Everything is made for a defined purpose anything which is not intended for further use is termed waste. In the scientific and industrial eras combined with the increasing population, the turnover of products has gone very high increasing the quantum of urban solid waste. With the increased need for health care in a changing society the role of hospitals/nursing homes comes to the forefront.
Hospital waste or types of healthcare waste should include any material generated in healthcare establishments including aqueous and other liquid waste.
Hospital waste means any solid, fluid, or liquid waste material including its container and any other intermediate product which is generated during short-term and long-term care consisting of observational, diagnostic, therapeutic, and rehabilitative services for a person suffering or suspected to be suffering from disease or injury and for parturient or during research of production and testing of biological during immunization of human being.
Types of Healthcare waste facilities are responsible for managing healthcare waste generated within their facilities, as well as waste generated through activities in the community. These facilities must undertake proper segregation, collection, in-house transportation, pre-treatment, and waste storage before handing it over to a Common Bio-medical Waste Treatment Facility (CBWTF) operator.
Therefore, proper management of healthcare waste at these facilities necessitates that all categories of staff understand and adhere to the technical requirements for waste handling as per the Biomedical Waste Management Rules, 2016.
Classifications of Waste Generated from Healthcare Sectors
1. Bio-Medical Waste
It refers to any waste produced during diagnosis, treatment, or immunization of humans or animals as well as related research activities, or during the production or testing of biologicals in health camps. This includes all waste from healthcare facilities that could potentially harm human health or the environment if improperly disposed of. Such waste is considered infectious and must be managed according to the Biomedical Waste Management Rules of 2016 to prevent adverse effects on health or the environment.
Around 10% to 15% of the total waste generated by healthcare facilities constitutes biomedical waste. This category includes materials that have come into contact with patients’ blood, secretions, infected body parts, biological fluids, chemicals, medical equipment, pharmaceutical waste, laboratory discharge, sharp objects like needles and glassware, and plastics.
According to the Biomedical Waste Management Rules of 2016, this waste is categorized into four types based on how it is segregated and color-coded. Each category includes specific types of biomedical waste, as given below:
- Yellow Category
- Red Category
- White Category
- Blue Category
These categories are divided as per the types of waste under each category as follows:
| Category | Type of Waste |
| Yellow | Human Anatomical Waste
Human tissues, organs, body parts, and fetus below the viability period (as per the Medical Termination of Pregnancy Act 1971, amended from time to time). |
| Animal Anatomical Waste
Experimental animal carcasses, body parts, organs, and tissues, including the waste generated from animals used in experiments or testing in veterinary hospitals or colleges, or animal houses. |
|
| Solid Waste
Items contaminated with blood, body fluids like dressings, plaster casts, cotton swabs, and bags containing residual or discarded blood and blood components. |
|
| Discarded Medicine
Pharmaceutical waste like antibiotics, and cytotoxic drugs including all items contaminated with cytotoxic drugs along with glass or plastic ampoules, and vials. Etc. |
|
| Chemical Waste
Chemicals used in the production of biological and used or discarded disinfectants. |
|
| Chemical Liquid Waste
Liquid waste is generated due to the use of chemicals in the production of biological and used or discarded disinfectants, Silver X-ray film developing liquid, discarded Formalin, infected secretions, aspired body fluids, liquid from laboratories, and floor washings, cleaning, housekeeping and disinfecting activities, etc. |
|
| Discarded linen, mattresses, beddings contaminated with blood or body fluid, routine mask & gown. | |
| Microbiology, Biotechnology, and other clinical laboratory waste (Pre-treated) | |
| Microbiology, Biotechnology, and other clinical laboratory waste: Blood bags, laboratory cultures, stocks or specimens of microorganisms, live or attenuated vaccines, human and animal cell cultures used in research, industrial laboratories, production of biological, residual toxins, dishes, and devices used for cultures. | |
| Red | Wastes are generated from disposable items such as tubing, bottles, intravenous tubes and sets, catheters, urine bags, syringes without needles, fixed needle syringes with their needles cut, vacutainers, and gloves. |
| White | Waste Sharps Including Metals
Needles, syringes with fixed needles, needles from needle tip cutters or burners, scalpels, blades, or any other contaminated sharp object that may cause punctures and cuts. This includes both used, discarded, and contaminated metal sharps. |
| Blue | Broken or discarded and contaminated glass including medicine vials and ampoules except those contaminated with cytotoxic wastes. |
2. General Waste
General waste includes all waste other than biomedical waste that has not been in contact with hazardous waste or infectious materials, chemicals, or biological secretions, and does not include sharp objects. This type of waste typically includes:
- Newspaper, paper, and cardboard boxes
- Plastic water bottles
- Aluminum cans from soft drinks
- Packaging materials
- Food containers after removing leftover food
- Organic or biodegradable waste, mainly food waste
- Construction and demolition waste
These general wastes are classified as wet wastes and dry wastes and should be collected separately. The quantity of general waste is around 85% to 90% of the total generated from the facility.
3. Other Wastes
Other wastes include electronic devices such as batteries and radioactive materials that are not classified as biomedical waste. They must be disposed of according to specific regulations: the E-waste (Management) Rules of 2016, the Batteries ( Management & Handling) Rules of 2001, and the rules or guidelines established under the Atomic Energy Act of 1962, depending on the type of waste generated.
Guidelines for Management of Healthcare Waste Categories as per Biomedical Waste Management Rules, 2016
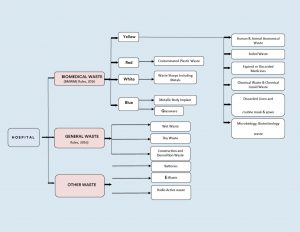

Figure 1: Categorization & Classifications of Wastes in Health Care Facilities.
Color Coding and 4 types of dustbins in hospitals used for Waste Segregation & Collection
According to Schedule I of the Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules of 2016, healthcare facilities (HCFs) must use specific color-coded dustbins and types of containers/bags for segregating and collecting biomedical waste generated within the facility.
| Category | Type of Waste | Colored Container & Type of Container | Treatment Options as per Schedule I |
| Yellow Category |
|
Yellow-colored non-chlorinated Plastic Bags.
NOTE: |
Incineration/deep burial |
| Red Category |
|
Red Colored Non-Chlorinated Plastic Bags (having thickness equal to more than 50u) and containers. | Autoclaving/microwaving/chemical treatment |
| White Category |
|
White Colored translucent puncture-proof, leak-proof, tamper-proof containers. | Autoclaving/microwaving/chemical treatment and destruction/shredding |
| Blue Category |
|
Puncture-proof, leak-proof boxes or containers with blue-colored markings. | Disposal of wastes and secured landfill |
Bio-Medical Waste Collection
Time of Collection
- Daily Collection: Ensure daily collection from each hospital ward at fixed intervals.
- Timing Adjustments: Schedule collections based on waste generation patterns throughout the day.
- Separate Collection: Avoid collecting general waste concurrently with biomedical waste.
- Visitor Waste Management: Collect general waste immediately after visiting hours to prevent accumulation.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Provide PPE to staff handling biomedical waste.
Packaging
- Filling and Sealing: Fill biomedical waste bags and sharp containers up to three-quarters full and seal them promptly.
- Sealing Methods: Use ties or plastic tags to seal bags to avoid stapling.
- Availability of Replacement: Ensure replacement bags or containers are readily available at collection points.
- Labeling Requirements: Label bags and containers with biohazard symbols, including details like date, type of waste, quantity, and sender’s and receiver’s information.
- Barcode Compliance: Affix barcoded labels on the bag as per CPCB guidelines.
Labeling
- Biohazard Symbols: Clearly label all bags, containers, and bins with biohazard or cytotoxic symbols as per BMWM Rules, 2016.




Interim Storage
- Minimization: Discourage interim storage of biomedical waste in patient care areas.
- Designated Areas: Store biomedical waste temporarily in designated, low-traffic areas if necessary.
Treatment Option for Bio-medical Waste Types
| Treatment Options | Biomedical Chemical Processes |
| Thermal Processes Low-heat Systems (93-177oC) |
|
| High-heat Systems |
|
| Mechanical Processes |
|
| Irradiation Processes |
|
| Biological Processes |
|
| Considerations for Processing Incineration |
|
| Autoclaving |
|
| Microwaving |
|
| Deep Burial |
|
| Sharp Materials Disposal |
|
| Radioactive Waste |
|
| Mercury Control |
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is clinical waste, and how is it different from infectious waste?
Ans. Clinical waste includes all waste generated from medical facilities, including non-infectious materials like packaging and expired medications, whereas infectious waste refers to waste contaminated with pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms.
Q2. What are the proper disposal techniques for biomedical waste, particularly sharps waste?
Ans. Sharp waste like needles and scalpels, must be disposed of in puncture-proof containers specifically designed for sharps disposal. These types of containers are sealed and handled carefully to prevent injuries and potential infections during disposal.
Q3. How does improper medical waste management contribute to the spread of diseases?
Ans. Improper management of biohazardous waste can lead to contamination of the environment and increase the risk of spreading infectious diseases. Pathogens present in medical waste, if not managed correctly, can infect healthcare workers, patients, and the normal public.
Q4. What is some risk associated with inadequate handling of pathological waste?
Ans. Pathological waste which includes tissues, organs, and body parts, poses significant health risks if not properly managed. Exposure to such waste can lead to infections or exposure to hazardous chemicals used in treatments.
Q5. Why is it important for medical facilities to use appropriate medical waste containers?
Ans. Medical waste containers are designed to safely store and transport various types of medical waste, including biohazardous materials and sharps. Using proper containers minimizes the risk of accidental exposure and ensures compliance with regulations for safe disposal.
DigiNerve is constantly evolving to enhance your experience while you’re on your journey to becoming a Top Doc. We are excited to bring you the latest updates with our commitment to ensure a seamless journey on the go.
Read on the July edition (Vol – 1) of our monthly newsletter to know the latest updates.
CONTENT UPDATES
PostGrad Course Updates
Dermatology MD:-
1. Chat show on ‘Discussion on Leprosy’ by Dr. Vivek Vasudev Pai, Dr. Shraddha Mahobia, and Dr. Samira Siddiqui Khatoon Mohd. Hanif has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- To learn the approach to a patient with leprosy.
- To understand the current scenario of leprosy and the National Strategic Plan for 2023-2027 for India.
- To learn the approach to patients with lepra reactions and relapse.
- To understand the management of patients with ENL reactions and relapse.
Pediatrics MD:-
1. Chat show on ‘Approach to a Child with Asthma’ by Dr. Piyush Gupta and Dr. Prawin Kumar has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Clinical presentation of asthma in children.
- How can a diagnosis of asthma in children be established?
- What is the role of the Pulmonary Function Test (PFT) in the diagnosis of asthma.
- Management of Asthma in Children.
Medicine MD:-
1. 8 new topics have been added to the following modules:
| Module | Section | Topic |
| Rheumatology | Long Case Discussions | Gout |
| Infectious Diseases | Clinical Scenarios | Amoebic Liver Abscess |
| Systemic Fungal Infections | ||
| Japanese Encephalitis | ||
| Critical Care Medicine | Decision Making | Central Venous Line |
| Intubation in Critically Ill Patients | ||
| Cardiology | Basic Sciences | Treadmill Test |
| Endocrinology and Diabetes | Long Case Discussions | Approach and Management of Hyponatremia |
Note: The topics mentioned above also include 39 new self-assessment and 16 benchmark trials.
Update Your DigiNerve App for Better Experience.
To read the updates shared in the Monthly Newsletter June (Vol-2), click here.
Cystoid macular edema is a condition of the retina in which fluid builds up in the macula central area responsible for clear central vision.
This condition involves ocular inflammation precipitated by cataract surgery, known as pseudophakic CME. It reported incidence after cataract surgery a common complication of 0.1-2.35%.
CME is the most common cause of decreased vision in patients following complicated cataract surgery, occurring much more frequently than either retinal detachment or endophthalmitis. Although CME was clinically recognized and described over 50 years ago much remains unknown about it.
Patients after cataract surgery are at risk for developing CME, a common complicated surgery leading to reduced vision. There are certain demographics that are considered a higher risk, including patients with diabetes, diabetic retinopathy, uveitis, posterior capsule rupture, vitreous prolapse, and previous retinal vein occlusions. Male gender and old age have also been identified as risk factors.
Pathophysiology of Macular Edema
Inflammation plays a large role in the pathogenesis of CME. Pro-inflammatory mediators substances such as Nitric oxide, Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (anti-VEGF injections), Prostaglandins, cytokines, and other mediators are involved in the inflammatory process that can occur following modern cataract surgery. This inflammation process leads to the destruction of the blood-retinal barrier causing increased vascular permeability. This results in edema of the inner nuclear layer, edema of the outer plexiform layer, accumulation of sub-retinal fluid and ultimately thickening of the retina.
The precise pathophysiology of CME has yet to be fully understood, several factors have been implicated in its development, including vascular instability, vascular traction, and relative ocular hypotony.
CME can lead to permanent vision loss, even after the edema resolves. This is believed to occur due to structural changes in the photoreceptors, which are more prevalent in chronic cases of CME.
Evaluation & Diagnosis
There are different methods for evaluating CME including non-contact and contact slip lamp biomicroscopy, FFA, Fundus stereo photography, indirect ophthalmoscopy, and OCT. Currently, FFA and OCT are the most used investigative tools.
Slit-lamp Biomicroscopy
They are typically conducted using a 78D lens and a 90D lens in the initial step to evaluate macular edema. This microscopic evaluation method reveals the location and presence of macular thickness, exudates, and cystoid changes.
CME is characterized by a unique stellate or radially oriented pattern in the peri-foveal thickness of cysts, attributed to the oblique arrangement of the Henle fiber layer.
Outside the macular region, edema presents a honeycomb appearance caused by the perpendicular alignment of the outer plexiform layer. A central cyst linked to CME may resemble a macular thickness. However, performing the Watzke-Allen test using slit lamp biomicroscopy with a 90D lens reveals an intact vertical without a central break.
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography
FFA can identify areas of retinal capillary leakage. The Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) classifies diabetic macular edema into diffuse focal types based on the extent of fluorescein leakage associated with microaneurysms.
According to ETDRS criteria, focal diabetic edema shows 67% or more leakage linked to microaneurysms, intermediate exhibits 33% TO 66% leakage, and diffuse displays less than 33% leakage associated with microaneurysms.
In the early phase of fluorescein angiography, choroidal fluorescence may be partially obscured by significant edema, whether cystoid or non-cystoid especially if the edema is turbid due to lipid-laden macrophages. Dilation of the fine capillary network of telangiectatic retinal vessels around the fovea may be evident in the arteriovenous phase.
In late-phase imaging, hyperfluorescence results from dye leakage from retinal vessels, influenced by the extent of dysfunction in the retinal vascular endothelium. This hyperfluorescence can appear as cystic or irregular staining, filling cystoid spaces rapidly with pronounced leakage or appearing later if leakage is less significant.
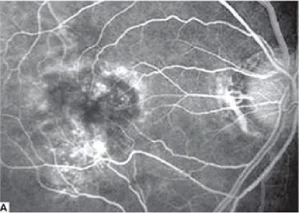

Fig.1.A: Fluorescein angiography shows cystoid macular edema.


