | Period of Training in Weeks | Total Weeks | ||
| II MBBS | III MBBS Part 1 | III MBBS Part 2 | ||
| Electives | 0 | 4 | 0 | 4 |
| General Medicine | 9 | 4 | 14 | 27 |
| General Surgery | 7 | 4 | 10 | 21 |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | 7 | 4 | 10 | 21 |
| Pediatrics | 4 | 4 | 5 | 13 |
| Community Medicine | 4 | 4 | 0 | 8 |
| Orthopaedics | 2 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| Otorhinolaryngology | 0 | 3 | 4 | 7 |
| Ophthalmology | 0 | 3 | 4 | 7 |
| Psychiatry | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Radio-diagnosis | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 |
| Dermatology | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Dentistry | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Anaesthesiology | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 |
| Total | 33 | 36 | 62 | 134 |
6. Marks Distribution for Various Subjects for University Annual Examinations
For the university exams, there shall be two theory papers of 100 marks each and a practical examination of 100 marks for all the MBBS subjects of the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd (Part 1) phases of MBBS (except FMT).
The Forensic Medicine and Toxicology subject comprises one theory paper of 100 marks and one practical examination of 100 marks.
The exams of Final MBBS exams shall be as per the NExT regulations.
7. Electives
Electives on topics in areas such as Research Methodology, Use of Artificial intelligence and Computers in Health and Medical Education, Health Management, Health economics, Indian System of Medicine, Medical Photography /Clinical Photography, Global Health, Evidence-based Medicine, Art and Music in Medicine, Literary Activities, etc. may be provided by the college/ institution.
Based on both electives, the learner is required to submit a learning log book.
75% attendance in the electives and submission of log book maintained during electives is required for eligibility to appear in the final MBBS examination/NEXT.
8. Eligibility to appear for the Professional Examination
For a student to be eligible to sit for examinations, there shall be a minimum of 75% attendance in theory and 80% in practicals.
Students will not be permitted to take the Third Professional – Part II examination/NEXT if they do not have at least 75% attendance in the electives.
9. Internal Assessment
Internal assessment includes participation in the learning process including assignments, preparation for seminars, clinical case presentation, preparation of clinical cases for discussion, clinical case study/problem-solving exercises, and participation in projects for health care in the community.
Internal marks are not added to the summative assessment.
Competencies and skills marked in daily records and the log book are considered for the internal assessment evaluation.
There must be a minimum of three internal assessments for each topic in the first and second professional years, and a minimum of two assessments for each subject in the third and final professional years. Each clinical posting in a given professional year must have a post-posting clinical assessment done.
To be eligible to appear at the final university examination for a given subject, students must receive at least 50% of the total marks (combined in theory and practical in clinical; not less than 40% in theory and practical separately) in internal assessment in that subject. The results of the internal evaluations will count towards a distinct head of passing on the final test.
10. University Examinations and Result
The Prof exam shall include Long-Answer Questions -LAQ), Short-Answer Questions (SAQ), and objective-type questions.
A viva/oral examination shall evaluate the candidate’s approach to patient management, emergency preparedness, attitude, ethics, and professional values. The ability of the candidate to read standard investigative data, X-rays, specimen identification, ECGs, etc. will also be evaluated.
If a subject has two theory papers, the learner must receive at least 40% aggregate of the possible marks on the combined total of the two papers to pass the subject.
A candidate must receive 50% aggregate marks and 60:40 (minimum) or 40:60 (minimum) in a university-conducted examination, taken separately for Theory and Practical (which includes viva voce and practical/clinical components) in order to be declared as passed in that subject.
There shall be no grace marks to be considered for passing an examination.
A candidate cannot enroll in the second professional if they fail the first professional examination.
A candidate who fails the second professional examination may enroll in the third professional part I training, but he or she may not sit for the exam until the second professional examination has been passed.
A candidate who does not pass the third Professional (Part I) test will be permitted to enroll in the third Professional Part II training, but he will not be permitted to sit for the examination until the second Professional examination has been passed.
The Chapter 2 of the NMC Update describes the broad outline of the National Exit Exam, including general features of steps 1 and 2, NExT scores, nature of scores, minimum passing score, etc.
General Features of the NExT Exam
The NExT Exam shall comprise two separate exams referred to as “Steps”.
Step 1: Theoretical Examination
Step 2: Practical/Clinical and Viva Voce Examination
NExT Step 1
1.NExT Step 1 shall be a theoretical and Computer-based/Online examination.
2. It shall comprise one or more types of multiple-choice questions.
3. This shall be a Centralized Common All India Examination that will be held by a body designated by the commission as the conducting authority.
4. The examination shall include six papers covering topics from both Part 1 and 2 of the III MBBS/Final MBBS programme:
- Medicine and allied disciplines
- Surgery and allied disciplines
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
(Applied aspects of all subjects covered under I MBBS and II MBBS and Applied aspects of all subjects covered under III MBBS/Final MBBS Part l)
5. Students who have completed their III MBBS/Final MBBS course from a recognized medical college shall be eligible to appear for the examination.
6. NExT Step 1 Examination shall be held twice a year in the months of May and November tentatively.
7. There shall be no restriction on the number of attempts to participate in NExT Step 1 provided that the candidate has completed both the NExT Step 1 and NExT Step 2 exams within ten years of enrolling in the MBBS Course.
8. There is no cap on the number of times for attempting the NExT Step 1 Regular Examination to improve your score but you can only go for the improvement after completing your NExT Step 2.
9. The III MBBS/Final MBBS Part 1 and III MBBS/Final MBBS Part II Practical/clinical examinations will continue to be held conventionally unless otherwise stated by the Commission and the NExT Step 1 will replace the traditional university/institutional Theory Examinations of the III MBBS/Final MBBS Part II.
NExT Step 2
1. The NExT Step 2 shall be a Practical/Clinical and viva voce examination comprising seven clinical subjects/disciplines:
- Medicine and allied disciplines
- Surgery and allied disciplines
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics and PMR (Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation)
2. The exam shall be objectively structured, clinical case-based, and use simulated cases and patients to evaluate practical and clinical skills as well as clinical decision-making and communication abilities expected of an Indian medical graduate.
3. The exam must be taken in person or live, and it must be administered by the relevant state health universities or institutions in accordance with the norms and directives given by the Commission. The Commission will choose the university or institution that is permitted to conduct NExT Step 2 for the relevant colleges where there are no state health universities.
4. The Regular NExT Step 2 Exam shall be held twice a year.
5. A NExT Step 2 Supplementary Examination is only open to candidates who have failed in one or more (up to three) of the seven subjects and are required to repeat specific subjects. It will be held twice a year. If a candidate fails in more than three subjects, then they will have to appear in supplementary exams of all the seven subjects.
7. As long as the candidate has completed both the NExT Step 1 and NExT Step 2 Examinations within ten years of enrolling in the MBBS programme, there is no restriction on the number of attempts to participate in NExT Step 2.
NExT Scores
1. Nature of Scoring
- The marks in NExT Step 1 must be calculated as a whole number, which will serve as the Raw Scores with the proper decimals. Also, equivalent Percentages (marks out of a maximum of 100) with the proper decimals may then be calculated.
- The outcomes of the NExT 2 exams will only be reported as Pass/Fail depending on the acquisition of the relevant competence that is being evaluated.
2. Minimum scores for passing
- The minimum score to pass shall be 50% of the total or half of the maximum possible Raw for NExT Step 1.
- To pass the NExT Step 1 exam, you must receive a minimum of 50% (50 out of 100) in each of the six papers or half of the maximum possible Raw Scores.
- The requirements for passing NExT Step 2 include a successful demonstration of having acquired the competencies that are evaluated, with a pass/fail result being given.
3. Calculation of NExT Step 1 scores for determining merit for the purpose of admission to Postgraduate courses in broad specialties
- The sum of the raw scores earned in each paper or topic in a single NExT 1 exam will be used to calculate the Total Marks for determining the merit, particularly for admission to broad specialization Postgraduate Courses.
- The candidate must follow the generation of a rank application process as stipulated by the Commission from time to time in order to determine rank for admission into Postgraduate courses in broad specializations in a given academic year. Only individuals who have submitted an application for rank generation will be eligible for admission for that cycle of the academic year.
- The NExT Step results will be valid for five years in order to determine merit, notably for admission to broad-specialty postgraduate courses. If a candidate has appeared in the NExT exam cycle then the score of the latest given NExT step 1 exam will be considered.
- Tie-breaker rule for rank generation:
-
- Normalized sum of raw scores obtained in each paper in NExT step 1 although the method of normalization will be notified later.
- Candidate with the lower attempts in NExT step 1 will be placed higher in the merit list.
- Candidates will be given higher rank based on the higher marks in the following order of preference:
-
-
- Medicine and allied disciplines
- Surgery and allied disciplines
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
-
4. Utility of NExT Scores
- An MBBS student from a college recognized by the Commission shall be eligible for compulsory internship only if they pass in each of the six theory papers of NExT Part 1 and also pass in III MBBS/Final MBBS (Part 2) Practical/Clinical Examination.
- A medical student who has completed their undergraduate studies abroad at an institution recognized by the Commission and who has met the necessary requirements outlined in the Commission’s Foreign Medical Graduate Regulations is eligible to participate in the mandatory rotating internship programme only if they pass in all six NExT Step 1 Theory Papers.
- A medical graduate who received their training in India or outside of India will be entitled to register in the Indian Medical Register and State Medical Register and obtain a license to practice modern medicine in India, only if, they have completed the internship for the appropriate length of time and have successfully passed the NExT Step 2 (Practical / Clinical) Examination. You must fulfill all the requirements as per the Registration of Medical Practitioners and Licence to practice Medicine Regulations, of NMC. Also, all the other requirements are considered appropriate by the Commission, Concerned University/Institution and duly applicable at that time.
- For admission to PG medical courses in broad specialty subjects, a candidate must meet the following criteria:
- Candidates must meet the conditions outlined for NExT Part 1 and 2, making them eligible for a license to practice modern medicine in India.
- Must engage in common counselling by a designated authority granted by the Central Government or Commission.
- The NExT Step I Scores may be used by the Government of India, the State Governments, any organization of the Government of India, the State Governments, or any autonomous or private body/institution for the purpose of employment, provided that the necessary authorization has been sought and authorized by the National Medical Commission or other appropriate authorities as determined to be appropriate.
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 1 (Preliminary)
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 3 (General Information)
The NExT Exam latest news includes Chapter 1 (Preliminary) and Chapter 2 (Broad Outline) and Chapter 3 (General Information).
The core objective of the NExT exam is to provide consistency in summative evaluations conducted across the nation in relation to the minimal requirements for a medical graduate’s education and training.
The National Exit Test (NExT), shall serve as a licentiate examination for validating a medical graduate’s eligibility to register for practice the contemporary system of medicine in India.
NExT will also act as an entrance exam for admission to PG medical education in broad medical specialties by determining the eligibility and ranking of the MBBS students.
The National Exit Exam shall be applicable to:
- All undergraduate medical students seeking the MBBS degree at all medical colleges that have been accredited by the National Medical Commission along with Institutes of National Importance (INIs) are subject to the National Exit Test (NExT).
- All foreign medical graduates who have been granted approval by the NMC for the purposes of obtaining a license to practice medicine as a registered medical practitioner in India and for enrollment in the State Register or the National Register in such a manner as may be specified by regulations.
- Anyone with a medical degree aiming to pursue an academic course, an observership, or any other purpose that may be specified and allowed by the NMC by appropriate notification or rules from time to time.
- Anyone with the granted medical license practicing in India wishes to pursue PG degree can take the NExT exam.
According to the draft released, the NExT comprises two separate examinations, referred to as “Steps”.
Step 1: Theoretical Examination
Step 2: Practical/Clinical and Viva Voce Examination
The Commission shall from time to time determine, by appropriate regulations and/or notification, the applicable method of employing the NExT results for admission to Postgraduate Courses in wide medical specialties by means of common counselling by the designated authority.
There is no confirmation yet on the academic session to which the NExT exam will be applicable but when it will come into force, all other corresponding and equivalent examinations shall be phased/ceased out.
It is still to be decided by the Commission Central Government, State Government, that the existing examinations, however, shall continue for as long as may be necessary or the analogous existing exams will be replaced by the NExT. The Commission will decide when it is necessary and will notify the use of scores and normalization of various examinations and the NExT, when applicable concurrently, for such purposes as may be appropriate.
Chapters 2 and 3 of the update include the complete structure of the NExT Examination, objectives, exam pattern, eligibility, distribution of subjects, nature of scoring, timetables, and more.
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 2 (Broad Outline)
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 3 (General Information)
After completing 12th standard, students who want to pursue their career in medicine must take the NEET-UG entrance examination. Around 15 lakh aspirants appeared for the exam last year which itself is a huge number for a total of about 78,000 thousand medical seats in India. Hence, it is highly competitive to get admission into the MBBS programme. As the NEET-UG exam is approaching on May 7 this year, students should polish their skills and stick to their preparation strategy. Strictly following the preparation tips and putting consistent efforts will keep you ahead of the competition.
Here’s are some last-minute reliable preparation tips for the NEET-UG Exam.
Practice mock paper with your timers on: This will help you in analyzing the exam pattern, evaluating your level of understanding of the topic, and of course, developing time management skills.
Solve previous year question papers: Solve previous year papers of at least last 10 years. This will give you an idea about the exam pattern, type of questions asked from the chapter and topic. It will boost your confidence.
Don’t study from multiple resources at the last moment: Before exams, always prefer to study from NCERT books and notes. This will help you with quick revision and covering the entire syllabus with focusing more on the important topics for NEET-UG exam.
Refrain from studying new chapters and concepts: The NEET-UG 2023 syllabus is vast, and it is not possible to grasp everything in one go. In case you have missed any difficult concept, refrain from starting anything in the last days because studying any topic from the beginning and then making notes is time taking which in turn increases pressure and workload. Instead, it is advised to practice the topics you have already learned and have a tight grasp over it.
Put consistent efforts: As the syllabus is quite extensive and the level of complexity is high, you must put in consistent effort to practice and revise every topic properly.
Practice, Practice and Practice: Practice as much as questions you can. Practise formulae, flowcharts, schematic diagrams, tables, graphs, remember the conversions and values of the variables, and other crucial topics. It plays a critical role in scoring well in the exams. Write and learn all the shortcut approaches which are easy to memorize the concept and recall during exam.
Prioritize Chapters: Prioritize the maximum weightage and important topics during the last period of your preparation.
Important Units of Physics for NEET-UG:
- Mechanics
- Heat and Thermodynamics
- Waves
- Magnetism
- Modern Physics
- Electricity
- Optics
Important Units of Chemistry for NEET-UG:
- Atomic structure
- Equilibrium
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Coordination Compounds
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids
- s, p, d, and f -block Elements
- Hydrocarbons
Important Units of Biology for NEET-UG:
- Evolution
- Biotechnology
- Structural organisation in animals
- Animal kingdom
- Biomolecules
- Plant physiology
- Cell & Cell Cycle
- Genetics
- Ecology
- Diversity of Living Organisms
- Human Physiology
- Human Health and Diseases
- Human Reproduction
Maintain your physical and mental health and take proper sleep: Maintaining good health is equally important as effective preparation. It is advised to take some time to meditate and exercise and keep yourself healthy. Remain calm and don’t overexert yourself. Negligence in terms of health will keep all your efforts at stake.
Be confident: Don’t panic in the last days of your preparation. Revise thoroughly what you have prepared so far and avoid comparing yourself with your fellows. Have faith in yourself and stick to your preparation, just avoid procrastination. Identify your pain areas, clear your doubts and practice more.
Prepare in advance: Read all the instructions provided on the admit card and strictly adhere to it. Avoid carrying the barred items and get dressed as per the NEET-UG exam dress code. Arrange all your required documents and valid ID proof for the exam day prior.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Keep in mind that if you fall sick all your efforts will go in vain. Hence, take proper sleep, eat healthy food, and do exercises to keep yourself healthy.
Do’s and Don’ts on the Exam Day
- Check your exam centre location prior to your exam or visit once to avoid being late on your exam day.
- Go through the instructions regarding exam day, dress code, barred items, required documents and photographs and more.
- Be very careful while bubbling in the OMR answer sheet.
- Start your exam with the subject you are more confident in and manage your time effectively.
- Don’t waste your time in thinking over a question much and do the next.
- Don’t rely on guesswork. There is a negative marking in the NEET-UG exam and hence, guesswork can reduce your overall score.
- Strictily adhere to the dresscode guidelines issues by NEET authority.
- Concentrate on your last-minute revision.
- Don’t let yourself feel dehydrated.
- Remain focused and attentive.
- Read all the instructions carefully before starting the exam to avoid any mistake.
- Double check your OMR sheet before submitting.
- Do not carry any barred/prohibited items.
- Stay positive and determined.
List of Barred Items
- Any type of study material, and stationery items such as, papers, pens, writing pads, geometry boxes, logbook, calculator, etc.
- Any communication devices such as mobile phones, Bluetooth, earphones, microphones, health band, smart watches, etc.
- Accessories like watch, wallet, bracelets, googles, cap, etc.
- Any ornaments and metallic items
- Any food item and beverage
- Any kind of cheating material
Things to carry at the Examination Day
- You must carry the following things to the Exam Centre:
- NEET-UG admit card with the passport size photograph affixed on it
- One passport size photograph to be affixed on the attendance sheet
- Valid Identity proof and PwBD certificate, if required
- Proforma downloaded with the admit card and one post card size photograph (4” * 6”) with white background must be affixed on the proforma and hand over to the invigilator at the exam centre.
Dress Code
You must follow the instructions regarding the dress code. If you don’t follow dress code, it will create chaos during frisking and you will be not allowed to sit in the exam. You must keep the following things in mind:
- Long sleeves clothes are not allowed to wear.
- Clothes with large buttons are not allowed.
- Accessories like studs, earrings, rings, etc. are not allowed.
- If any candidate is coming in the cultural customary dress for examination at any exam centre, you must report at least an hour before the reporting time.
- Shoes are not permitted. Slippers, sandals, and low heel footwear are allowed.
Your consistent efforts and determination will pay off, just have faith in yourself.
Click here to know more about NEET-UG Entrance Examination.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. What is the exam date of NEET UG 2023?
Ans. The NEET-UG entrance exam will be held on 7th May, 2023.
Q2. What is the pass mark for NEET?
Ans. The cut off marks for NEET-UG as per 2022 is 117 out of 720. But these cut-off marks are not to get admission to variety of medical undergraduate courses.
Q3. Which is the conducting body for NEET-UG?
Ans. The NEET-UG entrance examination is conducted by National Testing Agency (NTA).
Q4. Which dresses are not allowed for NEET?
Ans. You must keep the following things in mind:
- Long sleeves clothes are not allowed to wear.
- Clothes with large buttons are not allowed.
- Accessories like studs, earrings, rings, etc. are not allowed.
- If any candidate is coming in the cultural customary dress for examination at any exam centre, you must report at least an hour before the reporting time.
- Shoes are not permitted. Slippers, sandals, and low heel footwear are allowed.
The subjects included in the fourth year of MBBS curriculum are General Medicine, Dermatology, Psychiatry, General Surgery, Anaesthesiology, Orthopaedics, Obstetrics & Gynecology and Pediatrics.
A medical student must always refer to the latest editions of the book to get the updated information revised according to the CBME curriculum.
Here’s a list of recommended books for MBBS 4th Year students:
Best Books for General Medicine
| Book | Author | Desciption |
| An Insider’s Guide to Clinical Medicine | Archith Boloor & Anudeep Padakanti |
✓ X-rays, Spotters, Common Medicines, and Instruments are included that assists in making an early diagnosis. ✓ Contains thorough material organised in little boxes and figures, making it a convenient resource for revision. ✓ Discusses model cases and conventional presentations. ✓ Only book including chapters on mental disorders, geriatric evaluation, and rheumatology. ✓ Case sheet and diagnostic formats are included for cases in each system. ✓ With clear conceptual explanations and lots of visual memory aids, it is simple to read. |
| Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates: Medicine | Archith Boloor & Ramadas Nayak |
✓ Includes all the reading material a medical student at the undergraduate level would need. ✓ Simple to read, filled with visual memory and intellectual explanations. ✓ It is a ready reckoner since it contains complete information in little boxes and figures. ✓ High-yield points for the MRCP, NEET, and other competitive examinations have been included. |
| Self-Assessment & Review Medicine (Part A & B) | Mudit Khanna |
✓ ‘Essential Revision Notes’ are provided before each chapter to revise all relevant and crucial topics in a more systematic manner. ✓ The book methodically approaches “medicine” by segmenting its information into clinical chapters and then into logical ideas and themes. ✓ Harrison’s and CMDT’s most recent editions have been completely updated and reviewed in the book. ✓ Presents the most crucial information in a way that is “simple to recall,” including flow diagrams and tabulation. ✓ Includes a big database of questions from prior entrance exams. ✓ Dedicated section for IBQs. |
| Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine (Volume I & Volume II) | J. Larry Jameson, Anthony S. Fauci, Dennis L. Kasper, Stephen L. Hauser, Dan L. Longo, & Joseph Loscalzo |
✓ More than a thousand clinical, pathological, and radiographic images, and schematic diagrams are included. ✓ Clinically relevant decision trees and algorithms for diagnosis and treatment are included. ✓ The latest version has been completely updated with pertinent new chapters and significant revisions throughout the field of internal medicine. |
Best Books for General Surgery
| Book | Author | Description |
| SRB’s Manual of Surgery | Sriram Bhat M |
✓ Each chapter begins with surgical anatomy and physiology, important pertinent investigations, and a discussion of many issues in a systematic order to give readers a flow of ideas and materials with clear language. ✓ Every chapter is aligned in accordance with the CBME curriculum. ✓ Case scenarios are supplemented with brief clinical details and related images. ✓ Throughout all chapters, novel therapy modalities, concepts, and recent advancements are introduced. ✓ The book provides complimentary online learning resources:
|
| Surgery Essence | Pritesh kumar Singh |
✓ The annexures contain triads, signals, investigations of options, and subjects based on the “most prevalent” types of questions to save time and aids in revision. ✓ IBQs are added for the PG entrance exam preparation. ✓ Synopsis is included before questions to help students understand the ideas and save time. ✓ New pattern based on NBE (wider coverage, concept development, one-liner approach) is included. ✓ Solved Multiple-Choice Questions (PGMEEs 2022-1985), including all recent ones (2022-2013) are added. ✓ Crucial information is highlighted in gold. ✓ Line diagrams and mnemonics are also provided. |
| SRB’s Clinical Methods in Surgery | Sriram Bhat M |
✓ Each chapter includes information on clinical assessment techniques, investigations, and a concise summary of all surgically relevant disorders. ✓ Basic general examinations are appropriately described using examples. ✓ Provides thorough instructions for clinical evaluation along with top-notch images and graphics. ✓ The book emphasises the need of thorough clinical examinations for determining the best diagnosis, course of therapy, and follow-up. ✓ Every topic includes discussion of differential diagnosis. ✓ Several chapters offer case discussions to show students how precisely clinical examination questions are phrased. ✓ Clinical pearls are included as surgical wisdom in a few chapters and are crucial while treating surgical patients. ✓ At the conclusion, there are chapters on instruments, X-rays, and specimens for a rapid glance during the practical exam in surgery. ✓ Students can scan the QR codes and access the case demonstration videos(typical surgical situations). |
| Bailey & Love’s Short Practice of Surgery: International Student’s Edition (set volume 1 & 2) | Norman Williams, P Ronan O’Connell & Andrew McCaskie |
✓ Chapter contains summary boxes with important information throughout the text. ✓ Tables, pictures, and diagrams’ uniform design and format make it easier to grasp difficult ideas. ✓ Also contains algorithms to help the reader comprehend patient care pathways. ✓ The book highlights recent significant advancements in surgical practise and those that are predicted to have a significant impact over the next ten years. ✓ Also covers paediatric surgery and organ transplantation in more detail. ✓ Readers may access supplemental material on the dedicated Bailey & Love website, which also has extended content, videos, and other tools. ✓ The pillars of safe clinical practise continue to be a thorough history taking, observation, logical reasoning, technical expertise, and postoperative patient care and is explained in the book for the students. |
Best Book for Psychiatry
| Book | Author | Description |
| Review of Psychiatry | Praveen Tripathi |
✓ The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, has been completely revised (DSM-5). ✓ This book has been developed keeping in mind the demands of students preparing for different postgraduate entrance examinations and MCI screening test. ✓ Updated completely with ICD-11. ✓ INI-CET pattern questions have been updated. ✓ Issues like the Mental Health Care Act have been updated. ✓ Updated based on the 10th editions of the Comprehensive Textbook of Psychiatry by Kaplan and Sadock and the 7th edition of the Short Textbook of Psychiatry. ✓ Includes IBQs. |
Best Books for Pediatrics
| Book | Author | Description |
| Review of Pediatrics & Neonatology | Apurv Mehra, Meenakshi Bothra Gupta & Taruna Mehra |
✓ To help students become familiar with current trends and test patterns, the book is enhanced with more than 3200 MCQs that are organised chronologically with recent questions. ✓ Provides a brief, point-by-point summary of each chapter, including high-yield points, mnemonics, and flow diagrams. ✓ The chapters have been divided into three sections: General Paediatrics, Neonatology, and Systemic Paediatrics. ✓ Developmental stages, prominent characteristics of significant metabolic illnesses, significant genetic syndromes, a list of “Most Common” and many other crucial high-yielding topics for last-minute review are included in the annexures. ✓ Over 500 completely coloured photos are included. ✓ Under the guise of an “integrated approach,” questions with an emphasis on images have been offered. |
| Ghai Essential Pediatrics | Vinod K. Paul & Arvind Bagga |
✓ Excellently drawn tables, graphs, and flowcharts are provided throughout the book and explanations are simple to grasp. ✓ Every chapter generally has “Suggested Reading” at the conclusion in case a student wishes to go more into the subject. ✓ The chapters on growth, adolescent health, vaccination, infection, the gastrointestinal system, malignancies, and inborn metabolic defects have all undergone considerable rewriting and revision in the latest edition. ✓ With a wide range of distinguished authors, this paediatrics textbook is the most favoured and trusted in India for both undergraduate and graduate students. |
| Exam preparatory Manual for Undergraduates: Pediatrics | Snehal Patel, Halak Vasavada |
✓ Sample case presentations with frequently asked questions in viva are part of a special practical paediatrics chapter. ✓ A brand-new chapter on Covid-19 and the Covid 19 vaccinations contains myths, tragedies, and brilliant ideas is included in the latest edition of the book. ✓ For typical ward operations and competences, there are brief video snippets. ✓ Include clinical case studies at the conclusion of each chapter. ✓ Rational investigative technique, bedside realistic interpretations of frequent investigations are included. ✓ Important clinical tips in each topic—a must remember. ✓ Using flowcharts, tables, and figures, create a reader-friendly question-and-answer presentation. |
| UG Textbook of Pediatrics | Piyush Gupta |
✓ Diagrams, flowcharts, and clinical pictures are abundant throughout the book to aid with comprehension and recall. They really make up the majority of the book. ✓ The text is succinct, to the point, and yet comprehensive; it is interwoven with numerous Tables and Boxes, where necessary. ✓ Case Studies that demonstrate the typical outcomes of common diseases in children are sprinkled throughout the book as an addition. ✓ Each significant topic is followed by “In A Nutshell” overview of the main ideas. So, only reading these boxes can revise the entire text. ✓ The sentences are brief, the paragraphs are concise, and the jargon has been deconstructed to make the text easier to read. ✓ The design uses colour coding to identify treatment, case studies, revision points, tables, boxes, and recommended reading. |
Best Books for Orthopaedics
| Book | Author | Description |
| Essential Orthopedics: Principles & Practice (2 Volumes) | Manish Kumar Varshney |
✓ Updated and thoroughly edited to reflect the latest developments in the treatment of elective orthopaedic disorders. ✓ An orthopaedic trauma primer with a list of frequently occurring fractures has been included to the annexures. ✓ The foundational sciences of orthopaedics have been thoroughly covered. ✓ To establish linkage, sections are separated into bodily areas. ✓ The growth of Malunions, Musculoskeletal Imaging, Preoperative Planning, Nanotechnology, Orthopedics in the Digital Renaissance, and Neglected Trauma to Bones and Joints (Annexure 4) are a few of the new chapters that have been introduced. ✓ Addition of a large number of pertinent images and figures, as well as tabulation. ✓ Enhanced with more than 2200 insightful graphics. |
| Fundamentals of Orthopedics | Mukul Mohindra & Jitesh Kumar Jain |
✓ Simplifies and thoroughly covers orthopaedic problems that are on the edge, including the spine, polytrauma, metabolic bone disorders, arthritis, skeletal dysplasia, brachial plexus palsy, thoracic outlet syndrome, and soft tissue sarcomas. ✓ New chapter on sports injuries and their recovery is introduced. ✓ Offers more than 1000 well labelled photos with similes that show all clinical and radiological symptoms in orthopaedics as well as commonly used tools and implants. ✓ Discusses High-Yield Points at the conclusion of each topic that are directed towards the prevalent style of multiple-choice questions (MCQs) ✓ Includes questions from previous year’s MCQs with textual references for the answers. |
| Orthopedics Quick Review (OPQR) | Apurv Mehra |
✓ Succinct is exam-oriented material. ✓ Flowcharts that are self-explanatory. ✓ Images and diagrams that complement the text can help pupils comprehend fundamental ideas more clearly. ✓ Simple to remember mnemonics. ✓ After each chapter are possible Retro Analysis questions. ✓ “Summary of Ortho” is provided for quick review. ✓ Every student aiming for the Top Ranks in the PGMEE must read OPQR because Ortho is a subject that determines rank. ✓ In each topic, important topics are underlined. ✓ Genuine High Yield Questions with a fast revision designation are provided. |
| Chapman’s Comprehensive Orthopaedic Surgery (5 Vols.) | Michael W Chapman & Michelle A James |
✓ Offers in-depth coverage of the diagnosis, medical, surgical, and rehabilitative aspects of musculoskeletal problems. ✓ The 285 chapters and 12 speciality divisions are included. ✓ Detailed coverage with more than 13,000 additional tables, flowcharts, and 3D images in full colour are provided. ✓ Surgery methods are bulleted. ✓ Boxes on Pitfalls, Complications, and Tips & Tricks are provided. ✓ ‘Information at a glance’ is crucial thanks to the authors’ point of view. ✓ The digital edition comes with improved functionality and a video library. Videos are included in Chapters 45, 48, 138, 156, 158, 193, 259, 263, and 281. |
| Essential Orthopaedics | Maheshwari & Mhaskar |
✓ It becomes “all-in-one” book for UG students and residents when an annexure on “Clinical Methods” is included. ✓ Free online resources include clinical cases, multiple-choice questions, and practise tests. ✓ There are Competency/Learning Goals listed at the start of each chapter. ✓ A section titled “Additional Information: From the Point of View of Entrance Exams” is provided at the end of each chapter. ✓ Reviewing the definitions of various orthopaedic terminologies is made easier by the annexed “Orthopaedic Terminology” section. ✓ Each chapter ends with a question titled “What have we learned?” for a fast recap. ✓ For improved readability and comprehension, some graphics and X-rays have been changed. |
| Manipal Manual of Orthopaedics | Vivek Pandey |
✓ Content is readable, accurate, and pertinent. ✓ For ease of comprehension, the whole material has been split into two sections: trauma and cold orthopaedics. ✓ Includes pertinent graphs, flowcharts, schematics, and radiographs. ✓ For ease of comprehension and writing in exams, the majority of conditions provide the therapy as an algorithm with a written explanation. ✓ Has a tonne of revision boxes with Key Information, Notes, and Points-to-Remember highlighted. ✓ A brief description of the anatomy precedes each condition, which is then followed by pathology, clinical signs, a diagnosis, tests, and treatments. |
Best Books for Obstetrics & Gynecology
| Book | Author | Description |
| DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics (Including Perinatology & Contraception) | Hiralal Konar |
✓ Content is written in clear, plain language. ✓ Every chapter has the same, uniform information. ✓ 790 line drawings, pictures, photographs, boxes, tables, flowcharts, MR images, ultrasonograms, and skiagrams are included to enhance the text. ✓ Each chapter has undergone a comprehensive update and reorganisation to reflect modern obstetric treatment of the highest calibre. ✓ A lot of revisions and updates have been made to Ch. 13 Normal Labor, Ch. 39 Intrapartum Fetal Monitoring, Ch. 31, 32, and 33 on Perinatal Care, and Ch. 34 Analgesia and Anesthesia in Obstetrics. ✓ For ease of navigation, a list of the most used acronyms has been supplied. ✓ The supplemental reading material for advanced learning can be accessed with the QR codes. This strategy aims to support and get graduate students ready for their numerous exams. |
| DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology | Hiralal Konar |
✓ This book’s presentation, which includes high-quality graphics and design, voluminous illustrations (366), excellent pictures (330), and imaging studies, is what makes it stand out. ✓ There are several tables, boxes, flowcharts, and algorithms included for repeatability and simplicity of study. ✓ The essential points are at the end of each chapter to offer an outline overview of the whole chapter. This is helpful for quick and simple review. ✓ Viva questions along with explanations and answers are given for the clinical and viva voce portions of the exam. |
| Self-Assessment & Review Gynecology | Sakshi Arora Hans |
✓ Completely edited and updated from Novak’s Gynecology, 15th edition, and William’s Gynecology, 3rd edition. ✓ Updates are based on the most recent revisions and recommendations. ✓ Contains a clear, full-color depiction of the text. ✓ Contains over 158 coloured pictures, USG, HSG photos, equipment, and specimens. ✓ Includes annexure tables for last minute revision. ✓ Includes all most recent tumours staging and treatment (Cervix, Vulva as per FIGO guidelines). ✓ Must-read material for taking a gynaecology test, including undergraduates, international medical graduates, interns, and post-interns. |
| Self-Assessment & Review Obstetrics | Sakshi Arora Hans |
✓ Content is thoroughly revised according to Williams Obstetrics 25/e. ✓ With the most recent question trends in mind, new pattern questions have been introduced to each chapter. ✓ Additional questions with images. ✓ Added a manual for CTG. ✓ Includes annexures for last-minute changes. ✓ Includes details of significant Instruments, Dopplers, and Ultrasounds. ✓ Topic of HIV is included. |
| Bedside Clinics in Gynecology | Arup Kumar Majhi |
✓ Chapters have been updated and edited as per the CBME curriculum. ✓ Topics covered in this book include history-taking and examinations, clinical cases, instruments, operations, specimens, and images. ✓ Includes all the topics that will be covered in the oral and practical exams. ✓ Enriched with 330 graphics and over 845 unique pictures. |
| Ward Rounds in Obstetrics & Gynecology | K Srinivas & Sunanda R Kulkarni |
✓ Incorporates case-based discussions and a problem-based learning strategy. ✓ Each chapter begins with the case history, examination, and investigations before addressing the topic followed by pertinent questions and pertinent responses. ✓ The book offers skill-transfer exercise in the form of in-depth case analyses, which are extremely helpful for both undergraduate and graduate students. ✓ This book’s discussion of intensive care unit (ICU) rounds, postoperative ward rounds, the examination of a victim of sexual assault, cardiac disease in pregnancy discussed by both the obstetrician and the cardiologist, some frequently encountered problems like vulval hematoma and fever in pregnancy, the use of bedside ultrasound in obstetrics, the discussion of invasive foetal procedures, etc. are some other unique aspects of the book. |
Best Books of Anaesthesiology
| Book | Author | Description |
| Anaesthesia Essence | Pritesh Singh & Usica Chandan |
✓ The latest edition of the book is thoroughly revised and updated including exam pattern questions, important annexures and image-based questions. ✓ The content is updated from Miller 8th/e, Morgan 5th/e, Lee 13th/e, Wiley 7th/e, Barash 7th/e, Stoelting 6th/e, Dorsch 5th/e. ✓ The book also provides the free online exam support. |
| Short Textbook of Anaesthesia | Ajay Yadav |
✓ Best for last-minute revision. ✓ Concentrates on the subjects that appear most frequently in pre-PG exams. ✓ A handy reference for anaesthetists in practice. ✓ Nine parts separate the text to make reading more comfortable. ✓ Key points are highlighted in italics. ✓ Each chapter’s conclusion includes a list of key points. ✓ Tabular overview of the themes has been provided, wherever necessary. ✓ Recent advancement and innovations in medications, tools, and methods are also included in the content. ✓ The American Heart Association’s (AHA) 2015 update serves as the foundation for CPR recommendations. |
Best Book for Radiology
| Book | Author | Description |
| Review of Radiology | Rajat Jain & Virendra Jain |
✓ Based on information and ideas from the CT and MRI (Haaga), CME Series, Som and Curtin 5th/e, Dahnert 8th/e, Grainger 6th/e, Sutton, Scott, and Rumack 4th/e textbooks. ✓ Updated image-based questions. ✓ New INI-CET pattern questions are included. ✓ Contains questions from the JIPMER, WBPGMEE (2018), All India (1991–2012), AIIMS (Nov 2021–1991–2012), DNB (2012–1991–2018), and Other State Examinations (2016-1991). ✓ The content included in General Radiology, Systemic Radiology, Radiotherapy and Nuclear Scans, Few Thumb Rules in Radiology, Image-based Questions is not only intended to prepare students for exams but also for their future clinical training and day-to-day hospital employment. |
Best Book for Dermatology & Venereology
| Book | Author | Description |
| Review of Dermatology | Saurabh Jindal |
✓ Full-color images that are incorporated with the chapter’s content. ✓ Mnemonics, high-yield charts, and memory aids are included. ✓ Conceptual diagrams have been hand-simplified in each chapter. ✓ For last-minute revision, there is a short review section at the end of each chapter. ✓ Based on Fitzpatrick 8/e, Rook’s 9/e, Bolognia 3/e, Habif 5/e, Andrews 11/e, McKee 4/e, King Holmes 4/e, Lever 10/e, and IAL 2/e of the newest standard textbooks. ✓ 807 additional full-color images and 200 additional full-color graphics are included. |
To get conceptual clarity on MBBS courses online, click here
With the time and technology, medical field has undergone major changes in terms of diagnostic measures, operative and non-operative approach leading to advanced medical techniques like precision medicine, gene editing, artificial intelligence, stem cell therapy, artificial disc replacement, robotic assisted surgery, minimally invasive spine surgery and lot more. Advancement has led to the path of much diversified and specialized medical fields.