Fig.1.B: Clinical photograph shows vitreous incarceration into the wound.
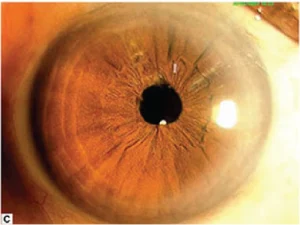

Fig.1.C: Clinical photograph post-vitreolysis.
Cystoid Macular Edema Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Clinicians utilize OCT to assess macular edema stemming from conditions such as age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, hereditary retinal degeneration, retinal vein occlusion, edema after cataract surgery, epiretinal membrane, and history of uveitis. Due to its high reproducibility, OCT has emerged as the preferred diagnostic tool for diagnosing and monitoring CME. OCT allows clinicians to identify, locate, and measure fluid accumulations, enabling accurate assessments and ongoing monitoring.
Furthermore, OCT’s ability to categorize different diseases supports prognosis, assists in disease management, predicts patient outcomes, and aids in treatment planning.
- Diabetic Macular Edema: Various patterns of fluid accumulation are visible on OCT scans in patients with diabetic macular edema.
- Diffuse Retinal Thickening: It is defined by retinal thickening exceeding 200um in height and width, featuring regions of reduced reflectivity, particularly noticeable in the outer retinal layers.
- CME: It is characterized by intraretinal fluid accumulation within well-defined spaces of low reflectivity typically around the outer plexiform layer but involving the photoreceptor and inner retinal layers.
- Posterior Hyaloid Traction or Taut Posterior Hyaloid Membrane: This is identified by the presence of a highly reflective membrane on the inner retinal surface, which causes traction and elevation of the retina.
- Subretinal Fluid: It is identified as a dome-shaped dark area situated between the neurosensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium.
- Tractional Retinal Detachment: This is identified by a peak-shaped retinal detachment caused by traction from proliferative membranes on the retinal surface or within the vitreous. This condition appears as a low signal area beneath the highly reflective border of the detached retina.
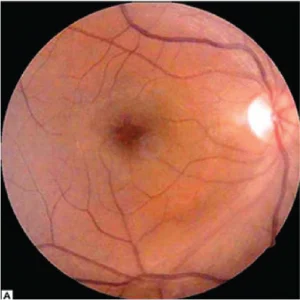

Fig 2.A Color fundus photograph shoes postoperative cystoid macular edema.
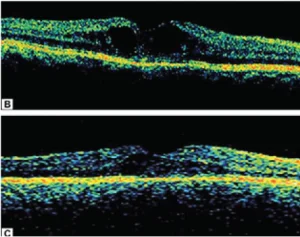

Fig. 2.B Optical coherence tomography shows increased macular thickness with cystoid cavities.
Fig.2. C. Optical coherence tomography shows marked resolution of cystoid space with decrease in macular thickness following sub-Tenon triamcinolone injection.
Radiation Retinopathy
OCT allows clinicians to assess radiation retinopathy using a 5-point grading system, which correlates with visual acuity.
- Grade 1: Foveola-sparing non-cystoid macular edema.
- Grade 2: Foveola-sparing cystoid macular edema.
- Grade 3: Foveola-involving non-cystoid macular edema.
- Grade 4: Mild-to-moderate foveola-involving cystoid macular edema.
- Grade 5: Foveola-involving severe cystoid macular edema.
Juvenile X-linked Retinoschisis
It classifies juvenile X-linked retinoschisis into different types in OCT findings:
- Type 1 or Foveal: Absence of both lamellar schisis on OCT and peripheral schisis on the ophthalmoscopy.
- Type 2 or Foveolamellar: Presence of lamellar schisis on OCT without peripheral schisis on the ophthalmoscopy.
- Type 3 or Complex: Lamellar schisis on OCT and peripheral schisis on the ophthalmoscopy.
- Type 4 or Foveoperipheral: Presence of peripheral schisis on the ophthalmoscopy.
The finding of juvenile X-linked retinoschisis is the presence of a spoke-wheel pattern in the macula, observable in high magnification in patients ages 30 or younger.
On OCT patients with uveitis exhibit diffuse macular edema, CME, and subretinal detachment.
Treatment for Cystoid Macular Edema (CME)
A stepwise medical treatment approach is crucial for managing CME, which involves systemic and ocular pharmaceutical agents. Surgical procedures may also be needed in certain cases.
Systemic Therapy
Many patients develop macular edema as a secondary manifestation of other health conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, or inflammatory conditions, it is essential to address these underlying systemic issues.
Some research shows that strict glycemic control can be effective in delaying the onset and progression of diabetic retinopathy in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Intravitreal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor
The primary approach for macular edema across various pathologies is intravitreal injections of anti-VEGF agents. Clinicians currently use three formulations of intravitreal anti-VEGF therapies.
Bevacizumab is a 148-kDa humanized full-size monoclonal IgG1 antibody that targets all subtypes of VEGF-A, available in a concentration of 1.25mg/0.05mL.
Ranibizumab offered in concentrations of 0.3mg/0.05mL and 0.5mg/0.05mL, is a 48-kDa humanized monoclonal antibody fragment that targets all subtypes of VEGF-A.
Aflibercept, provided in a concentration of 2mg/0.05mL, is a 115-kDa fusion protein that targets VEGF-A, VEGF-B, and placental growth factors.
Ocular Topical Treatment
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Using topical steroids and NSAIDs prevents prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting the COX enzyme. Common ocular side effects of topical NSAIDs include burning, stinging, and conjunctival redness. Clinicians should also consider steroid-related adverse effects, such as increased intraocular pressure (IOP), delayed wound healing, and susceptibility to infections.
The latest treatment algorithm for CME, developed by the Jampol lab, involves a combination treatment of typical NSAIDs with topical corticosteroids, such as diclofenac and fluorometholone. If there is no improvement in duration after treatment of 4-6 weeks, an alternative NSAIDS like nepafenac or bromfenac may be prescribed. If vision does not improve after 4-6 weeks of nepafenac or bromfenac treatment, consideration may be given to using an intravitreal corticosteroid injection. Additionally, for cases of treatment-resistant CME, subtenon triamcinolone should be considered as a therapeutic option.
Surgical Treatment for Macular Edema
Vitrectomy is frequently performed for macular edema caused by epiretinal membrane (ERM) thickening of the macula. It is less commonly done for macular edema unless it is related to vitreomacular traction syndromes or taut posterior hyaloid face (TPHC) syndrome, which is often associated with diabetic retinopathy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is intraocular lens implantation and how does it improve visual outcome?
Ans. It is a surgical procedure in which a synthetic lens is implanted into the eye to replace the natural lens affected by cataracts. This procedure restores patients’ clear vision by focusing light onto the retina, which results in improving visual outcomes for patients.
Q2. What are some common postoperative complications after uncomplicated cataract surgery?
Ans. Postoperative complications may include temporary discomfort, dry eye symptoms, mild inflammation, and rarely infection. These complications are manageable with postoperative treatment and follow-up care.
Q3. How does diabetes affect cataract surgery and intraocular lens transplantation?
Ans. Cataract surgery outcomes in diabetic patients may influenced by diabetic retinopathy. It requires preoperative assessment, monitoring of retinal thickness, and surgical techniques to achieve optimal results and minimize risks.
Q4. What is the role of subconjunctival injection in postoperative treatment after cataract surgery?
Ans. Subconjunctival injections of medications such as steroids or antibiotics can be used postoperatively to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. It is a localized treatment approach that helps in managing immediate postoperative complications effectively.
Q5. What causes postoperative inflammation after intraocular surgery?
Ans. It includes cataract surgery which is typically triggered by surgical manipulation within the eye. This manipulation can lead to intraocular inflammation characterized by redness, swelling, and discomfort in some patients.
Q6. How common is edema among patients after cataract surgery and what are the risk factors?
Ans. Edema, or swelling of the retina or cornea, can occur after cataract surgery, particularly in patients with diabetes more prone to inflammation. Proper postoperative management including anti-inflammatory treatments, helps mitigate these risks and ensure optimal visual recovery.
The surgical instrument is a medical device for performing particular actions or achieving desired effects during surgery procedures or operations such as providing access for viewing or modifying biological tissue.
Over time, various surgical instruments and tools have been invented for different surgical procedures. Some common surgical instruments are designed for general use in all kinds of surgeries, while others are designed for specific specialties or medical procedures.
These instruments are essential tools enabling surgeons to access soft tissue, remove bone, dissect and isolate lesions, and treat or eliminate abnormal structures.
Larger/basic medical instruments for surgery are used for the initial exposure, while finer instruments are utilized for navigating delicate structures encountered during procedures.
Surgical Instruments List is Classified According to their Functional Use into the Various Categories
1. Cutting and Dissecting Instruments
These types of surgical instruments are used for cutting skin, dissecting tissues, soft tissues, and even bones through anatomical planes.
2. Grasping and Handling Instruments
Surgeons use these instruments to grasp or hold delicate tissues to help a closer view of their surgical field, one of the most common instruments used for this purpose is forceps including tissue forceps.
3. Clamping and Occluding Instruments
These surgical instruments are used for clamping blood vessels or other tough tissue to keep them away from the area during surgical procedures.
4. Retracting and Exposing
Surgeons used retractors to have a better view of the surgical area. It is used to retract heavy tissues while minimizing trauma during the procedure.
5. An Instrument for Improvement Visualization
Special surgical instruments are designed to visualize internal structures that are not visible externally such as speculums, endoscopes, anoscopes, and proctoscopes.
6. Suturing and Stapling Instruments
These instruments help in crafting to bring together the edges of skin or soft tissue nearby.
7. Suctioning and Aspiration Instrument
In surgical and dental settings, the presence of blood and fluids can obscure underlying structures. Surgeons utilize specialized instruments to clear these fluids from the surgical field, such as the Poole abdominal tip for laparotomy, the Frazier tip for brain and orthopedic surgery, and the Yankauer suction tip for oropharyngeal procedures.
8. Dilating and Probing Instruments
Dilating instruments are used to enlarge orifices like urethra or cervical os. These instruments come in various sizes, from small to large, with surgeons typically beginning with smaller sizes and incrementally, are inserted into natural openings such as the urethra, vagina, or common bile ducts to explore these body cavities.
Here Are Some Common Instruments for Surgical Procedures
1. Scalpel Blades
These instruments are used for initial incision and cutting tissue. It consists of a blade and handle. Surgeons refer to these instruments by their blade numbers.
#10 Blade: Used for making large skin incisions, e.g. in laparotomy.
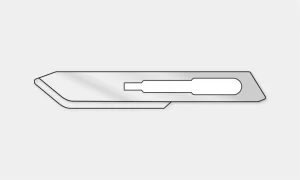

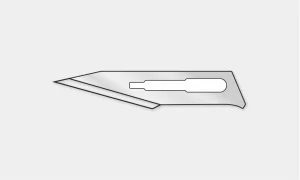
#11 Blade: Used for precise or sharply angled incisions.

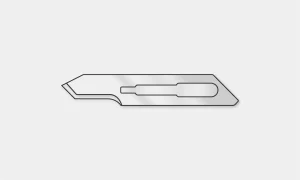
#15 Blade: This one is the smaller version of the #10 blade used for finer incisions.
2. Surgical Forceps
Also called grasping forceps, thumb forceps, locking forceps, or pick-ups, are used for grasping objects or tissue. Can be non-toothed at the tip or toothed (serrated).
Tissue Forceps: It is non-toothed forceps used for traction during dissection and fine handling of tissue.
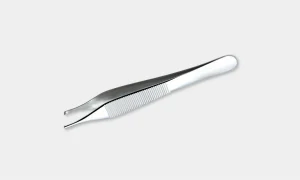

Adson Forceps: These forceps are toothed at the tip and used for handling dense tissue such as skin closure.


Bonney Forceps: These are heavy forceps used for holding thick tissue e.g. fascial closure.
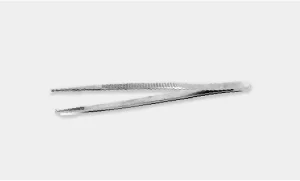

DeBakey Forceps: This is used for atraumatic tissue grasping during dissection.
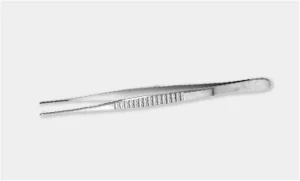

Russian Forceps: Used for grasping traumatic tissue during dissection.
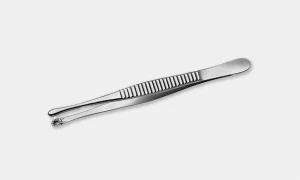

3. Clamps
Also known as locking forceps, these are some ratcheted instruments used to hold objects or tissue or provide hemostasis. It can be traumatic or atraumatic.
Allis Tissue Forceps: These are straight along the long axis with a gap to accommodate the tissue between. Sharp teeth at the tip which interlock on closing with minimal crushing of tissues. Used to hold thin structures.
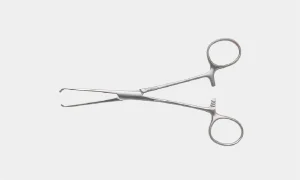

Babcock Tissue Forceps: Its non-traumatic type of forceps, fenestrated and curved blades allow a bulky amount of tissue to be held between. Used to hold soft and firm tissues like the appendix, fallopian tube, ureter, etc.
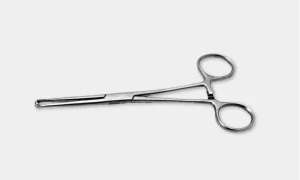

Kocher’s Hemostatic Forceps: It has a single sharp tooth at the tip of one blade and a groove at the tip of the other blade. The blades are conical blunt with transverse serrations on the inner margins.
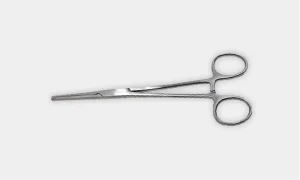

Hemostatic Clamps: Is a non-toothed clamps used in blunt dissection and also used to grasp tissue or vessels that are tied off.
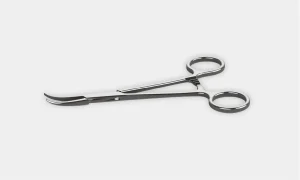

Kelly Clamp: These are the larger size variations of hemostatic instruments with the same function for grasping larger tissues or vessels.
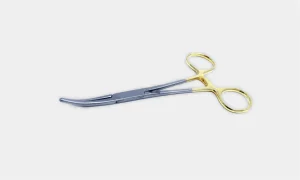

4. Scissors
Used for cutting tissue, suture, or for dissection. Surgical scissors can be curved or straight and used for cutting finer and heavy structures.
Mayo Scissors: These are heavy scissors available in different varieties and also known as suture scissors. Straight scissors are used for suture cutting while curved scissors are used for cutting heavy tissue.
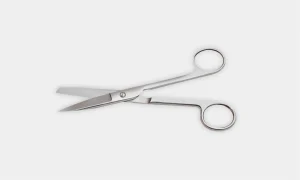

Metzenbaum Scissors: These are lighter scissors used for cutting delicate tissue i.e. heart and for blunt dissection.
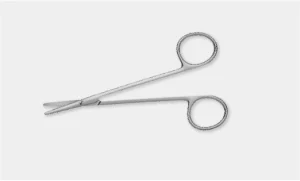

Pott’s Scissors: These are fine scissors used for creating precise incisions bein blood and vessels.
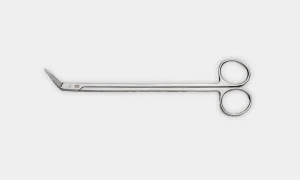

Iris Scissors: Used for precise dissection and cutting fine sutures. It serves a multipurpose role for ophthalmic procedures.

5. Needles & Sutures
Needles come in various shapes and cutting edges for different applications. Sutures can be non-absorbable or absorbable and can be available in different sizes.
The shape and curvature of the needle allow use in specialized applications. Straight needles are used for skin and subcuticular suturing while curved needles are used in most general surgical procedures.
There are different types of needles which include:
Conventional Cutting Needle: It is triangular with sharp edges, and one edge faces the inside of the curved needle. This needle is used for tougher tissues such as skin.


Tapered Needle: It is round and tapers to a simple point. It is commonly used in softer tissue such as the intestine but may also be used in tougher tissue such as muscle.

6. Sutures
There are different types of sutures, their classification, and common uses, along with the suture sizes:
| Absorbable | Non-Absorbable | ||
| Braided | Monofilament | Braided | Monofilament |
| Vicryl® Polysorb® |
Monocryl® Maxon® PDS® Chromic Gut |
Silk | Prolene® Surgipro® Monosof® Nylon |
| Internal Anastomosis | Fascial Closure Subcuticular Skin Closure |
Vessel Ligation | Skin Closure Reapproximate Lacerations |
The number associated with surgical sutures denotes the size or diameter of the suture material. Here’s what these numbers typically mean in the context of sutures:
- Lower numbers before the dash (#5, #4) indicate thicker sutures.
- Higher numbers before the dash (#3, #2) indicate thinner sutures.
- More zeros after the dash (#4-0, #3-0) indicate finer sutures.
7. Retractors
It varies in different forms, retractor are used to hold an incision open, hold back tissues or other objects to maintain a clear surgical site, or reach other structures. They can either be hand-held or self-retaining retractors via a ratcheting mechanism.
Retractors can be used in various forms in surgery, such as holding incisions open, and retracting tissues or objects to ensure a clear surgical field, or reaching deeper structures. They come in handheld retractor versions or self-retaining types with a ratcheting mechanism for stability.
Deaver Retractor: These are large retractors with broad S-shaped blades. The long handle ends in the form of a hook for better grip. It helps in retracting intra-abdominal cavity viscera like the spleen, and liver during surgeries.


Army-Navy Retractor: It is used to gain exposure to skin layers.


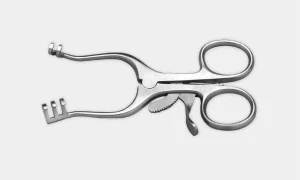
Weitlaner Retractor: Self-retaining retractors for exposing smaller or deep surgical sites. Also known as “Wheaty”.

Richardson Retractor: It can be used to hold back deep tissue structures.

Bookwalter Retractor: Self-retaining retractor system helps in anchoring to the operating table.


Malleable Retractor: Can be customized and bent. Also helps protect the intestines during abdominal closure.


Rake Retractor: Hand-held retractor equipped with sharp teeth used to hold back surface structures.

8. Special Surgical Consideration
Surgical subspecialties typically utilize specialized equipment tailored to their specific procedures. This guide provides a concise introduction to some of these equipments for better familiarity:
Laparoscopic Instruments: These instruments are similar to those used in open surgery, which fit through narrow ports placed through the skin, it work via conducted ports.


Camera & Lens: Camera is a held-hand component, which connects to various lenses. Lenses available with multiple view angles to get better visualization of anatomical structures.


Light Source: It is a fiber optic cable that connects with the lens to illuminate the field of vision.


Insufflator: Used for injecting carbon dioxide into the abdominal cavity which creates space for trocar placement and surgical procedures.


Veress Needle: A technique for creating pneumoperitoneum involves blindly inserting a needle into the abdomen and then injecting gas.

Trocars: Transabdominal ports are used for inserting laparoscopic instruments, as well as for insufflating or extracting specimens. They are available in various sizes such as 5mm, 10mm, and 12mm.


Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are some essential instruments for delicate tissue manipulation in microsurgery?
Ans. Instruments used for microsurgery, such as fine forceps for tissue reflection or specialized needle holders like mayo-hear needle holders, are important. These instruments allow precise handling of connective tissue to ensure optimal surgical outcomes.
Q2. How are deep wounds in the abdominal wall managed during surgery?
Ans. Surgical instrumentation for deep wounds includes precise suturing with needle holders, and suction tubes for maintaining a clear field, and these key instruments are designed for delicate tissue manipulation. These tools help surgeons achieve effective closure and enhance surgical outcomes.
Q3. What is the grade of surgical instruments?
Ans. Various types of stainless steels are used to produce surgical instruments; however, there are two main types: 300 series and 400 series. The 400 series stainless steel is hard and used for instruments that require a cutting surface.
DigiNerve is constantly evolving to enhance the user experience while you’re on their journey to becoming a Top Doc. We are excited to bring the latest updates with our commitment to ensure a seamless journey on the go.
Read our monthly newsletter’s June edition (Vol – 2) for the latest updates.
CONTENT UPDATES
PostGrad Course Updates
OBGYN MD:-
1. 5 new topics have been added to the following modules:
| Section | Module | Topic |
| Gynecology | Menstrual Abnormalities | Menopause Hormonal Therapy |
| Obstetrics | Procedural Videos | Caesarean Section |
| Third Stage of Labour and its Complications | Postpartum Psychiatric Illness | |
| Medical Disorders in Pregnancy | Case Discussion: Pregnancy Induced Hypertension | |
| Labour (Normal and Abnormal) | Management of Abnormal Labour |
Note: The topics mentioned above also include 25 new MCQs and 10 benchmark trials.
2. Chat show on ‘Primary Amenorrhea’ by Dr. Aswath Kumar and Dr. Lilly Varghese has been added to the course:
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Different etiologies of primary amenorrhea
- Important subtypes: Clinical features
- Investigations
- Management: Hormonal and surgical treatment
Surgery MS:-
1. Chat show on ‘Management of Head Injury’ by Prof. (Dr.) Nilay Mandal and Dr. Arjun Dasgupta has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the chat show were:
- Initial assessment of a head injury patient
- Prevention of secondary injury and management of raised ICP
- Types of head injury and their radiological findings
Professional Course Updates
MRCOG Part 2:-
1. Webinar on ‘Discussion of Important Questions and Doubt Clearance (MRCOG-2 EMQs)’ by Dr. Richa Saxena has been added to the course.
Learning Outcomes of the webinar were:
- To discuss important questions of MRCOG part 2 exam.
- To prepare for exam with the help of carefully curated questions with detailed explanations, images and flowcharts.
- To ease the journey of clearing MRCOG exam.
- To understand latest patterns of questions as per RCOG curriculum (EMQs).
Technology Updates
1. Inclusion of HYQs
A new section of High Yield Questions has been included in the courses- Cracking MRCOG- PART 1 and Part 2. It comprises HYQs from the year 2016-2022.
2. Free Access to Dr. Wise
An additional benefit of 10 queries for non-subscribers.
3. Customised Question Bank Generator
- A new feature of Customised Question Bank Generator has been added, under the course of Cracking MRCOG Part-1.
- Beneath the ‘Test’ section, users can generate questions in the ‘Practice’ or ‘Test Mode’ as per the choice of difficulty level and as per the number of questions required.
Update Your DigiNerve App for Better Experience.
To read the updates shared in the Monthly Newsletter July (Vol-1), click here.
Epidemiology is a field of medical science that focuses on studying the distribution of disease in human populations and factors that influence this distribution, primarily through statistical methods.
Epidemiology focuses on a group of people and often examines past data. Originating from 19th-century efforts to understand the origins of human diseases, its primary role continues to be identifying human populations at high risk of specific diseases to implement preventive control measures.
Epidemiology uses various methods to analyze population disease characteristics such as mortality rates, incidence rates, and prevalence rates.
In this field, studies are categorized as descriptive studies or analytic studies, depending on the aim of the study to characterize a disease or validate conclusions derived from surveys or lab findings.
Classification of Epidemiology
| Classification | Description |
| Descriptive Epidemiology | Focuses on describing the distribution of disease and health events in populations over time and space. |
| Analytical Epidemiology | Investigates the causes and determinants of disease by analyzing associations between exposure and outcomes using observational studies. |
| Experimental Epidemiology | The basic concepts of this type conduct controlled experiments to study disease causation by manipulating exposure variables under controlled conditions. |
| Clinical Epidemiology | Applies epidemiological principles to clinical practice to improve diagnosis, treatment, and patient outcomes. |
| Social Epidemiology | Examines how social factors (e.g. socioeconomic status) impact health outcomes and disparities in health within populations. |
| Environmental Epidemiology | Studies the impact of environmental factors (pollution, climate) on human health and disease. |
| Molecular Epidemiology | Combines epidemiological methods with molecular biology to study disease causes at a molecular level, including genetic and biomarker research. |
| Infectious Disease Epidemiology | Focuses on the distribution and determinants of infectious diseases within populations, including transmission dynamics and outbreak investigation. |
| Chronic Disease Epidemiology | Investigate the distribution, determinants, and prevention of chronic diseases (e.g. heart disease, diabetes) within populations. |
| Nutritional Epidemiology | Examines the role of nutrition in disease prevention and health promotion, control of health problems, focusing on dietary patterns and nutrient intake. |
Overview of Epidemiological Studies
Epidemiologic studies can be divided into two descriptive methods and analytical methods. Analytical studies are designed to assess the relationship between exposure and diseases or other health outcomes to test hypotheses whereas descriptive epidemiology primarily describes the distribution of exposure and disease within populations and can generate hypotheses, analytical studies are structured to test hypotheses about these associations rigorously.
Epidemiological method studies can be classified as prospective or retrospective. In a prospective study, data collection begins before the exposure and outcomes are determined.
In a retrospective study, data collection starts after the exposure (and often the outcome) has already occurred.
In epidemiological study design, it’s important to understand some important key terms:
- Exposure: It refers to the risk factor or agent (such as experience or procedure) that is hypothesized to have caused the disease under investigation. In statistical terms, exposure corresponds to the independent variable.
- Outcome: This is the disease or endpoint that is being measured or evaluated about the exposure. In statistical terms, the outcome represents the dependent variable.
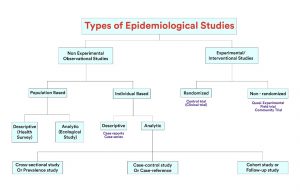

Fig 1: Types of Epidemiological Studies
Epidemiological studies are classified into several types, these come under experimental and observational designs with commonly used analytical studies given below:
1. Experimental Studies
It involves the design process of conducting research in a systematic and controlled manner to maximize precision and enable clear conclusions about a hypothesis statement. Experimental design is the structure’s method of altering independent variables to observe their effect on dependent variables under controlled conditions, ensuring rigorous control over influencing factors for accurate conclusions in scientific research.
These tests minimize the impacts of the variable to maximize the dependability of the results. In this study design experimental units such as people, plants, or animals are divided into two groups: the Experiment Group, which receives the treatment or intervention, and the Control Group which represents baseline conditions.
The collection of different conditions is termed independent variables, experimental variables, or treatment variables.
Types of Experimental Studies
There are mainly three types of experimental research designs:
| Experimental Studies | Description |
| Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT) | In this trial, subjects are randomly assigned to one of two groups: one (the experimental group) receiving the intervention that is being tested, and the other (the comparison group or control) receiving an alternative (conventional) treatment. |
| Quasi-Experimental Study | The basic concepts in this type of research design attempt to establish a cause-and-effect relationship. The main difference with a true experiment is that the groups are not randomly assigned. |
2. Observational Studies
This type of study comes in a variety of aims and forms to estimate the disease prevalence or health status within a defined area at a specific period and increase our comprehension of disease causes, risk factors, and protective factors.
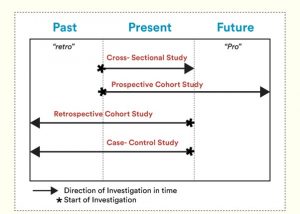