Spine surgery is a specialised field that involves the diagnosis, treatment and surgical management of conditions that affect the spine and surrounding structures. Spine surgeons play a crucial role in providing both surgical and non-surgical treatments to help patient achieve better spine health and overall quality of life. There are various sub-specialties within the spine surgery, including Orthopaedic spine surgery, Neuro spine surgery, Pediatric spine surgery, Spinal Oncology, Spine deformity surgery, and minimally invasive spine surgery.
Spine surgery is a complex medical procedure which requires specialised knowledge and expertise. While both orthopaedic surgeons and neurosurgeons can perform the spine surgery, there are differences in their training, experience and approach to the surgery depending on the different spine deformity or injury. The experience and expertise of the surgeon are important factors to consider while choosing a surgeon for spine surgery. Both types of surgeons have a stake in the spine since it serves as the junction between the neurological system and the musculoskeletal.
It is crucial to understand that sophisticated spine surgery is performed by both neurosurgeons and orthopaedic surgeons. These specialisations are combined in the newly developing specialty of “spinal surgery”.
Neurosurgeons for Spine Surgery:
Neuro spine surgeons are medical doctors who specialise in the diagnosis, treatment and surgical management of conditions that affect the nervous system, including the spine, spinal cord and peripheral nerves. They are trained to diagnose and treat conditions such as brain tumors, head injuries, spinal cord compression, herniated discs spinal stenosis and traumatic spinal injuries. Neuro surgeons who specialize in the spine surgery undergo additional training and subspecialty course in the domain that focusses on the spine conditions.
The neuro spine surgeons also treat conditions like stroke, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease and spinal cord injuries. During the training period, they gain expertise in the latest surgical techniques including the microsurgery and minimally invasive surgery as well as non-surgical treatments.
Neuro spine surgeons work closely with other specialists, including neurologists, pain management physicians, oncologists and physical therapists to provide the comprehensive approach to patient care.
Orthopaedic Surgeons for Spine Surgery:
Orthopaedic spine surgeon is a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of conditions affecting the spine, including vertebrae, discs, spinal cord and surrounding ligaments and muscles.
They perform variety of spine surgeries such as spinal fusion, laminectomy, and discectomy. Orthopaedic surgeons who specialise in the spine surgery focusses on the structural issues of the spine, such as alignment and stability, and may use instrumentation such as rods, screw and cages to correct the issue. They are trained in both surgical and non-surgical treatment of conditions such as herniated disc, degenerative disc diseases, scoliosis, spinal stenosis, spinal deformities to alleviate pain and restore function. They opt for the minimally invasive techniques for spine surgery, which lead to less pain and quicker recovery.
Orthopaedic Surgeon and Neurosurgeon for Spine Surgery
The main difference between the orthopaedic spine surgeon and neuro spine surgeon is their training and focus on the area of treatment.
Neurosurgeons who perform spine surgery opt a different approach than the orthopaedic surgeons. Neurosurgeons focus mainly on nerves and spinal cord and may use the techniques such as microdisectomy and laminotomy to decompress the nerves and treat conditions like spinal cord tumors and vascular malformations whereas orthosurgeons focus mainly on structural issues of the spine and related muscles and ligaments.
While both the orthopaedic spine surgeon and neuro spine surgeon perform the similar surgeries such as spinal fusion, laminectomy and discectomy, their training and approach may differ based on their specialty. Orthopaedic spine surgeons may approach spine surgeries from a biomechanical perspective while neuro spine surgeons may focus more on the neurological aspects of spine surgery.
It is prime responsibility of a spine surgeon to utilize the latest technologies and techniques that includes minimally invasive surgery to provide the most effective treatment options for their patients. In some cases, both the specialists work together as part of a multidisciplinary team to provide the best possible care.
How to become a Spine Surgeon in India?
After completing grade 12th with the PCB stream, becoming a spine surgeon in India typically involves the following steps:
-
- Obtain a medical undergraduate degree: First, you will need to obtain a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) degree from a recognized medical college or university in India. This typically takes five and a half years to complete including one-year internship at a hospital or medical institution recognized by the Medical Council of India (MCI). For getting admission into medical college for MBBS degree, you will be mandatorily required to clear the NEET-UG entrance exam with the required cut off score and rank.
Click here to read complete information regarding NEET-UG entrance examination.
- Obtain a medical undergraduate degree: First, you will need to obtain a Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) degree from a recognized medical college or university in India. This typically takes five and a half years to complete including one-year internship at a hospital or medical institution recognized by the Medical Council of India (MCI). For getting admission into medical college for MBBS degree, you will be mandatorily required to clear the NEET-UG entrance exam with the required cut off score and rank.
-
- Obtain a master’s degree: To become a spine surgeon, you have options to choose your PG specialty. You will need to clear the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test-postgraduate (NEET-PG) or INI-CET entrance examination for admission to a MD/MS program in India. You can pursue a 3-year Master of Surgery (MS) degree in Orthopaedics or General Surgery.
Click here to enroll in the MBBS courses online for NEET-PG preparation.
You also have an option to pursue DNB course in Neurosurgery/Orthopaedics. For admission to DNB courses, you must clear the DNB-PDCET entrance examination with the required cut off and score.
- Obtain a master’s degree: To become a spine surgeon, you have options to choose your PG specialty. You will need to clear the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test-postgraduate (NEET-PG) or INI-CET entrance examination for admission to a MD/MS program in India. You can pursue a 3-year Master of Surgery (MS) degree in Orthopaedics or General Surgery.
-
- Complete a Residency: After completing your master’s programme, you will need to complete a residency program in area of your PG expertise. This will provide you with the necessary clinical experience and training in the surgery specialty.
-
- Obtain a super specialisation degree: After completing MS/DNB degree, you may need to further pursue the super specialisation in Neurosurgery (M.Ch) for pursuing a career as a spine surgeon. You have to successfully clear the NEET-SS entrance examination for admission to M.Ch courses.
-
- Fellowship in Spine Surgery: After completing the residency of your respective medical course, you need to pursue a fellowship program in spine surgery to specialize in this field. Students who have earned a DNB, MD, MS, M.Ch, or DM in the relevant speciality are eligible for entry to the NBEMS fellowship programme. Anyone with a medical degree in DNB/MS Orthopaedics or DNB/M.Ch Neurosurgery who have passed the FET (Fellowship Entrance Exam) and meets the requirements for admission to fellowship programmes at the various NBE-accredited medical colleges, institutions, and hospitals in India is eligible to participate in the centralised counselling for the allocation of FNB Spine Surgery seats solely on the basis of merit and preference. There are many institutes in India which offer fellowship program in spine surgery.
Click here to learn latest surgical techniques with the case-based spine surgery videos by the eminent surgeons.
- Fellowship in Spine Surgery: After completing the residency of your respective medical course, you need to pursue a fellowship program in spine surgery to specialize in this field. Students who have earned a DNB, MD, MS, M.Ch, or DM in the relevant speciality are eligible for entry to the NBEMS fellowship programme. Anyone with a medical degree in DNB/MS Orthopaedics or DNB/M.Ch Neurosurgery who have passed the FET (Fellowship Entrance Exam) and meets the requirements for admission to fellowship programmes at the various NBE-accredited medical colleges, institutions, and hospitals in India is eligible to participate in the centralised counselling for the allocation of FNB Spine Surgery seats solely on the basis of merit and preference. There are many institutes in India which offer fellowship program in spine surgery.
-
- Obtain your fellowship and License: Student who pass the Fellowship Exit Examination are recognised as Fellow of the National Board (FNB) or Fellow of the National Board – Post Doctoral (FNB-PD) at the NBEMS annual convocation.
Once you have received your certification and completed your education and training, you will need to obtain a license to practice as a spine surgeon in India. You will need to register with the Medical Council of India (MCI) or the respective state medical council in order to practice medicine in India.
As a spine surgeon, it is important to keep your knowledge and skills up to date by regularly attending conferences, seminars, and workshops on spine surgery. This will help you stay updated with the latest techniques and advancements in the field and latest surgical and non-surgical approaches.
It is highly important for the medical students to carefully choose their medical specialty and subspecialty. Medical professional pursuing the course or fellowship in neurosurgery or orthopaedics and is interested in the spine surgery specialty can enroll in online spine surgery courses 2023. These courses provide detailed real life case demonstrations of spine surgery.
Orthopaedic surgeons and neurosurgeons may learn about the most recent methods and techniques in the field of spine surgery from the Ganga Videos on Spine Surgery course, a collection of 50 spine surgery videos. It includes minimally invasive and neurosurgical techniques, as well as treatments for spinal deformities, all carried out by renowned and skilled surgeons. The key feature of the course includes 10 hours of video lectures, 31 lecture notes, over 60 benchmark trials, and 150 self-assessment questions.
This spine surgery online courses include video lectures that demonstrate operations together with the clinical information about the patient, pertinent images, a brief explanation of the process, the actual surgical procedure, potential problems, post-operative treatment, and follow-up.
Brief summaries of the important topics are discussed in the lectures to help the candidates. Multiple-choice questions that are given at the conclusion of each lecture allow applicants to gauge their level of comprehension of the subject. To improve students’ understanding, video lectures and study guides are supplemented with clinical research investigations and benchmark trials.
Overall, becoming a spine surgeon in India requires a significant amount of education and training and lot of hard work and patience, but it can be a rewarding career for those who are dedicated to help patients with spine-related conditions.
The second year of MBBS is quite important as it includes all the foundational subjects. Microbiology, Pharmacology, and Pathology subjects are included in the second year of the MBBS curriculum. They serve as a strong foundation in the MBBS journey and hence, conceptual clarity over these subjects is a must for every medical student. Apart from the three subjects, the second-year curriculum includes AETCOM (Attitude, Ethics, Communication Module), Sports and extracurricular activities, postings, and a pandemic module. All the students must refer to the latest edition of the books during the study so that they remain updated with the latest advancements in the subject and newly added chapters and modules according to the new CBME pattern.
There are a variety of books available in the market but choosing the right one is crucial. One must choose a standard book that is in lucid manner and includes highly illustrative images, flowcharts, tables, must-know topics, questions with explanations, and most of all, it must be according to the new CBME pattern.
Here’s a list of recommended books for MBBS 2nd year students:
Best Books on Microbiology for MBBS Students:
| Subject: Microbiology | Authors | Description |
| Essentials of Medical Microbiology | Apurba Sastry & Sandhya Bhat |
✔ This is the only textbook in “Clinical Microbiology” that is centered on infectious syndromes, updated according to the CBME curriculum. ✔ It has simple language and bulleted writing that is easy to read. ✔ Summary boxes for laboratory diagnosis and therapy are provided separately for easy viewing. ✔ After each chapter, there are essay questions with clinical case studies and MCQs. ✔ The book additionally has a Covid-19 chapter and the AETCOM module. ✔ References are taken from the CDC and WHO websites, the Harrison 20th edition, the Mandell 9th edition, the Bailey & Scott’s 14th edition, as well as many health care programmes and recommendations including the ICMR, NCDC, RNTCP, NACO, NVBDCP, IAP Immunization, and GPEI. ✔ Only textbook in microbiology that is designed according to the PG entrance exams. |
| Review of Microbiology and Immunology | Apurba Sastry & Sandhya Bhat |
✔ The latest edition of the book includes the most recent laboratory diagnosis, therapy, and epidemiology in every chapter. ✔ The book includes updates on bacterial medication resistance and information on the Zika virus, Ebola virus, polio eradication, Dengue vaccine, vaccine-derived polio viruses (vdpvs), and MERS-CoV. ✔ Newer molecular techniques (lamp, real-time PCR, biofire film array, etc.) as well as CSSD, Malditof, Vitek, and Bact/Alert Virtuo are featured. ✔ The epidemiology of meningococcal meningitis, pneumococcal vaccinations, DPT vaccine, TB (genexpert, mgit, truenat, drug susceptibility testing methodologies, most recent RNTCP recommendations), melioidosis, scrub typhus, and the yaws eradication campaign have all undergone significant updates. ✔ Updated laboratory findings for hbv and HCF diagnosis, therapy, and PEP. ✔ Updates on the poliomyelitis vaccine schedule, epidemiology, and end game strategy are also covered. ✔ Completely updated with the most recent references from Harrison (19th and 20th editions), Park (24th edition), Jawetz (27th edition), Apurba Sastry’s Essentials of Medical Microbiology (2nd edition), and Ananthanarayan (10th edition). ✔ Separate annexures section with pertinent, quick-fire subjects for exams are provided. ✔ Sections including immunology, parasitology, and mycology are given more attention. ✔ Contains several tables, flowcharts, and mnemonics that aid students in understanding. |
| Self-Assessment & Review Microbiology & Immunology | Rachna Chaurasia & Anshul Jain |
✔ “Revision at a Glance,” a single unit that highlights the most crucial aspects. ✔ Mnemonics and simple text to make learning easier. ✔ Offers a comprehensive treatment of parasitology and immunology. ✔ Citations from more recent printings of classic works, such as Harrison 20/e, Ananthanarayan 10/e, Jawetz 27/e, etc. ✔ Presents the most crucial information in a style that is simple to recall, including flow diagrams and tabulation. ✔ Detailed explanations of the most recent NEET question types. |
| Ananthanarayan and Paniker’s Textbook of Microbiology | R Ananthanarayan and CK Jayaram Paniker
Editor: Reba Kanungo |
✔ Recent developments in disease detection, molecular diagnostics, quality assurance, infection prevention and control, public health and epidemiology, and preventative techniques, including national programs, have been covered in up-to-date information. ✔ The format of the discussion is the same for all syndromes, and it includes information on the important etiological agents of each system, their disease spectra, pathogenesis, clinical features, epidemiology, and the strategy for laboratory diagnosis and treatment of each of the clinical entities described. ✔ For quick reference and memory, each chapter in this part includes one or more tabular columns summarising the causes of the numerous syndromes associated with each organ system. ✔ The organisms included in these tables are color-coded according to their respective organ system etiological relevance. |
Best Books of Pathology for MBBS Students:
| Subject: Pathology | Authors | Description |
| Textbook of Pathology | Harsh Mohan |
✔ There are 30 chapters in total in the updated version, divided into three sections: Systemic Pathology (Ch. 15–30), Haematopoietic and Lymphoreticular System (Ch. 11–14), and General Pathology (Ch. 1–10). There are also three appendices. ✔ “Must-know” boxes after each topic summarising essential elements for a quick review of the material in a very short amount of time. ✔ After most chapters, one or more clinical cases based on a prevalent or significant disease relevant to that chapter are provided, together with a brief history, examination results, and any subsequent research discoveries. ✔ The addition of significant review questions (both long-answer type and short notes on subjects) at the end of each chapter, to help the student prepare and visualize what to write in the test, is another new feature of the redesigned version. ✔ The updated baby book includes short-answer questions that are frequently asked during viva-voce examinations as well as newer MCQs that now include explanations. ✔ Newer and Modified Images: Prof. Ivan Damjanov graciously provided schematic, gross images, and photomicrographs for the better understanding of the students. |
| Essentials in Hematology and Clinical Pathology | Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai |
✔ Over 135 drawings, 27 photomicrographs, 18 pictures, and 146 tables have been provided to make learning simple and quick. ✔ Essay questions, quick-answer questions, and more than 300 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) are included to help students to assess their understanding of the key ideas. ✔ Appendices 1 and 2 include Reference Values of Frequently Performed Important Laboratory Tests and Recent WHO Classification of Tumors of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, respectively. ✔ Disorders of Red Cells, Disorders of White Cells, Disorders of Hemostasis, and Clinical Pathology make up the book’s four parts. ✔ Tables, diagrams, flowcharts, and key boxes for memorizing easily. |
| Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates Pathology | Ramadas Nayak |
✔ This version is a comprehensive guide for passing all pathology exams. ✔ Better quality photomicrographs or illustrations have been used in place of figures and illustrations in a few chapters. ✔ The book is divided into three sections: general pathology, hematological and clinical pathology, and systemic pathology. This book has 28 chapters. ✔ This book fills a void by offering fundamental knowledge to a student in a nutshell. |
| Rapid Review of Hematology | Ramadas Nayak & Sharada Rai |
✔ Illustrations in various colors (e.g., for etiopathogenesis, clinical presentation, complications, peripheral blood smear, and other relevant laboratory tests). ✔ Bullet-pointed text for concise reading. ✔ Text reinforced with 59 flow charts and tables, 25 photomicrographs (including X-rays and clinical photos), and 64 drawings. ✔ Text boxes to emphasize important points. ✔ Clinical scenario interpretation. |
| Review of Pathology and Genetics | Sparsh Gupta & Gobind Rai Garg |
✔ Special points like “NEET busters” have been added for last-minute review. ✔ IBQs with Solutions ✔ Golden points are provided at the start of each chapter. ✔ Most authenticated question banks. ✔ PGMEEs 2021-1985 Solved MCQs with all current questions for 2022. ✔ A new format that is organized chapter-by-chapter to make it easier for the students to learn antegrade. ✔ In the text, new conceptual and clinically significant material has been emphasized. ✔ Many flowcharts and diagrams are used to swiftly review the concepts. ✔ References are taken from the Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease, 10th edition. ✔ Golden nuggets and other details from the 10th edition of Robbins are provided separately. ✔ Questions from previous year exams are underlined in the text. ✔ Simple-to-understand Mnemonics. ✔ Chapter on significant stains and bodies is included. |
| Comprehensive Image-Based Review of Pathology | Sushant Soni |
|
Best Books of Pharmacology for MBBS Students:
| Subject: Pharmacology | Authors |
Description |
| Essentials of Medical Pharmacology | K.D. Tripathi |
✔ Chapters that have been revised and updated to reflect new medications and treatment recommendations. ✔ The book contains a wide range of subjects, from fundamental pharmacological ideas to real-world therapies and the advancement in medication and treatment. ✔ Novel medications that work by altering the function or turnover of these molecules have been included in a new chapter on “Nitric Oxide and Vasoactive Peptide Signal Molecules.” ✔ Drugs that are marked in India have been given priority, and their top brand names and dosage forms are included. ✔ A list of acronyms is supplied at the book’s opening. ✔ All newly marketed medications are mentioned. ✔ Charts that categorize drugs visually, aiding in the development of pictorial memory. ✔ There have been several new figures, charts, tables, and highlight boxes added. ✔ Place a strong emphasis on “evidence-based medicine” by often citing reliable research and endpoint trials. ✔ The “Problem Directed Study” at the end of the majority of chapters offers a therapeutic decision-making activity. ✔ Contains appendices on Solutions to Problem Directed Study, Prescription in Pregnancy, Drugs in Breastfeeding, and Drugs and Fixed Dose Combinations Prohibited in India. ✔ The book concludes with a brief list of pertinent resources for additional study. |
| Review of Pharmacology | Govind Rai Garg & Sparsh Gupta |
✔ Facts and ideas based on KDT 8th, Katzung 13th, Goodman Gilman 13th, Harrison 20th, and CMDT 2022 newest versions. ✔ A distinct chapter with explanations of mathematical issues. ✔ Includes IBQs and MCQs with explanations. ✔ In each chapter, recent advancements are mentioned. ✔ “New FDA-approved Drugs” annexures are separate documents. ✔ Mnemonics can help you recall important information about novel medications. ✔ Annexures of the “Drug of Choice” for various ailments. ✔ The benefits of both antegrade and retrograde study. ✔ Simple to-remember mnemonics. |
| Pharmacology for Medical Graduates | Tara V Shanbhag, Smita Shenoy |
✔ Questions based on the format used by examiners for both theoretical and practical sections. ✔ Language is simple to grasp because of the concise headers and specific pharmacological descriptions. ✔ Information is presented clearly and point-by-point, which is helpful for UG students preparing for exams. ✔ Adding basic illustrations, self-explanatory flowcharts, tables, and student-friendly mnemonics to the text. ✔ New subjects have been presented, such as CNS stimulants, drugs for the treatment of psoriasis, and medications for acne vulgaris. ✔ We acknowledge the inclusion of definitions, and treatment plans by WHO standards (for TB, leprosy, malaria, and HIV), RNTCP guidelines (for TB), and JNC guidelines (from 2003) for the categorization of blood pressure. ✔ The Tara Shanbhag’s Pharmacology for Medical Graduates fully revised edition will be helpful for both working physicians and medical students. |
To get conceptual clarity on MBBS courses online, click here.
Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) is an undergraduate degree in medicine. The course is of four and a half years, followed by one year of compulsory rotational internship. There are a total of 19 subjects in the MBBS curriculum.
There are three subjects in the first year of the MBBS, Anatomy, Biochemistry, and Physiology. There are numerous books available for the MBBS subjects but choosing the right set of books is highly important.
Here’s a list of recommended books for MBBS 1st year students:
Best Books of Anatomy for MBBS Students:
| Subject: Anatomy | Author | Description |
| Self-Assessment and Review of Anatomy | Rajesh K Kaushal |
|
| New Across: A Complete Review of Short Subjects | Saumya Shukla, Siddharth Dixit, Anurag Shukla & Khushi Shukla |
|
| Human Anatomy | BD Chaurasia, Krishna Garg |
|
| Gray’s Anatomy for Students | Raveendranath Veeramani, Sunil Jonathan Holla, Parkash Chand & Sunil Chumber |
|
| Cunningham’s Manual of Practical Anatomy | Rachel Koshi |
|
Best Books of Biochemistry for MBBS Students:
| Subject: Biochemistry | Author | Description |
| Self-Assessment and Review of Biochemistry | Rebecca James Perumcheril |
|
| Textbook Of Biochemistry for Medical Students | DM Vasudevan, Sreekumari S & Kannan Vaidyanathan |
|
| Biochemistry | U. Satyanarayana & U. Chakrapani |
|
| Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry (South Asian Edition) | Denise R. Ferrier SAE Editors: Ritu Singh, Rajeev Goyal |
|
| Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry | Kathleen Botham, Peter J. Kennelly, Owen McGuinness, P. Anthony Weil, Peter Kennelly, Victor Rodwell | The book includes the following important topics:
|
Best Books of Physiology for MBBS Students:
| Subject: Physiology | Author | Description |
| Principles of Physiology | Debasis Pramanik |
|
| Review of Physiology | Soumen Manna |
|
| Crisp Complete Review of Integrated Systems Physiology | S Krishna Kumar |
|
| Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology (South East Edition) | John E. Hall, Michael E. Hall
Adaption Editors: Mario Vaz, Anura Kurpad, Tony Raj
|
|
| Textbook of Physiology | A.K. Jain |
|
To get conceptual clarity on MBBS courses online, click here.
Can you crack NEET PG in 2 months? The answer is yes! However, cracking NEET PG in 2 months is no easy feat and requires serious dedication, diligence, and hard work. Cracking NEET-PG in 2 months is possible with frequent revision of all the concepts an aspirant has learned in his/her MBBS years. There is no doubt that NEET PG is one of the toughest exams in India but learning how to crack NEET PG in first attempt is even harder. Given the vastness of the syllabus, the fierce competition, and the limited time frame, let’s figure out exactly how you can channel all your motivation towards learning how to prepare for NEET PG 2023 in 2 months.
- Create A Dedicated Study Schedule – Forming a study schedule that details exactly what topics you need to study and when to study is essential in the path to cracking NEET PG in 2 months. By analysing the syllabus and assessing your weak points, you can create a highly effective and productive timetable for NEET PG 2023 preparation in 2 months. By creating a personalised and productive timetable for NEET PG preparation in 2 months, you can get started each day without having to waste time deciding what you need to study as it will all be planned out for you to simply follow.
Here’s a 2 Months subject-wise revision plan for NEET-PG 2023:
| Part | Number of days to complete each subject | Total number of days |
| PART 1 | ||
| Anatomy | 3 days | 9 days |
| Physiology | 2 days | |
| Biochemistry | 2 days | |
| Solve NEET PG practice questions and previous year’s question papers | 2 days | |
| PART 2 | ||
| Microbiology | 2 days | 12 days |
| Pathology | 3 days | |
| Pharmacology | 3 days | |
| Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 day | |
| Solve NEET PG practice questions and previous year’s question papers | 3 days | |
| PART 3 | ||
| Community Medicine & PSM | 3 days | 10 days |
| ENT | 2 days | |
| Ophthalmology | 2 days | |
| Solve NEET PG practice questions and previous year’s question papers | 3 days | |
| PART 4 | ||
| Dermatology | 1 day | 13 days |
| Medicine | 5 days | |
| Psychiatry | 1 day | |
| Pediatrics | 1 day | |
| Solve NEET PG practice questions and previous year’s question papers | 5 days | |
| PART 5 | ||
| Surgery | 5 days | 16 days |
| Anaesthesia | 1 day | |
| Orthopaedics | 1 day | |
| Radiology | 1 day | |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | 3 days | |
| Solve NEET PG practice questions and previous year’s question papers | 5 days | |
| Solve one NEET-PG mock exam every two weeks to boost your preparation and manage time | ||
Every aspirant has their own competencies so you can personalize the above shared plan according to your difficulty level of any subject.
2. Practice Previous-Year Papers – Studying past years’ papers can help you adjust to the method of questioning while also providing good practice. Your 2-month study plan for NEET PG 2023 should be loaded with as many relevant past papers and sample papers as possible. By slotting breaks to only attempt these papers after several rounds of revision, you can make the most out of your 2 month study plan for NEET PG 2023.
Click here to know the important topics of Pharmacology for NEET-PG.
3. Revise Thoroughly – Memorising and understanding such a large syllabus is not an easy task, especially when your plan rests on how to prepare for NEET PG 2023 in 2 months. Thus, the answer for cracking NEET PG in 2 months comes through the form of repeated bouts of revision. Make sure you periodically revise topics you’ve already studied, either through mock tests, other self-assessment, or even repeatedly reading your notes. Try flowcharts, mnemonics, flashcards to memorize well.
Click here to know the important topics of Community Medicine for NEET-PG.
4. Learn To Sacrifice – If you want to know how to prepare for NEET PG 2023 in 2 months, the simple solution is learning to prioritise and sacrifice certain things. During your 2 month study plan for NEET PG 2023, you will come across some topics that are personally too difficult or time-consuming, so plan to clear your concepts of these topics first. For this, you can resort to online platforms like DigiNerve which provides best content by India’s top faculty.
Click here to know the important topics of Microbiology for NEET-PG.
Now that the question of ‘Can you crack NEET PG in 2 months’ has been answered, and guidelines for an effective timetable for NEET PG preparation in 2 months have been given to you, get started! For more tips on how to crack NEET PG 2023 in first attempt, click here and clear your concepts with DigiNerve.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. When will be NEET PG 2023 exam conducted?
Ans. NEET-PG 2023 exam will be conducted in the month of March.
Q2. Will NEET-PG 2023 be held?
Ans. Yes, NEET-PG will be held in 2023 as per the notifications till now. The NExT exam is likely to be held from year 2024.
Q3. How many times a year is NEET PG held?
Ans. The NEET-PG exam is held once in a year.
The National Eligibility Cum Entrance Examination-Post Graduate (NEET PG) is a medical entrance exam that goes around in the minds of MBBS students all the time, and getting a good rank to secure an MD/MS seat is a dream for all MBBS graduates.
Remember,
Perseverance makes all the difference.
Getting a high rank in the exam is a tough task, but not impossible. To score 600+ marks in NEET PG 2024, you must plan an effective preparation strategy, keeping in mind subject weightage, the pattern of the exam, high-yielding topics, and the best preparation books. Considering the vast syllabus and the competition, an aspirant should start the preparation in the early phase itself.
Here are some reliable preparation tips to secure a good rank in the NEET PG 2024 entrance examination.
Preparation Tips for NEET PG 2024
1. Make an effective preparation strategy
Keeping in mind the time left for the exam, prioritize your schedule. Make a realistic plan you can stick to and devote your time according to the topics, including those that you haven’t started, those that are unclear, and those that you only need to revise once. Time management and work-life balance are the two factors that should be kept in mind for an effective plan, especially during postings. Knowing the exam pattern and subject weightage would also help you prepare a better preparation strategy.
Below is a 3-month effective preparation strategy to crack NEET PG 2024.
Subject-wise time division:
| Part | Number of days to complete | Total days |
| PART 1 | ||
| Anatomy | 5 days | 13 days |
| Physiology | 3 days | |
| Biochemistry | 3 days | |
| Revision | 2 days | |
| PART 2 | ||
| Microbiology | 5 days | 19 days |
| Pathology | 5 days | |
| Pharmacology | 4 days | |
| Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 days | |
| Revision | 3 days | |
| PART 3 | ||
| Community Medicine & PSM | 7 days | 15 days |
| ENT | 2 days | |
| Ophthalmology | 3 days | |
| Revision | 3 days | |
| PART 4 | ||
| Dermatology | 3 days | 17 days |
| Medicine | 5 days | |
| Psychiatry | 3 days | |
| Pediatrics | 3 days | |
| Revision | 3 days | |
| PART 5 | ||
| Surgery | 7 days | 26 days |
| Anaesthesia | 3 days | |
| Orthopaedics | 3 days | |
| Radiology | 3 days | |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | 6 days | |
| Revision | 4 days |
Keep the rest of the time for quick revision and practicing previous year’s NEET PG practice questions.
2. Analyze your level of understanding
Analyze your level of understanding of the syllabus and subjects for the NEET PG exam. Divide your time and make your study plan as per your level of understanding in the subject and module. Don’t ignore the subjects which seem boring to you as doing so can prove to be the wrong decision ever. It is hence advised to make short notes and flashcards of the important dates, events, and information for quick revision, especially in scoring subjects such as PSM.
3. Set your target
As per your preparation strategy, set your daily, weekly, or monthly targets and keep up your pace. Completion of the tasks will boost your confidence every time. For instance, you can set your target as completing at least two previous year’s papers in a week depending upon your schedule. It is advised that while solving the question papers, make sure you read about the incorrect options along with the correct answer to upskill your preparation. Always read the question and options carefully. Don’t jump to the conclusion and try to rule out the incorrect options while practicing and reading about them.
Don’t get overburdened with tasks. Take breaks.
4. Revision
Don’t just read topics; get your concepts cleared to improve retention. Learning and revising should go together. If you have read any topic today, then revise it within 5–10 days and don’t leave it for later, as you’ll be loaded with more topics by then. So, regular revision is a must to brush up on your concepts. This technique of balancing learning and revising helps in memorizing well and reduces last-minute pressure.
Always prefer to study from your notes, including flowcharts, tables, and mnemonics for the NEET PG exam.
For instance,
A. The mnemonic ‘SAMPLE history’ is to remember all the events for the diagnosis.
Signs and symptoms
Allergies
Medications
Past medical history
Last meal
Events
B. Another mnemonic to remember for pain is SOCRATES.
Site
Onset
Character
Radiation
Associated symptoms
Timing
Exacerbating or relieving factors
Severity (/10)
5. Practice MCQs
Solving MCQs gives you exposure to the NEET-PG 2024 exam pattern. After completing each topic, go through its self-assessment questions, which benefit your learning in two ways: first, you’ll be able to assess your level of understanding of the topic, and second, you’ll know the types of MCQs that can be framed from the topic in the exam.
This practice also helps you analyse the topics, which in general have more direct questions, or IBQs, clinical case-based questions, and more. This helps you enhance your problem-solving skills.