Fig 2: Three most common observational studies shown in the image.
There are various types of observational studies, two examples include case-control studies, longitudinal cross-sectional studies
| Types of Observational Studies | Description |
| Cross-sectional Study | It is a type of observational research that analyses data of variables collected at one given point in time across a sample population or pre-defined subset. This study type is also known as cross-sectional analysis, transverse study, or prevalence study. |
| Cohort Study | In this study, participants who do not have the outcome at baseline are followed over a period to estimate the incidence of the outcome. In this type of study design, the temporary between the exposure and outcome is well defined. The studies may be prospective retrospective or a mixture of both. |
| Case-control Study | It is designed to help determine if an exposure is associated with an outcome. First, identify the cases (a group known to have the outcome) and the controls (a group known to be free of the outcome). |
| Ecological Study | It compares large groups of people instead of individual differences in things such as cancer rates. The groups can differ by location, for example, city, county, or country. |
| Longitudinal Cross-sectional Study | It employs continuous or repeated measures to follow particular individuals over prolonged periods, often years or decades. |
Understanding the Epidemiological Risk Measures
It is crucial to understand the epidemiological risk measures for evaluating health outcome risks and developing effective public health strategies.
These risk measures provide valuable insights into the relationship between exposures and health outcomes, helping researchers and policymakers informed decisions.
1. Relative Risk (RR)
It measures the ratio of the probability of an event occurring in an unexposed group. It quantifies the strength of the association between an exposure and an outcome.
For example: In RCT, the incidence of heart disease among patients taking a new drug (exposed group) is 10%, while the incidence among those not taking the drug (unexposed group) is 5%. The relative risk of heart disease associated with taking the drug is calculated as:
RR= Incidence in exposed group/ Incidence in unexposed group = 10%/5% = 2
This means that individuals taking drugs have twice the risk of developing heart disease compared to those not taking drugs.
2. Absolute Risk (AR)
It refers to the actual probability of an event occurring in a population. It provides a baseline measure of risk without comparing different groups.
For example: In a cohort study following 1000 individuals over 10 years, 100 developed diabetes. The absolute of developing chronic diseases over 10 years in this population is:
AR= Number of individuals who developed chronic diseases/ Total number of individuals in the study = 100/1000 = 10%
This indicates that the overall risk of developing Chronic diseases in this population over the specified period is 10%.
3. Population Attribute Risk (PAR)
It estimates the proportion of cases of diseases in a population that can be attributed to a specific exposure or risk factor.
For example: In a community, smoking is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer. Suppose 20% of cases of lung cancer in this population are attributed to smoking. The PAR risk of lung cancer due to smoking is:
PAR = Proportion of cases attributed to smoking X Incidence in exposed group/ Total incidence in the population.
If the total incidence of lung cancer in the population is 100 cases per year and smoking contributes to 20% of these cases, then the PAR would be 20 cases per year (20% of 100).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the scope of Epidemiological studies?
Ans. These studies encompass a wide range of health conditions, from communicable diseases such as influenza to chronic conditions such as diabetes. With these studies, public health specialists investigate the occurrence of disease within populations to analyze factors influencing health outcomes.
Q2. How does epidemiology contribute to understanding the burden of disease?
Ans. Epidemiological research quantifies the burden of disease by assessing factors such as mortality rates, disability impacts, and economic costs. This data informs public health practices by identifying high-risk groups and helps in the allocation of disease prevention and treatment.
Q3. What role do environmental factors/ external factors play in epidemiological studies?
Ans. Environmental factors such as pollution and climate change, and external factors like socioeconomic status and healthcare access, are critical determinants of health studies in epidemiology.
Q4. What are the key concepts of epidemiology?
Ans. Epidemiology focuses on studying disease occurrence and distribution, analyzing disease processes such as transmission and incubation periods, and assessing environmental exposures. The crucial aims of epidemiology are to identify risk factors, inform health services, and understand the dynamics of disease within populations.
The skeleton is the framework of bones, it is a type of connective tissue, reinforced with bone cells and calcium. Bones include a yielded core known as bone marrow, it is a spongy soft tissue that fills the cavities in bones and holds cells that create red and white blood cells.
Bones are responsible for protecting organs from potential damage and help support our body enabling movement.
In various types of bone fractures, the severity of the fracture depends upon the strength and direction of the force, with the bone involved.
What are the Different Types of Bone Fractures?
| Common Types of Bone Fracture | Description |
| Close (Simple Fracture) | Bone breaks without piercing the skin. |
| Open (Compound Fracture) | Bone breaks through the skin’s surface, causing an open wound. |
| Greenstick Fracture | Incomplete fracture is where the bone bends and cracks but doesn’t completely break. |
| Hairline Fracture | Minor crack in the bone’s surface without full separation. Most common form of stress fracture. |
| Complicated Fracture | Bone breaks and causes damage to surrounding tissues and organs |
| Avulsion Fracture | The tendon or ligament pulls off a fragment of bone. |
| Compression Fracture | Bone collapse due to pressure, often in the vertebrae. |
| Transverse Fracture | The fracture line is horizontal across the bone shaft. |
| Oblique Fracture | The fracture line is diagonal across the bone shaft. |
| Spiral Fracture | Fracture lines spiral around the bone, often caused by a twisting force. |
Fractures can occur not only in limbs such as arms and legs but also in critical areas like the head, chest, spine, or pelvis.
Injuries to bones like skull or ribs are the regions that can be particularly challenging due to the complex structures they protect.
Managing fractures in these areas often requires more than basic first-aid techniques and may involve complex medical interventions. These kinds of fractures represent life-threatening injuries that require emergency assistance.
Let’s dive into these complex fractures:
1. Compression Fracture: It typically occurs in vertebrae (bones of the spine), where the affected bone is compressed or collapses. It can result from trauma, such as falls or road traffic accidents, or from conditions like osteoporosis, which is the most common cause of compression fractures.
2. Skull Fracture: It occurs when one or more bones that make up the skull are broken, these fractures can vary in severity depending on the force and direction of the impact. It may also called a traumatic brain injury or TBI. Mild breaks cause few problems and heal over time and severe fractures can lead to bleeding around the brain, leaking of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), infection, brain damage, and seizures. The role of different skull bones, including the temporal, parietal, and occipital bones is crucial in understanding the potential consequences of a fracture:
- Temporal Bone: Bone is found on the sides and base of the skull. It is relatively thin, typically around 4mm thick. The temporal bones include important structures like the middle and inner ear, as well as some blood vessels.
- Parietal Bones: These bones form the sides and top of the skull. They are thicker than temporal bone, ranging from 5 to 10 mm thick.
- Occipital Bone: Located at the back and base of the skull, the occipital bone is the thickest among these three, typically measuring around 15 mm in thickness.
Skull Fractures are Classified into Various Types of Fracture Based on their Location
| Type of Skull Fracture | Description | Mechanism of Injury |
| Linear Fracture | Also known as a fissured fracture that is often thin and may be missed on X-rays, making it more detectable during MRI or CT-scan. It typically occurs due to a heavy blunt blow to the head, resulting in a linear break in the skull’s continuity. | Direct Impact or blunt trauma to the skull. |
| Basilar Skull Fracture | Occurs at the base of the skull, involving bones such as the temporal, occipital, and sphenoid bones. | Associated with head trauma it can lead to leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the nose or ears. |
| Diastatic Fracture | Fracture involves separation along sutures, which is common in young adults. A frequent site is the sagittal suture, where widening or separation occurs due to significant trauma. | Sudden force causing separation of sutures. |
| Depressed Fracture | Known as a signature or ala fracture, results from a small, focused impact such as from a hammer. It causes inward indentation of the skull’s surface, often damaging both outer and inner layers of bone. |
Direct blow from a heavy weapon or object with a small striking surface. |
| Pond/ Indented Fracture | Commonly seen in infants, this fracture leaves a visible dent or indentation on the skull’s surface. It’s also referred to as ping pong ball fracture and is caused using obstetric forceps during childbirth. |
Obstetric forceps apply pressure during delivery. |
| Gutter Fracture | Occurs on the outer surface of the skull due to the tangential impact of an oblique bullet, resulting in a groove-like depression along the bone. It’s characteristic of glancing bullet wounds. |
Trajectory of an oblique bullet causing an outer surface fracture. |
| Comminuted Fracture | Multiple bone fragments caused by a heavy blunt blow, this fracture pattern resembles a spider web with intersecting lines and fragments displaced from the impact site. | Severe blunt force trauma leading to shattered bone fragments. |
| Ring/ Foramen Fracture | Bones may be broken around the foramen magnum, the hole in the base of the skull through which the brain stem exits and becomes the spinal cord. This may result in injury to the blood vessels and nerves exiting the foramen magnum. | Impact involves the base of the skull, such as falls or specific blows to the head. |
| Motorcyclist Fracture | Common among motorcyclists, these fractures occur at the skull base, typically from lateral impacts. They are classified into Type 1 (Hinge), Type 2(Frontal to contralateral), and Type 3 (Anterior) based on specific patterns of fracture propagation. |
Lateral force transmitted across the skull, typical in motorcycle accidents. |
| Bow Out Fracture | Involves fractures of the orbital wall (median, posterior, or floor) caused by blunt trauma, resulting in an outward blowing or displacement of bone. It commonly occurs due to forceful impact on the eye area. | Blunt force trauma causes fractures of the orbital bones. |
What are Some Common Causes of Bone Fracture?
Bone fractures can result from various causes, including:
- Trauma: Falls, sports, injuries, motor vehicle accidents, and direct blows to the body result in traumatic bone fractures.
- Osteoporosis: In this condition, bones become weak due to loss of bone density. In this condition, even minor stresses and falls can cause a fracture.
- Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Repetitive motions can strain bones over time which leads to stress fractures. These fractures develop gradually with small cracks and repetitive impact, which is common in athletes.
- Pathological Conditions: Diseases that weaken bones, such as bone cancer (resulting in pathological fractures), osteogenesis imperfecta (brittle bone disease), or infections like osteomyelitis, can make bones more susceptible to fractures.
What are Some Common Symptoms of Fracture?
- Bone fractures cause pain due to inflamed nerve endings in the bone lining (periosteum) and muscle spasms around the fracture site.
- Fractured bones bleed, which leads to swelling and seepage of blood into surrounding tissues, which adds to the pain.
- Bruising around the fracture site may appear as dark red or purple marks due to blood leakage.
- Due to muscle and tendon integrity, movement of the injured limb still be possible, so mobility alone does not rule out a fracture.
- Arteries damage can result in a cool, pale area distal to the injury, while nerve damage may cause numbness in the same area.
What is the Treatment Plan for the Bone Fracture?
Treatment for bone fracture depends upon the complication and level of severity to make sure the bone pieces are lined up accurately through surgical procedures or surgical traction.
Types of Treatment Based on Fracture Location and Site Include
- Braces: provide support to the bone
- Splints: to stop the movement of the fractured limb
- Plaster Cast: provide rigid support and immobilization
- Traction: for complex fractures to align and stabilize
- Surgically inserted Metal Rods or Plates: In severe cases of fracture that do not heal properly with other methods, metal implants such as metal rods, screws, or metal plates are surgically placed to hold bone fragments.
Few Surgical Treatments Depending on the Location and Severity of the Fracture
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): It is the procedure of realigning the fracture bone fragments ( open reduction) and stabilizing them with internal fixation devices such as metal plates, screws, or metal rods.
- External Fixation: In these types of cases fractures open like a bone protruding through the skin or severely unstable, external fixation may be used. It involves placing metal pins, and screws into the bone above and below the fracture, which are connected to external fragments. Commonly used for fractures of the long bones in the arms and legs.
- Intramedullary Rodding: This procedure includes a metal rod inserted into the hollow center (Medullary canal) of the long bone to stabilize and align the broken bone fragments.
- Joint Replacement: Also known as arthroplasty, becomes necessary in some cases in which fractures severely affect the upper portion of the femur bone, a crucial component of the hip joint, or the humerus bone, integral to the shoulder joint.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the difference between a closed fracture and an open fracture?
Ans. A closed fracture occurs when the bone breaks but does not penetrate the skin. It is typically less complicated and carries a lower risk of infection compared to an open fracture, in which bone breaks through the skin. An open fracture requires immediate medical attention to prevent complications such as infection.
Q2. How are head injuries diagnosed and treated?
Ans. Head injuries can vary from mild concussions to severe traumatic brain injuries (TBIs). This diagnosis involves a thorough physical exam and imaging tests like CT scans to assess the extent of the damage.
Treatment options depending on the severity include rest, medication for pain and swelling, with recommended physical therapy which restores range of motion and strength.
Q3. What can do to keep bones strong and reduce the risk of fractures?
Ans. To maintain strong bones and reduce the risk of fractures, it’s important to engage in regular weight-bearing exercises, consume a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Following medical advice and gradually returning to normal activity and daily activities can support bone healing and restore mobility.
Overview
Ventilation is an important area of respiratory care and aims to ensure the proper gas exchange within the lungs.
The respiratory and cardiovascular systems collaborate to supply oxygen O2 to tissues and release carbon dioxide, CO2.
When patients experience respiratory difficulties, there is often an elevation in CO2 levels in their blood gases.
Strategies to address this include airway clearance through suction and mechanically augmented respiratory parameters such as atmospheric pressure rate, respiratory rate, pressure, or volume to enhance ventilation.
To achieve the required pressure for mechanical ventilation, access to the airway is imperative. This access is typically facilitated through methods such as:
- Oral or nasal endotracheal tube (ETT)
- Tracheostomy Tube
- Well-sealed mask for non-invasive ventilation
These methods ensure efficient delivery of ventilatory support, thereby aiding in maintaining adequate gas exchange in the lungs.
There are two primary common modes of ventilation:
- Invasive Ventilation: Utilized for unconsciousness patients.
- Non-invasive Ventilation: Suitable for conscious patients.
These various techniques of mechanical ventilation are important topics for exams like NEET-PG/next and FMGE.
What are the different types of ventilator modes?
Different methods/modes of ventilation, offers tailored treatment plan that respond to the patient’s specific pathology and requirements.
| Controlled Modes | Supported Modes | Combined Modes | Spontaneous Breathing |
| Volume Control | Pressure Support | AUTOMODE: Volume Control- Volume Support | Continuous Positive Airway Pressure |
| Pressure Control | Volume Support | AUTOMODE: Pressure Control – Pressure Support | Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure |
| Pressure-Regulated Volume Control | Non-Invasive Ventilation- Pressure Support | AUTOMODE: Pressure-Regulated Volume Control – Volume Support | |
| Non-Invasive Ventilation – Pressure Control | Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation: Volume Control+ Pressure Support | ||
| Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation: Pressure Control+ Pressure Support | |||
| SIMV: Pressure-Regulated Volume Control+ Pressure Support |
There are different types of Ventilator modes which are divided up into pressure or volume-controlled modes, this modern approach classifies ventilatory modes based on three characteristics: the triggers (Flow versus pressure), the limit (what determines the size of the breath), and the cycle (What ends the breath).
1. Controlled Mandatory Ventilation (CMV)
Also known as Assist-Control Ventilation, is a mode of mechanical ventilation where each mandatory breath is either as assist or control breath, all delivered with the same preset volume or partial pressure.
This mode is particularly suitable for patients who require minimal breathing effort, as the ventilator fully controls the patient’s total breathing. CMV is indicated in patients with severe neurological alterations, deep sedation, shock, or respiratory failure. CMV is a common way to decrease the intracranial pressure after head injury.
It ensures consistent ventilation regardless of the patient’s inspiratory efforts. It’s crucial to note that CMV does not eliminate work of breathing entirely, as the diaphragm may still be active.
Therefore, patients should be heavily sedated, and drugs like fentanyl, dexmedetomidine, or midazolam can be used to achieve this level of sedation.
Features of Controlled Mandatory Ventilation:
- Physical Character: Pressure is being controlled.
- Tidal Volume: Tidal Volume is around 7-8ml/Kg.
- Patient Efforts: No efforts from the patient’s side.
- Usage: Typically used in heavily sedated patients.
- Effect on BP and Urine Output: May lead to decrease in BP and urine output due to controlled ventilation.
2. Assist-Control Ventilation
It is a mode of mechanical ventilation where each mandatory breath is either an assist or control breath, all delivered with the same preset volume or partial pressure.
This mode is particularly suitable for patients who require minimal breathing effort, as the ventilator fully controls the patient’s total breathing. CMV is indicated in patients with severe neurological alterations, deep sedation, shock, or respiratory failure. CMV is a common way to decrease intracranial pressure after a head injury.
It ensures consistent ventilation regardless of the patient’s inspiratory efforts. It’s crucial to note that CMV does not eliminate the work of breathing, as the diaphragm may still be active.
Therefore, patients should be heavily sedated, and drugs like fentanyl, dexmedetomidine, or midazolam can be used to achieve this level of sedation.
Features of Controlled Mandatory Ventilation:
- Physical Character: Pressure is being controlled.
- Tidal Volume: Tidal Volume is around 7-8ml/Kg.
- Patient Efforts: No efforts from the patient’s side.
- Usage: Typically used in heavily sedated patients.
- Effect on BP and Urine Output: This may lead to a decrease in BP and urine output due to controlled ventilation.
3. Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation (SIMV)
SIMV is a ventilator mode that offers partial mechanical assistance while allowing the patient to breathe spontaneously.
Unlike Assis-control ventilation, in SIMV, the patient’s breaths are partially on their own, reducing the risk of hyperinflation or alkalosis. Mandatory breaths are synchronized with spontaneous respirations, providing support when needed.
SIMV may increase the work of breathing and reduce cardiac output, potentially prolonging ventilator dependency. The addition of pressure support to spontaneous breaths can alleviate some of the work of breathing.
SIMV is often used as a weaning mode, allowing patients to gradually regain their respiratory function. Moderate sedation is typically required to ensure patient comfort and synchronization with the ventilator.
SIMV is indicated for conditions such as high risk of hyperventilation/respiratory alkalosis due to increased respiratory rate, pulmonary edema, acute respiratory distress syndrome, neuromuscular disorders, and cardiac thoracic surgery. It’s typically avoided in patients with shock and head injuries.
Features of Controlled Synchronized Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation:
- Physical Character: Respiratory rate (RR) is 14/min.
- Tidal Volume: Tidal Volume is 400ml/Kg.
- Patient Efforts: Allows for some spontaneous sedation.
- Usage: Can be used in patients with no or slight sedation.
- Effect on BP and Urine Output: May have less impact on BP and urine output due to less protective ventilation compared to CMV.
4. Pressure Control Ventilation
It is a common ventilator mode that offers less risk of barotrauma compared to assist control ventilation and SIMV, as it does not allow for patient-initiated breaths. In PCV, the respiratory flow pattern decreases exponentially, reducing peak pressures and improving gas exchange.
However, there are no guarantees for volume especially when lung mechanics are changing, making it traditionally preferred for patients with neuromuscular disease but otherwise normal lungs.
Pressure is fixed manually, and the ventilator decides the volume. PCV is mainly used for conditions like Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). A major drawback of this mode is the risk of endotracheal tube obstruction due to secretions, leading to reduced volume reaching the patient’s lungs and resulting in respiratory acidosis due to poor oxygenation and increased CO2 levels.
Features of Pressure Control Ventilation:
- Physical Character: Operates on pressure control, maintaining set inspiratory pressure.
- Tidal Volume: Not designed specifically as a weaning mode.
- Patient Efforts: Facilitates spontaneous breathing efforts.
- Usage: Commonly employed in pediatric patients due to its adaptability.