6. Solve Previous year’s questions
Solving PYQs is a must. This makes you familiar with the exam pattern and monitors your progress. It is advisable to practice PYQs with your timer on. Time management plays a vital role in the examination. PYQs for the NEET-PG exam will help you get familiarized with the NEET-PG 2024 exam paper pattern along with the types of questions asked. This practice also instills confidence in you.
7. Focus on high-yielding topics
Make a proper list of subjects with their high-yielding topics, and make sure you don’t miss any for the exam. Make proper notes on these topics and revise them properly while solving MCQs and PYQs.
Click here to know the important topics of Microbiology for NEET-PG.
Click here to know the important topics of Community Medicine for NEET-PG.
Click here to know the important topics of Pharmacology for NEET-PG.
Click here to know the important topics of Pathology for NEET PG.
8. Prioritize your health
While keeping up your pace for NEET PG 2024, don’t exhaust your body and mind. Keep yourself healthy to study effectively. It can be easy to develop harmful habits like bingeing on junk food, skipping workouts, isolating oneself excessively, or even sinking into a depressed state of mind while preparing for NEET PG.
However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating wholesome foods, engaging in brief bursts of much-needed socialization, and regularly monitoring your mental health are of the utmost importance, particularly if you want to score 600+ in the NEET PG 2024. Make sure you get proper sleep, minimize your level of stress, and meditate. It is important to stay focused and have a positive mindset. Have faith in yourself. Keep yourself hydrated and stay away from distractions.
To get conceptual clarity on MBBS courses online, click here.
Ever since medicine has been in existence, so has pathology. Knowledge of pathology is essential to understand the illness, from the cause and investigation of the disease to diagnosis and treatment. Learning all the terminologies used in pathology lab reports is also important. It will be very difficult to treat patients and prevent disease progression without a complete understanding of the subject.
The whole subject, as far as an undergraduate student is concerned, deals with
- Etiology: The cause of the disease
- Pathogenesis: Steps in which certain events occurred that finally led to the disease
- Histopathological examination, of any disease: Involves dealing with gross appearance and microscopic examination.
Branches of Pathology
Pathology subject has two types of branches:
- Morphological Branches include:
- Histopathology
- Surgical pathology
- Experimental pathology
- Forensic pathology and autopsy work
- Cytopathology
- Exfoliating cytology
- Interventional cytology
- Hematology
- Non-morphological Branches include:
- Clinical pathology
- Clinical biochemistry
- Microbiology
- Immunology
- Medical genetics
- Molecular pathology
- Molecular cytogenetics
Important topics of Pathology for MBBS students
General pathology forms the base for the units that lie ahead.
General pathology will introduce you to terms that will be used time and again, so if you do not understand those terminologies, you will never be able to comprehend systemic pathology. For example, terms like hyperplasia, metaplasia, etc. will be used very commonly, and if you are not aware of what they mean, then it will be very hard to understand diseases.
Hematology is another part of Pathology. You must do your best while studying this unit, because all your basic knowledge about examining the blood test reports, and your skills in investigating a patient of anemia, will come from here.
Other high-yielding pathology topics for NEET PG 2023 include Inflammation, Anemia, Macrocytic Anemia, Acute Leukemias, Chronic Leukemias, Thalassemia, Lymphadenopathy, etc.
From the systemic pathology, units like the Kidney, GIT, Lungs, and Hepatobiliary system are highly important for NEET PG aspirant. Not just this, Tuberculosis and Diabetes Mellitus are two diseases you cannot skip, because of their increasing prevalence in India.
Watch below video lectures on high-yielding Pathology topics by top Pathology faculty.
Recommended books for Pathology
One of the favorites among students and the highly recommended book is Jaypee publishers’ “Textbook of Pathology” by Prof. Harsh Mohan. The book has a single volume and the language and content are easier to understand. The histopathology diagrams include both microscopic pictures and hand-drawn images, which makes it easier for students to memorize and reproduce those images in the exams. There are appropriate flowcharts and a lot of tables, which take lesser time to read and learn.
Another recommended book for Prof exam preparation is Prof. Ramadas Nayak’s “Pathology Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates”. The book has covered all the topics lucidly with illustrations, tables, flowcharts, etc. The book is highly recommended for notes and revision.
For the practical part of pathology, there is another book by the author, Prof. Harsh Mohan, titled, ‘Practical Pathology’. This book will be very helpful for lab sessions and practical examinations. It has histopathology of most of the slides and specimens that form a part of your practical viva.
Paper Pattern of Prof Exams
After the advent of Competency-Based Medical Education in 2019, the pattern of examination changed. Now, you will have two papers of 100 marks each, unlike earlier, where two papers of 40 marks each were taken. There will be a practical for 100 marks after your university exams. Hence, pathology as a total will carry 300 marks.
How to study Pathology?
You will often hear from your teachers that, Pathology is a very volatile subject, which is true. But does that mean you will never be able to learn it? Well, absolutely not. The key to mastering pathology is revision. Revision, revision, and only, revision.
Studying things once and expecting to remember you entirely in the exam will never work. Rather, regularly reading and revising will help you a lot in the long run.
Here are a few tips that will help you a lot to study Pathology in MBBS:
Stick to one book
Do not refer to multiple books. Doing so will only create confusion. Also, while revising for exams, you do not have a lot of time to revise your syllabus, hence you mustn’t increase your load by referring back to multiple books. Thoroughly read Harsh Mohan’s Textbook of Pathology and practice the diagrams well. You can practice the self-assessment questions from various resources.
Find online Pathology courses
It has been time and again proven that our pictorial and visual memory is very strong and long-lasting. Hence, watching videos, and attempting image or video-based questions related will help you a lot and feed things into your memory for a longer duration.
DigiNerve offers Pathology for UnderGrads online course, developed and mentored by the most renowned authors, Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak, and Dr. Debasis Gochhait. The course has been enriched with their knowledge and experience which will help in fulfilling your study needs completely. All the topics are arranged in a sequential hierarchy to avoid confusion. The video lectures along with self-assessment questions and notes help you in concept-building. The lectures follow a case-based approach supported by video demonstrations. The lectures are richly illustrated including clinical, radiological, histological, and gross images along with flowcharts and tables for easy understanding and quick recall.
The course also focuses on practicals in pathology including gross specimens that are highly important for examination.
Make notes
Pathology subject is hefty, hence, keep your notes handy. This will help you to go through the highlights of each chapter in the least time during revision. Make tables and flowcharts while you study in class or watch video lectures. This will help you a lot in last-minute revision.
Practice diagrams
To have an edge over other students, you should practice diagrams frequently. Diagrams and flowcharts will fetch you more marks. You should be extremely well-versed in histopathology diagrams. The pathology book by Prof. Harsh Mohan provides excellent histopathology diagrams, which are easily reproducible in exams.
Pay attention in lab sessions
Do not ignore your practical classes. You can get to learn a lot in those few hours. You will get familiar with gross specimens and histopathology slides of various diseases there. Understand it all there and then, and half of your theory will be prepared in your lab only.
To get conceptual clarity with the help of MBBS courses online, click here.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q 1 – What is Pathology?
Ans : Pathology is referred to as the ‘study of diseases’. It is a branch of science that deals with structural and functional changes in diseases, which present with clinical signs and symptoms.
Q 2 – Why is it important to study Pathology?
Ans : It is important to study Pathology to understand the illness, from the cause and investigation of the disease to diagnosis and treatment. It becomes very difficult to treat patients and prevent disease progression unless you have a good knowledge of pathology subject. Learning all the terminologies used in pathology lab reports is also very crucial.
Q 3 – Which book should I read for Pathology?
Ans : “Textbook of Pathology” by Prof. Harsh Mohan is the most recommended pathology book for in-depth learning and scoring high in exams. Another recommended book for prof exam preparation is Ramadas Nayak’s “Pathology Exam Preparatory Manual for Undergraduates”.
Q4 – Can I refer to online resources for studying Pathology?
Ans : Yes, online resources can be very helpful in concept building and learning. One such affordable and reliable resource is DigiNerve’s Pathology for UnderGrads course. The course is designed as per the new CBME curriculum. It consists of video lectures, notes, and self-assessment questions along with clinical case discussions and practicals in pathology.
INI-CET is a combined national-level entrance examination for admission to the medical postgraduate courses – MD, MS, DM (6 yrs), MCh (6 yrs), and MDS at INI institutes (Institute of National Importance). The INI-CET January session 2023 exam is around the corner. Getting admission to INI institutes is highly challenging and a dream for MBBS students. This is a highly competitive task to secure a seat in the renowned medical colleges in India.
Remember, Perseverance is the key.
The INI-CET exam is going to be held on 13th Nov 2022 for admission to the AIIMS INI-CET January session 2023.
Mode and Scheme of INI-CET January 2023 exam
| Particulars | Description |
| Mode of Examination | Computer-based test (CBT) |
| Duration | 3 hours (180 minutes) |
| Number of questions | 200 |
| Types of questions | Objective type |
| Marking Scheme | +1 mark for every correct response and -1/3 for every incorrect response |
Important things to know:
- If more than one candidate scores the same, then this tie-breaker situation is resolved by applying the following criteria sequentially:
-
- Less negative marks
- Older by age
- Candidates equal to 8 (eight) times the number of postgraduate seats available in each category will be called for the first and second rounds of seat distribution based on the INI-CET merit list.
- Spot Round Counseling will only be conducted if the seats will remain vacant even after the open round counseling.
List of Participating Institutes for INI-CET January 2023 Session
| S. No. | Name |
| 1 | AIIMS, New Delhi |
| 2 | AIIMS, Bhopal |
| 3 | AIIMS, Bhubaneswar |
| 4 | AIIMS, Jodhpur |
| 5 | AIIMS, Nagpur |
| 6 | AIIMS, Patna |
| 7 | AIIMS, Raipur |
| 8 | AIIMS, Rishikesh |
| 9 | AIIMS, Bibinagar |
| 10 | AIIMS, Bhatinda |
| 11 | AIIMS, Deoghar |
| 12 | AIIMS, Mangalagiri |
| 13 | AIIMS, Raebareli |
| 14 | JIPMER, Puducherry |
| 15 | NIMHANS, Bengaluru |
| 16 | PGIMER, Chandigarh |
| 17 | SCTIMST, Trivandrum |
Here’s the tentative seat distribution (Category-wise) for admission to various MS/MD/DM (6 years)/MCh (6 years)/MDS courses at AIIMS, New Delhi and other 12 AIIMS through the INI-CET entrance examination for the January session of 2023.
Table 1: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, New Delhi:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 17 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biophysics | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 9 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Lab. Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Medicine | 11 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 11 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 10 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Palliative Medicine | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 10 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 10 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis & Internventional Radiology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Surgery | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatrics & Preventive Dentistry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MDS | Prosthodontics | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Neuro Surgery M.Ch (Direct 6 year Course) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Paediatric Surgery M.Ch (Direct 6 year Course) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DM | Infectious Diseases DM(Direct 6 year Course) | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 2: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bhopal:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Table 3: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bhubaneswar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 9 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obst. & Gynecology | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physiology | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | PMR | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Table 4: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Jodhpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology & Critical Care | 17 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Paediatrics | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Paediatric Surgery (M.CH. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DM | Radiation Oncology (D.M. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 5: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Patna:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 18 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 9 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | FMT (Forensic Medicine & Toxicology) | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Medicine | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG (Obstetrics & Gynaecology) | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MCh | Pediatric Surgery (MCh 6 Years) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 6: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Raipur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 13 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MD | Anatomy | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 9 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 8 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 7 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 7 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry (MDS) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 7: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Rishikesh:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Respiratory Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Periodontics (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCH 6 Years | Pediatric Surgery (MCH 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Plastic, Reconstructive & Burns Surgery (M.CH. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Neurosurgery (MCH 6 yrs) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 8: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Nagpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics (MDS) | 0
|
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 9: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bibinagar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | FMT | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Peediatrics | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Table 10: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bathinda:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 11: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Deoghar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | FMT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 12: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Mangalagiri:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 13: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Raebareli:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Last-Minute Tips for INI-CET Exam:
- Candidates must carry all the asked documents such as INI-CET admit card, passport size photograph, valid photo ID proof, and a copy of MCI registration certificate with them on the exam day.
- Reverify all your documents before coming to the exam hall.
- Candidates are advised to go through all the guidelines issued by AIIMS for the examination.
- Candidates must reach the INI-CET exam center before time to avoid any chaos.
- Avoid Stress and be confident.
- Eat healthy and sleep well.
- Time management is a must before and during the exam.
To get conceptual clarity on the MBBS courses online, click here
MBBS course, in the initial two years, revolves around non-clinical and para-clinical subjects. These subjects form the foundation for the clinical subjects that are a part of the last two years of the course.
It has been more than two and a half years since COVID-19 began, and ever since then, lives have changed for the good and bad. More than anything else, what we know now as medicos is, that a single microorganism can do wonders when it comes to projecting virulence. Lately, due to those same reasons, this chapter in our microbiology book has gained importance, and this subject, as a whole, is now in the sheer limelight.
As medical students, it seems difficult to develop an interest in subjects that do not seem to have any visible application, like microbiology, and other non-clinical subjects, like biochemistry. However, irrespective of the specialty, you’ll be in, you will be expected to have complete knowledge of all your undergraduate subjects, and that is when you’ll be known as a Top Doc. For this reason, you can’t ignore any of your nonclinical subjects, no matter how boring they might seem.
Microbiology course for undergrads is not as disinteresting as most students think it is. Especially after the introduction of the new Competency-Based Medical Education (CBME), the way of learning and teaching microbiology has been improvised a lot whereas the core syllabus isn’t changed much. Earlier, it was based on organism-based approach, but it has now been completely changed to systemic approach, focusing on each of our body’s systems separately and then classifying diseases accordingly.
As an undergraduate, to excel in the university exams, you must know the examination pattern and the important topics of the microbiology subject.
Changes in the MBBS Prof Exam Pattern
The MBBS prof examination pattern is a little different from what batches before 2019 had appeared for. Earlier, the paper had 2 parts of 40 marks each, with 20 marks of practical. From 2019 batch onwards, the pattern has changed to 2 parts of 100 marks each, and a 100 marks practical, i.e., a total of 300 marks for each of the MBBS 2nd year subjects. The exam now consists of MCQs, case scenarios, short answer questions, and long answer questions.
So, whenever you begin reading microbiology for your final exams, start from the beginning because the entire microbiology is an extension of general microbiology. If your general microbiology is weak, you will never gain confidence in the rest of the syllabus.
Recommended books for Microbiology for UnderGrads include “Essentials of Medical Microbiology” and “Essentials of Medical Parasitology” by Dr. Apurba Sastry and Sandhya Bhat.
Important Topics of Microbiology in MBBS
Let’s know the important topics in Microbiology from MBBS prof exam’s and entrance examination’s perspective.
A medico can easily get to learn all the important topics with Dr. Apurba Sastry’s “Essentials of Medical Microbiology” book. Besides the book, one can also get conceptual clarity with the online course – Microbiology for UnderGrads by Dr. Apurba Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat, and Dr. Deepashree R. This course is aligned with the textbook by the same author.
GENERAL MICROBIOLOGY MODULE
- Contributions of Louis Pasteur
- Koch’s Postulates
- Bacterial cell wall
- Flagella
- Bacterial growth curve (a must-know topic)
- Anaerobic culture methods
- Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
- Horizontal gene transfer
- Antimicrobial resistance
- Exotoxin vs endotoxins
- Isolation techniques for viruses
- Classification with examples (parasites and fungi)
IMMUNOLOGY MODULE
- Innate immunity vs acquired immunity
- Active immunity vs passive immunity
- Definitions of antigen, hapten, super antigens
- Structure of an antibody
- Various classes of immunoglobulins
- Monoclonal antibodies
- Basic mechanism of precipitation reaction and agglutination reaction
- ELISA (in detail)
- MHC
- Cytokines
- Hypersensitivity reactions with their types
- Mechanisms and examples of autoimmunity
- Mechanism of graft rejection
- Types and examples of vaccines
Before you begin reading the systems, there are chapters on sterilization and disinfection, which have gained more importance after COVID-19. These are highly important chapters because they will teach you basic things like biomedical waste management, PPE kits etc.
So, there are a few questions that are very frequently asked from
STERILIZATION AND DISINFECTION
- Healthcare-acquired infections (definition, and examples)
- The steps of hand washing (will rarely come as a theory question but this holds practical application)
- Types of masks
- Steps of donning and doffing
- CAUTI and VAP
- Definitions of sterilization, disinfection, and cleaning
- Autoclave
- ETO
- Disinfectants (according to the levels)
- Methods to test the efficacy of sterilant
- Color coding of dustbins
- Definition and management of needle stick injury
- Water surveillance
SYSTEMIC MICROBIOLOGY MODULE
Bloodstream & Cardiovascular Infections
- Infective endocarditis
- Acute rheumatic fever
- Fuo
- Typhoid
- Scrub typhus
- Brucellosis and leptospirosis
- HIV (in detail)
- Dengue
- Malaria
- Leishmaniasis
- African sleeping sickness
- Lymphatic filariasis
- Systemic candidiasis
Gastrointestinal Tract Infections
- Mechanism of diarrhea and agents
- Lab diagnosis of diarrhea
- Food poisoning
- Botulism
- Types of E.coli
- Shigella
- Cholera
- Rotavirus diarrhea
- Intestinal amoebiasis
- Giardiasis
- Intestinal taeniasis
- Trichura
- Entrobias
- Ascariasis
- Hookworm
The Hepatobiliary System
- Hepatitis
- Liver abscess
- Hydatid cyst
Skin & Musculoskeletal System Infections
- Diabetic foot
- Staph aureus infections
- Streptococcus pyogenes infections
- Gas gangrene
- Lab diagnosis of leprosy
- HSV infections
- VZV infections
- Measles
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis
- Cutaneous larva migrans
- Superficial mycoses
Respiratory Tract Infections
- Agents of respiratory tract infections
- Diptheria
- Pneumonia
- Tb (a very important topic for us as Indians because this disease is very common in our country)
- Influenza
- Coronavirus (which you cannot skip)
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Aspergillosis
CNS Infections
- Meningitis
- Tetanus
- Rabies especially the vaccine prophylaxis
- Cerebral malaria
- Sleeping sickness
Urinary tract Infections
- Pathogenesis of UTI
- Syphilis, especially the lab diagnosis
- Agents of UTI
- Chancroid
- Chlamydia infections
Miscellaneous Infections
- Congenital syphilis
- Oncogenic viruses
- Zoonotic infections
- Bite wound infections
You will also have to prepare for the practical exam, wherein, passing the practical exam is as important as the theory exam. Moreover, because it holds a weightage of 100 marks, you cannot go unprepared.
Click here to watch online microbiology video lecture snippets by Dr. Apurba Sastry.
Must know topics for practical examination
- Basic staining techniques, like gram staining and Zn staining, Albert staining
- Bacterial colony characteristics and their biochemical identification reactions
- Principles behind the reactions and their reagents.
- parasites and how to prepare mounts of stool specimens
- OSPE stations where several instruments used in the microbiology lab can be kept for spot identification.
Important Topics for Microbiology subject in MBBS (For NEET-PG and INI-CET entrance examinations)
During your MBBS, not just the university exams, but your focus should also be on the early preparation of your competitive exams if you dream to settle in a decent post-graduation specialty. There are two main exams currently being held in India, the INI-CET and NEET PG 2023/NEXT. The weightage of microbiology in the INI-CET is approximately 14-16 questions every year and in NEET PG 2023 almost 10 questions are asked every year.
Some of the important topics are mentioned below:
General Microbiology
Includes bacterial cell wall, bacterial toxins, hot air oven, autoclave, chemical antiseptics and disinfectants, disinfection in a healthcare setting, mac conkey agar, bacterial gene transfer (transformation, transduction, and conjugation), lytic and lysogenic phase of a bacteriophage life cycle, and bacterial growth curve.
Bacteriology
Includes morphology, virulence factors, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and lab diagnosis of Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Pneumococcus, Enterobacteriaceae (coliforms-proteus, shigella, salmonella), Vibrio, and Mycobacterium (tuberculosis).
Slight overview of Neisseria, Clostridium, Pseudomonas, Brucella, Mycoplasma, wound infection (staph), and invasive diarrhea is important.
Cover UTI, STDs (Syphilis), Meningitis, and FUO.
Virology
Study Orthomyxoviruses: Influenza (Hemagglutinin, Neuraminidase, Antigenic drift, and shift), Hepatitis B, lab diagnosis, Corona, HIV, ELISA, and a slight overview of Herpes.
Cover Picornavirus: Polio, Rabies virus
Mycology
Include Classification, Dermatophytes, Mycetoma, Rhinosporidiosis, and Histoplasmosis.
Cover Opportunistic: Aspergillosis, Candidiasis, Zygomycosis, Cryptococcus, and Pneumocystis
Parasitology
Life cycles, morphology, lab diagnosis, and clinical manifestations of Ascaris, Trichuria, Enterobius, Echinococcosis (Hydatid cyst), Entamoeba, Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Plasmodium, Leishmania and Wuchereria, Taenia, Ancylostoma, and Toxoplasmosis.
Don’t miss out on these important topics to score high in exams. Undoubtedly, all of us have a different method of learning and DigiNerve has got you covered in all situations. If you are among those who grasp more from visual learning, Microbiology for UnderGrads is one of the best online microbiology course designed by renowned authors, Dr. Apurba Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat, and Dr. Deepashree R. This online microbiology course comprises highly illustrative video lectures and notes, along with self-assessment questions and case studies. The lectures follow the new CBME approach to provide conceptual clarity and score high in the prof as well as entrance examination.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What are the major topics of microbiology?
The important topics for microbiology include Bacterial cell walls, bacterial toxins, hot air ovens, autoclaves, chemical antiseptics, and disinfectants. In the Bacteriology module, Morphology, virulence factors, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, and lab diagnosis of Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Pneumococcus, Enterobacteriaceae (coliforms-proteus, shigella, salmonella), Vibrio, Mycobacterium (tuberculosis) and in Parasitology module, Life cycles, morphology, lab diagnosis, and clinical manifestations of Ascaris, Trichuria, Enterobius, Echinococcosis (Hydatid cyst), Entamoeba, Giardia, Cryptosporidium, Plasmodium, Leishmania and Wuchereria, Taenia, Ancylostoma, and Toxoplasmosis are important topics for exams.
-
Is microbiology important for NEET PG?
Yes, microbiology is important for the NEET PG exam. Approximately, 10 questions come from the microbiology subject in the NEET PG entrance examination every year.
-
How to learn Microbiology for MBBS online?
A medico can subscribe to the online microbiology course or access the online video lectures available on youtube. Microbiology for UnderGrads is one of the best online microbiology courses designed by renowned authors, Dr. Apurba Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat, and Dr. Deepashree R. This online microbiology course comprises highly illustrative video lectures and notes, along with self-assessment questions and case studies. The lectures follow the new CBME approach to provide conceptual clarity and score high in the prof as well as entrance examination.
-
Which is the best book for microbiology for MBBS students?
The recommended books for Microbiology for UnderGrads include “Essentials of Medical Microbiology” and “Essentials of Medical Parasitology” by Dr. Apurba Sastry and Sandhya Bhat.
The National Medical Commission (Undergraduate Medical Education Board) has issued new guidelines and the academic calendar for MBBS 2022-2023 batch on 12th Oct 2022.
As per the new NMC guidelines, the classes for the first-year MBBS batch will start on 15th Nov 2022.
Academic Calendar for the 2022-2023 MBBS Batch
According to the new NMC guidelines, there is a change in the academic calendar of MBBS 2022-2023. However, the duration of the MBBS course is the same i.e., 5.5 years including a one-year rotational internship.
| Professional Year | Time Frame | Subjects | Months(Teaching + Exam + Results) |
| 1st | 15th Nov’22 to 15th Dec’23 | Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry | 13 months |
| 2nd | 16th Dec’23 to 15th Jan’25 | Pathology, Microbiology, and Pharmacology | 13 months |
| 3rd (III-part-1) | 16th Jan’25 to 30th Nov’25 | Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, Community Medicine/PSM | 10.5 months |
| 4th (III-part-2) | Dec’25 to May’27 | General Surgery, General Medicine, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, ENT, Ophthalmology |
17.5 months |
| Internship | 1st Jun’27 to 31st May’28 | As per the CRMI 2021 Regulations | 12 months |
| PG | 1st Jul ‘28 |
For the academic year 2022-2023, the one-year compulsory rotational internship will start from the 1st June 2027 and end on 31st May 2028, as per the CRMI 2021 regulations.
The following guidelines have been issued by the NMC for the 2022-23 MBBS batch:
- The MBBS batch will commence on 15th Nov 2022.
- The college vacations and examination schedules may be notified as per the affiliated universities of the respective colleges.
Other board guidelines are as follows:
- Regarding Electives – 2 blocks of 15 days each are to be adjusted by the colleges for
- Pre/para-clinical branches
- Clinical branches
- In the 2022-2023 academic batch, the supplementary exams will be conducted with a gap of 1 month from the regular exams and the results will be declared within 15 days.
- There shall be no supplementary MBBS batches.
- The remaining rules and regulations shall remain the same as per the GMER (Graduate Medical Education Regulations) 1997. You can visit the site for GMER 1997 details: https://www.nmc.org.in/rules-regulations/graduate-medical-education-regulations-1997/
- The Yoga and Family Adoption Program through village outreach shall continue for the 2021-2022 MBBS Batch.
Along with the changes in the curriculum and the guidelines mentioned above, a few more notifications have been issued by the NMC from the 2022 batch:
- The NMC has created an Anti-Ragging Committee and Dr. Aruna V. Vanikar, President, UGMEB has been appointed as the chairperson of the committee.
- In the NMC notification stated on 4 Oct 2022, the implementation of HMIS (Hospital Management Information System) is mandated in all medical colleges.
- The NEET UG counselling link is active from 11th Oct 2022 on the MCC official website: https://mcc.nic.in.
Click here to read about the NMC NExT Exam update 2023 including the guidelines, complete structure, exam dates and more.
Forensic Medicine & Toxicology is one of the important subjects, included in the 3rd Prof of the MBBS curriculum. The word ‘forensic’ has been derived from the word ‘forensis’ which means forum. FMT course in MBBS makes a medico learn the application of the knowledge of forensic medical sciences to legal issues. Toxicology includes the study of toxic elements, poisons’ properties, activities, toxicity, fetal dose, detection, quantification, therapy, and autopsy results. In this course, a medico is well informed about their medico-legal responsibility during the practice. Thus, forensic toxicology focuses on the legal and medical consequences of the toxic effects of chemicals on humans. In US & Europe, Forensic Medicine is also known as Legal Medicine or State Medicine.
Objectives of FMT course in MBBS
- The course provides complete knowledge of the law in regard to medical practice, medical ethics, and code of conduct.
- It talks about the medico-legal facets of medicine.
- The purpose of the course is to make undergraduate students much capable of observing and legally inferring correct conclusions. The students are also made to learn the way of handling and keeping track of criminal cases or medico-legal cases in an integrated manner.
- It provides knowledge of the administration, relevant medical laws, procedures, and their requirements.
- The Forensic Medicine course must not be thought as just a passing subject, its significance is well-ascertained during medical practice.
- Practically, a medico must develop a basic awareness of the legal system, observe, and analyze cases carefully, and act calmly.
Course Content
The MBBS course curriculum of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology:
Part I: FORENSIC MEDICINE
- General Introduction
- Forensic Pathology
- Clinical Forensic Medicine
- Medical Jurisprundence
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Forensic Sciences
Part II: TOXICOLOGY
- General Toxicology
- Clinical Toxicology
- Environmental Toxicology
- Analytical Toxicology
Along with the theory lectures, the MBBS course curriculum also includes practical and demonstration sessions in Forensic Medicine & Toxicology.
Pre-requisite for success in FMT
The four things are pre-requisite for success in FMT:
- Power of Observation
- Power of Deduction
- Wide range of exact knowledge
- Power of constructive imagination
Tips on how to approach FMT the right way
- Read from Recommended books
- “Review of Forensics Medicine & Toxicology (5th edition)” by Dr. Gautam Biswas. The book has many features like, each chapter starts with the Learning Objectives, further categorized into (a) must know and (b) desirable to know topics. It also includes important topics, MCQs, image-based questions, and case studies at the end of each chapter.
- “Principles of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology” by Rajesh Bardale
- “Essentials of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology” by KS Narayan Reddy, and OP Murty
- Focus on Conceptual clarity
A student must focus on clearing the concepts for a better understanding of the subject. Mugging up in medical sciences doesn’t help in the long run. FMT is a blend of theoretical medico-legal knowledge along with practical sessions on criminal cases, post-mortem cases, chemical injuries, and a lot more. So, it is important to clear all your doubts and focus on conceptual clarity to excel in the subject.
- Simplify your learning with notes
Making notes help filter down the lengthy content of the syllabus. It helps in learning and memorizing concepts easily. It proves for a great benefit during the last-minute revision. Notes also help in memorizing the topics at the time of explanation during lectures and marking important points. They are the best for a quick revision before exams.
- Focus on high-yield topics:
Some of the important topics in FMT are:
- Legal Procedure
- Identification
- Thanatology
- Asphyxia
- Injuries
- Rape
- General toxicology
- OPC poisoning
- Snakebite
- Medicinal poisoning
Watch this video to know the right way to approach FMT in MBBS
- Attend Case Demonstrations
Medical is not just reading books and learning. It is more of practical knowledge and application of the theory into the practical and real world. In medical science, case studies and demonstrations are a must. A medico should never skip any case demonstration session. They form a base for treating the patients in their medical practice efficiently. It is crucial to enhance your FMT learning with practical sessions and case studies. A medico can also understand the case demonstrations via visuals and 3D imaging available in the online MBBS courses.
- Memorize well
The easiest and the best way to memorize is to learn through flowcharts, images, charts, and tables. Learning in a structured format helps in memorizing well in long run. It helps in correlating the topics and clearing the concepts. Try to make your mnemonics for learning to make the most of your visual memory.
- Practice Assessment questions
The best way to analyze your learning is to go through maximum self-assessment questions. It helps in a recap of the topic studied. It also gives a green light to the conceptual clarity of the topic. It not only improves knowledge but is highly beneficial from an exam perspective. A medico can opt for online FMT courses that provide frequently asked self-assessment questions.
Online Lectures to boost your learning
The Forensic Medicine & Toxicology for UnderGrads course has been developed and conducted by a renowned faculty and author, Dr. Gautam Biswas, who is known for his publications “Review of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology”, “Recent Advances in Forensic Medicine and Toxicology volume-1 and 2”, and “Manual of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology”.
The course is well equipped with highly illustrative video lectures with 1400+ self-assessment questions and worthy notes. Case scenarios and case demonstrations are also included in the online FMT course.
The lectures for the course interestingly cover every relevant topic. The course’s content is clear and succinct with flowcharts, animations, brief videos, photographs, tables, differentiation, and line diagrams to help students understand concepts better. It includes case studies at the very beginning and discussion at the end of sessions along with live videos to explain the concept/procedures. Relevant MCQs have been integrated in every lecture including few image-based MCQs after each topic are also provided with explanation. It covers points to remember at the end for viva and forthcoming NEET PG 2023 exams. The FMT online course is designed for medical students to help them be ready for both their university exams and the NEET PG/NExT Exam.
To get conceptual clarity on Clinical Forensic Medicine, Click here.
Table of Content – Forensic Medicine & Toxicology for UnderGrads course
- Orientation
- General Information
- Forensic Pathology
- Clinical Forensic Medicine
- Medical Jurisprudence (Medical Law and ethics)
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Forensic Laboratory investigation in medical-legal practice
- Thanatology
- General Toxicology
- Pharmaceutical Toxicology
- Sociomedical Toxicology
- Jurisprudence and Forensic Medicine – Qbank
- Toxicology – Qbank
All these modules include detailed sub-topics as per the CBME curriculum.
Scope of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology
- Forensic Scientist
- Forensic Expert
- Clinical Investigator
- Criminologist
- Research Associate
- Forensic Medicine Professor
- Jobs at Intelligence Bureau
- Forensic Analyst at Investigation firms
- Manager Forensic Advisory
- Forensic Pathologist
- Medical Officer
- Toxicologist
A medico must keep all senses open while dealing with FMT cases and willingness to work is a must.
FAQs
-
Where can I study FMT online?
Dr. Gautam Biswas’s Forensic Medicine & Toxicology for UnderGrads course is an online FMT course which is well equipped with highly illustrative video lectures, concise notes and 1400+ self-assessment questions. Case scenarios and case demonstrations are also included in this course.
-
What is FMT in MBBS?
FMT discloses the medico-legal facets of medicine. The purpose of the course is to make undergraduate students much capable of observing and legally inferring exact conclusions. The students are also made to learn the way of handling and keeping track of criminal cases or medico-legal cases in an integrated manner. A medico is well informed about their medico-legal responsibility during their medical practice.
-
How do I pass forensic medicine in MBBS?
Make sure not to skip any lecture and case demonstration sessions. Make notes and study on regular basis. You can also opt for an online FMT course to boost your learning with the help of video lectures, case demonstrations, notes, and self-assessment questions for practice.
A cataract is referred to as the development of any opacity in the lens or its capsule. It may occur either due to the formation of opaque lens fibers (congenital and developmental cataracts) or due to a degenerative process leading to the opacification of normally formed lens fibers (acquired cataracts).
Classification:

The Etiological Classification includes the following types of cataracts:
- Congenital and Developmental Cataract
- Acquired Cataract
- Senile cataract
- Traumatic cataract
- Cataracts in systemic diseases
- Electric cataract
- Radiational cataract
- Toxic cataract
The Morphological Classification includes the following types of cataracts:
- Capsular Cataract
- Subcapsular Cataract
- Cortical Cataract
- Nuclear Cataract
- Polar Cataract
SENILE CATARACT
Senile cataract is also known as Age-related cataract and is the most common type of acquired cataract. It affects equally all persons of either sex above the age of 50 years. The condition is usually bilateral, but in most cases, one eye is affected before the other.
ETIOLOGY
Some of the risk factors associated with Senile cataracts:
- Age: It is the most important factor.
- Sex: Its prevalence is greater in females.
- Heredity
- Ultraviolet Irradiations: It is responsible for the early onset and early maturation of senile cataracts.
- Dietary factors: Diet deficiency in certain proteins, amino acids, and vitamins (riboflavin, vitamin A, C, E).
- Dehydration Crisis
- Smoking: When a person smokes, it leads to the accumulation of pigmented molecules like 3-hydroxykynurenine and chromophores, which lead to the yellowing of the lens.
HOW LENS LOSES ITS TRANSPARENCY?