- Effect on BP and Urine Output: May exert less influence on blood pressure and urine output as it allows for spontaneous breathing, potentially improving oxygenation without significantly impacting cardiovascular function.
5. Pressure Support Ventilation
PSV is a spontaneous mode of ventilation where each breath is initiated by the patient but supported by constant pressure inflation.
It operates two mechanisms: CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) and PEEP (Positive End-Expiratory Pressure), which helps open the alveoli. PSV allows the patient to determine inflation volume and respiratory rate, although pressure remains controlled by the ventilator.
Therefore, it can only augment spontaneous breathing, typically with pressures ranging from 5-10cm H2O, especially during weaning. PSV can be delivered through specialized face masks.
Features or Pressure Support Ventilation:
- Physical Character: Works on pressure control
- Tidal Volume: Not a weaning mode.
- Patient Efforts: Facilitates spontaneous breathing.
- Usage: Often used in pediatric patients.
- Effect on BP and Urine Output: This may have less impact on BP and urine output, as it allows for spontaneous breathing and may improve oxygenation.
6. Volume Control Ventilation
In the mode of ventilation, the ventilator delivers a predetermined tidal volume to the patient with each mandatory breath. This mode is typically synchronized with the patient’s inspiratory effort, ensuring that the desired tidal volume is consistently delivered. Volume control ventilation is commonly used in patients with normal lung compliance and resistance, as it helps maintain a consistent ventilation pattern.
Another mode of volume ventilation is Assist-Control Ventilation (ACV). ACV combines the features of volume control ventilation with the ability to support spontaneous breathing efforts. In this mode, the ventilator delivers a set tidal volume with each breath initiated by the patient.
Features of Volume Control Ventilation:
- Physical Character: Operates on volume control, delivering a predetermined tidal volume.
- Tidal Volume: Delivers a set tidal volume.
- Patient Efforts: Patient effort can initiate the breath, but the ventilator ensures that the desired tidal volume is delivered.
- Usage: Commonly used in patients with normal lung compliance and resistance.
- Effect on BP and Urine Output: Volume control ventilation may increase intrathoracic pressure, which can have an effect on blood pressure and urine output. However, the impact can vary depending on the patient’s condition.
7. PEEP (Positive End-Expiratory Pressure)
PEEP level helps to keep the alveoli open at the end of expiration and helps in increasing partial pressure, thereby aiding in improving patient oxygenation. This increase in intrathoracic pressure typically leads to a reduction in venous pressure and carbon dioxide levels. However, it is essential to note that while a decrease in blood pressure might occur, it doesn’t necessarily always result in decreased urine output. Positive End-Expiratory Pressure, expressed in centimeters of water (cmH2O), applies pressure at the end of exhalation, thereby preventing the air sacs in the lungs from collapsing and further improving oxygenation.
8. CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure)
It is commonly employed to assess a patient’s readiness for extubating, particularly when minimal ventilation support is required.
It maintains a constant circuit pressure as specified by the operator throughout ventilation. Pressure Support Ventilation is often combined with CPAP, providing positive pressure assistance throughout the breathing cycle.
PSV can be delivered through a mask and is utilized in conditions such as obstructive sleep apnea, especially when utilizing a nasal mask.
Additionally, it can be used to delay intubation or manage acute exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, respiratory distress syndrome, or acute lung injury.
9. Airway Pressure Release Ventilation
It delivers a constant high artificial airway pressure to ensure oxygenation, while ventilation occurs through the release of that pressure.
During the majority of the cycle, a continuous high pressure is applied for a set duration followed by a brief period of lower pressure. The concept revolves around maintaining constant alveolar volume during the extended T high phase (covering 80%-90% of the cycle), enhancing oxygenation.
This extended period of high pressure, often termed an open lung strategy minimizes the repetitive inflation and deflation of the lungs observed in other ventilation modes, thus mitigating the risk of ventilator-induced lung injuries.
APRV offers a unique approach to optimizing respiratory mechanics in critically ill patients in the intensive care unit, reducing the respiratory effort required for ventilation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are potential complications associated with the intermittent Mandatory Ventilation mode?
Ans. One notable complication of IMV is breath stacking, characterized by a spontaneous breath occurring immediately after a mechanical breath. This sequence can elevate Peak Inspiratory Pressure (PIP), posing a risk of barotrauma and cardiac compromise.
Q2. How do ventilators work in the Intensive Care Unit ICU?
Ans. In the ICU, mechanical ventilators, provide positive pressure ventilation, adjusting ventilator settings like inspiratory time and respiratory cycles to optimize oxygenation. They support patients with respiratory failure while considering factors such as venous return and the effects of positioning, like the prone position, to improve the ventilation-perfusion ratio.
Q3. What happens when the ventilator pressure goes to zero during mechanical ventilation?
Ans. When the ventilator pressure drops to zero, the elastic recoil of the lungs pushes air out. However, the time allotted for exhalation may not be sufficient for all the air to leave the lungs completely.
Q4. What are the advantages of Pressure Control Ventilation?
Ans. Pressure control ventilation offers several advantages, it allows for precise control of alveolar pressure, promoting lung protective ventilation strategies. This ventilatory mode enables adjustment of inspiratory flow rates and initial ventilator settings tailored to individual needs. Respiratory therapists can optimize therapy by titrating the pressure support level, ensuring a favourable pressure gradient for adequate gas exchange.
The MS General Surgery curriculum provides advanced surgical procedures into specialized knowledge and surgical techniques which are crucial for clinical practice. MS Surgery, the program offers diverse surgical subspecialties. Through these rotations, medical students delve into diverse areas such as gastrointestinal surgery, oncology, vascular surgery, and more working under the guidance of seasoned practitioners.
This hands-on experience not only provides technical steps proficiency with innovative techniques or advanced procedures but also gives critical decision-making abilities which are important for navigating complex surgical techniques from valuable resources.
Additionally, the program maintains the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration, preparing medical students to work seamlessly within multidisciplinary healthcare teams to deliver optimal outcomes with safe surgery and patient management care.
Best MS Surgery Books for Students & Residents
1. SRB Textbook of Surgery by Sriram Bhat M
- Master the fundamentals of the general manual of surgery with a comprehensive review and up-to-date manual. This comprehensively revised edition offers insights into the latest advancements in cancer treatment and staging, with important surgical anatomy details for each advanced procedure or treatment. It covers all major general surgery key topics, featuring in-depth explanations of common conditions.
- This SRB textbook provides great exposure to various surgical specialties such as fluid and electrolyte management metabolic support, or wound healing which helps in building a foundation of practical procedures knowledge that empowers both medical students and young surgeons.
- The clear writing style, complemented by unforgettable diagrams and detailed artwork images of clinical cases, ensures that quick review information is effectively retained for success in exams and real-world practice.
- This student-centered guide becomes your constant companion, which provides a clear path to navigate any surgical challenge you may encounter during any surgical procedure.
2. Clinical Surgery Pearls by Babu R Dayananda
- In the field of surgery, this manual of surgery book focuses on the practical field of surgery, offering wisdom and insights from experienced surgeons. Gain a strong foundation with over 100 clear definitions of key topics with surgical terms to build a solid foundation. It includes more than 50 clinical cases, both comprehensive coverage and concise way. Each case represents a patient clinical scenario followed by thought-provoking questions to guide your analysis during practical examinations.
- It introduces the dedicated chapter for radiology and imaging techniques which helps medical students to interpret these visual tools with confidence. It also includes crucial tables and charts for instant access to critical surgical knowledge.
- Clinical Surgery Pearls utilizes highlighted boxes and charts to make learning easier and enjoyable for students, forget about the long and dense text-heavy books. With its student-centered approach, this book ensures that the learning process is not only informative but engaging.
3. Zollinger Atlas of Surgery by Robert Milton, Jr.
- Surgeons around the world swear by Zollinger’s Atlas Surgical Operations and for good reason. This book has been empowering surgeons and medical professionals for decades with safe and proven techniques with a wide range of surgical procedures.
- From gastrointestinal surgery to vascular surgery or endovascular procedures master a vast array of surgical intervention. There are other common operations given with guidance like hernia repair, bariatric surgeries, and lymph node biopsy, which exceed age, offering clear depictions of anatomy and surgical technique steps on single pages for operative procedures.
- This classic textbook has an exceptional format which makes it an invaluable resource for learning new essential procedures for patient management after surgery and refreshing your memory with this valuable resource.
- Whether you’re a surgery resident or a seasoned surgeon, Zollinger’s comprehensive approach caters to your needs. The tenth print edition expands the content with 19 new essential procedures with clinical pathways or surgical strategy, while each chapter offers a consistent format covering:
- Indications for surgery
- Preoperative preparation
- Anesthesia considerations
- Patient positioning
- Operative preparation and incision
- Step-by-step surgical procedure
- Closure surgical techniques
- Postoperative care
4. Mc Gregor Synopsis of Surgical Anatomy by G. A. G. Decker and D. J. du Plessis
- In the field of surgery, this book serves as a vital link between comprehensive anatomy textbooks and real-world surgical techniques. It prioritizes clinically relevant anatomical features that are designed to be immediately beneficial for senior medical students and surgery residents in operative surgery. This book provides coverage of the entire anatomical structure of the human body, its aim is not to be exhaustive for surgery residents.
- It serves as a concise and user-friendly surgery manual that complements the in-depth knowledge found in larger anatomy texts which makes it a valuable resource for quick review of classic reference and practical procedures approach of application for anatomical knowledge in the clinical practice.
- This textbook of surgery is a bestselling manual of surgery with an excellent source of expert guidance for surgery resident students, medical students, and others providing care for patients with surgical diseases.
5. Surgical practice guidelines- Bailey & Love’s Short Practice of Surgery, 27th Edition by Norman S. Williams, P. Ronan O’Connell & Andrew McCaskie
- Master your journey with Hamilton Bailey’s Demonstration of Physical Signs in Clinical Surgery. This book is an essential resource that covers concepts of strategy from surgical basics to nutrition in a clear and concise format with clinical pathways, unlike other heavy textbooks, it mainly focuses on key topics for exams. It is a must-have for any aspiring surgery residents and students.
- Bailey & Love’s Short Practice of Surgery provides comprehensive coverage with a strong foundation in the principles of surgery procedures, this textbook serves as an invaluable resource for surgery residency program students to refine their skills and advancement in surgical disease.
6. Bailey’s Head and Neck Surgery by Clark A. Rosen MD
- This textbook on surgery is designed to enhance skills for practicing otolaryngologists and otolaryngology surgery residency students. It provides focused concise, practical information across this complex field, this two-volume textbook ensures that surgeons and medical students stay abreast of current, evidence-based practices and clinical scenarios related to head and neck surgery.
- It includes 238 chapters covering key content ranging from Basic Science/General Medicine to surgical issues, this book edition incorporates new concepts with comprehensive coverage and clinical pathways on emerging areas for the practice of surgery procedures such as Pediatric Sleep Disorders and innovative techniques with Robotic procedures in Head and Neck surgery.
7. Basic Science and Clinical Evidence by Jeffrey Norton, Philip S. Barie
- It is a fully revised version with updated information on the evidence-based practice of surgery. It includes new sections on critical care and trauma with challenging surgical care for different populations such as elderly, pediatric, or obese patients, updated pre- and post-operative care of cardiac or bariatric surgeries, surgical infections, and intestinal transplantation.
- This book is divided into clinically oriented segments including surgical infections, cancer, cardiothoracic, gastrointestinal, and vascular surgery, and empowers surgeons to make informed surgical decisions based on the latest data in surgical practice.
8. Surgical Critical Care and Emergency Surgery by Forest Dell
- In this updated edition the team of emergency surgeons presents a comprehensive question-and-answer resource on the expanding field of surgical resources on the surgical critical care and acute surgery for injured surgical patients.
- For healthcare professionals attending to critically ill and injured surgical patients, this book provides surgical critical care, emergency surgery, burns, and trauma, and features vivid full-color surgical images for enhanced comprehension.
9. Anatomy for Plastic Surgery of the Face, Head, and Neck by Koichi Watanabe
- This book delves into the complex regional anatomy of these areas, equipping plastic surgery and otolaryngology residents with a comprehensive understanding of anatomical structures. It includes a detailed depiction of complex regional anatomy through illustrations and intraoperative and radiologic images.
- It also provides online access to instructional videos where respective authors guide beginner to intermediate readers through the anatomy of the face, head, and neck. This expert consult online access is an invaluable anatomical resource for plastic surgeons and otolaryngologists as well as residents in these specialties.
10. The Vascular Surgery Review Book by Dr. Thomas Creeden
- This book serves major pathologies in a concise, yet comprehensive reference tailored for aspiring vascular surgeons and those currently in training, including residents and vascular surgery fellows.
- It provides an invaluable resource for training or preparation through bulleted format form with effortless navigation through intricate information. This book provides a comprehensive overview of surgical pathology and treatments which helps with patient selection daily in clinical practice.
11. Solved Papers Surgery for PG Students (Topic Wise) by Arkaprovo Roy
- This textbook of surgery offers a compilation of solved papers from various postgraduate surgical entrance examinations such as AIIMS and NEET-PG. It covers an extensive range of concepts of strategy with key considerations in surgery and provides medical students an opportunity to sharpen their problem-solving skills.
- Students gain valuable insights into exam patterns, question formats, and essential surgical concepts from each solved paper.
Surgical Journals and Publications
1. International Journal of Head and Neck Surgery
- IJHNS is a platform for sharing the latest research on head and neck conditions. It publishes peer-reviewed articles of interest to a wide audience, including clinicians, allied health professionals, and researchers.
- Summarize current knowledge on head and neck diseases with a focus on evidence-based practice. The journal provides resources for surgeons that highlight important public health issues related to the head and neck. Share valuable clinical practice experiences and insights.
2. Indian Journal of Endocrine Surgery and Research
- The Indian Journal of Endocrine Surgery and Research is a leading essential resource for publication dedicated to advancing the field of endocrine surgery and its related sub-specialties. Stay up to date with the latest advancements through insightful research articles and compelling case reports or case series.
- With newly published articles surgery students or medical professionals can discover the benefits of a multidisciplinary approach to managing endocrine pathologies.
- These research articles will enhance their understanding of the management and treatment of endocrine pathologies. From complex thyroid surgery the breast diseases both malignant and benign, this journal provides a comprehensive coverage approach to enhance the surgical practice for safe surgery and better outcomes for patient care.
- The IJESR is your one-stop resource for surgeons, researchers, and healthcare professionals seeking to improve outcomes for patients in endocrine surgery.
Some More Recommended Books for MS Surgery Students & Residents
- Bedside Clinics in Surgery, Makhan Lal Saha
- IAGES Recent Advances in Minimal Access Surgery-3 (Robotic procedures & Innovative Technologies)
- Lectures on the ART of Surgery
- Fischer’s Mastery of Surgery, Seventh Edition
- Farquharson’s Textbook of Operative General Surgery, Tenth Edition
- Schein’s Common Sense Emergency Abdominal Surgery
- Hamilton Bailey’s Emergency Surgery
- Sabiston Textbook of Surgery: The Biological Basis of Modern Surgical Practice, 21st Edition
- Schwartz’s Principles of Surgery, 11th Edition
For surgical residents and experienced practitioners alike, navigating the complexity of MS surgery demands access to the best book for surgical techniques. From patient selection to invasive techniques, these comprehensive resources offer key content essential for mastering surgical procedures, across different levels of experience. For medical students or surgical residents exploring the latest advancements or referring to trusted techniques from previous editions, these books provide invaluable insights to optimize patient safety outcomes.
For more advanced readers online access for an immersive eBook experience, the realm of MS surgery books offers a treasure of favourite content. These books of technique provide complete content crafted by leading experts in the field.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are some essential textbooks for MS Surgery students?
Ans. Consider the SRB Textbook of Surgery for a strong foundation, Clinical Surgery Pearls for practical skills, and the Zollinger Atlas of Surgery for mastering surgical procedures.
Q2. How can I prepare for surgical entrance exams?
Ans. Practice problem-solving with books like “Solved Papers Surgery for PG Students” and utilize online resources from publishers like Jaypee Brothers, these are beneficial for surgery residency students.
Q3. Where can I find reputable surgical journals?
Ans. For general surgery, explore prestigious journals like BJS, JACS, and Annals of Surgery. For specific specialties, look for dedicated publications like the International Journal of Head and Neck Surgery.
The UPSC CMS is an abbreviation for “Union Public Service Commission-Combined Medical Services” Examination. It is a competitive examination that the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) of India administers. The CMSE is held every year to fill various medical positions in government agencies including the Indian Railways, Central Health Service, Municipal Corporation of Delhi, and several other central government health institutions. The CMS exam allows medical professionals to join the esteemed Indian government healthcare service organizations and support the country’s healthcare system.
The difficulty level of the exam is self-explanatory by the term UPSC; UPSC CMSE is a hard nut to crack. With smart study, consistent efforts, and a lot of practice, you will pass with flying colours. Make sure to start early and stick to a realistic study plan and reliable study resources.
In this blog, you will get detailed information about the UPSC CMS exam recruitment category, eligibility criteria, exam pattern, selection procedure, and syllabus.
To be eligible to sit in the exam, a candidate must be either:
(a) an Indian citizen, or
(b) a subject of Nepal, or
(c) a subject of Bhutan, or
(d) a Tibetan refugee who came over to India before the 1st January 1962 to permanently settle in India, or
(e) a person of Indian origin who has migrated from Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka, or East African Countries of Kenya, Uganda, the United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, 6 Malawi, Zaire, and Ethiopia or Vietnam to permanently settle in India.
Provided that a certificate of eligibility has been issued by the Government of India in favour of the candidate belonging to categories (b), (c), (d), and (e) mentioned above.
UPSC CMS Recruitment Category
UPSC CMS exam is conducted for the recruitment for the following categories and positions:
Category-I:
Medical Officers Grade in General Duty Medical Officers Sub-cadre of Central Health Services
Category-II:
Assistant Divisional Medical Officer in the Railways
General Duty Medical Officer in New Delhi Municipal Council
General Duty Medical Officer Gr-II in Municipal Corporation of Delhi
There are reservations for candidates belonging to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, Economically Weaker Sections, and Persons with Benchmark Disability as per the vacancies by the Government.
UPSC CMS Exam Pattern
Medical graduates with an MBBS degree along with completion of internship are eligible to apply for the UPSC CMS exam. There are two parts of CMSE, one is a written examination and the other is an interview. The CMSE comprises two theory papers followed by a personality test or interview. Here’s a breakdown of the exam pattern:
Part-I: Written Examination
The written examination comprises two papers:
Paper-I: This paper includes questions from General Medicine and Pediatrics subject. The exam Pattern 2024 for UPSC CMSE Paper-I is mentioned in the below table:
| Particulars | Details |
| Duration | 2 hours |
| Type of Questions | Objective type Questions (MCQs) |
| Total Marks | 250 |
| Total Number of Questions in Paper I | 120 (96 questions from General Medicine and 24 from Pediatrics) |
| Medium of Question Paper | English |
| Negative Marking | One-third of the marks assigned to a question are deducted for each incorrect answer.
If a candidate gives more than one answer, it will be treated as a wrong answer even if one of the given answers is correct and there will be the same penalty as above for that question. If a question is left blank i.e., no answer is given by the candidate, there will be no penalty for that question. |