Lens gets affected in different ways in nuclear and cortical senile cataracts. In cortical cataracts, there is a decrease in the soluble crystalline lens proteins, amino acids, and potassium associated with an increase in the concentration of sodium, which ultimately results in over hydration of the lens. While in nuclear cataracts, there is age-related nuclear sclerosis associated with dehydration and compaction of the lens. It is associated with an increase in water-insoluble proteins.
STAGES OF MATURATION
- In-nuclear type of Cataract
The sclerotic process continues and leads to the hardening of the lens and decreases the ability of accommodation. The changes start from the centre and spread towards the periphery slowly.
- In-cortical type of cataract
Firstly, there is a stage of lamellar separation which is the earliest sign where the formation of vacuoles occurs in the cortex. These changes are reversible. It is followed by a stage of an incipient cataract where wedge-shaped or saucer-shaped opacity is seen. Then comes the final three stages of cataracts: immature, mature, and hyper mature (morgagnian and sclerotic) cataracts.
CLINICAL FEATURES
The clinical features include the symptoms, signs, and complications.
Symptoms:
- Glare
- Uniocular diplopia
- Colored halos around light
- Poor colored discrimination
- Black spots in front of the eye
- Image blur and misty vision
- Deterioration of vision
Signs:
- Visual acuity: It is 6/9 to PL+ and PR in all quadrants
- Test for iris shadow: It is seen in immature cataracts.
- Colour of lens:
- In nuclear cataracts: amber, brown, black, reddish
- In immature senile cataract: greyish white
- In mature senile cataract: pearly white
- In morgagnian hyper mature cataract: milky white
- In sclerotic hyper mature cataract: dirty white
- Morphology of lens: It is best seen by slit lamp examination.
- Distant direct ophthalmoscopy:
- Absence of opacity: reddish yellow fundal glow observed
- Partial cataractous: black shadow against the red glow observed
- Complete cataractous: no red glow observed
Complications:
- Phacoanaphylactic uveitis
- Lens-induced glaucoma
- Subluxation or dislocation of the lens
Click here to watch the best online video lectures on lens and cataract.
MANAGEMENT OF CATARACT IN ADULTS
- NON-SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
To delay the progression of the disease:
- Vitamin E and aspirin can be taken
- Topical preparations containing iodide salts of calcium and potassium can be taken
-
- To treat the cause of cataract: control diabetes, remove cataractogenic drugs, removal of irradiations
- To improve vision in early stages of cataract: prescription of glasses, arrangement of illumination, use of dark goggles, and mydriatic agent.
- SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Indications:
- Visual Improvement
- Medical Indications
- Cosmetic Indications
PREOPERATIVE EVALUATION AND WORKUP
1.) Ocular examination
It includes the following parameters:
- Visual status assessment
- Pupil
- Anterior segment evaluation
- Intraocular pressure
- Examination of lids, conjunctiva, and lacrimal apparatus
- Dilated fundus examination
- Retinal function tests
- B- scan ultrasonography
- Electrophysiological evaluation
- Keratometry, corneal topography, and biometry
2. General medical examination of the patient
The medical examination should include the following:
- History of current medication
- Any family history
- Investigations
3. Preoperative medications
The preoperative prescribed medication includes:
- Antibiotics
- IOP lowering agents
- Mydriatic agent
- Anaesthetic agents
4. Surgery
- Earlier, couching was done in which the cataractous lens was pushed into the vitreous cavity, and it was the first surgery introduced.
- Then, crude extracapsular cataract extraction was done but soon it became unpopular due to marked complications.
- Later, intracapsular cataract extraction was introduced but nowadays it is not performed due to complications. It is reserved only in cases of subluxated or dislocated lens.
- Now comes the modern technique of extracapsular cataract extraction, which is the preferred method in all cases of cataract surgeries.
OVERVIEW OF EXTRACAPSULAR CATARACT EXTRACTION SURGERY:
In this method, the anterior capsule’s major portion is removed along with the anterior epithelium, nucleus, and cortex leaving behind the intact posterior capsule.
Indications:
- For almost all types of cataract surgeries in adults and children unless contraindicated.
Contraindications:
- In the subluxated or dislocated lens.
Advantages :
- Universal operation
- Posterior chamber IOL can be implanted after ECCE
- Postoperative vitreous-related complications are not seen
- Incidences of postoperative complications are much less like endophthalmitis, cystoid macular edema, and retinal detachment.
- Postoperative astigmatism is less
- Incidence of secondary rubeosis in diabetics is reduced
Different Techniques of Extracapsular Cataract Extraction:
- Conventional extracapsular cataract extraction
- Manual small incision cataract surgery
- Phacoemulsification
- Femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery
Presently, the phacoemulsification technique has become the preferred method of cataract extraction worldwide because the complications are much lesser as compared to other methods of cataract extraction.
However, in countries like India, manual small incision cataract surgery has the advantages of sutureless surgery as well as a low-cost alternative to phacoemulsification.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES FOR CHILDHOOD CATARACTS:
The surgical methods opted for the childhood cataracts, include:
- Lens aspiration
- Lensectomy
INTRAOCULAR LENS IMPLANTATION:
IOL is the method of choice for correcting aphakia.
Types Of IOLs:
- Based on the method of fixation in the eye, the different types of IOL are:
- Anterior chamber IOL
- Iris-supported lens
- Posterior chamber lenses
- Depending upon the material of manufacturing, the different types of IOL are:
- Rigid IOLs
- Foldable IOLs
- Thinner foldable IOLs
- Ultra-thin foldable IOLs
- Based on focusing abilities, the different types of IOL are:
- Monofocal IOLs
- Multifocal IOLs
- Trifocal IOLs
- Special function IOLs, the different types of IOL are:
- Aniridia IOLs
- Implantable miniature telescope
- Piggyback IOLs
- Spherical versus Toric IOLs
- Aphakic versus Phakic Refractive IOLs
Indications of IOL:
It is done in each and every case being operated for cataract unless and until it is contraindicated.
BIOMETRY is the calculation of IOL:
Nowadays online toric IOL power is calculated.
Equipment for Biometry:
- A-Scan Ultrasonic Biometer
- Optical Biometer
Techniques of IOL Implantation:
- Primary IOL Implantation refers to the use of IOL during any surgery for a cataract.
- Secondary IOL Implantation is done to correct aphakia in the previously operated eye.
POSTOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING CATARACT SURGERY
- The patient is asked to sit leaned back on chair for 30 minutes.
- Any NSAIDs may be given orally for mild to moderate postoperative pain.
- The bandage or eye patch is applied till the next morning. The eye is inspected for any postoperative complications.
- Antibiotic eye drops are used 4 times a day for 7-10 days.
- Topical steroids eye drops are given 3 to 4 times a day and are taken for 6-8 weeks.
- Topical ketorolac or any other NSAIDs with eye drops are given 2 to 3 times a day for 4 weeks.
- Topical timolol eye drops
To get conceptual clarity in Ophthalmology online, subscribe to CBME & NEET-oriented Ophthalmology for UnderGrads course.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What causes senile cataract?
Ans: Senile cataract etiopathogenesis is not exactly clear, but it is mainly due to the age factor. Other factors are also responsible like heredity, ultraviolet radiation, dietary factors, dehydration crisis, and smoking.
-
What is the most common type of senile cataract?
Ans: Nuclear sclerotic type is the most common of senile cataracts in which there is progressive sclerosis of the nucleus of the lens. It makes the lens inelastic and decreases the accommodation ability, which hampers the light rays to pass.
-
Is senile cataract curable?
Ans: Yes, senile cataract is curable. It can be treated through surgeries like extracapsular cataract extraction and intracapsular cataract extraction.
-
What happens if cataracts are left untreated?
Ans: If the cataracts are left untreated, they lead to various complications like phacoanaphylactic uveitis, lens-induced glaucoma, and subluxation or dislocation of the lens.
Performing invasive and non-invasive treatments on the human body is the surgeon’s basic role. The surgeon attempts to assist the patient in overcoming the disease by assisting the patient with deformities and injuries through the operation. Surgery has a variety of specialties; one can become an eye surgeon, general surgeon, neurosurgeon, cardiovascular surgeon, plastic surgeon, orthopaedic surgeon, or oncologist. You would have observed that the surgeons have a crew supporting them, who make all the necessary preparations before the procedure may begin and assist during the surgery. A surgeon is a medical professional who operates or conducts surgery on patients. Along with doing elective and preventive surgeries on the patients, these medical professionals also perform diagnostic procedures.
Why Consider to Become a Surgeon in India?
India is the second-most populous nation in the world, and its healthcare industry has only grown since its independence. With the growing population and requirement for healthcare facilities, the demand for doctors is increasing.
While we all aim to achieve specific goals in our lives, we all know that we enjoy the journey more than we appreciate the realization of our goals. The field of medicine is fascinating too. Being in a position of understanding the human body and knowing how to bring it back on track and the experiences in between are the ones that you will cherish for your lifetime. Moreover, the satisfaction of saving lives goes far beyond the feeling of anything. Being a doctor is an honor and a responsibility of a lifetime.
There can be millions of reasons to pursue a career in medicine and become a doctor which can be listed here. However, the most important reason is your call. The pathway to becoming a doctor is not an easy one. If you want to become a doctor, you need self-motivation and an unshakable reason for pursuing a career in medicine that should come from within.
How to become a Surgeon in India
Here are a few guidelines that you must follow if you want to become a surgeon in India:
- Passing the 12th Grade: Candidates must first complete their 12th grade or pre-university course (PUC) in physics, chemistry, and biology (PCB) with the necessary cut-offs to become a doctor.
- Clearing NEET-UG: Students are now required to qualify for the NEET entrance examination. With about 76,928 medical seats available, it is the only entrance exam for MBBS admission in India to MCI-recognized medical colleges. After you get the required percentile, depending on the cut-off marks and attending counseling procedure paves a way for admission to the MBBS course.
- Completing MBBS course: One of the most well-known graduate degrees for becoming a doctor in India is MBBS, and those who achieved the required percentile in the NEET exam are qualified to pursue MBBS. This 5-and-a-half-year program offers Pre, Basic, and Paramedical topics. A medico gets to learn Medicine & Surgery in MBBS. Additionally, students must complete a 12-month required rotational internship during their MBBS. After successful completion of your MBBS degree, you become eligible for higher studies in Medical Sciences.
- Clearing NEET-PG: The NEET-PG (National Eligibility Entrance Test-PG), which is administered by the National Board of Examination, would be the basis for admission to MS courses in medical colleges in India. For admission to AIIMS and JIPMER and other INI- Institutes, the INI-CET examination is conducted. Candidates must meet particular examination Eligibility Criteria to pursue an MS degree in an Indian medical college. Further, selection and admissions to medical colleges depend on the cut-off score and merit list.
- Pursuing an MS degree: The next step after earning an MBBS degree and clearing the NEET PG exam is to earn a PG degree, with MS being one of the most popular PG courses following MBBS. Your path to becoming a surgeon begins with this degree.
Developing both practical and theoretical skills is a requirement of medical college training. Students who are in their last years of medical school must work with patients in clinics and hospitals. Volunteering at community clinics or hospitals helps medical students stand out from their competition. A successful career as a surgeon will be paved by a residency program with a competent mentor in addition to the qualifications and skills for becoming a surgeon.
To get conceptual clarity in MBBS course subjects, access the best online video lectures.
Responsibilities after becoming a surgeon
The following duties often fall under the purview of surgeons:
- Analyzing and evaluating a patient’s medical situation and medical history.
- Engaging in conversation with the patient and addressing any worries they may have regarding their general health and well-being.
- Prescribing the necessary tests and examinations to identify the underlying causes of the patient’s condition.
- Examining and evaluating the test results to diagnose and determine any conclusions.
- Communicating the patient’s most recent state and offering evidence to back up the most recent conclusions.
- Creating and suggesting a remedy to address the issue or perform any surgery if required.
- Following up, reviewing, and assisting patients in taking care of their health as needed to aid in their recovery.
Right Way to Approach Surgery
Some MS Specialisations
- General surgery
- Orthopaedics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Injury medicine and surgery
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Ophthalmology
- Laparoscopic Surgery
- Cosmetic surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Cardiac surgery
- Pediatric surgery
MCh degrees (MCh, or Master of Chirurgiae, is a Latin abbreviation for general surgery) with any specialization from an institution approved by the MCI are required for people who seek to advance their sub-specialization in any field, such as plastic surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, or urology. The MCh degree typically has a lot of research requirements. All candidates who pursue the MCh program must be full-time residents during the three-year training term. MCh can be done as a 5 years course after MBBS or 3 years after MS.
Job Roles
You can choose from several surgical specializations depending on your interests. Types of Surgeon’s Job Roles include:
Neurosurgeon: Covers all elements of brain surgery, including spinal surgery, skull base surgery, pediatric neurosurgery, and a variety of other neurological conditions.
Cardiothoracic Surgeon: Includes Congenital surgery, thoracic surgery, heart failure surgery, transplant surgery, oesophageal surgery, and cardiac surgery are all included in this. In this kind of surgery, conditions affecting the heart, oesophagus, chest, and lungs are treated.
Pediatric Surgeon: From the time a baby is born until they reach adolescence, these surgeons deal with pediatric surgical difficulties.
Orthopaedic Surgeon: Surgery performed on bones, joints, and soft tissues like ligaments, muscles, and nerves are done by orthopaedic surgery, which includes foot, ankle, and knee surgery, rheumatoid, and sports surgery, as well as fractures.
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon: They perform the surgery on the face and neck. Correcting face deformities, managing facial damage, and basic surgery to complex head and neck surgeries are all included in the procedures.
Other subspecialties surround vascular, colorectal, breast, endocrine, upper and lower gastrointestinal, kidney, liver transplantation, and a lot more.
Top Surgical Recruiting Firms in India
In India, there are many reputed hospitals where working will feel like a dream:
- Fortis Escorts Heart Institute, Delhi
- Jaypee Hospital, Noida
- Fortis Hospitals
- Apollo Hospitals Group
- Sri Ramakrishna Multi-Speciality Hospital
- Narayana Health
- Max Healthcare and Super Speciality Hospitals
Salary and PayScale of Surgeons
While surgeons in private institutions earn lakhs per month, those working in government hospitals are paid a set wage of 1 to 2.5 lakh. An entry-level surgeon makes about Rs. 9,71,000 annually. A general surgeon with experience can expect to make about Rs. 24,63,000, compared to a mid-career surgeon with 5 to 10 years of experience who can make about Rs. 11,71,000. The income varies depending on various factors, such as the number of surgeries performed, experience, type of surgeon, area of employment, and so on.
Possibilities for a Surgeon
The more accomplishments you have under your belt, the better. The use of technology to do operations with the aid of robots and other instruments will increase your worth and make you an asset to your organization, which is another area where surgeons may set themselves apart. Specialization is undoubtedly a key element that will elevate your status in society; nevertheless, be careful while selecting a speciality because each one requires time and money. Moving to a semi-urban location is another excellent strategy to boost your possibilities. Due to the rapid growth, one may anticipate the opening of new hospitals in these places to draw in more patients from nearby rural areas.
Future of Surgery
Both technology and surgical techniques have seen a significant change recently. The techniques and tools are being improved, which greatly lowers the risk for the patients. The use of robotic surgery and minimally invasive techniques is one direction we anticipate the future of surgery to take. The new techniques have been adopted by many hospitals, and they also hasten recovery times significantly. The doctors can now treat the patient with the aid of micro-cameras. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicines are two other developing areas of surgery. The medical professionals here use biomaterials to aid the patient’s recovery. An illustration would be the use of stem cells or scaffolds to assist a patient with an illness. The subject is still changing. The ability for people to develop organs from patient cells is soon to come.
The demands of this job can be physically and psychologically taxing. A surgeon’s position calls for in-depth medical expertise, as well as precision, devotion, and skill. A career as a surgeon is rewarding since it improves people’s quality of life. It is not an easy job to save a life, it requires lots and lots of hard work, sleepless nights, and years of practice. The average surgeon’s income is quite lucrative, which opens several intriguing career options. Surgeons typically have a lot of work on their plates, including monitoring patients, doing procedures, attending meetings, and completing paperwork. They occasionally might also have extra duties including mentoring junior physicians and conducting research.
To get access to the best online Surgery course for MBBS students, Click here.
Pathology is a branch of medical science that involves the study and examination of the origin and cause of diseases. It facilitates all aspects of patient consideration, from diagnostic testing and treatment advice to using cutting-edge genetic technologies and disease prevention. It is essential to the study of clinical medicine because it serves as a link between many academic disciplines and medicine. By studying Pathology in MBBS, medicos learn how to diagnose the disease or condition including the cause and degree of severity, track the development of the illness, examine the effectiveness of the therapy and manage the patient.
To know the right way to approach pathology in MBBS, Click here.
Why is pathology one of the best fields of study?
The basis for all clinical medicine, including patient care, diagnostic procedures, and treatment strategies, is pathology. To develop potential treatments for diseases, pathologists experiment with cutting-edge technology and carry out a variety of clinical procedures. They make every attempt to develop a more effective method of combating viruses, infections, and other serious health issues. Pathologists play a very crucial role in research, advancing medication, and devising new therapies to battle infections/viruses, contaminations, and infectious diseases.
Some of the fields of Pathology that students can opt for include:
• Clinical Pathology – A clinical pathologist is knowledgeable about the key components of laboratory medicine and various clinical branches. They typically have training in hematology, microbiology, chemical pathology, and many more. A clinical pathologist typically works in a rural town, community hospital, medium-sized medical practice, or other non-metropolitan centers.
• Forensic Pathology – A forensic pathologist’s primary responsibilities include identifying the cause of death and reconstructing the events leading up to it. This is completed in a careful, meticulous manner. The performance of autopsy exams of the internal and external body organs and determining the cause of death is a significant aspect of the function.
• Anatomical Pathology- This area is concerned with disease tissue diagnosis. Anatomical pathologists need to have a thorough knowledge of the pathological and clinical aspects of various diseases.
• General Pathology- A general pathologist typically works in a big rural town, community hospital, medium-sized private practice, or another non-metropolitan setting. They undergo various diagnostic procedures, blood sampling procedures, and various laboratory tasks.
• Chemical Pathology – Another branch of pathology that addresses the full spectrum of disease is chemical pathology. It includes identifying changes in a broad range of chemicals (proteins, electrolytes, and enzymes) in blood and body fluids in connection with numerous disorders.
• Immuno Pathology – Similar to hematology, the discipline of immunology frequently combines clinical work with laboratory medicine (the testing of patient samples, interviewing, examining, and advising patients about clinical problems).
• Microbiology – Diseases due to infectious organisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites are the focus of microbiology.
Digital Pathology:
It can speed up the delivery of more accurate diagnostic results while minimizing the impact of human error. The processes used in digital pathology allow it to complete routine tasks more quickly without compromising the quality of the work. Digital pathology is slowly gaining specific support for teaching, tissue-based research, medication development, and the global practice of human pathology throughout the world. Digital pathology is quickly gaining attention. It is an invention devoted to lowering laboratory costs, enhancing operational effectiveness, increasing productivity, and enhancing treatment choices and patient care.
Best way to learn Pathology in MBBS
Refer to Dr. Harsh Mohan’s ‘Textbook of Pathology’
The book includes references as well as the most recent WHO classification of neoplasms and current diagnostic criteria for common diseases. It adheres to a straightforward, clear, replicable, and user-friendly format. Additionally, Prof. Ivan Damjanov generously contributed schematic, gross, and photomicrographs with higher quality and greater resolution to the book. To make it easier for beginners to recognise the structures in the images, each image is labelled. Each topic’s conclusion includes a distinctive eye-catching colour box that summarises the topic’s important themes in bullets for quick review. At the end of each chapter, the book also offers significant review questions (both long-answer types and short-notes on themes) to help the reader get ready and visualise what they will write for the exam.
Enroll in Dr. Harsh Mohan’s Pathology For Undergrads online course
The course is aligned with Dr. Harsh Mohan’s ‘Textbook of Pathology’. The course focuses on the causes, and mechanisms of disease development (pathogenesis), morphologic changes in cell structure, and the effects of these changes (clinical manifestations). The course’s five key features are General Pathology, Hematology, Systemic Pathology, and Clinical Pathology, including Exfoliative Cytology, Body Fluids, and Cytology in Clinical Care. Pathology practicals include gross specimens that are significant from the perspective of an examination.
Check out Dr. Harsh Mohan’s online course – Pathology for UnderGrads
Pathology in MBBS is an exceptionally wide branch, where more than 19 kinds of specializations coexist. Depending upon their specializations, abilities, and interests, pathologists work either in research facilities, clinics, healthcare centers, or pathology centers. Frequently, they give advice and even decide the most ideal treatment in the event of complicated diseases. The pathological reports are a must for better diagnosis and treatment. The reports help specialists to examine the patient, diagnose diseases, and treat them accordingly. Pathologists utilize gross, microscopic, immunologic, genetic, and molecular modalities to determine the presence of disease and work closely with healthcare specialists, radiologists and researchers. They can sub-specialize in various disciples, like gastroenterology, gynecologic pathology, blood sicknesses, clotting disorder, microbiology, lung and breast cancers, and more.
Introduction
- Glaucoma (aka “Kala Motia” in Hindi) is also known as “Silent thief of Sight”, as patients suffering from advanced glaucoma gradually develop irreversible blindness and tunnel-like vision. Patients with advanced glaucoma are not even able to perform their daily routine tasks effectively.
- Glaucoma is very characteristically known by the optic nerve changes and progressive damage to the optic nerve. The changes in the optic nerve results in the characteristic disc appearance and corresponding changes in the visual field.
- The cause for maximum cases is unknown and therefore, primary glaucoma is either idiopathic or has some genetic cases which are yet not precisely known.
- Raised Intraocular Pressure (IOP) is not a part of the definition of glaucoma, as it is just a risk factor.
Broad Classification

- Classification helps to plan a treatment strategy
Key players of diagnosis
For the precise diagnosis, there are five things to keep in mind:

Elaborating the above-mentioned key players in detail:
- Intraocular pressure
Normal IOP:
- According to the studies, normal IOP has a very wide range but for practical purposes, Mean IOP (GAT): 15±3 mmHg (Range 12-18) is considered.
- The “magic number of 21” is a figure of the past, an obsolete concept.
- In a graphical representation, Normal distribution with a slight skew towards higher values is seen.
- Remember many factors, in addition to glaucoma, influence IOP and can be divided into 2 categories (i) those that exert a long-term influence (e.g., genetics, age, gender, refractive error, and race), and (ii) those that cause short-term fluctuations in the pressure (e.g., time of day, body position, exertion, lid, and eye movement, various ocular and systemic conditions, general anesthesia, and some food and drugs).
Diurnal variation of IOP:
- IOP doesn’t remain the same throughout the day.
- IOP value is generally higher in the morning than in the afternoon; normal fluctuation is about 2-5 mm Hg in a day.
- If the fluctuation is not in the normal range within a day, then this IOP damages the optic nerve over a prolonged period.
Applanation Tonometry:
- Clinically, Goldmann Applanation Tonometer (GAT), a gold standard tonometer is used to measure the IOP. This is one of the most reliable ways of measuring the IOP.
GAT is mounted on a slit lamp and the patient sits on the other side. In the biprism of the applanation tonometer, the doctor can see two green mires under a cobalt blue filter and the endpoint of the pressure is reached when the inner margins of these superior and inferior hemispheres touch each other.
NOTE: Never start treating the patient based on one reading of IOP. Make sure to take 2-3 different readings at different periods on different days to ensure the most reliable reading of IOP.
IOP Paradox:
“Everything within 12-18 mm Hg range is not normal and everything beyond 18 mm Hg is not abnormal”.
There are two paradoxical conditions:
- Paradox 1: When there is GON, i.e., Glaucomatous optic nerve damage but the IOP < 21 mmHg, there is damage to the nerve and visual fields. This entity is called Normal/ Low Tension Glaucoma (NTG/LTG).
- Paradox 2: When the IOP value is > 21 mmHg and there is no optic nerve damage and the visual fields are perfectly fine, this entity is known as Ocular Hypertension (OHT; Normal variant).
NOTE:
- Remember, Refrain from using the word “Normal” in the clinical case scenarios because a range that is normal for one may not be normal for the other.
- If baseline IOP is > 30 mmHg, it is reconfirmed once and the patient should be started on therapy without the need for performing a diurnal IOP recording.
Central Corneal Thickness (CCT):
- It is measured by an instrument named Pachymeter.
- Normal corneal thickness is around 520-550 microns.
- It is an independent predictor of Glaucoma.
- Goldmann applanation tonometer calibrated for CCT of 520 mm: a thinner CCT underestimates true IOP, and thicker CCT overestimates.
- A very thin or very thick cornea can impact the decision-making process regarding the need to treat, or the aggressiveness of the therapy.
-
Optic Disc/ Optic Nerve Head: Normal Vs. Glaucoma
In the optic disc, the central part which is paler than the peripheral part is called the cup, and the reddish-orange part over the cup is called the neuro-retinal rim (NRR)and the entire neural tissue lies here.
There are a few things we need to consider, for the cup is to disc ratio measurement mentioned below:
- We can consider Optic disc as a ‘Donut’. The central part is empty, i.e., non-neural tissue but the peripheral part has neural tissue (NRR), and we should focus on the health of NRR.
- Cup: Disc Ratio: The central part is the cup and the blood vessel are coming and bending out on the neural rim. It is referred to as Cup Diameter/ Disc Diameter.
- Colour Cup: We must not interpret cupping by just looking at the color of the cup.
- Contour Cup: The important point to consider is the bend of the blood vessels coming out of the blood. It tells the exact margin of the cup.
- Correlate with the disc size: Usually, large discs have large cups and this cupping is physiological. However, a small disc with even a small cup must be examined with caution as it is more prone to develop glaucoma because the nerve fibres are tightly packed. Glaucomatous eyes with small discs may have pseudonormal cups.
- High interindividual variability: There is an immense amount of variability in individuals of the same race and in different races.
- ISNT Rule:
- It is the health of the neural rim that accounts for the health of the optic nerve.
- As a rule, the inferior neural rim of the optic disc is the thickest followed by the superior rim followed by the nasal rim, and the temporal rim is the thinnest. This is called the ISNT Rule.
- Nearly 80% of healthy optic nerves follow the ISNT rule. 20% of normal individuals can have different thicknesses of the rims but with all the other tests, we can rule out glaucoma in those individuals.
- In advanced cases of glaucomatous optic neuropathy, there occurs concentric NRR loss.
Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy (GON):
- Glaucoma is a disease that begins with asymmetry. Initially, the cupping in one eye is different from the other eye. When the asymmetry of the cup: disc ratio between the two eyes is more than 0.2, a person is labelled as Glaucoma Suspect.
Characteristics features of GON include:
- Generalized or focalized increase in the optic cup size and the cup: disc ratio
- Vertical enlargement of the optic cup (especially at the superior and inferior poles)
- Asymmetric cupping (0.2 cup-disc ratio difference) between the two eyes
- Narrowing or notching of the neural rim
- Splinter/ Drance hemorrhages
- Changes in vessel configuration and caliber
- Increased visibility of the lamina cribrosa pores
Accurate documentation with an optic disc drawing at baseline is important and can be supplemented with stereo-optic disc photography. Changes in disc findings are more sensitive indicators of the presence and progression of the disease
- Gonioscopy
- To classify the anterior angle chambers into Open Angle Glaucoma and Closed Angle Glaucoma, a lens called a Gonioscope to view the angles.
- Why can’t we see the anterior chamber angle with the slit lamp or direct observation?
There is a small protrusion of the scleral tissue which projects anteriorly to the angle just like the watch glass fitted into the rim of a wristwatch. Similarly, because of the projection of scleral tissue, the cornea is fitted like a watch glass. There is a total internal reflection at the cornea-air interface and the light rays do not get out to reach our eyes. So, the curvature of the cornea creates internal reflection and therefore we need an additional lens called a Goniolens.
- What does a Goniolens do?
Gonio lens permits the visualization of the angle by eliminating the cornea as a refracting surface by placing a concave surface against the cornea.
So, these different glasses allow visualization of the angles using obliquely inclined mirrors.
-
- What if the angles are closed?
- Once angle closure is diagnosed, categorize the stage of angle closure
- Find out the whether the angle closure is appositional or synechial. If the goniolens. is pressed in the centre of the cornea, the aqueous from the centre is displaced towards the angle and open it up artificially. This means that the angle closure is appositional. But if there were adhesions between the iris and the cornea or the lens, there are synechia, then whatever amount of displacement of aqueous is there, it will not open the angles and this is called Synechial angle closure.
- When to do gonioscopy?
All Glaucoma patients need to undergo:
-
-
- Initial examination
- Repeat every 1-2 years as the human body is dynamic and with age, health conditions keep on changing
-
- What is seen through the Goniolens?
- Schwalbe’s line (SL)
- Trabecular meshwork (TM)
- Scleral spur (SS)
- Ciliary body band (CBB)
In Secondary Glaucoma,
- Pigmentary Glaucoma: Mascara line is seen which has a lot of pigments.
- Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma: Sampolesi’s Line
- Angle recession: Seen in the case of trauma
- NVG: Abnormal blood vessels as seen in the Neovascular Glaucoma.
- Visual field
- Visual field testing is known as Perimetry.
- Up to 37% of optic nerve fibers need to be lost before a VFD is found on automated perimetry, usually progressing from mid-peripheral or paracentral VFD in the earlier stages, to loss of central fixation points and temporal visual field loss in advanced
- Standard automated full-threshold static perimetry is preferred; use the same test strategy for comparison.
- Glaucoma visual field defect respects the horizontal meridian. Defects respecting vertical meridian, are likely due to neurophthalmic problems.
- Reliable tests are crucial and influenced by learning, patient comprehension and cooperation, artifacts, and other ocular pathology.
- Characteristic traits of glaucomatous visual field defects:
- Asymmetrical along the horizontal midline
- Located in the mid periphery(5-25° of fixation)
- Reproducible
- Not attributable to any other pathology
- Localized
- Correlating with the appearance of optic disc
- Whenever there is thinning of the inferior neuro-retinal rim, there will be superior optic nerve defect and vice versa.
- After analyzing the structural changes, match them with the corresponding functional defects.
- Retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) analysis: RNFL thinning detected with optical coherence tomography (OCT) is useful to diagnose early glaucoma. Use in conjunction with the other parameters.
- Risk Factors
- Elevated IOP
- Myopia
- Optic nerve changes
- Family history of glaucoma
- Increasing age
- Race
- Diabetes mellitus
- Cardiovascular disease
Treatment:
The main goals of treatment are:
- To preserve visual function with stable optic nerve and visual field status in the patient’s lifetime, by controlling IOP within the target range and addressing other risk factors, and
- To maintain quality of life.
IOP lowering by medication, laser, or surgery is the mainstay of treatment to prevent glaucoma development and retard progression.
(Detailed discussion in a subsequent blog)
Putting it all together!!
- Does this patient have glaucoma?
- If not, how high is the risk of developing glaucoma?
- What other tests need to be done?
- When do you see this patient back?
- When/How do you start treatment?
- What is the prognosis for this patient?
‘Basic Toolkit for Glaucoma’ by Dr. Parul Ichhpujani
To get conceptual clarity in Ophthalmology online, subscribe to CBME & NEET-oriented Ophthalmology for UnderGrads course.
Dr. Parul Ichhpujani
MS, MBA
Professor at Glaucoma Services
Department of Ophthalmology, Govt. Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh, India
Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore is a private medical college, hospital, and research institute. CMC is one of the best private medical colleges in India. In and around Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, this institute has a network of primary, secondary, and tertiary care hospitals. Dr. Ida Scudder is the founder of CMC Vellore. The college is affiliated with the Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University, Chennai. CMC, Vellore is approved by NMC (National Medical Commission). It is ranked as one of the top medical colleges in India. The institution offers admission to various disciplines of sciences: medical science, nursing, allied health sciences, some other master’s and doctoral programs, and post-graduate engineering programs.
The college offers admission to various programs including:
- Undergraduate medical course (MBBS)
- Medical postgraduate courses (diploma, degree, and higher speciality courses)
- Certification courses
- Postdoctoral fellowship courses
- Distance education program
- Undergraduate nursing program
- Nursing postgraduate courses (diploma, degree, and fellowships)
- Allied health sciences degree courses
- MBA in hospital and health systems management (HHSM)
- MS Bioengineering
- Tech. Clinical Engineering
- D. Medical Sciences
MBBS in CMC Vellore
MBBS is a four-and-a-half-year course followed by one year compulsory rotating residential internship. In CMC, Vellore, the MBBS course comes under the group A category. As per the CBME curriculum, the undergraduate course in medicine comprises three phases.
Three phases in MBBS Curriculum
| Phases in MBBS Curriculum | Duration | Subjects Included |
| 1 (Pre-Clinical Phase) | 13 months | Basic Sciences, Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Introduction to Community Medicine, Humanities, and Professional Development |
| 2 (Para-Clinical Phase) | 12 months | Pharmacology, Pathology, and Microbiology |
| 3 (Clinical Phase) | Part 1: 13 months
Part 2: 13 months |
Forensic Medicine, Community Medicine, Ophthalmology, and Otorhinolaryngology.
Medicine and Allied Specialties, Surgery & Allied Specialties, Child Health, and Obstetrics & Gynecology. |
Block postings and Internship at CMC Vellore
As per the guidelines of the National Medical Commission,
- Along with regular classes, medical students also have to undergo block postings after phase 1 of their MBBS course at community health centers, mission hospitals, and secondary care centers.
- A medical student also has to compulsorily complete the rotational internship for 12 months. They are posted in the discipline of community health, medicine, surgery, obstetrics & gynecology, orthopaedics, emergency medicine, and short elective subjects.
- At CMC, Vellore, the students are allocated community health centers, mission hospitals, and secondary care centers for internships.
Admission procedure
Admission to the MBBS undergraduate course in CMC, Vellore solely depends on the NEET-UG score. An aspirant to get admission at CMC needs to qualify and crack the NEET-UG (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) examination with a good score.
Eligibility to get admission at Christian Medical College
- Candidate must have completed 10+2 higher secondary schooling or equivalent examination, and the last two years of education must include Physics, Chemistry, and Biology/Biotechnology as major subjects with English from the Tamil Nadu State board or any other equivalent examination board.
- Candidates must have attained a minimum of 50% marks in all the subjects, Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English individually for the general category, and a minimum of 40% aggregate for BC, MBC, SC/ST candidates is required in a single attempt. The criteria mentioned are subject to change as per the state & university guidelines.
- At the time of admission, a candidate must have completed 17 years of age or should complete the mentioned on or before 31st December of the said year.