Paper-II: This paper includes questions from Surgery, Obstetrics & Gynecology, and Preventive and Social Medicine subjects. The Surgery subject also includes ENT, Ophthalmology, Traumatology, and Orthopaedics subjects. The table below mentions the exam scheme for UPSC CMSE Paper-II 2024:
| Particulars | Details |
| Duration | 2 hours |
| Type of Questions | Objective type Questions (MCQs) |
| Total Marks | 250 |
| Total Number of Questions in Paper II | 120 (40 questions from each subject, Surgery, OBGYN, and Community Medicine) |
| Medium of Question Paper | English |
| Negative Marking | One-third of the marks assigned to a question are deducted for each incorrect answer.
If a candidate gives more than one answer, it will be treated as a wrong answer even if one of the given answers is correct and there will be the same penalty as above for that question. If a question is left blank i.e., no answer is given by the candidate, there will be no penalty for that question. |
Part-II: Interview/Personality Test
After passing the written test, candidates are invited by the Union Public Service Commission for an interview/personality test to determine their fit for the open positions.
The personality test carries 100 marks. The interview is designed to complement the written examination for measuring the general knowledge and academic study skills of the applicants as well as to function as a personality test to evaluate the candidate’s critical thinking skills, absorption capacity, and overall capacity for social cohesiveness, sound judgment, and moral character, initiative, and leadership potential. Basically, it aims to assess the candidate’s personality, communication skills, and suitability for the posts in medical services.
Final Selection
The final selection is done based on the combined marks obtained in Paper-I, Paper-II, and the Interview/Personality test.
Recruitment of a number of candidates is based on the vacancies in the particular position. Succeeding applicants are assigned to different Group-A positions within the public health system. The particular positions and openings change every year.
It’s significant to note that the Paper-I and Paper-II syllabuses contain a broad variety of medical science-related topics. A wide range of medical topics, including clinical disciplines, general knowledge, and current events, are covered in the CMSE curriculum. To score well on the test, candidates must have a solid comprehension of these topics. It is a crucial aspect of a good preparation strategy to know and understand the syllabus of the CMS exam. It leads to effective time management.
UPSC CMS Syllabus
UPSC CMS Syllabus Paper I:
General Medicine subject includes the following topics:
- Cardiology
- Respiratory diseases
- Gastro-intestinal
- Genito-Urinary
- Neurology
- Hematology
- Endocrinology
- Metabolic disorders
- Infections/Communicable Diseases
-
- Virus
- Rickets
- Bacterial
- Spirochetal
- Protozoan
- Metazoan
- Fungus
- Nutrition/Growth
- Diseases of the skin (Dermatology)
- Musculoskeletal System
- Psychiatry
- General
- Emergency Medicine
- Common Poisoning
- Snakebite
- Tropical Medicine
- Critical Care Medicine
- Emphasis on medical procedures
- Patho physiological basis of diseases
- Vaccines-preventable diseases and Non-vaccines preventable diseases
- Vitamin deficiency diseases
- In psychiatry – Depression, psychosis, anxiety, bipolar diseases, and Schizophrenia
Pediatrics subject includes the following topics:
- Common childhood emergencies
- Basic newborn care
- Normal developmental milestones
- Accidents and poisonings in children
- Birth defects and counselling including autism
- Immunization in children
- Recognizing and managing children with special needs
- National programmes related to child health
UPSC CMS Syllabus Paper II:
Surgery subject includes the following topics:
- General Surgery
- Wounds
- Infections
- Tumours
- Lymphatic
- Blood vessels
- Cysts/sinuses
- Head and neck
- Breast
- Alimentary tract
-
- Oesophagus
- Stomach
- Intestines
- Anus
- Developmental
-
- Liver, Bile, Pancreas
- Spleen
- Peritoneum
- Abdominal wall
- Abdominal injuries
- Urological Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Otorhinolaryngology/E.N.T.
- Thoracic surgery
- Orthopaedic surgery
- Ophthalmology
- Anaesthesiology
- Traumatology
- Diagnosis and management of common surgical ailments
- Pre-operative and post-operative care of surgical patients
- Medico-legal and ethical issues of surgery
- Wound healing
- Fluid and electrolyte management in surgery
- Shock pathophysiology and management
Obstetrics and Gynecology subject includes the following topics:
- Questions on applied anatomy
- Questions on applied physiology of menstruation and fertilization
- Questions on infections in the genital tract
- Questions on neoplasm in the genital tract
- Questions on displacement of the uterus
- Normal delivery and safe delivery practices
- High-risk pregnancy and management
- Abortions
- Intra Uterine growth retardation
- Medicolegal examination in OBGYN including the rape
Family Planning subject includes the following topics:
- Conventional contraceptives
- D. and oral pills
- Operative procedure, sterilization, and organization of programmes in the urban and rural surroundings
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy
Preventive Social & Community Medicine subject include the following topics:
- Social and Community Medicine
- Concept of Health, Disease and Preventive Medicine
- Health Administration and Planning
- General Epidemiology
- Demography and Health Statistics
- Communicable Diseases
- Environmental Health
- Nutrition and Health
- Non-communicable Diseases
- Occupational Health
- Genetics and Health
- International Health
- Medical Sociology and Health Education
- Maternal and Child Health
- National Programmes
- Management of common health problems
- Ability to monitor national health programmes
- Knowledge of maternal and child wellness
- Ability to recognize, investigate, report, plan, and manage community health problems including malnutrition and emergencies.
You can also enroll in online MBBS courses to get conceptual clarity over MBBS subjects by the top medical faculty of India. You have the opportunity to learn and get your concepts clear in Surgery by Dr. Sriram Bhat M, Microbiology by Dr. Apurba S Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat and Dr. Deepashree R, Medicine by Dr. Archith Boloor, Pathology by Prof Harsh Mohan, Prof Ramadas Nayak, and Dr. Debasis Gochhait, and similarly other MBBS subjects by subject’s eminent faculty. The comprehensive knowledge of MBBS subjects and problem-solving capabilities will directly impact your CMS exam.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. Is UPSC CMS conducted every year?
Ans. Yes, the UPSC CMS exam is conducted every year and the recruitment is based on the number of vacancies for a particular post in various government health organizations.
Q2. What is a career after CMS?
Ans. UPSC CMSE is conducted for the recruitment of the Medical Officers Grade in General Duty Medical Officers Sub-cadre of Central Health Services, Assistant Divisional Medical Officer in the Railways, General Duty Medical Officer in New Delhi Municipal Council, and General Duty Medical Officer Gr-II in Municipal Corporation of Delhi
Q3. Who conducts the CMS exam?
Ans. The CMS exam is a competitive examination conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) of India.
Q4. What is the pattern of UPSC CMS exam?
Ans. There are two parts of CMSE in which part-I is a written examination and the part-II is an interview. The CMSE comprises two theory papers followed by a personality test or interview.
The Part-I written examination comprises two papers: Paper-I and Paper-II.
The National Medical Commission (NMC) has achieved the coveted World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) Recognition Status for a tenure of 10 years. This is a prestigious achievement for India’s medical education. This esteemed award proves NMC’s steadfast dedication to the highest standards in medical education and accreditation.
The WFME recognition will now enable Indian medical graduates to pursue postgraduate training and practice in other countries that require WFME recognition, such as Australia, USA, Canada, and New Zealand.
The World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) is a global organization dedicated to raising the standard of medical education all over the world. The WFME accreditation programme is crucial in ensuring that medical institutions uphold and adhere to the highest levels of global education and training standards.
Dr. Yogender Malik, Member of the Ethics and Medical Registration Board and Head Media Division at NMC, on this remarkable achievement, said, “WFME’s recognition underscores that the quality of medical education in India adheres to global standards. This accolade empowers our students with the opportunity to pursue their careers anywhere in the world, while also making India an attractive destination for international students due to our globally recognized standards.”
Under this accreditation, all the 706 existing medical colleges in India will be considered WFME accredited, and the new colleges being set up in the coming 10 years will also be considered as WFME accredited. This will also benefit NMC in enhancing the quality and standards of Indian medical education by aligning them with global benchmarks. This will facilitate academic collaborations and promote continuous improvement and innovation in medical education.
Now NMC being WFME accredited has opened the doors for all the medical students for ECFMG and USMLE. All Indian students will become eligible to apply for the Education Commission on Foreign Medical Graduates and United States Medical Licensing Examination.
The National Medical Council, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in a press release dated 20th September 2023 has announced this remarkable update.
Global health comprises the biological and clinical facets of diseases along with the social, economic, political, and environmental determinants of health. The ability to confine health issues inside national borders has diminished as the globe becomes more linked.
The contribution of technology to the medical sector is unparalleled. With the years passing by technology is improving at the highest pace in the medicine sector. Nowadays, the use of AI, and the development of new therapies, drugs, drug development, and surgical procedures, have made complex medical procedures less complex and paved a path to minimally invasive surgeries. Millions of individuals throughout the world are having their lives improved as a result of these developments.
Global health has improved recently despite several obstacles like poverty, pandemics, disease outbreaks, conflicts, and climate change. Maternal and child fatalities have dropped significantly and since the development of new vaccinations, infectious illness spread has also been reduced. Governments and organisations have also boosted their funding for global health concerns and also significantly invested in newer technologies. The current developments in the healthcare industry are beneficial to global health and are an area with significant potential to enhance the health of people all over the world and in the medical field. We can improve the health of people all across the world by addressing the issues and embracing the possibilities.
Medical students and professionals must keep themselves updated and knowledgeable about the recent advancements in healthcare as it is going to impact their career growth to a great extent. To escalate the growth of your medical career, it is mandated to upskill.
The recent advancements in the global healthcare and medicine field are significant for several reasons. By offering more precise diagnoses, earlier illness detection, and more individualised treatment regimens, they have the potential to:
- Improve the quality of care for patients.
- By enabling remote monitoring and care and minimising the need for in-person visits, healthcare may be made more accessible and cheaper.
- Increase the effectiveness of healthcare delivery by simplifying administrative procedures and facilitating information exchange between healthcare professionals.
- Develop novel therapies and preventative measures to lessen the impact of chronic illnesses.
- Boost public health by keeping track of and rapidly and efficiently addressing illness outbreaks.
Below mentioned are technological advancements in medicine and global healthcare:
Artificial Intelligence and Healthcare
With the introduction of unprecedented tools for patient care, treatment, and diagnosis, artificial intelligence (AI) is drastically changing the healthcare industry.
For researchers interested in global health, AI-driven health interventions fall into four categories: diagnosis, patient morbidity or mortality risk assessment, disease outbreak prediction and surveillance, and health policy and planning. Machine learning, signal processing, data mining, natural language processing, and other forms of AI are applied in the healthcare sector.
Here are a few current applications of AI in healthcare:
- Diagnosis and treatment: Artificial intelligence (AI) paves the way for the screening of disease and can analyse medical images like X-rays and scans to identify illnesses early and more accurately than humans. AI may be used to create individualised treatment regimens for individuals based on their unique traits and requirements. Other applications of artificial intelligence being used in medicine include Digital chest radiographs, cervical cancer screening, estimating perinatal risk factors, and characterising and predicting the global spread of the Zika virus.
- Drug discovery: Artificial intelligence (AI) may be used to search through extensive databases of chemicals and compounds to find possible new medicines. AI may also be used to foresee how pharmaceuticals would react in the body, lowering the possibility of adverse effects.
- Personalised medicine: Artificial intelligence (AI) may be used to examine a patient’s genetic information, medical history, and lifestyle choices in order to develop a personalised treatment plan that has the highest chance of success.
- Risk assessment: AI may be used to predict the risk of disease and figure out how likely a patient is to have cancer or heart disease. Patients can utilise this knowledge to guide lifestyle adjustments that will lower their risk.
- Healthcare administration: AI may be used to automate processes like appointment scheduling, patient record management, and claim processing. This might free up medical personnel to concentrate on treating patients.
- Telemedicine: Platforms that employ AI in telemedicine can be used to offer doctor consultations via the Internet. Patients with limited access to healthcare in remote locations may particularly benefit from this.
- Robotics: Surgery, pharmaceutical dispensing, and other medical services can be carried out by AI-powered robots. This might aid in enhancing the effectiveness and precision of healthcare delivery.
- Big data analytics: Using AI, enormous databases of healthcare data may be analysed to spot trends and patterns. The diagnosis and treatment of illnesses can be made better with the use of this knowledge.
- Virtual assistants: AI-driven virtual assistants may be used to set up appointments, answer patients’ inquiries, and offer information about their conditions. The patient experience may be enhanced as a result of this.
The future of AI in healthcare is very promising. The use of AI in healthcare is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we diagnose, treat, and manage diseases. In the years to come, as AI technology advances, it is anticipated to have a more significant influence on the healthcare industry.
Advances in Gene Editing Technology
The science of gene editing is expanding quickly. The way we treat illnesses is changing as a result of gene editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9. These technologies can be used to fix genetic flaws that lead to disease or to add new genes that can offer disease protection.
The following are some of the developments in gene editing technologies that are being investigated for medical applications:
- CRISPR-Cas9: A protein called Cas9 is used by CRISPR-Cas9 to cut DNA at a precise spot. This enables precise gene replacement, deletion, and insertion. The most popular gene editing technology, CRISPR-Cas9, is being researched for a number of uses, including the treatment of HIV, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and hereditary illnesses.
For instance, in cancer patients, CRISPR-Cas9 is being utilised to create novel cancer medicines that can target and eliminate cancer cells. CAR T-cell treatments, a sort of immunotherapy that employs a patient’s immune cells to combat cancer, are being developed by researchers utilising CRISPR-Cas9.
- Base editing: A more recent gene editing technique, base editing allows you to alter specific DNA nucleotides without actually cutting the DNA. Compared to CRISPR-Cas9, this makes it less likely to result in unwanted side effects. For the therapy of conditions including cystic fibrosis and Duchenne muscular dystrophy, base editing is being researched.
- RNA editing: An approach to gene editing that can target RNA molecules rather than DNA. This can be utilised to treat conditions like certain cancers that are brought on by RNA alterations.
- Gene therapy: Gene therapy is a treatment that involves introducing genes into cells to correct a genetic defect. Numerous illnesses, including cancer, HIV, and hereditary ailments, have been treated by gene therapy.
These are only a handful of the gene editing innovations that are being investigated for medical applications. Technology’s continued advancement will probably have a significant influence on how we manage diseases in the years to come.
Development of Precision Medicine
A person’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environment are all taken into consideration when developing a medical treatment plan in precision/personalised medicine. This may result in a more effective and targeted treatment with fewer adverse effects.
Personalising medicine may be done in a variety of ways. Typical strategies include:
- Genetic testing includes examining a person’s DNA to see if there are any mutations or variances that might impact their likelihood of contracting a certain disease or their reaction to a particular medication.
- Biomarkers are quantifiable indications of a biological condition or state. Biomarkers can be used to monitor a patient’s response to therapy or to spot those who are most likely to catch a particular disease.
- Environmental factors, such as pollutant exposure, food, and exercise impact how people respond to therapy as well as the development of many diseases.
Precision medicine is becoming more and more feasible as we understand more about the human genome and the part genetics plays in disease. We can create more effective and focused therapies that may result in improvement by taking into consideration a person’s particular demands.
Here are some examples of current applications of precision medicine:
- High-risk cancer patients are identified via genetic testing, and targeted medicines are created that are more efficient for those who have certain genetic alterations.
- Biomarkers are being utilised to monitor an individual’s risk of developing heart disease and to pinpoint those who will benefit from certain therapies the most.
- Scientists are examining the genetic component of Alzheimer’s disease and creating targeted treatments that might be more efficient for those who carry particular genetic abnormalities.
Some of the challenges and limitations of precision medicine include cost, accuracy, accessibility, and regulation.
Personalised medicine is a promising subject with the potential to enhance millions of people’s lives despite these difficulties. It is anticipated to become more accessible, inexpensive, and accurate as technology advances.
Development of Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare
Telemedicine and remote healthcare allow patients to receive care from a doctor or other healthcare provider without having to travel to a doctor’s office or hospital. This can help with healthcare access, particularly in remote locations. The COVID-19 pandemic has spurred telemedicine and remote healthcare development to a great extent. These services are increasingly enticing to patients and providers alike because of the requirement to maintain social distance and avoid in-person visits to healthcare institutions. There are several advantages to telemedicine and remote medical care, such as better access to healthcare, lower healthcare expenses, increased patient satisfaction, and better patient results.
Remote healthcare services and telemedicine come in a wide variety. The most popular ones are Tele-education, remote patient monitoring, and virtual doctor appointments.
Additionally, there are several drawbacks to telemedicine and remote treatment, such as security and privacy issues, a lack of financing, technical issues, and a shortage of skilled providers.
Despite these impediments, telemedicine and remote healthcare are expanding quickly and playing a bigger role in the healthcare system. These services are expected to become progressively more common and available as technology advances.
Here are some of the future trends in telemedicine and remote healthcare:
- Increasing the use of artificial intelligence (AI): AI may be applied to personalise treatment regimens, increase the precision of diagnoses, and keep track of patient’s health.
- Development of novel telehealth technology: More thorough and individualised treatment will be feasible thanks to new gadgets like wearable sensors and virtual reality headsets.
- Expansion into new areas: Telemedicine and remote healthcare will be utilised to deliver care in new areas, such as managing chronic diseases and mental health.
Application of 3D Printing in Healthcare
3D printing in medicine is being used to create customised medical items including prostheses, implants, and surgical guides. This innovation might save expenditures while raising the standard of treatment. A rapidly developing technology, 3D printing has a wide range of potential uses in the healthcare sector. Among the most widespread applications of 3D printing in the medical field, some are mentioned below:
- Producing patient-specific medical devices: 3D printing may be used to produce personalised medical items like implants, prostheses, and surgical guides that are tailored to the anatomy of a single patient. In addition to lowering the risk of problems, this can enhance the device’s fit and functionality.
- Building medical models and educating healthcare professionals: 3D printing may be used to build accurate representations of the human body’s organs, tissues, and tumours. These models can be used to aid in the planning and execution of intricate treatments as well as the education of patients about their conditions. This can assist them in picking up new abilities and methods, as well as in practising approaches in a secure setting.
- Creating novel medications and treatments: Tissue scaffolds for cell culture and intricate drug delivery systems may be made using 3D printing. This can aid in the development of novel treatments and medications by researchers for a number of disorders.
- Customising care: Using 3D printing, it is possible to develop treatments and drugs that are specifically suited to the requirements of a certain patient. This might increase the therapy’s efficacy and security.
Here are some specific examples of how 3D printing is being used in healthcare today:
- A company named Materialise has created a 3D-printed breast implant that is specifically designed for women with tuberous breasts. This type of breast deformity is often difficult to treat with traditional implants, but the 3D-printed implant can provide a more natural and comfortable fit.