NEET-UG Exam Pattern for admission to MBBS at CMC Vellore
The NEET-UG exam is conducted by National Testing Agency (NTA) once a year. The following are some important points to keep in mind:
| Particulars | Description |
| Exam Mode | Offline (pen & paper based) |
| Type of Examination | Multiple choice questions |
| The total number of questions | 200 questions (180 MCQs must be answered) |
| NEET total marks | 720 marks |
| Marking scheme | +4 for each correct answer and -1 for every incorrect answer |
| Total duration | 3hrs 20 mins |
| Languages | The exam is conducted in 13 different languages, namely, English, Hindi, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Marathi, Odia, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, and Punjabi |
NEET Exam Section-wise Distribution:
In all 4 Subject sections, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Zoology, there are two sections, section A comprises 35 questions and section B comprises 15 questions out of which 10 are to be answered. Each question carries 4 marks.
Number of Seats for 2022-2023 at CMC, Vellore
The total number of MBBS candidate seats is 100 and the seat distribution is as follows:
- All India open category: 16 seats
a. One candidate is selected by Govt. of India under the ‘Central Pool Scheme’.
b. 20% i.e., 3 seats are reserved for the SC/ST candidates. - Minority Network Category & CMC, Vellore staff quota: 84 Seats
Steps to get admission into CMC Vellore
- Fill out the application form for an undergraduate course from the CMC, Vellore official site.
- Provide your NEET application form details.
- Submission of the receipts of the certification forms from Minority Network Organizations (if applicable).
- Apply to the Tamil Nadu Selection Committee for the counseling process in the relevant category.
- The selection is based on the NEET-UG score and candidates are required to fill the NEET-UG score and rank on the CMC, Vellore admission site.
- Submission of the Arno & rank of TN Management Quota.
- Be updated with the release of the merit list.
- Counseling by Tamil Nadu Selection Committee, DME, Chennai.
All these steps are to be done in the stipulated period as provided by the college. So, be updated.
Admission Process after Counseling at CMC, Vellore
- After the counseling procedure, the candidate is required to register for the course by paying the tuition fees and completing other formalities, and submitting original certificates.
- The admission confirmation is approved by Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University. Until the approval, admission continues to be provisional.
- After the confirmation of the MBBS admission at CMC, Vellore, a candidate needs to submit their original required documents at the university campus.
- All the candidates getting admission to CMC, Vellore need to undergo a medical fitness check-up and the admission gets confirmed only after the medical fitness clearance by the Medical Board, CMC, Vellore.
MBBS Course Fee at CMC, Vellore
The fees to be paid at the time of registration for admissions to the MBBS course at CMC, Vellore is mentioned in the table below:
| Particulars | Fees (in rupees) |
| Tuition fees | 3,000 |
| One-time College fee at Admission | 10,300 |
| Other Annual Fee | 25,105 |
| One-time payment to the University | 14,425 |
| Total | 52,830 |
*The course fee may change in the coming years depending upon the University rules and regulations.
MBBS Cut-off at CMC, Vellore
Based upon the analysis of the previous years’ cut-offs, the estimated NEET-UG cut-off marks for the MBBS course for admission at CMC, Vellore are mentioned below:
| Category | Estimated Cut off Score |
| General | 600 |
| Minority | 380 |
| Institutional/Staff | 500 |
| SC/ST | 520 |
To get the conceptual clarity on the MBBS courses online, click here.
Medical Postgraduate Courses at CMC, Vellore
In CMC, Vellore Admission to PG Degree, Diploma, PG diploma courses, and fellowship courses come under the Group B category. Admission to the MD/MS courses is done based on the NEET-PG score. All the students need to get into the NEET-PG merit list for admission to the PG courses with the required cut-off score.
PG Courses and Number of Seats
The Christian Medical College offers admission to various post-graduate specialization courses.
- The CMC Vellore provides admission to MD courses for various subjects along with the number of seats mentioned below:
| MD Specialization Courses | Number of Seats |
| Anaesthesiology | 33 |
| Anatomy | 4 |
| Biochemistry | 2 |
| Community Medicine | 6 |
| Dermatology Venerol & Lep. | 5 |
| Emergency Medicine | 3 |
| Family Medicine | 2 |
| Geriatrics | 3 |
| General Medicine | 16 |
| Microbiology | 4 |
| Nuclear Medicine | 2 |
| Pediatrics | 20 |
| Pathology | 8 |
| Pharmacology | 2 |
| Physiology | 4 |
| Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 4 |
| Psychiatry | 12 |
| Radiodiagnosis | 12 |
| Radiation Oncology | 8 |
| Respiratory Medicine | 4 |
| Transfusion Medicine | 3 |
- The CMC Vellore provides admission to MS courses for various subjects along with the number of seats mentioned below:
| MS specialization Courses | Number of Seats |
| Otorhinolaryngology | 8 |
| General Surgery | 10 |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | 17 |
| Ophthalmology | 9 |
| Orthopaedics | 12 |
Service Obligation at CMC, Vellore
- The service obligation of 3 years is mandated for all the MS/MD candidates, except for the clinical specialties (General merit category).
- Candidates admitted to the clinical specialties under the general merit category have a service obligation of 1 year.
- Candidates admitted to the pre-and para-clinical specialties under the general merit category, have no service obligation.
- For diploma courses, the service obligation period is a minimum of 2 years whereas, general merit candidates are exempted from the same.
- After the course completion, the service obligation is served at the CMC, Vellore or any of the associated mission hospitals.
Facilities available for the medical PG trainees
- Stipend
- Accommodation
- Research activity of each department
- Medical records department
- Recreation
- Staff/student health clinic
Fee Structure for the Postgraduate Medical Courses at CMC, Vellore
The fees to be paid at the time of registration for admissions to the Medical PG courses (MD/MS) at CMC are mentioned in the table below:
| Particulars | 2 yr Post Diploma Degree (in rupees) | 3 yr PG Degree (in rupees) |
| Tuition fees | 800 | 1200 |
| One-time admission fees | 1200 | 30,000 |
| University fees | 1,35,610 | 1,35,610 |
| Others | 17,600 | 19,600 |
| Total | 1,74,010 | 1,86,410 |
*The course fee may change in the coming years depending upon the University rules and regulations.
NEET-PG Cut-off Score for MS/MD admission to CMC, Vellore
Based upon the analysis of the previous years’ cut-offs, the estimated cut-off marks for the medical PG specialization courses for admission at CMC, Vellore are mentioned below:
| Specialization | Estimated Cut-off Score |
| Anesthesiology | 400 |
| Anatomy | 460 |
| Biochemistry | 430 |
| Community Medicine | 500 |
| Dip. In Clinical Pathology | 480 |
| Dermatology Venerol & Lep. | 540 |
| Emergency Medicine | 500 |
| Family Medicine | 450 |
| Geriatrics | 380 |
| General Surgery | 460 |
| General Medicine | 590 |
| Microbiology | 450 |
| Neurosurgery | 500 |
| Nuclear Medicine | 500 |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | 380 |
| Ophthalmology | 400 |
| Orthopedics | 450 |
| Pediatrics | 440 |
| Pathology | 450 |
| Pharmacology | 600 |
| Physiology | 480 |
| Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 450 |
| Psychiatry | 360 |
| Radiodiagnosis | 450 |
| Radiation Oncology | 450 |
| Respiratory Medicine | 490 |
| Transfusion Medicine | 600 |
Certificate courses after MBBS
The certificate courses offered by the CMC Vellore for the MBBS graduates are mentioned below:
| Course Name | Duration | Number of Seats |
| Accident & Emergency Medicine | 2 years | 10 |
| Neonatology | 1 year | 1 |
| Palliative Medicine | 1 year | 2 |
| Acute Care Pediatrics | 1 year | 1 |
- CMC, Vellore also provides admission to various higher specialty and Postdoctoral diploma courses and allied health sciences courses.
- After completing MBBS, a medico can also pursue M.Sc. Epidemiology and Master of Public Health Administration.
CMC, Vellore Hostel Fees and Facility
- Hostel Facility for MBBS Students: MBBS students live in the campus hostels. The Bagayam campus of the CMC, Vellore has girls’ and boys’ hostels. The girls’ hostel is named as ‘Paradise on Earth’, while the boys’ hostel is named as ‘Mansion of the Gods’. Boys are required to submit the hostel charges (Deposits and advance) of10,000/- and girls Rs.8,000/-. The approximate living expenses per month for the hostel are Rs.6,000/- for boys and girls.
- Hostel facility for other courses: The women’s hostel and men’s hostel for the students of allied health courses are named as the ‘Fitch Hostel’ and the ‘Dorothy Joske Hostel’. The ‘Modale International Hostel’ is allocated for the elective course students/visitor observer students from overseas. The hostel and its charges vary as per the student’s course.
All the hostels are well equipped with all the necessities of a student and other facilities such as a Hostel Chapel, recreation room, gymnasium, library, dance room, music room, prayer room, mini kitchen, TV/Projector room. The food facility with vegetarian and non-vegetarian food is also available for all the residents.
How does DigiNerve help a medico?
DigiNerve is an EdTech initiative by Jaypee Brothers, a pioneer and market leader in health science publishing with a legacy spanning over 5 decades. It provides top-notch medical content to enhance conceptual clarity, clinical skills, and ace exams.
In terms of the calibre of the courses, the variety of subjects, the Gold Standard faculty, and the user-friendly interface, DigiNerve is unmatched.
- DigiNerve provides best online courses for MBBS subjects designed by eminent faculty as per CBME Curriculum and NEET Exam, such as
| MBBS Online Courses | Course Faculty |
| Community Medicine for UnderGrads | Dr. Bratati Banerjee |
| Forensics Medicine and Toxicology for UnderGrads | Dr. Gautam Biswas |
| Medicine for UnderGrads | Dr. Archith Boloor |
| Microbiology for UnderGrads | Dr. Apurba S Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat, Dr. Deepashree R |
| OBGYN for UnderGrads | Dr. K Srinivas |
| Ophthalmology for UnderGrads | Dr. Parul Ichhpujani, Dr. Talvir Sidhu |
| Orthopaedics for UnderGrads | Dr. Vivek Pandey |
| Pathology for UnderGrads | Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak, Dr. Debasis Gochhait |
| Pediatrics for UnderGrads | Dr. Santoah T Soans, Dr. Soundarya Mahalingam |
| Pharmacology for UnderGrads | Dr Sandeep Kaushal, Dr. Nirmal George |
| Surgery for UnderGrads | Dr. Sriram Bhat M |
- Apart from the MBBS and MD courses, DigiNerve brings the professional courses ‘Ultrasound in OBGYN Made Easy’ and ‘Basics of Infertility and IUI Made Easy’ by the top faculty Dr. Chaitanya Nagori and Dr. Sonal Panchal. After completion of the course, the candidates will earn a course completion certificate from Ian Donald Inter-University School of Medical Ultrasound.
- An Exam preparation course ‘Cracking MRCP Part 1’ by Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander and Dr. Archith Boloor, helps a medico with their preparation to crack the MRCP exam. Cracking MRCP Part 1 course is based on the curriculum devised by The Royal College of Physicians (RCP). The course has 15 online modules covering major specialties such as Clinical Sciences, Cardiology, Gastroenterology, etc. The course includes video lectures, e-chapters, 2500+ BOF questions, mock exams, and most of all high-quality notes.
FAQs
-
How many marks are required in NEET for MBBS in CMC Vellore?
Ans: The estimated cut off score for admission to CMC, Vellore is around 600+ in the NEET Examination for general category. For the OBC/SC/ST & Minority groups, the estimated cut-off score is around 500 marks. For sponsored & management quota students, the cut-off range is comparatively lower.
-
Is CMC Vellore a deemed university?
Ans: No, CMC Vellore is not a deemed University. It is a private college, affiliated with Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University, Chennai run by the Christian community.
-
Is CMC good for MBBS?
Ans: CMC Vellore is ranked 3rd as per NIRF ranking 2022 after AIIMS, Delhi, and PGIMER, Chandigarh. It is one of the best medical colleges in India.
Gynecology and obstetrics both focus on the female reproductive system. Gynecology deals with non-pregnant women whereas Obstetrics deals with pregnancy and the procedures and issues that go along with it, thus obstetrics deals with both the mother and the infant. To lower the risk of newborn disease and mortality, obstetricians closely collaborate with pediatricians and neonatologists on newborn care. They also remove cancers, fibroids, etc, surgically, although many gynecological problems require hormonal and other pharmacological therapy too.
What an obstetrician does:
The duties obstetricians carry out consist of:
- Obstetricians are in charge of collaborating with midwives to monitor and support a woman’s natural birth while she is in labor.
- One of their roles is to execute an episiotomy, which entails making precise cuts over the pregnant woman’s perineum to widen the birth canal.
- In some cases, assistance may be required to hasten protracted delivery to lessen maternal exhaustion and infant suffering (rising heart rate and possible brain damage to the baby). This makes use of methods like vacuum-assisted birth and forceps delivery.
- Caesarean (or C) section, calls for the baby to be surgically removed from the mother’s womb to lessen difficulties during labor. If a C-section is not used to hurry the delivery, difficulties could ultimately result in the baby’s death or physical harm.
- Therapy and diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. When the fertilized ovum is implanted somewhere other than the womb, it results in an ectopic pregnancy. It frequently ends up in the fallopian tubes.
What a gynecologist does:
Gynecologists employ a variety of diagnostic and curative techniques. The following are a few of the common gynecological procedures:
- Hysterectomy or uterus removal
- Removing ovaries
- Fallopian tubes are removed during surgery
- Hysteroscopy and colposcopy involve employing tools like endoscopes to inspect the uterus’ inside.
- Taking care of uterine fibroids
- Identifying and treating sexually transmitted diseases
- Diagnosing menstrual issues, such as absence, severe bleeding, irregular or no periods, etc.
- Examination of the reproductive organs with ultrasound.
Objectives of Learning OBGYN
The Obstetrics and Gynecology Department offers modern, comprehensive screening and therapeutic techniques in a sympathetic environment for women in all stages of life.
In addition to regular gynecology procedures and medical treatments, a dedicated team provides cutting-edge motherhood facilities for routine and high-risk pregnancies, post-delivery and family planning services, sterility screening and handling, and all endoscopic gynecological operations.
Moreover, the department addresses high-risk pregnancies using prenatal diagnostic tests such as infant color doppler, amniocentesis, and velocimetry investigations. It also includes colposcopy, pap smear, and HPV-CO testing for going through menopausal women for cancer screening.
Aspirants can get a variety of profitable jobs in India and overseas by enrolling in this course. You can pursue additional education, such as research studies at prestigious universities and research institutions. Medical specialties like gynecology, cancer, critical care, reproductive endocrinology, or maternal-fetal medicine are all open to you as a career option. In India, postgraduate training in obstetrics and gynecology is either a three-year master’s program or a two-year diploma program. You can pursue a sub-specialty training program in fellowships after finishing your residency training.
OBGYN in MBBS
In their fourth year of MBBS, undergraduate students who are studying OBGYN participate in case discussions in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. A medico must also do a one-month OBGYN internship in addition to this. They receive instruction in the labor room, family planning OPD and OT, and obstetrics and gynecology OPD’s wards and OTs throughout their internship.
PG in OBGYN
A three-year, full-time postgraduate programme in OBGYN aims at training students to provide care to each patient, both pregnant and non-pregnant, as well as a thorough superior assessment of the entire medical pathology associated with the female reproductive organs.
Students learn about the most recent society standards, benchmark studies, breakthroughs in PCOS, robotic surgery, and conducting clinical examinations in OBGYN MD course. In the specialty clinics, OPD, wards, labour rooms, and operating rooms, they perform the necessary tests, interpret the results, and carry out medical/surgical management. They are taught to assess pregnancy-related issues using medical skills, find solutions, and provide pertinent prognoses.
Watch this video to learn the right way to approach OBGYN MD
Ph.D. Scholars of OBGYN
Every Ph.D. candidate has the privilege of choosing their specialty area from a list that includes fetal development and growth, hereditary and genomics, gestational diabetes, parental hepatitis, preeclampsia, prenatal analysis, and screening. Additionally, topics like urogynecology, endometriosis, endometrium, and establishment, prenatal cancer, and genital level are also discussed.
List of Top 10 Colleges for OBGYN in India
Here is the most recent list of top obstetrics and gynecology colleges in India that have earned official NMC recognition. These universities have the highest rankings and are even regarded as the most reputable universities in India
| S.No. | Name of College | Affiliation |
| 1 | Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi | Delhi University |
| 2 | Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore | Manipal Academy of Higher Education (Deemed University), Manipal |
| 3 | Jawaharlal Institute Of Postgraduate Medical Education And Research (JIPMER), Pondicherry | Pondicherry University |
| 4 | Christian Medical College, Vellore | The Tamilnadu Dr. MGR Medical University, Chennai |
| 5 | Institute of Medical Sciences, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh | Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi |
| 6 | Kasturba Medical College, Manipal | Manipal Academy of Higher Education (Deemed University), Manipal |
| 7 | Christian Medical College, Ludhiana | Baba Farid University of Health Sciences, Faridkot |
| 8 | Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai | Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education & Research (Deemed to be University), Chennai |
| 9 | SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Kancheepuram | SRM Institute of Science & Technology, Chennai |
| 10 | Dr. DY Patil Medical College Pune | Dr. D Y Patil University (Deemed), Pimpri, Pune |
Top OBGYN course online for best guidance for NEET Exam preparation
There is a great opportunity in the medical sector, particularly for OBGYNs, as the need for healthcare professionals is on the rise. Below are a few reasons why you should consider pursuing a career in OBGYN.
- Rising demand for OBGYNs
The need for female OB/GYNs has grown dramatically over the past few years, despite the perception that the health care industry is dominated by men. Today, more women than ever before are asking to consult a female specialist. Talking to other women comes more easily to women, especially when discussing sexual or pregnancy difficulties. Additionally, since more than 70% of residents are now women, supply and demand favor female OBGYNs.
- Great Earnings
The field of Obstetrics and Gynecology holds a bright future and is one of the most prestigious. Gynecology is currently one of the most lucrative medical professions. It is possible to work in government organizations, clinics, private practices, and universities, as well as in the most prestigious hospitals in India. Additionally, the candidate could open a surgical clinic. Obstetrician/Gynecologist salary in India ranges from ₹10 Lakhs to ₹ 36 Lakhs. Salary estimates are based on 199 salaries received from Gynecologists, particularly from a large hospital network.
- Fulfillment at work
One of the reasons people have named OBGYN as the most fulfilling profession in the healthcare industry is because bringing new life into this world is indeed a great sight to behold. As an OBGYN, you’ll have the opportunity to be regularly involved in childbirth and assist new mothers in making decisions that will impact the health of the infant.Only a few OBGYNs specialize in high-risk pregnancies. Patients with preterm births, a history of miscarriages, or antenatal problems that could complicate childbirth are cared for by these specialists. You’ll also have the ability as an OBGYN to advance the industry by developing novel techniques and procedures that may one day be considered best practices.
- Jobs & Career
- Salary
Pharmacology is the study of the interaction of drugs with biological systems. This includes research on the chemical makeup, biological processes, physiological and behavioral impacts, mechanisms of action, and both therapeutic and non-therapeutic applications of pharmaceuticals.
Pharmacology is broadly categorized into two terms:
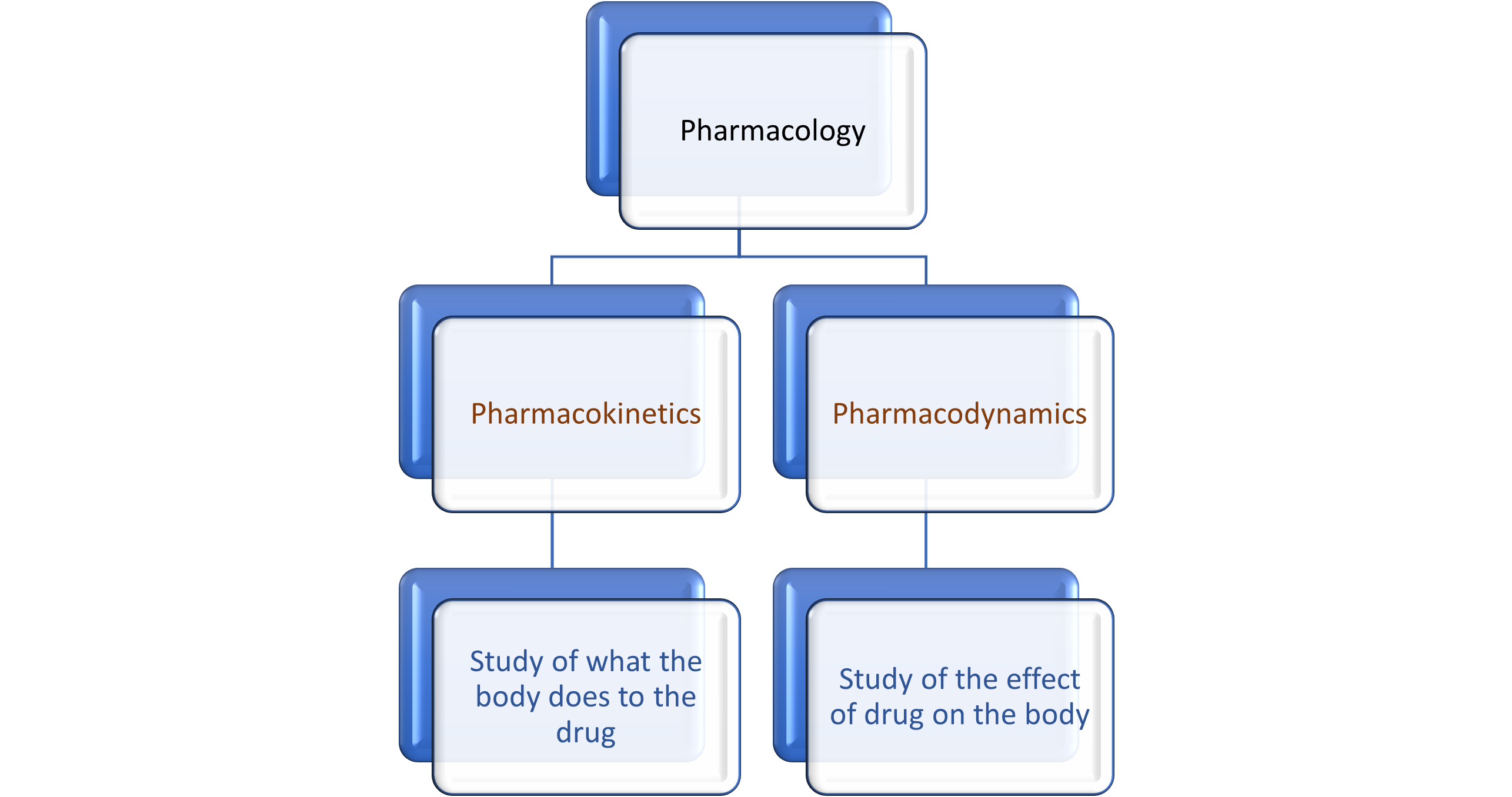

PHARMACOKINETICS IN PHARMACOLOGY
The term ‘Pharmacokinetics’ is derived from ancient Greek words, pharmakon meaning ‘drug’ and kinetikos meaning ‘moving’ or put in motion. Pharmacokinetics is a journey of a drug through the body, and in this, a drug passes through four different phases- Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion, which are called ADME properties.
The selection and modification of drug-dose schedules are aided by pharmacokinetic parameters.
Let’s discuss the pharmacokinetic parameters:
- ABSORPTION:
Absorption is the movement of a drug to the site of action from the site of administration. Various factors affect the extent and rate of absorption of the drug, such as routes of drug administration, dosage form, physiochemical properties of the drug, bioavailability, pharmacogenetic factors, etc.
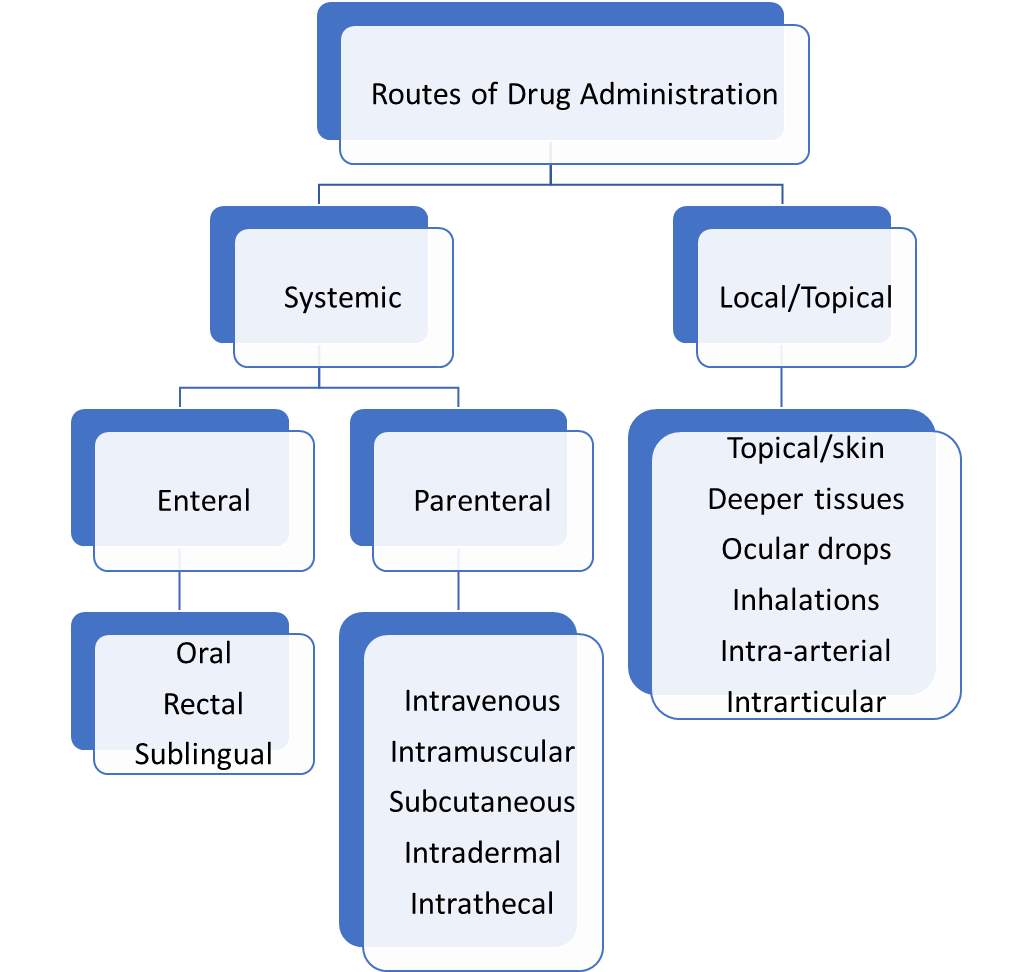

First Pass Metabolism: It is a phenomenon in which a drug is metabolized or transformed at a specific site before the drug reaches its site of action or systemic circulation, resulting in a lower concentration of the active substance. Examples of the drugs that undergo this phenomenon in the liver are propranolol, lidocaine, and clomethiazole; in the gut wall are sex hormones.
In the case of intravenous or intra-arterial administration, the drug bypasses the first pass metabolism and enters the circulation directly.
Watch this free video of one of the best online pharmacology courses in MBBS
Drug distribution is the process by which a drug travels from the administered site after absorption via the blood vessel walls to the sites of action.
The drug is distributed via various body fluid compartments, such as plasma, interstitial fluid compartments, and trans-cellular compartments.
Factors affecting the distribution rate of the drug:
- Protein binding of drug
- Plasma concentration of drug (Cp)
- Clearance
- Physiological barriers to distribution
- Drug affinity of drugs to certain tissues
3. METABOLISM:
Drug metabolism, also known as biotransformation, is the process by which the body metabolizes drug molecules. The principal site of drug metabolism is the liver.
Enzymes responsible for drug metabolism are classified into two categories:
- Microsomal enzymes: They are present in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of the liver, kidney, and GIT. Example: cytochrome P450.
- Non-microsomal enzymes: They are present in the cytoplasm, and mitochondria of different organs. Examples: esterase, amidase, and hydrolase.
Two Phases of Metabolism: Phase I metabolism converts a parent drug to polar active metabolites, via., oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis reactions, while phase II metabolism converts a parent drug to polar inactive metabolites including conjugation reactions.
Watch this video of Pharmacology for UnderGrads and gain an in-depth understanding of Pharmacology in MBBS.
Drug excretion refers to the removal of drugs in unchanged or modified form out of the body.
The major route of excretion:
- Renal excretion: It involves three major physiological processes, namely, glomerular filtration, active tubular secretion, and passive tubular reabsorption.
- Hepatobiliary excretion: The drug with a molecular weight of more than 300 Da and polar drugs are excreted in the bile.
- Gastrointestinal excretion: After the oral administration of a drug, a part of it is not absorbed and excreted in the feces.
- Pulmonary excretion: Volatile drugs, such as gaseous anesthetics, are excreted via the lungs into expired air.
Saliva, sweat, tears, breast milk, vaginal fluid, nails, and hair are considered the minor routes of drug excretion.
VARIOUS PHARMACOKINETIC PARAMETERS:
- Half-life: It is the time taken for the drug concentration in blood or plasma to reduce to half of the original amount, i.e. the amount of the drug in the body is reduced by 50%. A drug’s half-life varies from patient to patient because of a variety of patient and drug-specific factors.
The formula for the half-life is t½ = 0.693 × Vd /CL where,
Vd is the volume of distribution and CL is a clearance factor.
2. Order of Kinetics: For many medications, the most typical is First order kinetics, meaning that a fixed proportion of the drug is eliminated from the body at regular intervals of time. Only a few medications, like ethanol and phenytoin, undergo zero order kinetics wherein, a fixed quantity of the medicine is eliminated after each period.
3. Clearance of a Drug: It is the volume of plasma cleared or removed out of the drug by hepatic and/or renal excretion, among other organs.
Clearance = Rate of Elimination
Plasma drug concentration
And, Total clearance is calculated by Clt = Clh + Clr + Clothers where,
Clt = Total clearance
Clh = Hepatic clearance
Clr = Renal clearance
Clother = Clearance from all other routes
4. Steady-state plasma concentration: When a drug dose is administered regularly over a certain time, a steady state is reached. It is a point where the amount of medication absorbed and the amount removed from the body is in equilibrium. For instance, a medication that has a half-life of 6 hours will likely reach a steady state after being administered for more than 24 hours (More than 4 half-life).
To access online pharmacokinetics lecture notes, download the DigiNerve app.
Dr. Sandeep Kaushal
MD, MAMS, FCP(ACCP), FIMSA, MBPhS, ACME
Dean Academics, Professor, and Head,
Department of Pharmacology,
Dayanand Medical College and Hospital,
Ludhiana, Punjab
Pharmacology is the scientific study of the effects of drugs on living organisms. A drug is any chemical substance, natural or synthetic, that affects a biological system. Pharmacology may include studying how organisms process drugs, identifying and validating new targets for drug action, and designing and developing new drugs to prevent, treat, and cure disease. Pharmacology research is also an important part of the advancement of modern personalised medicine.
This industry provides numerous job opportunities, with pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers among the largest employers. Knowing the various career paths available to you if you have a pharmacology degree is very important. A pharmacology degree allows you to work in a variety of pharmacology degree jobs. In this article, we will look at pharmacology degree jobs, their average salaries, and primary responsibilities which will help you decide on your career in Pharmacology after pursuing your graduation.
- Pharmacist
The average base salary of a Pharmacist is ₹2,80,742 per year. If you have a pharmacology degree, you can work in a variety of pharmacology departments. A pharmacist’s job is to provide medication and treatment information. They may write prescriptions, respond to questions about drug interactions or side effects, and advise patients on dosages. Pharmacists typically work in community pharmacies or hospitals, and they may conduct drug or treatment research.
Learn the Tips and Tricks to learn Pharmacology
- Pharmacy Operations Manager
The average base salary of a Pharmacy Operations Manager is ₹ 4,37,289 per year. They are in charge of the day-to-day operations of a pharmacy department. They typically collaborate with medical professionals to meet the pharmaceutical needs of patients. They monitor inventory levels ensuring compliance with federal policies and keeping accurate records. They also supervise pharmacy employees.
- Pharmacologist
The average base salary of a Pharmacologist is ₹ 4,91,318 per year. A pharmacologist is in charge of scientific research, drug development, and evaluation. They perform laboratory testing to determine the overall safety and efficacy of medications. They also decide on dosage safety, including administration, age, and amount.
- Clinical Research Associate
The average base salary of a Clinical Research Associate is ₹ 3,29,875 per year. A clinical research associate is in charge of clinical research and trials. They frequently create testing procedures, select and set up trial sites, and monitor tests. They present protocols to ethics committees and write reports on each trial’s results. They ensure strict data collection and participation.
- Pharmaceutical Scientist
The average base salary of a Pharmaceutical Scientist is ₹ 7,03,365 per year. A pharmaceutical scientist conducts drug research and development in laboratory experiments. They study biological processes and evaluate the efficacy of new drugs in counteracting, correcting, or slowing harmful biological activity. They establish testing procedures to assess the short and long-term biological effects and interactions of pharmaceutical compounds. They also develop new approaches to existing medical problems and assist drug developers in other ways.
- Pharmaceutical Consultant
The average base salary of a Pharmaceutical Consultant is ₹5,04,206 per year. They assist pharmaceutical companies in becoming more efficient and providing better products to their customers. They assist clients by identifying operational problems, eliminating waste, and suggesting solutions, such as new technologies, like a business or management consultant who specialises in pharmaceuticals. A pharmaceutical consultant may assist with project management, cost forecasting, and recommending plans, such as clients and distribution methods. They also aid in the development of compliance policies.
- Quality Control Chemist
The average base salary of a Quality Control Chemist is ₹2,29,103 per year. A quality control chemist is in charge of ensuring that drugs and other formulations meet the established safety standards. They inspect raw materials and finished products for quality, test new ingredients, and help with product development. They conduct experiments to determine whether a drug is safe for use with their knowledge of chemistry, biology, and mathematics.
Watch this video lecture on NSAIDs – Anti-gout drug
- Environmental Monitor
The average base salary of an Environmental Monitor is ₹7,89,873 per year. An environmental monitor assesses the chemical and physical properties of environmental conditions, such as water or soil samples. They conduct research to identify sources of pollution in the environment. They may also review and update company policies and operating procedures for compliance with local and federal regulations.
- Regulatory Affairs Specialist
The average base salary of a Regulatory Affairs Specialist is ₹5,74,873 per year. They manage regulatory submissions to government agencies. They prepare applications and supporting documentation, as well as monitor FDA regulations governing clinical trials and product development. They keep in touch with government officials and may attend regulatory hearings or product approvals.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Technician
The average base salary of a Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Technician is ₹3,00,00 per year. A pharmaceutical manufacturing technician collaborates with other members of a team to create pharmaceutical products. They assist in the development of new products while adhering to proper safety and quality standards. They may also be in charge of the lab’s equipment and inventory.
- Medical Writer
The average base salary of a Medical Writer is ₹5,33,434 per year. A medical writer creates articles and reports that explain how to use pharmaceutical products for medical purposes. They typically collaborate with doctors, patients, or researchers to collect information for drug trials or treatment protocols. They also contribute to the creation of patient leaflets that contain information about each pharmaceutical, such as indications, descriptions, proper usage, methods of ingestion or application, and potential side effects or warnings.
- Lab Manager
The average base salary of a Lab Manager is ₹5,13,023 per year. A lab manager is in charge of seeing laboratory processes and staff activities. They help scientists, technicians, and medical professionals by providing lab support, adhering to safety protocols, and maintaining lab equipment. A lab manager organises a laboratory’s daily activities in order to maximise productivity.
- Pharmaceutical Sales Representative
The average base salary of a Pharmaceutical Sales Representative is ₹2,98,254 per year. They counsel physicians on the advantages of various pharmaceutical products for their patients. They research the competitive landscape of various pharmaceutical markets in order to promote their company’s products. A pharmaceutical sales representative may also monitor doctors’ prescribing habits and assist in the development of marketing strategies.
- Medical Writing Manager
The average base salary of a Medical Writing Manager is ₹13,91,567 per year. Medical writers who create promotional materials for new drugs and treatments are overseen by a medical writing manager. They may create press releases, blog posts, or other content to educate patients and the media about medical advances. They consult with clients directly to determine the scope of research reports.
- Analytical Chemist
The average base salary of an Analytical Chemist is ₹3,95,467 per year. An analytical chemist performs experiments to determine and analyse the chemical structure of various compounds. They are in charge of testing pharmaceutical products such as new drug formulations or over-the-counter medications. They frequently work in groups with other chemists and technicians.
Watch this video to learn about β Lactam Antibiotics–Cephalosporins, Carbopenems & Monobactam
- Medical Science Liaison
The average base salary of a Medical Science Liaison is ₹8,45,000 per year. A medical science liaison communicates drug and medical treatment information to physicians, patients, and the general public. They may collaborate with scientific teams, regulatory agencies, and pharmaceutical companies to provide clients with information about new products or clinical study results. They may also help with the recruitment of test participants for studies.
- Laboratory Technician
The average base salary of a Laboratory Technician is ₹2,48,718 per year. A laboratory technician provides clinical and basic research assistance to a laboratory scientist or physician. They prepare samples for analysis, monitor processes, and assess drug levels in blood tests. A laboratory technician may administer medication to animals in the lab to test for results and side effects, as well as perform tests to identify drug interactions, under the supervision of a medical professional.
- Microbiology Technician
The average base salary of a Microbiology Technician is ₹3,06,000 per year. A microbiology technician performs tests to identify pathogenic microorganisms and monitor the levels of bacteria in food and water. They help doctors by identifying different disease-causing microbes or the source of infection. They may also contribute to the development of new drugs and treatments by studying how microorganisms interact with different chemicals.
- Clinical Research Coordinator
The average base salary of a Clinical Research Coordinator is ₹2,51,331 per year. A clinical research coordinator collaborates with other members of a team to plan and manage clinical trials. They communicate with medical professionals and insurance companies to obtain approval for each study and to keep patient records for the duration of the study. They may also travel or work outside of business hours, depending on the study’s schedule and needs.
In conclusion, Pharmacology is one of the fastest growing sectors in the healthcare industry, and it is important to the sector’s sustenance. An Undergrad degree or a Postgrad degree or a Ph.D. degree in Pharmacology increases employment opportunities, career scope, and prospects. The advancement of science and technology has increased our understanding of diseases, their causes, and potential treatments, making pharmacology a discipline rich in potential and fraught with challenges. This industry will almost certainly continue to expand.
DigiNerve’s Pharmacology for UnderGrads
Learn pharmacology online by preparing with pharmacology online courses which are available vastly. All you need to do is research the best online pharmacology courses like Pharmacology for UnderGrads, in which modules are aligned with the standard pharmacology textbook, allowing students to take a systematic approach. The course clarifies fundamental concepts and keeps students up to date on the most recent advances.
Watch this to know more about the course and learn the right way to approach Pharmacology
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1 What can you do with a Pharmacology Degree?
Those who are interested in biology and chemistry may find a rewarding career in pharmacology. If you want to work in the pharmaceutical industry, learning more about the jobs available with a pharmacology degree can be helpful. In this article, we define pharmacology degrees, describe the courses they include, discuss the jobs you can get with one, and discuss the skills you can learn in pharmacology programmes.
Q.2 What does a pharmacology degree include?
Pharmacology programmes teach scientific concepts as well as practical pharmacology applications. Courses can vary in difficulty and progression depending on the level of degree and specific school. A pharmacology degree curriculum may include the following courses:
- Research Conduction
- Fundamentals of pharmacology
- Cell signaling and receptors
- Biomedical science
- Reproducibility in pharmaceuticals
- Biomedical statistics
- Bimolecular basics
- Protein chemistry
- Immunology
- Drug development
- Virology and pathogenesis
- Neuropharmacology
- Experimental treatments
- Endocrine pharmacology
- Drug metabolism
Q.3 What skills can you develop with a pharmacology degree?
Students in pharmacology programmes are prepared for successful careers in the pharmaceutical industry. A pharmacology degree can help them develop the following skills:
- Research skills
Research skills enable pharmacists to gather information and find solutions to problems. Note-taking, time management, communication, and problem-solving are examples of research skills.
- Attention to detail
The ability to pay attention to detail allows you to review materials with precision and accuracy while noticing minor details. This is a valuable skill that you can hone in a pharmacology programme by carrying out experiments and noting minor details during trials.
- Critical thinking
The ability to assess a situation, gather important information, identify problems, and offer workable solutions is referred to as critical thinking. Students in pharmacology learn to develop their critical thinking skills by completing exercises and collaborating with their peers to solve problems.
Pharmacology is the study of how medicines interact with biological systems. Research into medicines’ chemical make-up, biological functions, effects on physiology and behavior, mechanisms of action, and both therapeutic and non-therapeutic applications are all covered in this and are part of the 2nd year curriculum of MBBS. Since the treatment of patients requires medicines, knowledge regarding the subject is not going to hurt you, and the more knowledge you have, the better your treatments would be. Pharmacology in MBBS is often considered a volatile subject and a subject that has to be mugged up. This is not the case! Pharmacology is a beautiful subject, and it can be understood without mugging up, and there are quintillion applications for you in the future with the knowledge you acquire in Pharmacology. In this write-up, I would be telling you the various tips and tricks I personally have used and succeeded in learning and understanding Pharmacology. So let’s dive right into it.
Things to focus
The most important thing to address in any given topic in Pharmacology would be to understand
- What to study?
- How to study?
- How to memorize?
- What to write in the examination?
The first question
What to study?
This is a very important and relevant question that you need to understand. Let’s take the chapter on diabetes mellitus to make this idea clear.
Step 1: Understand normal physiology
The β-cells of the pancreas secrete insulin. Insulin stimulates the movement of glucose from the plasma into the skeletal muscles & adipose tissues. This will cause a reduction in plasma glucose.
Step 2: Disease pathophysiology
In Diabetes Mellitus pancreas is producing less amounts of insulin or the pancreas is producing normal amounts of insulin but insulin is not able to produce its action properly due to some defect in the insulin receptors. Both these will cause an increase in plasma glucose. This will result in hyperglycemia. Since the person is not able to utilize glucose he will be always hungry (polyphagia) since his body is interpreting that the body is not getting glucose because the person is not taking glucose. The higher levels of plasma glucose will be filtered by the kidneys and excreted in the urine. Glucose will draw water along with it which will result in urination (polyuria) and due to excessive loss of water, it will cause the person to be thirsty (polydipsia).
Step 3: Classify the drug classes depending upon the mechanism of action
In diabetes mellitus, the plasma glucose is elevated. The agents used for the management of DM would reduce plasma glucose. If there is a deficiency of insulin, we need to supplement insulin as in the case with type I DM (where there is reduced insulin secretion). Where the action of insulin is improper, we can use agents that will reduce plasma glucose. These agents act mainly by four mechanisms.
Group 1: Agents that increase the insulin secretion
Group 2: Agents that increase the action of insulin
Group 3: Agents that reduce the reabsorption of glucose from the kidney
Group 4: Agents that inhibit the gastrointestinal absorption of glucose
The action of drugs via these mechanisms will result in a reduction of plasma glucose.
Step 4: Individual groups of drugs
For explanation purposes, let’s discuss the agents that increase insulin secretion. These agents are classified as
- Sulfonylurea
- Meglitinide analogues
- GLP-1 agonists
- DPP-4 inhibitors
It becomes impossible to learn all the drugs named in your textbooks, so the easiest way to learn is to learn about groups of drugs and their common properties. Each group would have a prefix or a suffix with the base word.
For example, Sulfonylurea has the prefix ‘Gli’
- Glipizide
- Gliclazide
- Glibenclamide
- Glimepiride
Another example would be DPP-4 inhibitors which have the suffix ‘gliptin’.
- Sitagliptin
- Vildagliptin
This helps to remember a lot of names and classes of the drugs.
Step 5: Specific mechanism of action of the group of drugs
Let’s take the example of sulfonyl urea. As we know now that sulfonyl urea increases insulin secretion. Now we need to know the mechanism of action in depth. Normally the β-cells of the pancreas have K+ channels which move potassium from the intracellular to the extracellular. This results in the hyperpolarization of these cells. Sulfonyl urea blocks these K+ channels resulting in the depolarization of β-cells which cause insulin secretion.
Step 6: Understanding the peculiar pharmacokinetic properties of the drugs
Route of administration is one thing to consider. Oral bioavailability (very low or very high oral bioavailability), plasma protein binding (low or high protein binding), metabolizing enzymes (whether there are any potential interactions), and the predominant elimination method.
Step 7: Uses of the drug
First, write the primary use of the drug against disease, and then the secondary use related to the topic. Sulfonyl urea is only used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Step 8: Adverse effects
There is a practice of writing nausea and vomiting as adverse drug reactions for every drug, This will not fetch you any marks. Be very specific while mentioning the adverse effects of the drug. E.g. Since sulfonyl urea increases insulin secretion, sulfonyl urea can cause hypoglycemia as an adverse effect. Since insulin is an anabolic hormone, an increase in insulin secretion will result in weight gain.
Step 9: Interactions if any
Learn the therapeutically significant interactions. E.g., Sulfonyl urea increase insulin secretion, and the use of sulfonyl urea with insulin can cause hypoglycemia.
Step 10: Lastly, write down the Contraindications, if any
This is not applicable to all the drugs but write wherever required. This is must-know information for the effective treatment of any disease or illness. For example, Sulfa urea groups will cause hypersensitivity reactions in people who are already allergic/sensitive to drugs containing sulfa groups.
How to study Pharmacology?
Here are some tips and tricks to study pharmacology for MBBS in the easiest way,
- Consistency is the key to learning: No matter how many hours you study before the exam, unless you are regular in understanding & revising your concepts, you cannot ace any exam. Shortcuts and voracious reading at the end of exams can help you only a little bit. Be consistent.
- Focus on ‘must know’ topics: Always keep your prime focus on the ‘must know’ topics and learn and memorize them regularly to have a better understanding of the subject.
- Use Mnemonics and memory tricks for Pharmacology: Make your own mnemonics so that you can easily relate and memorize them for a longer time. For instance, for memorizing the adverse effects of sulfonyl urea, you can use the mnemonic “Hari has gained some weight”, in this sentence, H indicates Hypoglycaemia and weight gain would be the next important adverse effect.
- Make notes: The pharmacology subject has more content to learn and memorize and so is easy to forget. To solve this problem, make your own notes so that it helps in the revision of the topic and future reading as well. Taking notes during the lecture also helps a lot in learning and identifying key areas of the topic.
- Use flow charts, diagrams & tables: Flowcharts and diagrams are a very convenient and informative way of memorizing pharmacology. It helps to remember the core concepts, especially the mechanism of action of the drugs, normal physiology, pathophysiology of the disease, etc.
- Conceptual clarity: There is a lot to memorize in pharmacology, so don’t cram the lengthy textbooks, rather, focus on clearing the concepts, gaining in-depth knowledge of the topic by studying regularly in a proper manner, and asking doubts.
- Study sequentially: Understand the normal physiology and pathophysiology of the disease first before going into details of drugs. This will help you have a clear understanding of the topic.
How to memorize Pharmacology?
This is a frequently asked question, there is no shortcut to memorizing pharmacology but with repeated reading. Effective learning and conceptual clarity are a must to memorize pharmacology.
What to write in the Examination?
Write the answers in an orderly fashion highlighting the specific points in arranged format depending upon the question. Imagine this question in your examination, sulfonyl urea?
Your complete answer should include the following headings
- A brief introduction to diabetes mellitus
- Mechanism of action, in the case of sulfonyl urea, increases insulin secretion (a general mechanism) and sulfonyl urea inhibits the potassium channels in the β-cells of the pancreas thereby causing depolarization and release of insulin (a specific mechanism)
- Any peculiar pharmacokinetic properties
- Uses (Primary and then secondary both and more focus on the primary uses will fetch more marks)
- Specific adverse effects (don’t just mention nausea and vomiting always, BE SPECIFIC)
- Mention therapeutically significant interactions.
- Don’t forget to mention the precautions and contraindications, if any.
To learn the conceptual clarity in Pharmacology online, subscribe to CBME & NEET-oriented Pharmacology for UnderGrads course.
Dr. Nirmal George
MBBS, MD
Associate Professor
Sree Gokulam Medical College & Research Foundation (SGMC&RF),
Trivandrum, Kerala
Microbiologist: A scientist who researches microscopic life processes and life forms is known as a microbiologist. This includes researching the development, relationships, and characteristics of microscopic creatures like bacteria, algae, fungi, several kinds of parasites, and their hosts. Microbiology is used in many aspects of daily life, including food production, biodegradation, the production of commercial goods, and genetic engineering.
In private biotechnology firms and higher education, most microbiologists focus on a particular area of microbiology, such as bacteriology, parasitology, virology, or immunology. Thus, the goal of microbiology is to increase our fundamental understanding of microbes through the investigation of their morphology, metabolism, physiology, reproduction, and genetics. It’s possible that in the next few years, microbiology may be used in a variety of other ways that will be extremely advantageous to humanity in every way. To comprehend these organisms’ traits and identify them, microbiologists concentrate on their identification and growth. This is done with the overarching goal of preventing, identifying, and treating infectious diseases.
Work done by Microbiologists: Microbiologists in India work on a variety of projects that improve our quality of life, including monitoring the impact of microbes on climate change, inventing green technology, guaranteeing the safety of our food, and treating and preventing disease. Microbiologists research microorganisms like viruses, algae, bacteria, fungi, and a few sorts of parasites. They attempt to understand how these creatures live, develop, and interface with their surroundings. Most microbiologists work in research groups with different researchers and experts. By understanding microorganisms, microbiologists hope to provide answers to many significant global questions.
Watch the video to learn Major Healthcare-associated Infection
A wide range of professions in the industry (marketing, technical support, and regulatory affairs), education (teaching, museums, and scientific institutions), business (patent attorney or accountant), and communications (public relations, journalism, and publishing) are also open to microbiologists. The National Health Service organizations, the pharmaceutical and water sectors, as well as forensic science laboratories, employ the majority of those who work in hospitals, laboratories, and offices. The field of microbiology is wide and has connections to biochemistry and immunology, among other biological sciences.
• Healthcare microbiologists
Microbes can be helpful in both health and sickness since they are employed to create novel treatments that aid in the treatment of illnesses and diseases. Microbiologists must first understand how microbes function to tackle microbe-related issues and take advantage of their talents. They can then apply this knowledge to create new technologies, treat or prevent disease, and generally enhance our quality of life. To treat diseases, microbiologists are crucial. Many doctors and scientists work in medical facilities and labs, examining body fluids, blood, and human tissue to diagnose infections, track the efficiency of therapies, or detect disease outbreaks. In hospitals, universities, and medical school labs, some microbiologists hold clinical scientist positions where they conduct research and offer medical staff scientific guidance. To produce vaccines and enhance existing therapies, other microbiologists focus on bacteria that cause diseases like the flu or tuberculosis.
• Climate change and the environment
The carbon and nitrogen cycle are both critical to the functioning of the planet’s nutrition cycles and depend on bacteria. Some microbiologists’ research shows how microorganisms coexist with other animals in a variety of environments, including the ocean, salt lakes, and polar regions. Additionally, engineers and technologists collaborate with microbiologists to create cleaner energy sources derived from municipal and industrial waste.
• Food Availability and Agriculture
Millions of bacteria help us absorb nutrients from food and fight off harmful germs in our stomachs to keep us healthy. Microbiologists study how important soil bacteria are. Some focus on controlling plant diseases and pests, while others use microorganisms to manage weeds and insect pests. Others conduct studies on the microorganisms that afflict farm animals. Microbiologists are employed by numerous bioscience and food industries where they conduct research and create new goods.
Education:
The key steps to becoming a microbiologist after passing class 12th board exams are mentioned below:
• UG Preparation: Candidates can complete MBBS with Microbiology for UnderGrads including biochemistry or cell biology. The candidate should complete foundational courses in computer science, arithmetic, statistics, physics, microbial genetics, environmental microbiology, virology, and biochemistry. Candidates can also pursue B.Sc. with Microbiology. The candidates should be knowledgeable in lab sessions to pursue a career in microbiology in India. By enrolling in preparation classes, applicants should also start their PG admission preparation.
• PG Preparation: After finishing the UG course, the candidate can select to concentrate on PG courses that would work on the possibility of their vocation. M.Sc. in Microbiology can be sought after by the up-and-comers after the culmination of a B.Sc.
After getting your degree you also need to:
• Get some work experience: You might need to concentrate on acquiring work experience concurrently with or after your study. The study of microbiology offers opportunities for both intellectual involvement and practical application. You can apply for internships early on to acquire a good sense of the field and the career positions associated with it, depending on where your interest lies.
• Obtain a doctorate – You must earn a Ph.D. in your branch of microbiology if you intend to conduct independent research, work for a university or government research organization, or both. This covers academic practice, fieldwork, and education for conducting research. A post-graduate degree in a relevant topic with at least a 55% overall average is required for doctoral applications, which may additionally contain a minimum amount of relevant work experience.
Watch this to learn the right way to approach Microbiology
Few Career Opportunities for Microbiology Majors
Opportunities for employment in the government sector, hospitals, public health laboratories, research labs, and industrial laboratories are available to graduates with a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc) degree in microbiology (food, dairy, chemical, pharmaceutical, and genetic engineering companies). Students who pursue degrees beyond the B.Sc have job options in these fields, along with teaching positions in colleges and universities, which come with greater responsibility and commensurately better pay.
* Some of the possible positions are:
-Technician for research laboratories
-Food or dairy microbiologist
-Microbial environmentalist
-Clinical microbiologist or immunologist
-Quality control analyst
-DNA technologists
-Veterinary microbiologists
-Microbial public health specialist
-Biomedical scientists
-Research assistants
-Food technologists
-Environmental microbiologists
-Clinical microbiologists
-Industrial microbiologists
Microbiological graduates are in high demand for their strong scientific, analytical, and problem-solving abilities. It is open to both the public and private sectors. Qualified microbiologists are employed by companies working in agriculture, food, and beverages, chemicals, environmental agencies, private hospitals, research institutes, universities, pharmaceutical companies, and laboratories. Numerous respected companies in India hire skilled microbiologists, including Pfizer, the Indian Hotel Company, Mascot International, the Piramal Group, Sun Pharma, Fortis Hospitals, Apollo Hospitals, Lakshmi Life Sciences, and others. Microbiologists are in high demand worldwide. Opportunities in fields such as healthcare companies, forensic science labs, environmental groups, higher education institutions, food, and beverage, publicly supported research groups, pharmaceuticals, and many more businesses are available to those who hold a degree in microbiology.
Benefits of a Career in Microbiology:
The significant advantages of choosing a career in microbiology are:
• Microbiologists are interested in the study of microorganisms and their various properties, which has a positive impact on their careers. The individual’s career skill set can be improved by using cutting-edge technology to examine the test and culture medium. Additionally, the possibility of participating in the development of a novel vaccine or viral solution can benefit the microbiologist’s career.
• The development of new vaccinations that can stop the spread of illnesses and save millions of lives become possible because of microbiologists.
• Microbiologists research the traits of the bacteria that aid in the creation of various foods and related goods. As a result of their unique experience, millions of people now have access to food security.
Microbiology Career Salary
With the required qualifications, you can earn an annual salary of around INR 3 lakhs as a microbiologist. Working for the government or a private company will earn you a respectable income as well as perks and other benefits. The annual income depends on the area of microbiology that the candidate has specialized in; for instance, a microbiologist can earn over INR 8 lakhs at the senior level, while an industrial microbiologist can earn over INR 5 lakhs at the senior level. Microbiologists with master’s or doctoral degrees can earn extremely significant salaries in both industries. The salary will also depend on a variety of things, like the company, industry, job description, location, etc. Experience is crucial in this industry as it gives you the chance to discover a specific vocation that suits you.
Microbiologists with experience are paid more in this specialty. Microbiology is not easy. Instead, it requires a lot of hard work, but again it is still considered highly competitive in the industry because of this. Experts in the field of microbiology must be well-educated, and well-trained. The field of microbiology will prove to be the best fit for you if you feel at ease working in laboratories and behind the scenes in academic research. If you enrol in one of the top universities offering microbiology courses in India, the field has a wide range of potential applications and can provide you with several international chances.
The prime goal of the discipline of Community Medicine is preventing disease, promoting health, and prolonging life, by providing comprehensive health care for the holistic health of the community. Hence, the discipline goes beyond classroom teaching and bedside patient care, to reach out to the community with a focus on underprivileged and marginalized population.
Community Medicine is a branch of Medicine dealing with the promotion of health and prevention of diseases, involving people’s participation and utilizing professional management skills. It is primarily focused on providing primary, secondary, and tertiary care, control and prevention of outbreaks or epidemics, community diagnosis, health needs assessment, epidemiological assessment, research, and planning evidence-based health policies and programs. Hence, the discipline covers all the domains of learning viz. cognitive, affective, and psychomotor as shown below (Figure 1).
- Cognitive domain i.e. knowing the vision and mission of the discipline
- Affective domain i.e. feeling and understanding the needs and demands of the community
- Psychomotor i.e. identifying problems and designing and implementing measures to solve these problems.

Figure 1: The domains of learning Community Medicine
Recently, the undergraduate (UG) and postgraduate (PG) medical curricula in India have been updated and subsequently implemented across the country from academic session 2019 onwards for UG and 2020 onwards for PG courses, as Competency-Based Medical Education (CBME). At the undergraduate level, there is an integration of the related disciplines, designed to give the students a holistic understanding of the various subjects to function appropriately and effectively as a physician of first contact. The new CBME curriculum for Community Medicine for UG students provides several learning opportunities, to provide comprehensive care to the community by way of the Family Adoption Program, along with theory and practical classes throughout the first three phases of the course. In addition, there is an elective posting for eight weeks after the third phase, for which the students can choose any of the options offered including posting at health centers for primary health care to the community. Finally, during the Internship, the students are posted in District Hospitals to get sensitized to the real-life situation in rural areas.
How to prepare yourself for examination in Community Medicine?
Considering the various domains of learning that Community Medicine covers, a student is also evaluated during examinations on all these aspects. Hence, you should prepare yourself by (1) reading standard textbooks and class notes for knowledge and understanding; (2) making frequent visits to the community and the families allotted to you; (3) attending practical teaching sessions in the community and public health organizations for assessing the problems and their solutions. In addition, you should attend practical classes on identifying spot specimens and working out epidemiological and statistical exercises.
You should learn to understand priority topics and give focus accordingly. There are some ‘must know’ areas which you have to learn for passing your examination as well as for knowing the subject that will help you life-long in delivering comprehensive care. There are some areas within the subject that you ‘should know’ which will help you to perform well in examination as well as improve your competence in being a physician of first contact. You should give adequate focus and time to these areas for doing well in your examinations. Having covered these areas, there are some ‘nice to know’ areas that will help you to perform excellently and thus stand out among your fellow students and professionals (Figure 2).

Figure 2: Priority areas for learning Community Medicine
What are the prime focus topics for examination in Community Medicine?
As you understand, every topic is important for learning to help you perform well in your examinations as well as gain expertise to become a competent and effective professional person. However, for prioritization, you may consider the following areas most important.
- Epidemiology and Biostatistics
- Problems of vulnerable population groups viz. infant and under-five children, adolescents, antenatal and postnatal women, women in reproductive age group, and the program in India for providing care for these population groups
- Communicable and non-communicable diseases with objectives and strategies under the related national health programs
- Major determinants of health viz. nutrition, water and sanitation, entomology, biomedical waste management
- Problems and programs for other vulnerable populations viz. occupational groups and elderly population
- Health education and behavior change communication
- Health planning, evaluation, and management techniques
- Health care delivery system in India with the major landmark international and national policies related to healthcare delivery
What are the learning resources for Community Medicine?
Community Medicine is learned from both print and electronic learning materials as well as real-life situations. Some of the standard books that you may follow are given below. However, this is not an exhaustive list. You may read any other book of your choice.
- Kadri AM. IAPSM’s Textbook of Community Medicine
- Banerjee B. DigiNerve’s Community Medicine for UnderGrads Course
- Suryakantha AH. Community Medicine with Recent Advances
- Banerjee B. DK Taneja’s Health Policies & Programmes in India
- Banerjee B. Mahajan’s Method on Biostatistics for Medical Students and Research Workers.
In addition to these, there are reports and publications of the World Health Organization and Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, and other reputed national and international organizations, which are available on the internet, which you may read if interested.
A lot of Community Medicine can also be learned by following the current news, a great example of which is the recent COVID-19 pandemic for which various preventive and public health measures have been taken both globally and nationally.
Following what you have learned and disseminating messages of health promotion and disease prevention to those around you, will also help to improve your psychomotor skills.
What are the learning methods to perform well in examination in Community Medicine?
The secret of learning is to be regular, attentive, and hardworking. Since Community Medicine is taught right from the first year and continued for three and a half years, you should be regular throughout, failing which it will be difficult for you to catch up in the last moment. Hence, follow all the points given below.
- Attend all theory classes, practical sessions, and family visits, regularly and attentively
- Read the topic taught, after returning from class each day
- Try to understand the concepts and not only memorize
- Take class notes and make your notes for quick revision
- Focus first on priority areas i.e. ‘must know’ and ‘should know’
- Having understood these areas, you may try to move on to the ‘nice to know’ areas
- Revise multiple times
- Attempt solving previous years’ question papers and MCQs.
How will DigiNerve help you to learn Community Medicine?
The course material for Community Medicine for Undergrads on the DigiNerve app addresses all the domains of learning. The entire CBME syllabus has been split into five sections including one section on the practical aspect, with topics and units under each section. In the theory part covered in the first four sections, every aspect is discussed and explained in detail. The practical section presents how to study a family with an index case, along with pictures and salient features of spots and specimens, and how to solve epidemiological and statistical exercises to help you understand and work out by yourselves.
Watch this video to learn the Right way to approach Community Medicine by Dr. Bratati Banerjee.
So, welcome to the world of Community Medicine and happy learning!
Wish you all the best in your journey through the subject.
Dr. Bratati Banerjee
Director Professor, Department of Community Medicine,
Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi
In OBGYN, OB refers to Obstetrics or Obstetrician, a doctor who specializes in the care of women and their babies during pregnancy and childbirth. GYN stands for Gynecology or Gynecologist, a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of female reproductive disorders. OBGYN is a branch of medicine that deals with the entire female reproductive health of pregnant as well as non-pregnant females.
OBGYNs diagnose and treat diseases of the female reproductive organs. They treat various other women’s health issues such as hormonal problems, menstruation issues, contraception, infertility, and reproductive tract infections. They also hold the responsibility of childbirth via normal delivery, cesarian sections, pregnancy complications, fetal signs, and growth and also help women with psychological distress and counseling.
ADMISSION PROCEDURE
The following steps are undertaken by students who aspire to become an OBGYN:
- From the beginning, aspirants must complete the senior secondary education with the PCB stream with at least 50% marks.
- Further, they should crack the NEET UG exam to get admission to medical college (Government/ Private).
- After obtaining an MBBS degree, they need to appear for the NEET- PG entrance examination.
- A good score in NEET-PG gives a push to admission to the medical college for the OBGYN PG course.
- Aspirants must complete a junior resident responsibility to gain a post-graduation degree.
- After the successful completion, they must obtain a license and become board certified.
ELIGIBILITY FOR BECOMING AN OBGYN DOCTOR
- Candidates should have completed an MBBS degree from a college/institution recognized by the Medical Council of India (MCI) with a minimum of 55% marks.
- They must have undergone the one-year compulsory internship after completing the course.
- Candidates must clear the NEET PG exam to be eligible for admission to recognized universities/colleges.
- For the general category, the candidate must obtain at least 50th percentile marks in NEET PG for admission to MD/MS courses. For SC, ST, and OBC, the minimum percentage requirement is the 40th
- For the candidate with benchmark disability specified under the Rights of Persons with Disability Act 2016, for the GEN-EWS and unreserved category 45th percentile is required. For, SC/ST/OBC-NCL candidates, the minimum marks shall be 40th
- In some cases, admission to post-graduate medical courses may also include a group discussion/personal interview after the entrance examination depending on the college.
- Final confirmation of admission depends on the cut-off marks and the counseling procedure.
OBGYN IN MBBS
MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery) is an undergraduate medical sciences course with a duration of 5.5 years including an internship. Admission to the MBBS is solely based on an entrance examination. The NEET (UG) entrance examination is the only valid examination to get admission in MBBS in government or private medical colleges recognized by MCI (Medical Council of India). A student needs to get into the merit list and undergo the counseling procedure for admission to MBBS successfully.
After getting admission to medical college, a student needs to learn various subjects like microbiology, pathology, pharmacology, medicine, pediatrics, OBGYN, community medicine, surgery, and more.
Undergraduate students study OBGYN in their 4th prof, where they go through case discussions in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Along with this, a medico needs to complete a one-month OBGYN internship. During this internship, they get training in Obstetrics & Gynaecology OPD’s Wards and OTs, Labour Room, and Family Planning OPD and OT.
PG OBGYN AFTER MBBS
OBGYN is a three-year full-time postgraduate course in medical sciences. The course consists of a comprehensive, superior examination of the complete medical pathology related to the female reproductive organs, and provision of care to each non-pregnant and pregnant patient.
Admission to OBGYN MD is done through national-level entrance examinations like NEET-PG, and INI-CET. In PG OBGYN, students get familiar with the latest society guidelines, benchmark trials, and recent advancements in PCOS, Robotic Surgery, and performing clinical examinations. They are asked for pertinent tests, decipher the results, and implement medical/surgical management in the specialty clinics, OPD, wards, labor room, and operating rooms. They learn to use medical capabilities to evaluate troubles in pregnancy and discover techniques and relevant prognoses.
Watch this video to understand this important topic of OBGYN through case-based discussion
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS FOR PURSUING PG OBGYN
MBBS students need to undergo and crack the NEET-PG entrance examination for admission to medical college for PG OBGYN. The NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) is a national-level entrance examination for admission to pursue medical sciences; NEET UG for the undergraduate medical courses (MBBS, BDS, BAMS, BHMS), and NEET PG for the doctors to get admitted to various postgraduate courses (MD/MS) and diploma courses.
Admission for PG to government and private colleges depends on the ranking of the medicos in the NEET-PG entrance Examination. The examination body of NEET PG is the National Board of Examinations and further, the Directorate General of Health Services conducts the counselling and seat allotment process.
Institutes that are exempted from admission via the NEET PG exam are:
- AIIMSs
- PGIMER
- JIPMER
- NIMHANS
- SCTIMST
These institutes come under the INI (Institute of National Importance).
To get admission to INI (Institute of National Importance) institutions, medicos must get into the merit of the INI-CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test).
INI- CET is a combined entrance examination to the INI institutes for PG courses in medical Sciences [MD, MS, DM (6 years), MCh (6 years), and MDS]
List of Participating INI Institutes for INI-CET:
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bathinda, Punjab
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar, Odisha
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bibinagar, Telangana
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Deoghar, Jharkhand
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur, Rajasthan
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Mangalagiri, Andhra Pradesh
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Nagpur, Maharashtra
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, Bihar
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Raipur, Chhattisgarh
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh, Uttarakhand
- Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry
- Postgraduate Institute of Medical Science and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh
- National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore, Karnataka
- Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute of Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), Thiruvananathapuram, Kerala
NOTE:
MRCOG Examination:
This examination is specially designed by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists for OBGYN doctors to assess their skills, knowledge, and competencies. This exam comprises three parts- MRCOG Part 1, MRCOG Part 2 & MRCOG Part 3. Membership of RCOGs is awarded upon the successful completion of all three stages of the exam.
TOP COLLEGES FOR PG IN OBGYN
Some of the colleges for admission to PG-OBGYN are listed below:
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi
- Armed Forces Medical College, Pune
- IMS BHU- Indian Institute of Medical Sciences- Banaras Hindu University, Banaras
- Bangalore Medical College, Bangalore
- Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi
- Lady Hardinge Medical College, New Delhi
- JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research), Puducherry
- Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh
- King George Medical College, Lucknow
- Madras Medical College, Chennai
- Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu
- Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi
- VMMC College, New Delhi
- Goa Medical College, Panaji
COURSE STRUCTURE OF PG OBGYN
There are four papers:
PAPER I: Applied Basic sciences: Physiology and anatomy of the female reproductive system, pharmacological and hormonal roles, obstetric and gynecological markers – non-neoplastic and neoplastic, medical genetics, anatomical and physiological changes in the female reproductive tract during pregnancy, pharmacology of drugs used during labor and after birth
PAPER II: Obstetrics including Social Obstetrics & Diseases of Newborn: Prenatal Care: Risky Pregnancy, Obstetrics: Postpartum, Vaginal delivery, caesarean section, Hysterectomy, Destructive Surgery, Manipulation (external/internal pod version, manual placental removal, etc.), Medical Abortion – Safe Abortion – Case Selection, Complication Techniques, and Treatment, MTP, newborn.
PAPER Ill: Gynecology: Clinical gynecology, Family Welfare, and demography, Male and female infertility.
PAPER IV: Recent Advances in Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Along with four theory papers, doctors pursuing MD OBGYN have to do Practical Examinations in Obstetrics and Gynecology:
Clinical long case and short case including viva of:
- Instruments
- Pathological specimen,
- Medicines and X-rays, ultrasounds, etc.