- A team of researchers at the University of California, San Diego has developed a 3D-printed surgical guide that can be used to remove brain tumors with greater precision and accuracy.
- A company named Organovo has developed a 3D printer that can be used to create human tissue. This tissue can be used to study diseases, develop new drugs, and create personalized medical implants.
These are some of the numerous uses for 3D printing that are now being made in the medical field. As technology advances, it will probably have a bigger influence on the healthcare sector, enhancing the standard of treatment and enhancing accessibility for all.
The use of blockchain technology to increase the security and effectiveness of healthcare data exchange is one of the significant developments being made in the world of healthcare. Smart technologies, particularly wearable sensors, are being developed to extract therapeutically significant health-related data from physical (body) indicators like heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, respiration rate, and body motion. The technology has now also come up with immersive virtual and augmented reality training and education in the medical field.
Advancements in technology, increased investment in global health, partnerships, collaborations among the government, organizations, and individuals, and innovations altogether make a significant contribution to addressing the challenges to global health and improving health outcomes. The rapid pace of technical improvement has made these developments feasible. These technologies will have a bigger influence on global healthcare as they advance.
The NEET-SS was scheduled for the 9th and 10th of September this year but due to the G20 Summit in New Delhi, the NEET-SS 2023 exam dates have been revised. Now, the revised NEET-SS 2023 exam dates are 29th and 30th September 2023 and it will be conducted at various examination centres across the country.
The NEET-SS 2023 admit card shall now be issued on 22nd September 2023. The NEET-SS 2023 result shall be declared on 15th October 2023.
As per the NBEMS, the revised schedule of NEET-SS 2023 for different groups is as follows:
| Date of Examination | Group | Shift |
| 29th September 2023 | Medical Group | Morning Shift (9 AM to 11:30 AM)
Reporting at Test Centre starts at 7 AM; Entry closes at 08:30 AM |
| 29th September 2023 | Radiodiagnosis Group
Microbiology Group Pathology Group Psychiatry Group Surgical Group Pediatric group Anaesthesiology Group Pharmacology Group |
Afternoon Shift (2 PM to 4:30 PM)
Reporting at Test Centre starts at 12 PM; Entry closes at 01:30 PM |
| 30th September 2023 | ENT Group
Respiratory Medicine Group Obstetrics & Gynecology Group |
Morning Shift (9 AM to 11:30 AM)
Reporting at Test Centre starts at 7 AM; Entry closes at 08:30 AM |
| 30th September 2023 | Orthopaedics Group | Afternoon Shift (2 PM to 4:30 PM)
Reporting at Test Centre starts at 12 PM; Entry closes at 01:30 PM |
The revised schedule for admissions to DM/MCh courses shall be notified in consultation with the National Medical Commission and DGHS (MoHFW).
Know the Reliable Last Minute Tips for the NEET-SS 2023 Exam.
NEET-SS is a National Eligibility cum Entrance Test – Super Specialty, conducted by NBEMS. This year the NEET-SS exam is scheduled on 29th and 30th September 2023. The NEET SS 2023 admit card release date is 22nd September 2023. As the exam is just around the corner, it’s the time for final touchdown with the preparation and getting ready to sit and perform well in the exam.
The blog includes reliable last-minute tips, information regarding admit card and test day procedures, and the documents required to carry for your big day.
Some effective last-minute tips for all the NEET-SS candidates:
Review your notes and flashcards. It is highly advised to stick to your handwritten notes to save much of your time and aid in quick memorization. This will help you solidify your understanding of the topic.
Practice previous years’ papers and practice papers. This will assist you in becoming used to the exam’s format and help you pinpoint any areas that require further practice.
Attempt the Demo exam. To become familiar with the format of the computer-based test, a demo test will be made accessible on the website https://natboard.edu.in. Starting on August 25, 2023, applicants will be able to access the Demo test.
Focus on important and high-yield topics. Prioritize time and focus on the important topics to score high in the exam.
Sleep well the night before the test. You’ll be more awake and concentrated on test day as a result.
On the exam day, have a balanced breakfast. This will keep you energetic and focused throughout the exam.
Be on time for the exam. This will offer you some breathing room and mental preparation time before the exam starts.
Stay calm and focused during the exam. Don’t panic if you don’t know the answer to a question. Just skip it and come back to it later.
Before beginning the exam, carefully read the instructions. This will assist you in avoiding casual errors.
Before you submit your exam, double-check your answers. This will assist you in avoiding any mistakes and you’ll not miss any marks for review questions.
Keep your documents ready and your admit card printed before your exam day to avoid any last-minute chaos.
Here are some more suggestions to control your stress and anxiety:
While studying, take breaks. Avoid being overly worried or overwhelmed by getting up and moving about every 20 to 30 minutes.
Discuss your feelings or problems with a trusted person. This may be a friend, a member of your family, a teacher, or a counselor.
Practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation. You’ll be able to relax and concentrate better as a result.
Keep in mind that anxiety before a test affects everyone. Although feeling anxious is common, try not to let it control you.
Click here to learn about the NEET-SS 2023 exam in detail.
NEET-SS 2023 Admit Card
- The NEET-SS admit card 2023 release date is 22nd September 2023.
- The admit card will be available on the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences website and may be notified by SMS/Email alerts and website notice. The candidates will not get an admit card by mail or email.
- It must be downloaded from the NBEMS website and get their admit cards printed. Then, firmly paste the most recent passport-size photograph onto the designated spaces on the card m and adhere to the following requirements:
- Minimum 35×45 mm in size (and no bigger than the space designated on the admit card for pasting the photo), with at least 75% of the photo’s surface area devoted to the head and face.
- The image must be colored with a simple white background.
- A neutral look and a complete frontal view of the face must be shown in the photograph. No caps, stethoscopes, goggles, or additional accessories should be worn.
- The face in the photo shouldn’t have any reflections or shadows on it.
- The photo needs to be printed on high-quality paper with a resolution of at least 600 dpi, and it can’t contain kinks, scratches, or stains.
NEET-SS 2023 Test Day Procedures
- There will be staggered entry as per time slots given in the admit cards and the entry will be done in batches accordingly. Reach the “Reporting Counter” at the exam location at the time specified on the admit card.
- As there are staggered time slots to report, there won’t be a queue at the exam location entrance. Candidates must arrive at the exam site within the time window that will be communicated to them by SMS on their registered telephone number, one day before the exam. The reporting counter will close 30 minutes before the exam starts time. This will give enough time for security checks, identity checks, and examination check-in.
- The admit card mentions the exact street address and location of the test facilities. It is advised to become familiar with the locations of the test centres at least one day before the exam day and make sure to report on time. Please be aware that only candidates who have been granted an admit card will be permitted access to the test centre premises.
- There will be a barcode/QR code reader at the entry gates of the exam centre. It is required to present the admit card and ID proof to the exam functionary who is positioned across with a barcode/QR code reader for verification. The candidates will be made aware of the lab number issued to them.
Things to Carry in the Examination Hall
Printed copy of Barcoded/QR Coded Admit card with the photograph affixed on it.
Photocopy of Permanent SMC/MCI/NMC registration, to be retained by the test centre.
Any one of the following original and valid/non-expired Govt issued photo IDs:
- PAN Card
- Driving License
- Voter ID
- Passport
- Aadhaar Card (with Photograph)
If you want to show an e-Aadhaar card with the Aadhaar number written on it as identity proof, the e-Aadhaar card has to be a high-quality color printout with the photo visible. The picture must be clear and match the candidate presenting the e-Aadhaar Card without any wrinkles, stains, or scratches. In this case, the NBEMS’ decision is definitive.
It is required that the name on the photo identification and the name on the admit card must correspond. It is mandated to present the appropriate paperwork (Marriage Certificate/Divorcee Decree/Legal Name Change paperwork/Gazette notification for name change) to support a claim for change of name if the name has changed as a result of marriage or other circumstances.
I hope these pointers will help you in your NEET SS test preparation. Good fortune!
Chapter 3 of the NExT Exam 2023 update comprises the objective, distribution and level of questions, paper and distribution of subjects, and proposed schedule of both NExT step 1 and 2.
NExT Step 1
- Objective
This step is a computer-based exam with multiple choice questions aimed to ensure objectivity and address a higher level of knowledge assessing the competencies of a medical graduate.
- Distribution and knowledge level of Questions
- Majority of items must assess higher level comprehension, analytical skills, and clinical problem-solving that are in line with competencies to assure evaluation of higher domains of medical learning.
- The NExT Step 1 style is meant to discourage medical students from rote learning.
- Case studies and clinical case studies will make up the majority of the test; MCQ questions will be allocated roughly as follows across all subjects:
- Problem-solving and analytical skill types – 60% – 70%
- Comprehension type- 20% – 30%
- Recall type- 05% – 15%
- The level of knowledge necessary to get skills will be roughly
- Must Know: 60%
- Nice to Know: 30%
- May Know: 10%
- Pattern and Distribution of Subjects
- Six subject papers with corresponding weightage and time allocation will be included in the NExT Step 1 exam.
- Applied features of all other MBBS subjects, including forensic medicine and toxicology (FMT) as well as community medicine, will be mainstreamed within the pertinent clinical subjects.
- The subjects are listed below along with their appropriate item weightings and time allotments:
| Papers | Subjects | No. of Items | Duration |
| 1 | Medicine & allied subjects | 120 | 3.0 hours |
| 2 | Surgery & allied subjects | 120 | 3.0 hours |
| 3 | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 120 | 3.0 hours |
| 4 | Pediatrics | 60 | 1.5 hours |
| 5 | Otorhinolaryngology | 60 | 1.5 hours |
| 6 | Ophthalmology | 60 | 1.5 hours |
- Proposed Time Schedule of Papers
| Day | Subject | Duration | Break | Subject | Duration |
| 1 | Medicine & allied subjects | 3.0 hours | 2.0 hours | Paediatrics | 1.5 hours |
| 2 | No Examination | ||||
| 3 | Surgery & allied subjects | 3.0 hours | 2.0 hours | Otorhinolaryngology | 1.5 hours |
| 4 | No Examination | ||||
| 5 | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 3.0 hours | 2.0 hours | Ophthalmology | 1.5 hours |
NExT Step 2
- Objective
This step shall be a clinical/practical examination to be conducted after the successful completion of the internship. The objective of this step is to evaluate the competencies of the medical graduates in clinical diagnosis, patient and clinical decision-making, and practical and communication skills.
- Evaluation Methods
The examination will comprise Actual cases, Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE), and Simulations if possible.
There will only be two levels of grading available: “Competent” or “Pass”/”Not Competent” or “Fail” depending on the likelihood of satisfactory performance or unsatisfactory performance.
- Distribution of Subjects
The following subjects shall be evaluated during NExT Step 2:
- Medicine and allied subjects
- Surgery and allied subjects
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics and Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation (PMR)
- Time Schedule
The schedule and modalities of NExT Step 2 shall be decided by the National Medical Commission and the respective authorized Universities/Institutions after completion of the internship and the price of the admission process for the Postgraduate Courses of that year.
Time Schedule of NExT Examination and associated events
Proposed Time Schedule:
| S.No. | Event | Commencement Date of Exam | Completion Date |
| 1 | NExT Step I Regular | May/November | 1st week June/December |
| 2 | III MBBS /FINAL MBBS PART 2 Practical / Clinical University Examination | 1st Week June/December | 3rd Week June/December |
| 3 | Internship | 1st Week January/July
|
31st December/30th June of the following year |
| 4 | NExT Step 2 Regular | 3rd Week June/December | 4th Week June/December |
| 5 | NExT Step 2 Supplementary | 1st Week September/March | 3rd Week September/March |
| 6 | Post Graduate Admission | May-June (Counselling) | 30th June |
| 7 | Postgraduate Course | 1st July/1st Week January | — |
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 1 (Preliminary)
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 2 (Broad Outline)
The Chapter 2 of the NMC Update describes the broad outline of the National Exit Exam, including general features of steps 1 and 2, NExT scores, nature of scores, minimum passing score, etc.
General Features of the NExT Exam
The NExT Exam shall comprise two separate exams referred to as “Steps”.
Step 1: Theoretical Examination
Step 2: Practical/Clinical and Viva Voce Examination
NExT Step 1
1.NExT Step 1 shall be a theoretical and Computer-based/Online examination.
2. It shall comprise one or more types of multiple-choice questions.
3. This shall be a Centralized Common All India Examination that will be held by a body designated by the commission as the conducting authority.
4. The examination shall include six papers covering topics from both Part 1 and 2 of the III MBBS/Final MBBS programme:
- Medicine and allied disciplines
- Surgery and allied disciplines
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
(Applied aspects of all subjects covered under I MBBS and II MBBS and Applied aspects of all subjects covered under III MBBS/Final MBBS Part l)
5. Students who have completed their III MBBS/Final MBBS course from a recognized medical college shall be eligible to appear for the examination.
6. NExT Step 1 Examination shall be held twice a year in the months of May and November tentatively.
7. There shall be no restriction on the number of attempts to participate in NExT Step 1 provided that the candidate has completed both the NExT Step 1 and NExT Step 2 exams within ten years of enrolling in the MBBS Course.
8. There is no cap on the number of times for attempting the NExT Step 1 Regular Examination to improve your score but you can only go for the improvement after completing your NExT Step 2.
9. The III MBBS/Final MBBS Part 1 and III MBBS/Final MBBS Part II Practical/clinical examinations will continue to be held conventionally unless otherwise stated by the Commission and the NExT Step 1 will replace the traditional university/institutional Theory Examinations of the III MBBS/Final MBBS Part II.
NExT Step 2
1. The NExT Step 2 shall be a Practical/Clinical and viva voce examination comprising seven clinical subjects/disciplines:
- Medicine and allied disciplines
- Surgery and allied disciplines
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopaedics and PMR (Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation)
2. The exam shall be objectively structured, clinical case-based, and use simulated cases and patients to evaluate practical and clinical skills as well as clinical decision-making and communication abilities expected of an Indian medical graduate.
3. The exam must be taken in person or live, and it must be administered by the relevant state health universities or institutions in accordance with the norms and directives given by the Commission. The Commission will choose the university or institution that is permitted to conduct NExT Step 2 for the relevant colleges where there are no state health universities.
4. The Regular NExT Step 2 Exam shall be held twice a year.
5. A NExT Step 2 Supplementary Examination is only open to candidates who have failed in one or more (up to three) of the seven subjects and are required to repeat specific subjects. It will be held twice a year. If a candidate fails in more than three subjects, then they will have to appear in supplementary exams of all the seven subjects.
7. As long as the candidate has completed both the NExT Step 1 and NExT Step 2 Examinations within ten years of enrolling in the MBBS programme, there is no restriction on the number of attempts to participate in NExT Step 2.
NExT Scores
1. Nature of Scoring
- The marks in NExT Step 1 must be calculated as a whole number, which will serve as the Raw Scores with the proper decimals. Also, equivalent Percentages (marks out of a maximum of 100) with the proper decimals may then be calculated.
- The outcomes of the NExT 2 exams will only be reported as Pass/Fail depending on the acquisition of the relevant competence that is being evaluated.
2. Minimum scores for passing
- The minimum score to pass shall be 50% of the total or half of the maximum possible Raw for NExT Step 1.
- To pass the NExT Step 1 exam, you must receive a minimum of 50% (50 out of 100) in each of the six papers or half of the maximum possible Raw Scores.
- The requirements for passing NExT Step 2 include a successful demonstration of having acquired the competencies that are evaluated, with a pass/fail result being given.
3. Calculation of NExT Step 1 scores for determining merit for the purpose of admission to Postgraduate courses in broad specialties
- The sum of the raw scores earned in each paper or topic in a single NExT 1 exam will be used to calculate the Total Marks for determining the merit, particularly for admission to broad specialization Postgraduate Courses.
- The candidate must follow the generation of a rank application process as stipulated by the Commission from time to time in order to determine rank for admission into Postgraduate courses in broad specializations in a given academic year. Only individuals who have submitted an application for rank generation will be eligible for admission for that cycle of the academic year.
- The NExT Step results will be valid for five years in order to determine merit, notably for admission to broad-specialty postgraduate courses. If a candidate has appeared in the NExT exam cycle then the score of the latest given NExT step 1 exam will be considered.
- Tie-breaker rule for rank generation:
-
- Normalized sum of raw scores obtained in each paper in NExT step 1 although the method of normalization will be notified later.
- Candidate with the lower attempts in NExT step 1 will be placed higher in the merit list.
- Candidates will be given higher rank based on the higher marks in the following order of preference:
-
-
- Medicine and allied disciplines
- Surgery and allied disciplines
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Pediatrics
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Ophthalmology
-
4. Utility of NExT Scores
- An MBBS student from a college recognized by the Commission shall be eligible for compulsory internship only if they pass in each of the six theory papers of NExT Part 1 and also pass in III MBBS/Final MBBS (Part 2) Practical/Clinical Examination.
- A medical student who has completed their undergraduate studies abroad at an institution recognized by the Commission and who has met the necessary requirements outlined in the Commission’s Foreign Medical Graduate Regulations is eligible to participate in the mandatory rotating internship programme only if they pass in all six NExT Step 1 Theory Papers.
- A medical graduate who received their training in India or outside of India will be entitled to register in the Indian Medical Register and State Medical Register and obtain a license to practice modern medicine in India, only if, they have completed the internship for the appropriate length of time and have successfully passed the NExT Step 2 (Practical / Clinical) Examination. You must fulfill all the requirements as per the Registration of Medical Practitioners and Licence to practice Medicine Regulations, of NMC. Also, all the other requirements are considered appropriate by the Commission, Concerned University/Institution and duly applicable at that time.
- For admission to PG medical courses in broad specialty subjects, a candidate must meet the following criteria:
- Candidates must meet the conditions outlined for NExT Part 1 and 2, making them eligible for a license to practice modern medicine in India.
- Must engage in common counselling by a designated authority granted by the Central Government or Commission.
- The NExT Step I Scores may be used by the Government of India, the State Governments, any organization of the Government of India, the State Governments, or any autonomous or private body/institution for the purpose of employment, provided that the necessary authorization has been sought and authorized by the National Medical Commission or other appropriate authorities as determined to be appropriate.
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 1 (Preliminary)
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 3 (General Information)
The NExT Exam latest news includes Chapter 1 (Preliminary) and Chapter 2 (Broad Outline) and Chapter 3 (General Information).
The core objective of the NExT exam is to provide consistency in summative evaluations conducted across the nation in relation to the minimal requirements for a medical graduate’s education and training.
The National Exit Test (NExT), shall serve as a licentiate examination for validating a medical graduate’s eligibility to register for practice the contemporary system of medicine in India.
NExT will also act as an entrance exam for admission to PG medical education in broad medical specialties by determining the eligibility and ranking of the MBBS students.
The National Exit Exam shall be applicable to:
- All undergraduate medical students seeking the MBBS degree at all medical colleges that have been accredited by the National Medical Commission along with Institutes of National Importance (INIs) are subject to the National Exit Test (NExT).
- All foreign medical graduates who have been granted approval by the NMC for the purposes of obtaining a license to practice medicine as a registered medical practitioner in India and for enrollment in the State Register or the National Register in such a manner as may be specified by regulations.
- Anyone with a medical degree aiming to pursue an academic course, an observership, or any other purpose that may be specified and allowed by the NMC by appropriate notification or rules from time to time.
- Anyone with the granted medical license practicing in India wishes to pursue PG degree can take the NExT exam.
According to the draft released, the NExT comprises two separate examinations, referred to as “Steps”.
Step 1: Theoretical Examination
Step 2: Practical/Clinical and Viva Voce Examination