- Dummy Pelvis
- Family planning
THESIS: - Students identify relevant research questions
- Conduct a critical literature review
- Hypothesize
- Determine the most appropriate study design
- State the purpose of the research
- Preparation of test protocols
- Conduct the study according to the protocol
- Analyze and interpret research data and draw conclusions
- Write a research paper
- PG OBGYN students are also required to complete their OBGYN residency and postings.
Watch this video to learn the right way to approach OBGYN MD
SCOPE/JOB OPPORTUNITIES AFTER MD IN GYNECOLOGY & OBSTETRICS
Undoubtedly, the course is highly respected, job oriented, and lucrative. This opens doors to a variety of job prospects such as Maternal-fetal medicine specialists, Reproductive endocrinologists, Gynecologic oncologists, Female pelvic specialists, critical care medicine specialists, professors, clinical associates, junior consultants, senior residents, consultants, general physicians, researchers, private practitioners, govt. doctors, and private clinicians. Moreover, the OBGYN can go for research and higher studies in research centres and universities.
FAQs (Frequently asked questions)
Q1.What is the difference between an Obstetrician and a Gynecologist?
Ans. A gynecologist is mainly trained in female reproductive care whereas an obstetrician cares for pregnant women and newborns.
Q2. Who is the first female Surgeon General in India?
Ans. Mary Poonen Lukose was an Indian gynecologist, obstetrician, and the first female Surgeon General in India.
Q3. Can a person pursue OBGYN without an MBBS degree?
Ans. Yes, one can pursue a career in OBGYN after a BAMS degree if not MBBS. A diploma course in OBGYN can be done as well after a BAMS degree.
Q4. How can I enter the OBGYN field?
Ans. You can undergo a three-year postgraduate course in OBGYN (MS/MD) after doing MBBS or a two-year diploma program of postgraduate training in Obstetrics and gynecology.
Most students think that medical education is only about clearing the entrance exam and getting admission to MBBS. However, the reality is way different than this perception. Clearing the exam isn’t the final step, rather, is the beginning of the life of a medical student. A medical degree is considered one of the toughest degrees in the world. For a student, it’s definitely more work because of the unlimited workload and the time limit, which means a lot less sleep and a lot more stress.
Top Struggles of MBBS Students are:
- Adjusting with peers: Medical colleges are responsible for ensuring that graduates are knowledgeable, skilful, and professional to meet society’s expectations. Due to this, students have to prepare themselves for the vast syllabus while also adjusting with peers. There is huge peer pressure on medical students when it comes to adjusting themselves in the new environment due to high level of competition.
- Wow! You are smart, you should be a doctor: Medical might not be the hardest choice for aspirants but the journey is indeed very hard. Students put in all the efforts, and energy to enter the clinical world; the world that includes a lot of hard work, sleepless nights, countless hours of study, and whatnot. However, there are many students who give their 100 percent just to satisfy that One Big Dream of their family and relatives, at the cost of their happiness.
- Do you have a social life? When it comes to a medical student’s social life, the status is quite complicated. Students get trapped with books, assignments and practices, etc. that they can’t focus much on their social life. Although medicine is a very social course and being a healthcare professional, students must know how to deal with people. To take time out for social activities, students need to maintain a schedule that allows them to manage it all.
- Start the day and end the day with medicine: – The primary motivation is to enjoy studying. Exhaustion due to continuous studies can make medical college seem like a burden. So students must divert their attention from studies a bit and focus on “personal development.” This involves honing talents that fall outside the purview of academic study yet are nevertheless crucial for a doctor. For instance, participating in music or theatre can help students get used to performing or interacting in front of a large audience. This also helps them to confidently address and speak at a conference or simply to a group of their coworkers. There is a balance that needs to be achieved between working and enjoying life.
- You have to memorize so many new drugs, that your brain might explode: The most problematic situation that students face is that they need to cram names of thousands of new drugs and various syndromes, which is confusing. Also since these drugs are vast along with their own different characteristics, it is easy to forget a few. This is not the end, memorizing drugs also includes knowing their purposes, advantages, and disadvantages, after effects, and what all changes can be possible, which also includes how they respond in every individual’s body.
Watch Video to learn the right way to approach Pharmacology in MBBS
- The unending workload: – It is a popular talking point that a medical student’s life in med college is endless. The reason behind this is that medical courses are the longest courses in the educational world. It nearly takes a decade to become a fully qualified doctor. The entire journey demands a lot of hard work, sleepless nights, and a huge number of complications. It is not easy to maintain patience throughout this period and often students lose themselves in the wheel of practicals, rounds, syllabus, and examinations.
- Finance: – Finance is a huge problem for a medical aspirant. How? Not all medical aspirants belong to financially stable families, and neither do all receive government scholarships. Many students dream to become a doctor, but again finances remain a challenge. Medical studies are considered one of the most expensive education all over the world. It is a vast and expensive course. If a student does not have an adequate amount of money, pursuing a medical degree can be challenging. If this problem arises while a student is pursuing the course, students should always have a backup option.
- Exams Breakdown: – Exams have always been a huge load. Even the thought of it is scary because the syllabus is so vast that sometimes the duration of preparation tends to seem less. There’s no doubt medical life is filled with competitors, which makes the exam period even more stressful. Skipping topics is another aspect that makes it stressful while spending more time on important topics. Additionally, lack of sleep, headaches, and stress can easily lead to breakdowns.
- A good night’s sleep is a wonder for you: – Back-to-back classes, practicals, and whatnot get tiresome for them. Most students have sleepless nights because of assignments, many even suffer from sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality which is common during the internship. Researchers have paid much attention to the critical function that sleep plays in preserving mental health, advanced learning, and overall welfare. From 1st year to the final year, medical students are particularly prone to sleep-related problems due to the huge syllabus. So it is very important for students to at least have 6 – 8 hours of sound sleep.
Life of Students in the 1st year of MBBS:
Medical College is nothing like high school; it is challenging not simply because there is so much knowledge to gain, but also because students get to learn new skills. Students mostly in their first year, try to understand what kind of studying technique works to cover the syllabus. The first year is all about learning, failing and again understanding where you were wrong and then starting again.
Life in college doesn’t resemble the medical drama– Grey’s Anatomy in reality. No one goes to the clinical rounds in the first year itself. In the first year, students study Biophysics, Anatomy, and Histology and prepare for tests most of the days.
In the first year, it’s not all about saving lives. The only life students can save is theirs, by fixing a decent study routine for themselves, figuring out how to adjust their studies and things they like doing beyond studying and getting sufficient rest.
Life of Students in the 2nd year of MBBS:
It’s the best time to retrospect and make a schedule that can help students manage studies, social life, and sleep. The one benefit students have in their 2nd year is that they get familiar with the environment, faculty, and course too, so it becomes a bit easy for them to communicate and discuss their problems in the class or with the faculty. It gets even easier to make a schedule that can be followed given that students get quite familiar with the frequency of classes, practicals, and tests.
Life of Students in the 3rd year of MBBS:
It is very much like climbing one more step and reaching one step near to the goal of becoming a Top Doc. Becoming more focused on studies and attending a lot of practicals are included in the 3rd year. It is time for students to get exposed to the practical technicalities of the field. Students become familiar with everyday struggles in 3rd year; they feel the sensation of being worn out, because of classes and clinical rounds. They need to have some sort of framework, whether it be a paper journal or a schedule reminder turned on on their mobile phones.
Life of Students in the 4th year of MBBS:
The significant cause of the pressure students face in the final year is due to the major subjects like Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics, OBGYN, Orthopaedics, etc. which are highly important for NEET PG. They experience maximum stress when they start going for rounds. Medicine is a long-distance race, not a run. Regardless of whether students complete their last year, it isn’t the end. They still need to learn a lot more because now their real life as interns and saviours begin. It’s now time to put all the knowledge into application.
Get conceptual clarity in Medicine from Dr. Archith Boloor
Passing the final exam in MBBS is crucial to starting your career as a doctor. Students must focus on conceptual clarity to clear the final exams. Discipline and dedication are the keys to mastering the syllabus. Moreover, aspirants that are pursuing the MBBS program at any medical college must complete the internship. An internship is a term of learning, or, to put it in simple words, more practical work than theoretical training. The internship phase is where you put all of the theoretical information you’ve learned over the last four years into action.
You should have a proper plan if you are going to enrol yourself as a medical student, it is a long ride with lots of struggle, hard work, failures, and whatnot. The medical course is exceptionally vast due to the volume of material that needs to be learned along with both the basic scientific principles and the clinical abilities. Keeping in mind the surreal feeling that a doctor feels while saving someone’s life is something that can’t be put into words, and furthermore, the feeling of saving somebody’s life is simply inexplicable. Once your goal is set and you are ready for it, it is definitely going to be the best chapter of your life.
WHAT IS AN ADENOID?
Adenoid is a subepithelial collection of lymphoid tissue situated at the junction of the posterior wall of the nasopharynx. It is also known as nasopharyngeal tonsil, having vertical ridges of lymphoid tissue separated by deep clefts.
- It is covered by three epithelium i.e., transitional, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, and stratified squamous.
- Having no crypts and capsules.
- It is included in the waldeyer’s ring of lymphoid tissue.
- It is present at birth but shows physiological enlargement up to 6 yrs and then starts atrophy at puberty.
- It disappears by age of 20.
- It is seen in MRIs of all infants by the age of 5 months.
- The persistence of adenoids can be seen beyond the age of 15 years in case of allergy or infection.
- One in number
- Lymphatics from this tissue drain into upper jugular nodes directly or indirectly through retropharyngeal and Para pharyngeal lymph nodes.
- Arterial supply from ascending palatine branch of the al artery, ascending pharyngeal branch of the external carotid artery, ascending branch of the third part of the maxillary artery, and inferior thyroid artery’s ascending cervical branch.
- Sometimes inflammation of the adenoid lead to pain in the ear due to the same nerve supply as cranial nerves IX and X (referred pain) or can be due to eustachian tube obstruction.
ADENOID HYPERTROPHY
It is an obstructive condition due to the enlargement of the adenoid which can be physiological enlargement in childhood or due to some infections or allergic conditions.
WHAT IS THE ETIOPATHOGENESIS OF HYPERTROPHY?
- Recurrent sinusitis, rhinitis, or chronic infection of tonsils lead to chronic adenoid infection and hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue which results in adenoid hypertrophy.
- Allergy to the upper respiratory tract may lead to the enlargement of adenoids.
- Viral infections like EBV or bacterial infection of group A streptococci can lead to its enlargement.
- Exposure to smoking or pollution.
- Tumours of sinuses, lymphoma, and AIDS
- Due to diseases like GERD, there is a reflux of acid that will irritate the adenoid tissue leading to inflammation and resulting in hypertrophy.
HOW PATIENTS WILL PRESENT TO YOU IN OPD?
Signs and Symptoms
These depend not only on the size of the adenoid mass but also on the space that is available for enlargement in the nasopharynx. Excessive hypertrophy of the adenoid can lead to obstruction of the whole nasopharynx. In cases of enlargement, the patient may be asymptomatic but in severe enlarged and infected adenoids, the patient presents nasal, aural, and general symptoms.
- Nasal Symptoms
The commonest symptom is nasal obstruction due to recurrent sinusitis and this leads to mouth breathing. Nasal obstruction leads to interference in the suckling or feeding of a child. As respiration and feeding cannot occur together, the child fails to thrive as all his efforts go into breathing which will lead to suboptimal growth of the child. There will be nasal discharge due to choanal obstruction as the normal secretion cannot drain back into the nasopharynx and is associated with chronic maxillary sinusitis and the child has a wet bubbly nose.
When adenoids are acutely inflamed, epistaxis can occur when the patient blows his nose. Voice change can be seen i.e. toneless and losing nasal quality due to nasal obstruction and there will be rhinolalia clausa i.e. hyponasal or denasal speech due to lack of appropriate nasal airflow during speech.
- Aural Symptoms
Tubal Obstruction: Adenoid mass blocks the eustachian tube leading to retraction of the tympanic membrane and conductive hearing loss. Recurrent attacks of acute otitis media may occur due to the spread of infection through the eustachian tube. CSOM may fail to resolve in presence of infected adenoids. There will be fluctuating hearing loss due to differences in the size of the mass of the adenoid. Impedance audiometry test helps to identify fluid in the ear due to the presence of glue ear that is otitis media with effusion.
- General Symptoms
Adenoid Facies: Chronic nasal obstruction and mouth breathing lead to characteristic facial appearance.
- Dull expression because he is unable to hear and elongated face, open mouth, prominent and crowded upper teeth, hitched up upper lip, pinched up nose because the child is a mouth breather so there will be no use of nose for a long time for breathing that will lead to disuse atrophy of alar prominence, nasal crease and labial folds will be absent, high arched palate because the child is breathing through the mouth and as the mouth is continuously open, more air goes through the palate.
- Pulmonary hypertension: As the child snores a lot during the night and there is sleep apnoea (episodes of not breathing during sleep), the child gets up again and again during the night and is unable to have a good night’s sleep. This results in sleepiness and lethargy throughout the day. In sleep apnoea, so many episodes of deoxygenation happen that the pulmonary artery undergoes vasoconstriction which leads to pulmonary hypertension and results in right-sided heart failure. The final consequence is cor pulmonale.
- Aprosexia i.e. lack of concentration in studies.
How can the diagnosis be done?
- Posterior Nasal Rhinoscopy: Examination of postnasal space in young children using a mirror from which adenoid mass can be visualized.
- Nasal endoscopy: Done with the help of a rigid or flexible nasopharyngoscope which helps in assessing the size of adenoid mass from which grading can be done. It is done on cooperative children. It provides more details on the nasopharynx.
- Soft tissue lateral radiograph of the nasopharynx: Done if the child is uncooperative as it will reveal the size of the adenoid and also the extent to which nasopharyngeal air space is compromised. There will be very little breathing space in the nasopharynx in severely enlarged mass.
MANAGEMENT
Medical Management
If symptoms are not marked i.e. where there is acute infection, then the investigation is not needed since it can be addressed clinically too.
To decrease the size of the adenoid, the following measures can be taken:
- Breathing exercises
- Dietary changes
- Lifestyle modification
- Decongestant nasal drop (Oxymetazoline, Xylometazoline that will relieve nasal obstruction).
- Antihistamines e.g. levocetirizine are given if there is hypertrophy due to allergy.
- Antibiotics like Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid are given if it is due to infection.
- Intranasal steroid spray can be given like Fluticasone.
- Proton pump inhibitor can be given in case of GERD
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the last resolve because adenoids have immunological functions, and thus it is done only when symptoms become chronic.
- Adenoidectomy: It is done in a rose position in which the patient’s larynx is at a higher level in which the cervicothoracic joint and the atlantooccipital joint are in an extended position under general anesthesia. It is done using endoscopy by two methods i.e. cold (microdebrider, curettage) and hot (coblation, laser).
Indication of Surgery
- Sleep apnoea
- Chronic suppurative otitis media
- Recurrent sinusitis
- Dental malocclusion
Complication of Surgery
- Haemorrhage
- Coroner’s clot
- Eustachian tube injury
- Griesel syndrome
Contraindication of Surgery
- Velopharyngeal insufficiency
- Cleft palate
- Bleeding diathesis
- Acute infection
- Adenoidectomy + Tonsillectomy: It is done when there is a chronic tonsillitis infection. The child will be sedated in the operating room throughout the procedure. His tonsils and adenoids will be removed by the surgeon through the mouth. The skin won’t be cut in any way.
Indication of Surgery:
- Obstructive sleep apnoea
- Chronic tonsillitis
- Trouble swallowing
Complication of Surgery:
- Difficulty in breathing
- Fever
- Bleeding
- Dehydration
Most 3rd year students look for online resources to learn Community Medicine along with ENT. Watch this snippet to learn about Epidemiological Research.
FAQs (Frequently asked questions)
Q1. How an adenoid hypertrophy patient will present to you?
Ans. The child’s mouth would have been open for the past few weeks and he might not be responding. It would be seen only when the season changes or if the child is allergic to any substance.
Q2. Why an adenoidectomy is contraindicated in velopharyngeal insufficiency?
Ans. In velopharyngeal condition, the child is supposed to have regurgitation of food from the nose and hyponasal speech post-surgery so it is not advised to perform adenoidectomy in such patients.
Q3. How adenoid hypertrophy can be differentiated from an antrochoanal polyp?
Ans. In polyp, the crescent or Dodd sign is present whereas it is absent in adenoid hypertrophy.
During the preparation of Orthopaedics for NEET Exam, you must have an idea of what all important topics need to be thoroughly prepared. Moreover, a strategical approach while preparing for NEET PG 2023 Exam can help you cover everything within the given timeframe.
Some of the main topics that you must cover before appearing for the NEET PG 2023 Exam:
| Topics | Sub-Topics |
| 01- Bone & Joint Infection | · Bone and joint infection- septic arthritis · Bone and joint infection- osteomyelitis · Bone and Joint Infection- Skeletal Tuberculosis |
| 02- Bone Tumors | · Diagnosis especially Benign Tumors · Management Malignant Tumors |
| 03- Neurological Disorders | · Cerebral palsy · Poliomyelitis · Peripheral Nerve Injury, Brachial Plexus Injury |
| 04- Imaging | · Periosteal Reaction |
| 05- Metabolic Disorder | · Osteomalacia · Osteoporosis · Osteopetrosis and Paget’s · Achondroplasia |
| 06- Traumatology | · Upper Limb: Dislocation- Shoulder and Elbow Fractures- Clavicle, Humerus, Supracondylar humerus, Lateral condyle humerus, Colles and Carpo metacarpal injuries.· Lower Limb: Dislocations- Hip and Knee Fractures- Hip, Femur shaft, Patella, Tibia and Calcaneum. |
| 07- Pediatrics Orthopedics | · Pediatrics Orthopedics · CTEV* · Genu Varum |
| 08- Avascular Necrosis and Osteochondritis | · Avascular Necrosis · Polio · Dupuytrens contracture |
| 09- Arthritis | · Osteoarthritis · R.A and Ankylosing spondylitis · Gout |
| 10- Implants | · Prosthesis, orthoses and splints · Orthopaedic implants |
| 11- Fracture of Spine, Pelvis and Lower Extremities | · Fracture of spine · Fracture pelvis · Fracture acetabulum · Fracture proximal femur · Fracture shaft femur · Fracture distal femur, patella and proximal tibia · Fracture Both Bone Leg, Calcaneum and Foot Bones · Fracture of ankle · Knee and ankle ligament injuries · Miscellaneous Sports Injuries and Rehabilitation |
Watch the video to learn Fracture Intercondylar, Supracondylar and Lateral Condyle of Humerus.
Few points to keep in mind before starting your NEET- PG Exam preparation:
- Be familiar with the entire syllabus: The NEET-PG syllabus is vast and you must have an idea about every topic, short or lengthy. It is important to know the topics that are highly mandatory to cover so that you can bring out the best. Make sure you cut down on the extra information and focus on the most-asked topics saving time for revision.
- Create a Realistic Timetable: While following a fixed timetable, stay focused on your goal and prepare everything accordingly. Following a well-structured timetable will help you organize your time according to the length and depth of a topic. One thing that you have to keep in mind is that you must strictly follow the timetable you have made.
- Prepare Notes while Learning: This is one of the best methods while you are preparing for your exams. Making notes not only helps you study and concentrate but even helps with your writing and revising. You don’t have to go through everything before your exam day, just pick up your well-structured notes, start revising and you are good to go.
- High-Quality Study Material: Selecting the right material for your exam is very important. You might get a lot of sample books, papers, and mock tests online but with the help of teachers or online experts, you’ll get the right guidance. Clinical examinations, procedure videos, X-rays, implants and instruments are the most important to focus on in Orthopaedics. Doing all these might help you improve your speed and accuracy.
Following these tips consistently, might help you do well in your NEET-PG Exam and score high.
The purpose of studying Orthopaedics by the latest curriculum
The treatment of the musculoskeletal system is the main emphasis of the medical specialty of orthopaedics. Along with bones and muscles, this system also consists of joints, ligaments, and tendons. The curriculum aims to provide students with a basic understanding of the musculoskeletal system. The competency-based programme places a strong emphasis on evaluating students’ aptitude for accurately examining and diagnosing musculoskeletal problems.
MBBS Students should keep the following points in mind before approaching Orthopaedics for NEET PG:
- Do thorough research:
It is crucial to investigate and analyse the right way to study Orthopaedics. MBBS is one of the hardest degrees to obtain, but it’s not impossible if you do your homework and focus on your field of interest. While studying Orthopaedics, pay close attention to the textbook and do refer to supplementary information with the help of online orthopaedics lectures or videos. In addition to that, the best Orthopaedics book for medical students is Maheshwari’s Orthopaedics book, which covers information most precisely. It will help you to gain a better understanding of what is asked in the NEET PG 2023 Exam and get exposed to maximum case scenarios to make informed decisions in the future.
- Guidance from experts
Look out for lectures by India’s top faculty. You can also refer to online orthopaedics courses that are designed and taught by experts who have years of experience in the medical field. Attend webinars or doubt-clearing sessions if you are curious to learn or have difficulty understanding some topics. Also, approach your college faculty for instant guidance. If you want to enjoy learning orthopaedics, then the best course to check out would be Orthopaedics for Undergrads by Dr. Vivek Pandey.
- Ensure the notes that you have are accurate and easily understandable:
Every course has a specific set of materials to ensure that you read everything to better understand it. Having well-organized notes can be quite helpful because it gets easier to review them before the exam. Going through notes also helps in brushing up on knowledge and self-assessment. Medical books are excellent and informative, but without access to properly organised notes, it will be difficult for students to remember difficult concepts.
- Devote Time Wisely:
Choose wisely whether you want to go for online Orthopaedics learning or offline learning. Most toppers prefer to complete the textbook first and find different ways for clarity online. This could be by youtube videos, online courses for medical students, or lectures by eminent faculty. As it is known that NEET PG/NExT Exam will cover clinical case scenarios, however, most textbooks only cover limited case scenarios. This is the reason why students prefer learning online for better exposure to case discussions.
- Evaluation:
The only way to accurately evaluate how much you know about the fundamentals of orthopaedics is through a series of tests. To keep your memory sharp and assess your knowledge, look for a course that combines solid content with outstanding and frequent assessments. This will ensure you are aware of the most frequently asked questions and exam-ready.
Learn the right way to approach Orthopaedics in MBBS
How is Orthopaedics as a Career?
An orthopaedic specialist is referred to as an orthopaedist. Orthopaedists treat a range of musculoskeletal conditions including sports injuries, joint discomfort, and back disorders, using both surgical and nonsurgical methods. An orthopaedist often works as part of a large orthopaedic treatment team. This team may consist of some medical assistants like nurse practitioners, athletic trainers, occupational therapists, and physician assistants.
Several musculoskeletal problems are treated by orthopaedic surgeons. These diseases could be inherited or developed due to trauma or aging-related wear and tear. The field of medicine known as Orthopaedics is dedicated to the treatment of the skeletal system and all of its connected components. These components consist of Joints, Bones, Tendons, Muscles, and Ligaments.
Being an orthopaedic surgeon requires the following requirements:
- Graduate as a licensed doctor or a Doctor of Osteopathy from a recognised medical school.
- Complete 5 years of training in an orthopaedic residency programme that has been awarded by the Certification Council for Graduate Medical Education.
- A medical degree and, if desired, board certification to stay current and keep your certification, you must complete ongoing training and tests.
Some of the most typical ailments that an orthopaedist may treat are listed below:
- Bone fractures
- Back ache
- Injury to the soft tissues (muscles, tendons, and ligaments)
- Joint pain from arthritis
- A stiff neck
- Congenital conditions, such as scoliosis and clubfoot
Following are a few orthopaedic subspecialties:
- Trauma Treatment
- Foot and Ankle
- Spine Surgery
- Musculoskeletal Oncology (tumor)
- Hand and Upper Extremity
- Pediatric Orthopaedics
- Joint replacement surgery
- Sport Medicine
Scope in Orthopaedics
For those with a degree in orthopaedics, Orthopaedic surgeons have a wide range of employment options available to them, and their path to professional advancement is relatively direct.
- Orthopaedic surgeons have extensive expertise in conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system, including illnesses and injuries. It includes the muscles, tendons, bones, nerves, and ligaments.
- They address injuries like broken hips, degenerative diseases like osteoporosis and arthritis, as well as congenital issues like scoliosis.
- They can enlist in the military, including the army or navy.
- According to personal preference, an orthopaedist can begin their career working for prestigious hospitals in either the public or private sector.
- Holders of an orthopaedic degree have a wide range of additional choices, including the possibility of opening their own clinic and offering medical services to clients.
- Alternatively, as an orthopaedic doctor, you could choose to teach at colleges and universities or work in research. Orthopaedists with a doctoral degree can find employment in reputable public hospitals like AIIMS and PGIMER, as well as private hospitals like Fortis, Apollo, and others.
- They are also eligible for employment in the rehabilitation facilities that sports and defence groups have set up.
Surgery is a versatile subject in the study of medicine that helps in defining the patient’s course of treatment. Integration of surgery with important disciplines such as Anatomy, Pathology, Medicine, and others has become essential in the contemporary CBME curriculum. This has made it much easier for students to study the subject holistically and strengthen the foundation holistically.
Surgery for UnderGrads
It is a comprehensive resource that serves as a one-stop solution for undergraduate students’ academic needs. India’s one of the most prominent faculty and authors, Dr. Sriram Bhat, who is well-known for his book “SRB’s Manual of Surgery” has designed and taught this course. SRB’s Clinical Methods in Surgery, SRB’s Bedside Clinics in Surgery, SRB’s Surgical Operations: Text and Atlas, and Jaypee Gold Standard Mini Atlas Series Surgical Diseases are among his most popular titles. His extensive experience in both teaching and practising surgery has aided in the development of the entire course to meet the demands of undergraduate students. The course includes three pillars of surgery:
- Clinical Surgery: Initial Diagnosis
- Surgical Evaluation: When, what, why with images and other methods of evaluations
- Operative Surgery: Skill
The course’s main purpose is to get students to focus on the skill of observation, deduction, and knowledge, as well as the practical application of all the important concepts. By focusing on the essentials of the subject, the course aids in the development of a strong foundation. This makes it one of the best online surgery courses for MBBS students. The course is divided into 3 sections:
- General Surgery
- Systemic & Specialty Surgery
- Clinics in Surgery involve history taking, physical examinations, instruments, investigations, and operative surgery.
Clinical examination and differential diagnosis have been given top priority throughout the course. This will aid in the development of the student’s critical comprehension to effectively evaluate, diagnose, and manage the patient. Dr. Sriram Bhat has also demonstrated how to conduct a clinical examination in a variety of situations in real-life clinical scenarios along with the fundamentals of general surgery. This will aid in the development of concepts for all students. Surgical anatomy is a crucial element of operational surgery, and it has been covered alongside the majority of the structures and systems to provide students with a thorough understanding.
Surgical equipment and X-rays have their own part to familiarise students with the relevant information and application. They also serve as a valuable tool for last-minute revision before the final clinical tests because they are an integral part of the clinical exams. There are crucial questions for university examinations, PG entrance tests, and viva voce for each topic, as well as theoretical components with practical points for operative procedures.
This online surgery course is designed to meet the educational needs of both medical undergraduate and first-year postgraduate students.
The Course Includes:
- Video Lectures: 220 hours of in-depth video lectures covering 176 subjects provide detailed clarity for theory as well as clinical applications. Images and graphs are used to supplement these.
- Lecture Notes: 161 concise notes will assist students in skimming through the topics discussed during the lectures.
- MCQs for Self-Assessment: Students can assess their understanding of the topics by practising 2500+ MCQs.
- Physical and clinical examination in real-time clinical settings: This will help students to understand cases and arrive at differential diagnoses through reasoning.
Table of Content – Surgery for UnderGrads
General Surgery
Swellings
Examination of the swelling
Examination of the neck swelling
Clinical examination of swelling – video
Different swellings – Differential diagnoses
Differential Diagnoses – Neck Swellings
Ulcer
Examination of ulcer
Clinical examination of ulcer – video
Different ulcers – Differential diagnoses
Examination of Sinus and Fistula
Arterial Diseases
Clinical examination in arterial diseases
Clinical examination in vascular disease – Video
Peripheral arterial occlusive diseases
Lower limb ischaemia and management of arterial diseases
Aneurysms
Acute arterial occlusion
Upper limb ischemia and related conditions
Amputations
Vascular lesions and malformations
Venous Diseases
Examination of varicose veins
Video – Examination of varicose veins
Varicose veins
Venous ulcer, DVT, anticoagulants, VTE
Lymphatic System
Examination of lymphatic system and lymph nodes
Video – Examination of lymph nodes (in lymphatic system)
Surgical anatomy of lymphatics and lymphoedema
Hernia
Examination of hernia
Video – Examination of hernia
Hernia, general features, surgical anatomy
Inguinal hernia, features, management
Other hernias and technique of local anaesthesia in hernia
Ventral hernia – types and biomaterials used in hernia
Inguinoscrotal Swellings
Examination of inguinoscrotal and scrotal swellings
Examination of male external genitalia
Video – Examination of scrotum and male external genitalia
Diseases of the Scrotum
Diseases of the penis
Diseases of testis
Testicular tumours
Miscellaneous
Burns
Shock
Reconstruction
Haemorrhage
Infections
Electrolytes and fluid therapy
Nutrition
Obesity
Neoplasms
Hand and foot
Peripheral nerves
Transplantation
Adjuvant therapy
Day care surgery and surgical audit
Oral cavity
Examination of oral cavity
Video- Examination of oral cavity
Diseases of the oral cavity
Diseases of the alveolus, lip and tongue
Jaw, pharynx, larynx, nasal cavities
Examination of jaw tumours; Related diseases
Examinations of pharynx, larynx, nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses
Salivary Glands
Examination of salivary glands
Video – Examination of salivary neoplasms
Surgical anatomy and diseases of the salivary glands
Salivary neoplasms and their management
Qbanks
Systemic & Specialty Surgery
Thyroid
Examination of thyroid patient and evaluation
Video – Examination of thyroid swelling
Surgical anatomy of thyroid and congenital anomalies
Diseases of the thyroid gland
Thyrotoxicosis
Thyroid neoplasms
Thyroiditis, thyroidectomy
Parathyroid
Adrenal Glands
Breast
Examination in breast diseases
Video – Examination of breast lump
Surgical anatomy of breast and investigations in breast lump
Diseases of the breast
Carcinoma breast -– etiology, pathology, features
Management of carcinoma of breast
Dysphagia and Oesophagus
Examination of dysphagia and surgical anatomy of oesophagus
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) – 1
Oesophageal motility and other disorders of the oesophagus
Tumours of the oesophagus
Examination of Abdomen
Examination in chronic abdominal diseases
Examination of mass abdomen
Examination of acute abdomen
Video – Examination of chronic abdomen, mass abdomen and acute abdomen
Stomach
Surgical anatomy, investigations in diseases of the stomach
Diseases of the stomach
Small Intestine
Surgical anatomy and diseases of small intestine
Large Intestine
Large intestine – surgical anatomy and diseases
Diseases of large intestine
Intestinal Obstruction
Rectum and Anal Canal
Surgical anatomy rectum and anal canal
Examination of rectum and anal canal
Video – Examination of rectum and anal canal
Rectum and anal canal (carcinoma rectum)
Diseases of rectum and anal canal
Appendix
Surgical anatomy and diseases of the appendix
Diseases of appendix
Liver
Surgical anatomy of liver, functions of liver, liver function tests, liver trauma, liver cysts
Portal hypertension
Infections of the liver
Tumours of the liver
Hepatic resection, liver transplantation
Gallbladder
Surgical anatomy of gallbladder and congenital anomalies
Gallbladder stones (Gall stones) and acute cholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis, surgical jaundice and other conditions of the gallbladder
Gallbladder and biliary neoplasm and other condition
Cholecystectomy
Spleen
Surgical anatomy of spleen and Splenic Injury
Splenomegaly and related conditions
Splenectomy and other diseases of spleen
Pancreas
Surgical anatomy of pancreas
Acute Pancreatitis
Pseudocyst of pancreas
Chronic pancreatitis
Pancreatic tumours
Other surgical conditions of the pancreas
Abdominal Wall and Umbilicus
Diseases of abdominal wall and umbilicus
Abdominal Tuberculosis
Peritoneum
Peritoneum and peritonitis
Pelvic and subphrenic abscess, peritoneal, mesenteric and omental diseases
Retroperitoneum
Cardiothoracic Surgery
Diseases of thorax
Neurosurgery
Urology
Kidney, ureter
Urinary bladder
Prostate
Urethera
Trauma
Trauma (Wounds) – 1
Trauma – 2
Qbanks
Clinics in Surgery
History taking in surgery
General Physical Examination
Video – General examination
Surgical instruments
Surgical instruments video
Investigations in surgical patients
X-rays of surgical importance
Surgical pathology
Operative surgery
Anaesthesia and surgery
Learn the right way with Surgery for UnderGrads
Surgery is a much broader term, and learning about specific clinical disorders like the acute abdomen, surgical emergencies like testicular torsion and trauma, and obtaining more exposure to those who require more attention are all part of the MBBS syllabus. Surgery for UnderGrads is designed keeping in mind that students’ minds are trained in meticulous, correct appraisal and quick decision-making as a result of their exposure to cases. Therefore, it exposes them to common ‘surgical’ issues including skin lesions, ‘lumps and bumps,’ and hernias can also help enhance their knowledge.
Clinics in Surgery make sure that students can learn the fundamentals of obtaining histories, performing clinical examinations, and ordering the necessary investigations. Surgical clinics make students familiar with patients who have detailed histories and physical symptoms.
Students will also get the opportunity to improve their communication skills by learning how to explain difficult procedures and prognoses, as well as gain consent and deliver bad news in a kind and understandable manner to worried or depressed patients. A student’s knowledge of the reasons for a particular operation, the skill of cautious patient selection, the limitations of surgery, and its curative value improves in this situation. Undergraduates benefit from a unique educational experience in the operating room, which allows them to integrate and consolidate their information. In order to obtain a comprehensive knowledge of what is involved and how anatomy relates to pathology, students must be able to observe normal and pathological tissues as well as procedures up close.
Medical students may get the opportunity to learn about post-operative problems and the importance of careful, regular observation and contingency planning after the operation is completed. The course provides the student with unique insights into patient care and the opportunity to see the direct application of anatomy and physiology principles to clinical practise at each stage.
Best way to study Surgery
- Study Smart
There’s no doubt that during medical school, students are required to study extensively. It would be nearly hard to acquire the necessary skills and information to become a skilled doctor unless they put in the time and effort that is needed. Every medical student will study, collect knowledge, and uniquely organise their study hours to be more productive and efficient. Studying in a group might help them examine their knowledge by allowing them to discuss and ask questions. However, if their classmates aren’t as dedicated as they are, studying alone can help them avoid distractions.
- Sleep enough to wake up refreshed
Sleep deprivation is common during exam season when students overlook their own health in order to focus on revision. However, they need to be aware of the fact that a good night’s sleep provides them with a cognitive boost the next morning. It also ensures that they are healthy, study better, and feel more motivated. Being weary during an important lecture might divert them from their goal of being a Top Doc. Making a note of sleeping habits, creating a timetable, and sticking to it would help a lot.
- Volunteer for college societies
Participating in social events in MBBS helps students build their soft skills. Although the profession of a doctor requires skills and knowledge, it is equally important to have a sense of empathy. A great doctor is the one who understands, relates to, and connects with his or her patients, as well as their families. Communication is the key to understanding the physical and mental pain of the patient as well as being able to share the consequences and after-effects with them. This is required because doctors meet people from different social backgrounds, personalities, and behaviours regularly.
- Seek guidance from the right mentors
Mentors are the companions for life, the only difference being that they are way more experienced. In order to improve their skills and become highly qualified doctors, students must seek assistance from experts who can guide them patiently. Doctors who also teach at medical school have great worth and can guide students on the right path to their future job. Academic advisors, professors, and teaching assistants are the ones students seek advice from during their medical career.
Scope of Surgery after MBBS
Undergraduate students must complete their master’s degree to become a surgeon. Preoperative and postoperative care are both important aspects of becoming a surgeon, with the goal of returning patients to their natural physiologic state. Master of Surgery graduates’ career options and job prospects are as diverse as those of a physician in other specialties. Many people select this job because it allows them to witness a great deal of change. Surgeons must keep their abilities up to date in order to satisfy the changing needs of their patients. This is a fantastic job choice for those who like a challenge.
To diagnose and treat patients, modern hospitals require people with technological skills and competence. Students with a master’s in surgery can go for higher studies to gain an edge or update their skills. Aspirants can build a career as vascular surgeons, plastic surgeons, researchers, neonatal surgeons, and many more.
FAQs
Q1. Is surgery a good career to pursue?
A surgeon’s career can be immensely fulfilling because he or she has the opportunity to save people’s lives. In the operating room, a surgeon’s technical knowledge and talents have a noticeable impact on a patient’s health.
Q2. By when do you become a surgeon?
Surgical residents begin their training between the ages of 24 and 30 years old.
Q3. Can an MBBS doctor perform surgery?
An MBBS doctor without a PG degree is now prohibited from performing operations, anaesthetic treatments, or C-sections.
Pharmacology is the scientific study of how pharmaceuticals and chemicals impact living beings. A drug is any chemical molecule, natural or manmade, that has an effect on a biological system. It could include studying how organisms process medications, identifying and validating new drug targets, and designing and developing new drugs to prevent, treat, and cure disease.
Within the broad field of pharmacology, there are numerous sub-specialties- Pharmacodynamics is the study of medications’ impacts on biological systems, with a focus on the chemical characteristics, physiological, and behavioral consequences of drugs resulting from interactions with molecular targets like receptor proteins or enzyme systems. Pharmacokinetics, on the other hand, is the study of how biological systems interact with drugs. It includes studies of drug absorption, distribution, biotransformation, and excretion, which provide critical information for the design of drug treatment schedules in various patient populations and experimental animals, as well as the prediction of drug-drug interactions that may improve or compromise the efficacy and safety of therapeutic agents.
CBME-Based Pharmacology for UnderGrads
The curriculum in pharmacology has witnessed a change from dispensing pharmacy-based curriculum to an “applied” approach, where the emphasis is on how the student prescribes rationally, taking into view the various facets of the medicine and the patient. Traditional pharmacology education has been criticized for failing to prepare students for medical practise or to teach students how to use medications safely and rationally. The mention of these in the textbooks is perfunctory. The need for a change to a competency-based curriculum was thus felt worldwide, and hence, the new CBME Curriculum has emphasized the below-mentioned competencies for an undergraduate student.
- Be able to recognize common drug formulations, appreciate their benefits and drawbacks, and choose the best one for a specific illness.
- Be familiar with the national essential drugs list, the criteria used to create it, its benefits, and how to utilise it in practise.
- Select personal or P-drugs for common conditions and make a proper prescription for a specific patient.
- Be aware of the advantages and disadvantages of pharmaceutical promotion and be able to appropriately respond to them.
- Recognize commercial and non-commercial sources of drug information and use them to stay current and prescribe medications.
- Be aware of the dangers of misusing drugs in general, and antimicrobials in particular. Be able to analyze prescriptions using the WHO prescribing indicators and be able to use the same as a guide to their own prescribing behaviour.
- Communicate relevant drug and nondrug information about common diseases to patients in order to ensure drug therapy compliance.
- Be able to recognise, track, and report negative medication reactions.
- Understand the need of calculating medicine doses and determining accurate drug doses when necessary.
- Be able to advise patients on proper drug administration, including the use of specific equipment, as well as proper storage and disposal of medications.
Pharmacology for UnderGrads
Pharmacology for UnderGrads clarifies fundamental principles and keeps students up to date on the latest developments. It is one of the best online Pharmacology courses since the modules are aligned with the standard pharmacology textbook, making it easy for students to follow an organized approach.
The CBME curriculum has recently changed to emphasize the integration of all topics as well as the students’ clinical skills. The relevance of application-based learning has been emphasized in CBME, and the test questions are structured to measure students’ clinical knowledge. This course has well-integrated this unique way of studying the subject.
Pharmacology for UnderGrads was created under the guidance of Dr. Sandeep Kaushal and Dr. Nirmal George to make Pharmacology an exciting and entertaining trip without the need to memorize every drug and categorization. The faculty has discussed the art of studying pharmacology, including how to prepare for the theory, practical, and NEET/NEXT PG Exams.
The lectures are well-illustrated with pertinent visuals, flowcharts, tables, and boxes to help viewers grasp and recall information fast. The lectures’ animations assist students in connecting concepts to their daily lives. Each topic is supported by pharmacological notes and MCQs that serve as a revision aid. Additionally, each section is added with relevant questions with answer keys for self-assessment.
The Course Includes:
- Video Lectures: The course is enhanced by 70 hours of video lecture series.
- Lecture Notes: 77+ lecture notes assist students in speedy revision.
- Practicals: All of the necessary practicals have been covered to assist students in preparing for practicals and vivas.
- Self-Assessment Questions: 1500+ pharmacology MCQs with appropriate explanations are provided.
Table of Content – Pharmacology for UnderGrads
General Pharmacology
Rational Prescribing
Routes of Drug Administration
Factors Modifying Drug Action
Autonomic Nervous System
Adrenergic System: Actions & Endogenous Agents
Adrenergic System: Adrenergic Agonists
Adrenergic System: Adrenergic Antagonists
Autocoids
Prostaglandins
Respiratory System
Bronchial Asthma
Hormones & Related Drugs
Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Introduction
Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Antidiabetic drugs
Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Insulin
Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Mellitus: Ketoacidosis
PNS
CNS
Alcohols
Pharmacotherapy of Depression-1
Pharmacotherapy of Depression-2
Parkinson’s Disease
Antimania drugs
Anti-Psychotic Drugs
Opioids 1
CVS
Renal System
Diuretics
Blood and blood formation
Anticoagulants-I
GIT
Pharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer
Antimicrobials
Aminoglycosides
Anti-retroviral drugs
β-Lactam Antibiotics: Penicillin
Beta Lactam Antibiotics: Cephalosporins Carbapenems & Monobactam
Fluoroquinolones
Sulphonamides Antifolate Drugs
Tetracyclines and Chloramphenicol
Macrolides
Anti-Leprosy Drugs
Neoplastic Drugs
Ocular Pharmacology
Miscellaneous
Drug Development and Clinical Trials
Qbank
General Pharmacological Principles
Drugs Acting on Autonomic nervous System
Autacoids and Related Drugs
Respiratory System Drugs
Hormones and Related Drugs
Drugs Acting on Peripheral (Somatic) nervous System
Drugs Acting on Central Nervous System
Cardiovascular Drugs
Drugs Acting on Kidney
Drugs Affecting Blood and Blood Formation
Gastrointestinal Drugs
Antimicrobial Drugs
Chemotherapy of Neoplastic Diseases
Miscellaneous Drugs
Mistakes to avoid while studying Pharmacology
- Ignoring the taxonomy of significant drug families would be a big mistake.
- Undirected learning without a clear understanding of the purpose of reading a topic is a complete waste of time.
- Nausea and vomiting are surely the most common pharmacological side effects, however, it is highly necessary to focus on specific ones.
- Not placing enough emphasis on recalling the mechanism of action of a specific family of a drug.
- Reading dense notes with numerous references to diverse research that have no therapeutic application must be avoided.
- Relying primarily on books while ignoring other resources such as videos, flowcharts, and so on.
- Not practising enough MCQs and focusing only on the theoretical part instead of clinical discussions.
Easiest Way to Learn Pharmacology
- Choose the right reference material – After you’ve attended all of your lectures, you’ll require a lot of revision material. The ideal method would be to approach pharmacology books with MCQs, keynotes, and simple graphics. Apart from textbooks, watch CBME-based Pharmacology videos that aim to provide conceptual clarity.
- Take Good Notes — To avoid forgetting about a large number of medications in Pharmacology, take legible and informative notes during all of your lectures so that you may refer to them later. While writing improves memory, having visually appealing notes increases your chances of recalling concepts quickly throughout the exam. Organize the topics using flowcharts, tables, graphs, and graphics.
- Test your knowledge with your buddy – Keep assessing your knowledge whenever you are with your friends. This will ensure that you are on the same page as them and will help you to know the different techniques your friends use to remember the vast amount of drugs.
- Break down drugs by indication and class – Sort medications by what they’re used for, and then by their class. Indications, contraindications, and other characteristics of medications in the same class are often the same. Learn them in general terms; you can always return to your CPGs for specifics, but you must first know what to use. Also, while learning the physically equivalent system (respiratory drugs/cardiovascular drugs, etc.), learn pharmacological actions.
- Create your chart – Make a chart in alphabetical order and read it over and over again. The chart must include the drug name, the generic names, the dosages, the indications, the contraindications, as well as the mechanism of action, the drug type, and diseases or conditions it is given for.
- Practise Previous Years’ Question Papers –Solving previous years’ question papers is crucial in pharmacology. This can serve as a fantastic pre-exam practise test while also teaching you exam patterns and questioning techniques. By attempting as many questions as possible, you can get familiar with the test format and the important topics that are asked most often in the exam.
- Find a teaching methodology that works for you – If you need comprehensive understanding, leave some time for self-assessment daily. If you want to make learning interesting, DigiNerve’s Pharmacology for UnderGrads course adopts a CBME-based approach. Access video lectures, MCQs, notes, IBQs, and VBQs to stimulate visual memory.
Scope of Pharmacology
Pharmacologists must have a strong foundation in physiology, cell biology, biochemistry, and molecular biology to gain specific expertise and experimental methodologies for studying areas of drug action. Such study could focus on molecular interactions, cellular and subcellular signal transduction pathways, tissue and organ regulation, as well as integrated physiological or behavioural responses in organisms. The knowledge gathered assists in the development of novel medications as well as rational therapies, which entail the safe and effective use of drugs for therapeutic purposes. Furthermore, pharmacologists’ interdisciplinary knowledge provides them with a unique perspective on several biomedical difficulties, as well as improved employment opportunities in a variety of scientific domains.
Here are some professions to consider:
- Academic Researcher
- Biomedical Scientist
- Clinical Research Associate Clinical Scientist- Biochemistry
- Clinical Scientist- Immunology
- Medicinal Chemist
- Pharmacologist
- Research Scientist (Life Sciences)
- Research Scientist (Medical)
- Scientific Laboratory Technician
- Community Pharmacist
- Higher Education Lecturer
- Medical Sales Representative
- Medical Science Liaison
- Neuroscientist
- Patent Attorney
- Regulatory Affairs Officer
- Science Writer
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Q1. What are the types of pharmacology?
Ans. Pharmacology has two major branches:
- Pharmacokinetics is the study of how medications are absorbed, distributed, metabolised, and excreted.
- Pharmacodynamics includes a pharmacological mechanism of action, refers to the molecular, biochemical, and physiological impacts of medications.
Q2. What is the difference between pharmacology and pharmacy?
Ans. A drug can be broadly described as any human-made, natural, or endogenous chemical, and pharmacology is the discipline of medicine and biology concerned with the study of drug activity. The science and art of making and dispensing medications studied and created by pharmacologists is known as pharmacy.
Q3. How can I become a pharmacologist?
Ans. Pharmacologists need an advanced degree such as a Ph. D., Pharm. D., or M.D. Students who want to work in clinical pharmacology should have a medical degree.
Q4. What is the scope of studying Pharmacology?
A degree in pharmacology can lead to research positions in academia, industry, scientific civil service, and hospitals. You can work as a liaison between pharmaceutical corporations, doctors, and patients. Besides, product management or areas such as marketing and medical information are also approached.
Ophthalmology is a medical specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of eye diseases and their complications. Ophthalmology, once considered a minor discipline, has recently expanded to include a variety of subspecialties such as the cornea, pediatric ophthalmology, ocular oncology, glaucoma, ocular pathology, and neuro-ophthalmology.
Studying ophthalmology according to the previous syllabus made it difficult for students to figure out which topics they should emphasize more, how to organize their studies, what practical aspects/skills to know and acquire, and so on. The new CBME Curriculum focuses on core competencies and outlines the learning domain as well as the depth to which a concept should be explored. The AETCOM Module, which stands for Attitude Ethics and Communication, defines the competencies on which the curriculum is built. This is in place to ensure that graduates have the skills they need to meet patients’ needs in society.
DigiNerve’s Ophthalmology for UnderGrads has been conceptualized and designed in accordance with the new CBME curriculum. The aim is to help MBBS students get conceptual clarity and farewell in university exams as well as PG entrance exams. Dr. Parul Ichhpujani and Dr. Talvir Sidhu, the eminent faculty for this course, have addressed all of the subject’s essential aspects in their CBME-oriented Ophthalmology Course. This is one of the best online ophthalmology courses since it aims to provide students with specific competencies more effectively.
Some of the major books authored by Dr. Parul Ichhpujani are “Expert Techniques in Ophthalmic Surgery”, “Clinical Cases in Glaucoma: An Evidence-Based Approach”, and “Manual of Glaucoma”, while Dr. Talvir Sidhu is renowned for her book “Gonioscopy: A Text and Atlas” and “Gonioscopy: A video-assisted Skill Transfer Approach” (includes interactive DVD-ROM).
The faculty has covered the art of studying ophthalmology in order to prepare students for theory, practical, and NEET PG examinations. The orientation video itself provides them with a road map to approach the subject. This online ophthalmology course is designed to help MBBS students in strengthening the basics of Ophthalmology by providing them with advanced clinical vignettes. This provides clinical orientation to the subject.
Each topic includes an overview of the anatomy and physiology of that part, which will serve as a refresher for students. It will also assist them in comprehending the aetiology of various disorders, as well as providing a full description of how each ailment would manifest on ocular inspection. In this Online Ophthalmology Course, basic history-taking and clinical examination of the eye are demonstrated as an extended lecture to provide students with a full overview. The lectures are well-illustrated with clinical and radiological pictures, as well as flowcharts, tables, and boxes to enhance the visual memory of the students.
The Course Includes:
- Video Lectures: 21+ hrs of video lecture series that give you an edge over others.
- Lecture Notes: 33 lecture notes including simple advanced-case vignettes to enhance knowledge during preparation.
- Clinical Case-Based Discussion: The course includes various practical case scenarios which are usually not given in textbooks.
- Self-Assessment Questions: 1000+ practice questions are provided with relevant explanations
DigiNerve’s Ophthalmology for UnderGrads- Table of Content
Ocular Examination
Basic History And Ocular Examination
Visual acuity
Vision assessment
Refractive Errors
Extraocular muscles and Ocular motility
Strabismus to Amblyopia
Extraocular Muscles -Strabismus
Nerve Palsies
Lids and Adnexa
Lid and Adnexal Disorders-1
Lid and Adnexal Disorders-2
Orbit
Proptosis, Orbital Cellulitis and Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
Orbital Tumors
Conjunctiva
Red Eye by
Conjunctival Disorders
Cornea
Corneal Ulcer: Bacterial and Fungal
Corneal Ulcer: Viral
Eye donation and Eye banking
Sclera
Scleritis and Episcleritis
Anterior chamber and Uvea
Anterior Chamber
Uveitis
Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
Lens
Anatomy and Physiology
Cataract: History, Examination and Consent
Cataract: Diagnosis & Planning Surgery
Cataract Surgeries
Retina
Basics of Fundus Examination
Vascular Occlusions of Retina
Hypertensive & Diabetic Retinopathy
Retinal Detachment by
Management Modalities for Retinal Disorders
Optic Nerve
Diseases of Optic Nerve
Miscellaneous
National Programme for Control of Blindness and Visual Impairment (NPCB & VI) and Vision 2020
Ocular Trauma
Visual Rehabilitation in the Elderly
How to Study Ophthalmology?
Study from Reliable Resources: The new CBME curriculum stresses key competencies and outlines the learning domain as well as the level at which a subject must be learned. As a result, students must concentrate on locating the most relevant and reliable content which is as per the latest curriculum.
Watch Clinical Case Discussions: The online Ophthalmology course on DigiNerve is ideal for gaining conceptual clarity through clinical case discussions. This course was designed and developed in accordance with the new CBME curriculum. It comprises an extended presentation that includes a demonstration of basic history-taking and clinical examination of the eye to provide students with a full overview.
Practise from Exam POV: To receive maximum exposure for your university exams and NEET PG Exam, practise as many questions as possible.
Learn from best mentors: Find popular study resources by specialists who cover the art of studying ophthalmology as well as content as per theory, practical, and NEET PG exams. It’s helpful if your professor provides you with a strategy for approaching the subject.
Study Ocular Examination in depth: In each chapter, focus on anatomy and physiology, as well as the pathophysiology of various diseases, and a full explanation of how each condition would appear on the ocular examination. To strengthen your memory, look for clinical and radiological images, as well as flowcharts, tables, and boxes, wherever they are needed.
How to Study Ophthalmology for NEET PG?
When preparing for NEET-PG, it is essential to study from the appropriate books. Students are frequently enticed by texts that promise shortcuts. As the candidate approaches the subject, such books have a negative impact on their psychology. Therefore, referring to recommended books is critical, as these books help students to dodge doubts.
Some of the most important topics in Ophthalmology are:
- Lens – Surgeries, Ectopia lentis, Cataract, and related concepts, their complications, and solutions are very important. You should also be well-versed in the Anatomy and Physiology of lens.
- Cornea – Anatomy and Physiology, Keratitis, Congenital Anomalies of Cornea, and Cornea Degeneration
- Conjunctiva – Conjunctivitis, Trachoma, Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis, Phlyctenular Conjunctivitis, Dry Eye, Pterygium, and Pinguecula.
- Glaucoma – POAG, PACG, Secondary Glaucoma, and Surgeries and Drugs
- Orbit – Blunt Trauma, Orbit Fracture, Orbit Tumors, Proptosis, and Chalcosis
- Eye – Surgeries, and Ptosis (Measurement and Causes)
- Lacrimal – Epiphora, and Dacryocystitis Treatment
- Retina – CRVO, CRAO, CME, CSR, Diabetic Retinopathy, ARMD, Retinoblastoma, Retinitis Pigmentosa, BEST, Stargardt Disease, Coats Disease, Retinoscopy, Ophthalmoscope, and ROP
- Optics – Criteria, Definitions and Types of Refractive Error, Surgeries, and Contact Lens
- Neuro-Ophthalmology – Pathway, Reflex, Papillitis, Papilledema, Toxic Amblyopia, Squint, and Optic Neuritis
- Community Ophthalmology – NBCP & Xerophthalmia
Scope of Studying Ophthalmology
- Cataract Specialists or Surgeons: These are professionals who perform surgery to remove the natural lens and replace it with an artificial lens in order to alleviate the patient’s problem of opacity or blurred vision.
- Neuro-Ophthalmology Specialist: An expert in this profession deals with eye disorders related to the neurological system. Some serious concerns, such as optic nerve abnormalities impacting visibility, trouble controlling eye movement, double vision, and so on, require rapid treatment from a Neuro-Ophthalmologist. A specialist who is a master of Ophthalmology is essential for the study of both neurology and ophthalmology.
- Retina Specialists: These professionals deal with issues affecting the Retina. These issues are usually caused by injury or damage to the retina, which can occur as a result of retinal detachment, abrupt flashes, or floaters.
- Cornea Specialist: This expert is responsible for providing treatments and surgeries to address any damage, illness, or disease that affects the human eye’s Cornea, Conjunctiva, Eyelids, and Sclera. They must take preventative actions to prevent additional harm and to recover the injury that is affecting the patient’s vision.
- Oculoplastics Specialists: They are specialists who work to repair and remodel the eye. They deal with eyelid surgery and abnormalities in the orbit and lacrimal system, as well as disorders in the area surrounding the eyeball.
- Pediatric Ophthalmologist: Professionals in this discipline deal with any ocular problem that affects children’s eyes. Strabismus, genetic abnormalities, amblyopia, neoplastic disorders, conjunctivitis, and misalignment of the eyes are some of the primary significant problems that Pediatric Ophthalmologists treat.
- Ocular Immunology Specialist: The specialist’s job is to control issues with the human body’s immunology, which can lead to a variety of eye-related illnesses and diseases. Corneal ulcers, uveitis, sclerosis, and any sort of eye inflammation are examples of these illnesses. These specialists collaborate closely with general practitioners.
Additional jobs to choose from are Professor/Lecturer, ENT Specialist, Clinical Assistant, and Medical Consultant.
FAQs
1 – What’s the difference between an optometrist and an ophthalmologist?
Patient’s eyes are examined, diagnosed, and treated by optometrists. Ophthalmologists are doctors who specialize in the medical and surgical treatment of eye diseases.
2 – Is being an ophthalmologist a good career choice?
Ophthalmology is a nice blend of surgical and medical practise, and many people can focus on either of these. Those interested in surgery will need time to adjust to this microsurgical field, but with the correct instruction, anyone with basic hand-eye coordination can master it.
3 – Does ophthalmology have any scope for the future?
According to the Health Resources and Services Administration, by 2025, there will be a demand for about 22,000 ophthalmic surgeons. However, it was predicted that more than 6,000 physicians would fall short of the requirement.
4 – Is ophthalmology a simple subject to learn?
It is regarded as one of the most difficult branches to study and practise, requiring complete dedication as well as knowledge and developed skills. This branch of medicine is characterized by a variety of extraordinary traits.
5 – How do I go about becoming an ophthalmologist after completing my MBBS?
One must first obtain an MBBS degree and then pursue post-graduate studies in Ophthalmology to become a competent Ophthalmologist.
Microbiology is a complex, lab-intensive subject that necessitates conceptual clarity. To ace the subject, you’ll need a lot of memorization and logic, but with the correct books and lectures, you’ll start enjoying it. When it comes to resources, Dr. Apurba S Sastry’s “Essentials of Medical Microbiology” and “Paniker’s Textbook of Medical Parasitology” (based on the CBME curriculum) are two of the best. You won’t have the right understanding of organisms unless and until you look at them and study them, therefore getting proper exposure to practicals and going to labs is crucial. Read Dr. Apurba S Sastry and Dr. Sandhya Bhat’s “Essentials of Practical Microbiology” to gain a better understanding of practicals. This book will give you a hands-on experience with microbiology practicals.
To get conceptual clarity, the best way to study Microbiology online is by watching Microbiology video lectures by Dr. Apurba Sastry. His video lectures are only available on DigiNerve. The book’s TOC and the TOC of his video lectures are identical, and they complement each other. Microbiology for UnderGrads course is divided into 2 parts- (I) General Microbiology, Immunology, and Hospital Infection Control and (II) Systemic Microbiology. It aids in the development of a solid theoretical and practical foundation for undergraduate students. The lectures take a case-based approach with a discussion of topics, eliminating the need to consult many texts.
The Course includes:
- 150 hours of video lecture on 81 microbiology topics.
- 81 lecture notes with simple advanced-case vignettes.
- The lectures go over a variety of practical case scenarios that aren’t normally included in textbooks.
- Learning methodologies such as SDL and SGDs are based on the new CBME Curriculum.
- A series of 4000 must-know multiple-choice questions help students to assess their knowledge
The course also includes flow charts, diagrams, and graphics for easier recollection; pre-made notes save time when it comes to reviewing. DigiNerve provides Microbiology notes for MBBS preparation because taking notes might be time-consuming. For ease of understanding and memorization, the notes are illustrated by clinical, histological, radiological, and gross images. Furthermore, each topic has tons of multiple-choice questions (MCQs) to test your understanding.
CBME-Based Microbiology for UnderGrads Course
While the old curriculum focused on studying microbiology organism-wise, the new CBME curriculum takes a system-based approach to learn microbiology by classifying organisms as per respective systems of the body. This means it concentrates on organisms as a system, which is a more convenient way to understand the subject. Microbiology for UnderGrads is the first online microbiology course to integrate the system-based approach as per the New CBME Curriculum. Dr. Apurba Sastry has thoroughly explained everything as per the CBME curriculum. He has also discussed the most recent improvements, such as COVID-19.
The competencies on which the curriculum is based, are defined by the AETCOM Module, which stands for Attitude Ethics and Communication. This is introduced to ensure that graduates gain the skills needed to meet the demands of patients in society.
How does Microbiology for UnderGrads help you avoid mistakes?
As the MBBS Syllabus is so vast and concepts so complex, students tend to make some mistakes. These could be because of a lack of consistency, overconfidence, or under-confidence that can change the game for any student. There are some typical pitfalls to avoid when studying microbiology online to achieve success in your grades and career.
- Don’t take notes lightly – Take meticulous notes throughout all lectures so that you retain information faster, and have maximum content to revise. In case you have skipped making notes, you can access lecture notes on high-yield topics on DigiNerve. The content on the app is backed by Jaypee Brothers, a pioneer and global leader in health science publishing with a legacy spanning over 5 decades.
- Don’t be either insecure or overconfident – Insecurity can lead to trivial mistakes like second-guessing yourself and wasting time reading over answers you’ve already completed, both of which can make studying microbiology way stressful. Overconfidence, on the other hand, might lead to sloppy revision or a careless attempt. Practise maximum MCQs available on the app to gain confidence while assessing your knowledge simultaneously.
- Wave off any negative thoughts – You must keep in mind that one grade or course result has very little bearing on your overall medical journey to becoming a top doctor. Keep this in mind when you learn microbiology online and focus on conceptual clarity rather than marks. Dr. Apurba Sastry in his systemic approach to Microbiology discusses every topic comprehensively in his course- Microbiology for UnderGrads; this is the best online Microbiology course to gain conceptual understanding. After you’ve completed the needed studying for the day, try to find some time to unwind to help you regain a positive attitude for the next day.
- Isolating oneself – Socializing while studying microbiology online may not seem easy, but finding methods to connect with people, even if it is just virtually, may be extremely beneficial not only in terms of making you feel better but also in terms of boosting learning. You can meet like-minded people that inspire you to work harder by forming a study group to prepare for either exam or simply study microbiology online with Dr. Apurba Sastry.
- Ignoring Doubts – Avoid suppressing your doubts for fear of appearing foolish or unimportant. Ask your doubts while you study so that you achieve clarity before appearing for the microbiology exam. This will save you time in the long run, boost your confidence, and broaden your expertise.
The Easiest way to learn Microbiology
Microbiology is a boring subject to study for most students, but doing so from an online platform allows for a more fluid flow of knowledge and a better learning experience. Unlike previous medical microbiology courses, new microbiology courses on online platforms like DigiNerve include high-quality video lectures from India’s best academics, MCQs, notes, and much more. These will make microbiology enjoyable, productive, and engaging. Here are a few ideas to make Microbiology simpler to avoid any form of second-year slump
- Learn from India’s Eminent Faculty – How about studying from the author of your textbook himself? Luckily, DigiNerve’s Microbiology for UnderGrads Course is mentored by the renowned academician– Dr. Apurba Sastry. He is affiliated with JIPMER and has published 9 successful books, including the best-seller ‘Essentials of Medical Microbiology’, and around 47 specialized medical articles in acclaimed journals. Your education extends beyond simply learning from books when you have faculty like him on your side to guide you throughout your top doc journey.
- Choose the right reference material – You’ll need a lot of revision material once you’ve attended all of your lectures and the time for your microbiology exam arrives. Microbiology books with MCQs, keynotes, and easy-to-understand graphics are the best way to accomplish this. Apart from exam preparation material, DigiNerve has clinical and systemic Microbiology content that is CBME-based and aims to provide conceptual clarity.
- Maintain Good Notes – To not forget the vast syllabus of Microbiology, maintain legible and informative notes during all of your lectures so that you can use them later on. While writing boosts memory, visually appealing notes enhance your chance of recalling information instantly at the time of the exam. To boost your memory, refer to notes like those on DigiNerve, that are equipped with flowcharts, tables, diagrams, images, etc.
- Practise Previous Years’ Question Papers – Solving previous years’ question papers is crucial in microbiology. This can serve as a fantastic pre-exam practise test while also teaching you exam patterns and questioning techniques. By answering as many questions as possible, you will become familiar with the test format as well as the important topics that are asked most frequently in the exam
- Find a teaching methodology that works for you – If you need comprehensive understanding, leave some time for practicing self-assessment daily. If you want to make learning interesting, DigiNerve’s Microbiology for UnderGrads course adopts a systemic approach as per CBME Curriculum. Access video lectures, IBQs, and VBQs along with flowcharts, tables, and diagrams to stimulate visual memory.
Topics covered in Microbiology for UnderGrads by Dr. Apurba Sastry
Module 1: General Microbiology
- Introduction and History
- Microscopy
- General Bacteriology
-
- Bacterial Taxonomy
- Morphology and Physiology of Bacteria
- Laboratory Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections
- Bacterial Genetics
- Antimicrobial Agents and Antimicrobial Resistance
- Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infections
- Overview of Bacterial Infections
- General Virology and Overview of Viral Infections
- General Parasitology and Overview of Parasitic Infections
- General Mycology and Overview of Fungal Infections
- Normal Human Microbiota
- Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases
Module 2: Immunology
- Immunity (Innate and Acquired)
- Antigen
- Antibody
- Antigen-antibody Reaction
- Complement
- Components of Immune System
- Immune Responses
- Hypersensitivity
- Autoimmunity
- Immunodeficiency Disorders
- Transplant and Cancer Immunology
- Immunoprophylaxis
Module 3: Hospital Infection Control
- Healthcare-associated Infections
- Major Healthcare-associated Infection Types
- Sterilization and Disinfection
- Biomedical Waste Management
- Needle Stick Injury
- Antimicrobial Stewardship
- Environmental Surveillance (Bacteriology of Water, Air and Surface)
Module 4: Bloodstream and Cardiovascular System Infections
- Cardiovascular System Infections: Infective Endocarditis and Acute Rheumatic Fever
- Bloodstream Infections
- Enteric Fever
- Rickettsial Infections
- Miscellaneous Bacterial Bloodstream Infections
- HIV/AIDS
- Viral Hemorrhagic Fever (VHF)
- Malaria and Babesiosis
- Visceral Leishmaniasis and Trypanosomiasis
- Lymphatic Filariasis
- Systemic Candidiasis and Systemic Mycoses
Module 5: Gastrointestinal (GI) Infections
- Gastrointestinal Infective Syndromes
- Food Poisoning
- Gastrointestinal Infections due to Enterobacteriaceae
- Cholera, Halophilic Vibrio and Aeromonas Infections
- Miscellaneous Bacterial Infections of Gastrointestinal System
- Viral Gastroenteritis: Rotaviruses and Others
- Intestinal Protozoan Infections
- Intestinal Helminthic Infections
Module 6: Hepatobiliary System Infections
- Infective Syndromes of Hepatobiliary System and Abdomen
- Viruses Causing Hepatitis
- Parasitic Infections of Hepatobiliary System
Module 7: Skin, Soft Tissue and Musculoskeletal System Infections
- Infective Syndromes of Skin, Soft Tissue and Musculoskeletal Systems
- Staphylococcal Infections
- Beta-hemolytic Streptococcal Infections
- Gas gangrene and Infections due to Nonsporing Anaerobes
- Leprosy
- Miscellaneous Bacterial Infections of Skin and Soft Tissues
- Viral Exanthems and Other Cutaneous Viral Infections
- Parasitic Infections of Skin, Soft Tissue and Musculoskeletal System
- Fungal Infections of Skin, Soft Tissue and Musculoskeletal System
Module 8: Respiratory Tract Infections
- Infective Syndromes of Respiratory Tract
- Bacterial Pharyngitis
- Bacterial Lobar Pneumonia
- Bacterial Atypical (Interstitial) Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacteria Infections
- Pertussis
- Infections due to Non-fermenting Gram-negative Bacilli
- Myxovirus Infections of Respiratory Tract
- Coronavirus Infections Including COVID-19
- Miscellaneous Viral Infections of Respiratory Tract
- Parasitic and Fungal Infections of Respiratory Tract
Module 9: Central Nervous System Infections
- Infective Syndromes of Central Nervous System
- Bacterial Meningitis
- Tetanus
- Viral Meningitis and Myelitis
- Viral Encephalitis and Encephalopathy
- Parasitic and Fungal Infections of Central Nervous System
Module 10: Urogenital Tract Infections
- Infective Syndromes of Urinary Tract
- Infective Syndromes of Genital Tract
Module 11: Miscellaneous Infective Syndromes
- Ocular and Ear Infections
- Congenital Infections
- Organisms with Oncogenic Potential
- Zoonotic Infections
Module 12: Microbiology Practical
- Introduction
- Gram Staining
- Acid fast staining
- Stool Microscopy
- Specimen Collection
- Hospital Infection Control
- Problem Solving Exercise
Module 13: QBanks
Now that you know the best and most basic tips to help you ace your second year, click here to view DigiNerve’s Microbiology for UnderGrads course.
FAQs:
- Is Microbiology in MBBS difficult to study?
Microbiology is complex but if you study the right way referring to the best resources, you can ace it in the least amount of time. Access Dr. Apurba Sastry’s Microbiology for UnderGrads course to watch his video lectures, MCQs, and notes. His book – “Essentials of Medical Microbiology” is the most popular book to study Microbiology.
- What is the scope of studying Microbiology?
Graduates of Microbiology MD can find work in the private and public sectors of a variety of reputable institutions in India and overseas. The wide range of career options includes Biological Scientist, Physical Therapist, Dental Hygienist, Medical Scientist, Surgical Consultant, and so on.
- Which is the best app to prepare for Microbiology?
DigiNerve is the best app if you need conceptual clarity in Microbiology. Dr. Apurba Sastry’s video lectures and MCQs at the end of each lecture make Microbiology for UnderGrads the most sought-after course among MBBS students.