The Commission shall from time to time determine, by appropriate regulations and/or notification, the applicable method of employing the NExT results for admission to Postgraduate Courses in wide medical specialties by means of common counselling by the designated authority.
There is no confirmation yet on the academic session to which the NExT exam will be applicable but when it will come into force, all other corresponding and equivalent examinations shall be phased/ceased out.
It is still to be decided by the Commission Central Government, State Government, that the existing examinations, however, shall continue for as long as may be necessary or the analogous existing exams will be replaced by the NExT. The Commission will decide when it is necessary and will notify the use of scores and normalization of various examinations and the NExT, when applicable concurrently, for such purposes as may be appropriate.
Chapters 2 and 3 of the update include the complete structure of the NExT Examination, objectives, exam pattern, eligibility, distribution of subjects, nature of scoring, timetables, and more.
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 2 (Broad Outline)
Click Here to Read NMC NExT Exam Update – Chapter 3 (General Information)
Obstetrics and gynecology is among the vast medical PG specialties. In order to thoroughly cover all the topics, you must read from standard books and top-notch resources. A student may refer to textbooks, handbooks, practical or bedside medical books, and additional material, depending on the requirement.
List of PG OBGYN Books for PG Students and Residents
1. FOGSI’s Postgraduate Obstetrics: A Textbook (Volume 1) and FOGSI’s Postgraduate Gynecology: A Textbook (Volume 2)
- FOGSI’s Postgraduate Obstetrics Textbook and FOGSI’s Postgraduate Gynecology Textbook by Alpesh Gandhi, Parikshit Tank, and Ameya Purandare have found an indispensable place in the shelves of the OBGYN postgraduates and residents.
- In the latest edition, a thorough examination of the topic is given with appropriate consideration to its subspecialties, which include fetal medicine, endoscopy, reproductive treatment, urogynecology, and cancer.
- The book has ample illustrations of the topic, including key statements, diagrams, pictures, and tables.
- To aid with self-evaluation and test preparation, each chapter includes multiple choice along with short and long questions.
2. Williams Obstetrics
- Williams Obstetrics by Barbara Hoffman, Brian Casey, Catherine Spong, F. Gary Cunningham, Jodi Dashe, and Kenneth Leveno is among the most preferred book for obstetrics by medical students.
- The chapters in the book include Overview, Maternal Anatomy and Physiology, Placentation, Embryogenesis, and Fetal Development, Preconceptional and Prenatal Care, First and Second-Trimester Pregnancy Loss, The Fetal Patient, Labor, Delivery, The Newborn, The Puerperium, Obstetrical Complications, and Medical and Surgical Complications.
- Additionally, the book includes basic information on the anatomy, physiology, and prenatal care of the reproductive system.
- The latest edition of the book has been improved by the authors with more than 1,000 full-color images having a stronger focus on the rapidly expanding specialization of maternal-fetal medicine.
- This indispensable clinical companion puts successful outcomes within grasp with its cutting-edge design and examination of the most recent developments and protocols.
- The updated content includes topics such as maternal-fetal medicine, greater awareness of hypertension and bleeding, a deeper understanding of fetal difficulties, modern fetal imaging, genetics, prenatal diagnostics, and fetal diseases.
- The latest edition of the book contains more obstetrical sonography figures, and eye-catching illustrations, including sonograms, MRIs, graphs, and photomicrographs.
3. Williams Gynecology
- Williams Gynecology by F. Gary Cunningham, Kenneth J. Leveno, Jodi S. Dashe, Barbara L. Hoffman, Catherine Y. Spong, and Brian M. Casey is the only text that combines both a medical reference and surgical procedures atlas into one volume.
- The most recent information regarding topics including minimally invasive surgery, benign gynecology, and the subspecialties of urogynecology, gynecologic cancer, and reproductive endocrinology is brought together in this well-illustrated manual.
- Williams Gynecology offers thorough coverage of the full range of gynecologic healthcare and disease management, including benign general gynecology; reproductive endocrinology, infertility, and menopause; female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery; and gynecologic oncology.
- It contains 1,200 photos and illustrations, including 450 full-color figures depicting operative techniques.
- The section on ‘Aspects of Gynecologic Surgery and Atlas of Gynecologic Surgery’ contains procedures for reconstructing the female pelvis, minimally invasive surgery, and procedures for gynecologic cancers.
4. DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics (Including Perinatology & Contraception)
- DC Dutta’s Textbook of Obstetrics by Hiralal Konar is a highly preferred textbook for OBGYN students and residents as well as for general practitioners.
The latest edition of the book is crisp and is written lucidly. - The text in the book is supplemented with 790 line drawings, illustrations, photographs, boxes, tables, flowcharts, MR images, ultrasonograms, and skiagrams.
- The chapters have been thoroughly revised and updated including Ch. 13 Normal Labor, Ch. 39 Intrapartum Fetal Monitoring, Ch. 31,32,33 on Perinatal Care, and Ch. 34 Analgesia & Anesthesia in Obstetrics.
- The book features the key points for revision and better memorization.
- Must-know topics are highlighted in the chapters and evidence-based knowledge is focussed.
- One of the key features of the book includes the guidelines and recommendations of professional organizations like ROCG, WHO, NICE, FOGSI, and more.
For ease of navigation, a list of the most used acronyms has been supplied. - Additional features include The Kernel and the Beyond Series. The book material is organized to provide a topic-to-topic comprehension from the perspective of the exams.
- The supplementary reading material for advanced learning is highlighted by the QR codes. This strategy aims to support and get medical students ready for their exams.
5. DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology
- DC Dutta’s Textbook of Gynecology by Hiralal Konar is an indispensable resource for medical students, residents, and general practitioners.
- The book’s user-friendly layout and thoroughness make it a great resource.
- This book’s presentation, which includes high-quality graphics and design, voluminous illustrations (366), excellent pictures (330), and imaging studies, is what makes it stand out.
- There are several tables, boxes, flowcharts, and algorithms included for repeatability and simplicity of study. The main points are listed after each chapter to give a summary of the entire chapter. This is helpful for a quick and simple review.
- The book’s presentation, which is straightforward, transparent, clear, and succinct, represents the state-of-the-art.
- The latest edition of the book is thoroughly revised and updated to provide the most recent information on subjects including minimally invasive surgery, reproductive endocrinology, urogynecology, and gynecologic oncology.
6. Bedside Clinics in Gynecology
- The book Bedside Clinics in Gynecology by Arup Kumar Majhi is highly recommended for undergraduate, and postgraduate medical students and residents.
- New subjects have been added, and chapters have been updated and edited.
- The topics covered in this book include history-taking and examinations, clinical cases, instruments, operations, specimens, and imaging, research questions, an examination of a rape victim, and STDs and pelvic inflammatory disease.
- The book is enriched with 330 graphics and over 845 unique pictures.
- The majority of the chapters have been updated while maintaining the same format, and several newer ones have been introduced, including changes to cancer staging, management, Mullerian anomaly classifications, and many more.
7. Case Discussions in Obstetrics & Gynecology
- The Case Discussions in Obstetrics & Gynecology by YM Mala, Madhavi M Gupta, and Asmita M Rathore covers all the practical aspects of OBGYN through case discussions.
- The latest edition of the book has incorporated 14 new chapters along with thorough revision and updates in the other chapters.
- The book caters to the learning requirements for all the courses and examinations may it MBBS/MD/MS/DGO/DNB.
- Almost all typical obstetric and gynecological practical cases are included.
- The book contains viva questions that are often or regularly asked during case discussions for practical exams. Different scenarios have been developed to accommodate a wide range of questions, even within the same topic or case.
8. Tips and Tricks in Operative Obstetrics & Gynecology
- Tips and Tricks in Operative Obstetrics & Gynecology by Richa Saxena is highly beneficial to postgraduate students, trainee gynecologists, and obstetric and gynecologic consultants and practitioners.
- The book contains concise facts regarding different obstetrics and gynecological procedures.
- The information in this book helps obstetricians and gynecologists quickly understand the fundamentals of the numerous obstetric and gynecological operations.
- The latest edition explains the recent advances in the surgical aspects of gynecology.
- Each chapter comprises a unique style containing different headings, such as introduction, indications, pre and post-operative care, surgical steps, etc.
9. Ian Donald’s Practical Obstetric Problems
- Ian Donald’s Practical Obstetric Problems by Renu Misra is a must-have book for PG OBGYN students and practicing gynecologists.
- With an emphasis on useful advice and recommendations for handling both common and urgent situations, each chapter has been updated to give the latest recent diagnosis and management guidelines.
- The latest edition comprises recent advances in prenatal diagnosis, updated guidelines on managing thyroid dysfunction during pregnancy, HIV during pregnancy, premalignant and malignant diseases associated with pregnancy, revised labor curves, postpartum haemorrhage, and more.
- It also includes an updated appendix on drugs and vaccination during pregnancy and lactation and covers COVID-19’s effect on mothers and newborns.
10. Jeffcoate’s Principles of Gynecology
- The Indian Edition of Jeffcoate’s Principles of Gynecology by Narendra Malhotra, Jaideep Malhotra, Richa Saxena, and Neharika Malhotra Bora is considered the ‘Bible for Gynecologists’.
- It is among the most preferred OBGYN books for PG students, residents, surgeons, practitioners, and OBGYN consultants.
- With the most recent guidelines and developments in this subject in mind, new chapters, illustrations, images, and conversations have been included in this updated edition.
- New topics Adenomyosis, assisted reproductive technology, urinary tract infection, contraception, precocious and delayed puberty, pregnancy of unknown site, female genital mutilation, genetics in gynecology, and single incision laparoendoscopic surgery, etc. have been included in the latest edition.
- The author has maintained Prof. Norman Jeffcoate’s narrative approach while updating each chapter to reflect the most recent evidence.
Click here to get conceptual clarity on the OBGYN MD topics.
Pediatrics is a branch of medicine that focuses on the healthcare and management of infants, children, and adolescents under the age of 21. Medical professionals who specialize in this field are known as Pediatricians. They specialize in diagnosing and treating problems and illnesses related to infants, children, and youngsters. Most pediatric physicians treat common illnesses, minor injuries, and infectious diseases, and administer vaccination whereas pediatric specialists, such as pediatric endocrinologists, pediatric cardiologists, pediatric oncologists, etc. treat specific ailments and perform invasive and non-invasive treatment procedures.
Pediatricians are responsible to create awareness to control the spread of infectious diseases, reduce the infant mortality rate, provide counseling to adolescents, and more. They are responsible for the minutest things and needs of the child. From their nutritional needs to tracking their growth, a pediatrician has to take care of all.
Steps for Becoming a Pediatrician
Step1: Complete your senior secondary education
An applicant must have earned a minimum of 50% in each of the four major subjects—Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English—in their 12th grade from an accredited board.
Step 2: Crack the NEET-UG Entrance Examination.
Candidates must pass the National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test for Undergraduates (NEET-UG), a single window entrance exam to be considered for admission to MBBS, BDS, BAMS, BUMS, BHMS, and other undergraduate medical programs at approved/recognized Medical/Dental/AYUSH and other Colleges/Deemed Universities/Institutes (AIIMS & JIPMER) in India.
You must get a competitive score in the NEET-UG exam to go through the counselling and admission process to get admitted to a medical college for an MBBS program, which is a prime requirement for becoming a pediatrician.
Step 3: Complete your MBBS degree along with the internship.
Complete your MBBS degree with a minimum cumulative GPA of 50% along with a one-year compulsory rotational internship. You must pay special attention to the lectures, practical sessions, ward postings, seminars, conferences, etc. during your graduation since they establish a strong basis for your studies. At this point, you learn the fundamentals of every medical specialty. You will now be able to identify the area of interest in which you desire to pursue a postgraduate degree.
Click here to get conceptual clarity in the MBBS subjects.
Step 4: Crack the NEET PG or INI-CET entrance examination.
After completing your MBBS degree, you must crack the NEET PG or INI-CET exam with a competitive score to be admitted to medical postgraduate programs. While INI-CET is a national-level entrance examination for admission to MS/MD/DM (6 years)/MCh (6 years) and MDS courses at the INI Institutes, which includes AIIMS, JIPMER, etc., NEET-PG is a national-level entrance examination for admission to MS/MD/PG Diploma programs at various government and private universities.
Based on the admission exam scores, applicants choose their postgraduate specialization and college during the counselling process. An MBBS student must select an MD degree with a Pediatrics specialization to become a Pediatrician and to also pursue higher education in pediatrics. You also have the option to pursue MS in General Surgery if you want to pursue MCh Pediatrics Surgery and Pediatric Cardio Thoracic Vascular Surgery discipline in the future.
Step 5: Complete your PG degree.
Following admittance into a medical college with MCI accreditation, finish your three-year master’s degree and complete your PG dissertation. The PG curriculum comprises lectures, practicals, conferences, symposiums, workshops, clinical postings, meetings, OT ward postings, junior residency, and more.
Click here to master the concepts of PG Pediatrics.
Step 6: Complete your residency program and get licensed.
Complete your residency program and experience the world of pediatrics and medicine. Get your medical certificate and get licensed to practice as a Pediatric Specialist.
Step 7: Crack the NEET-SS entrance examination to pursue a super specialization.
After completing the MD degree and residency program, you can pursue DM, DrNB, or MCh courses and complete your super specialization. To get admission to Super specialty courses in Pediatrics disciple, you need to crack NEET-SS, an eligibility cum ranking examination.
To add more value to your career, you must go with super specialization courses, fellowship courses, and advanced-level certification courses.
Apart from doing super specialization, you also have the option to pursue research, join as a pediatrician in any healthcare facility, or join any child organization at various available posts.
List of Pediatric Subspecialties
- Neonatologist
- Pediatric Cardiologist
- Critical Care Pediatrician or Pediatric Intensivist
- Pediatric Endocrinologists
- Pediatric Gastroenterologists
- Pediatric Hematologists and
- Pediatric Oncologists
- Neonatal pediatricians
- Child nephrologist
- Pediatric allergist
- Pediatric Dermatologists
- Pediatric Urologists
List of DM Courses after completing MD Pediatrics
- DM Cardiology
- D.M. Clinical Haematology
- D.M. Endocrinology
- D.M. Medical Gastroenterology
- D.M. Medical Genetics
- D.M. Medical Oncology
- D.M. Neonatology
- D.M. Nephrology
- D.M. Neurology
- D.M. Pulmonary Medicine
- D.M. Pediatrics Gastroenterology
- D.M. Pediatrics Cardiology
- D.M. Hepatology
- D.M. Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology
- D.M. Infectious Disease
Top Medical Colleges to Pursue Pediatrics
- AIIMS, Delhi, and all other AIIMS
- CMC, Vellore
- Armed Forces Medical College, Pune
- PGIMER, Chandigarh
- Dr. D.Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, Pune
- KMC, Manipal
- Maulana Azad Medical College, Aligarh
- JSS Medical College, Mysore
- Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham, Coimbatore
- Lady Hardinge Medical College, Delhi
- University College of Medical Sciences, Delhi
- St. John’s Medical College, Bengaluru
Skills Required for Becoming a Pediatrician
A medico must develop the following skills to become a successful pediatrician:
- You must develop expertise in gathering, analyzing, and systematically presenting history and examination while giving proper weight to the most crucial information and downplaying the less crucial details.
- You must be efficient in non-invasive monitoring of BP, Pulse, respiratory, ECG, Saturation, etc.
- You must be fully aware of the investigative procedures involved in basic and minor treatments, non-invasive procedures, emergency conditions, etc. You must have complete knowledge of various diagnostic and investigative procedures such as tuberculin test, kidney biopsy, liver biopsy, urethral catheterization, blood sampling, etc.
- You must have a clean hand for practices such as the administration of injections, breastfeeding assessment, phototherapy, blood component therapy, oxygen administration, rehabilitation process, peritoneal dialysis, mechanical ventilation, and many more.
- It is highly important to have an in-depth understanding and practice of performing bedside investigations including, urinalysis, complete blood count, examination of CSF, shake test, gram stain, etc.
- You must be proficient in the management of pediatric emergencies, executing patient management plans, maintaining patient records, care and management of newborns and neonatal disorders, etc. You must make the patient comfortable and build trust with them so that they freely interact with you.
- Pediatrics is a field in which the sufferer/patient is not able to communicate effectively as they are infant and child and hence, here the challenge comes. You must have great communication skills to interact with a child and parents. You must be able to counsel parents on major topics such as breastfeeding, immunization, and disease prevention.
- You must be able to interpret the diagnostic tests and results and be able to decide the effective treatment plan for a patient. Sometimes, there may be unpredictable and out-of-control situations, but at that very moment, you must remain calm and make the correct decision for the first line of treatment.
- You must have great academic skills and be familiar with all the methodologies. You must be able to review the literature, plan the thesis and work accordingly.
During your pediatrician journey from day 1 to last, you must remember that patient safety is of paramount importance. During the training, procedures learned are practiced on models first, later in supervision and finally, you are allowed to perform independently.
Responsibilities of a Pediatrician
The following are the responsibilities of a competent pediatrician:
- Recognizing the health requirements of babies, children, and adolescents and fulfilling professional commitments following the National Health Policy and professional ethics.
- Has mastered the pediatric competencies necessary for practice in the community and at all levels of the health system.
- Additionally, they have mastered effective communication skills with children, families, and the community.
- They are also knowledgeable about recent advances and developments in medical sciences as they relate to children’s health.
- Teaching medical and paramedical professionals.
- Recognizes mental disorders and works with Psychiatrists/Child Psychologists to treat patients with such illnesses.
Salary and Scope of Pediatricians
Pediatrics is a booming and highly lucrative field of medical science. On average, a pediatrician’s salary is between 10-15 lakh per annum in the beginning which gets higher depending on various factors and experience level. Factors that affect the pay scale include geographical area, place of employment whether government or private sector, experience level, specialization, healthcare organization, and more.
Although in the beginning, you might get paid low and get fewer perks but being on the journey of becoming a skilled pediatrician will attract numerous opportunities, perks, and undoubtedly, huge respect in society.
The following is a list of Job Profiles associated with Pediatric Specialty:
- Lecturer/Professor
- Pediatrician
- Pediatric Consultant
- Physicians
- Clinical Research Associate
- Pediatric Surgeon
- Neonatologists
- Pediatric Oncologists
- Pediatric Endocrinologists
- Pediatric Cardiologists
Best Books for Pediatrics
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics
- PG Textbook of Pediatrics
- IAP Textbook of Pediatrics.
- Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease
- PICU Pediatrics
- AIIMS Protocols in Neonatology
- Drug Dosages in Children
- The Harriet Lane Handbook
- Piyush Gupta’s Clinical Methods in Pediatrics
- IAP Color Atlas of Pediatrics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q 1. What should I do after 12th to become a Pediatrician?
Ans. After completing class 12th, you must prepare and attempt NEET-UG entrance exam. Crack the entrance with competitive score to get admission in MBBS program.
Q 2. What is the salary of pediatrician in India?
Ans. Pediatrics is a booming and highly lucrative field of medical science. On average, a pediatrician’s salary is between 10-15 lakh per annum in the beginning which gets higher depending on various factors and experience level. Factors that affect the pay scale include geographical area, place of employment whether government or private sector, experience level, specialization, healthcare organization, and more.
Q 3. What are the specialization in pediatrics?
Ans. The specialization in Pediatrics include Neonatologist, Pediatric Cardiologist, Critical Care Pediatrician or Pediatric Intensivist, Pediatric Endocrinologists, Pediatric Gastroenterologists, Pediatric Hematologists and Pediatric Oncologists, Neonatal Pediatricians, Child Nephrologist.
In the world of medicine, gynecology is one of the most demanding specialties. A gynecologist focuses on female reproductive health and deals with research pertaining to women’s health. It primarily addresses the condition of the breasts and the female reproductive organs (vagina, uterus, and ovaries). They are medical professionals who diagnose and treat gynecological problems and provide patients with guidance on contraception and reproductive issues. Gynecology (female health), obstetrics (pregnancy & delivery), and reproductive medicine are the specialties in which a gynecologist must be proficient. Gynecology refers to diagnosing, treating, and preventing infections and disorders of women’s reproductive organs, whereas obstetrics refers to a specialty in maternity care.
Steps for becoming a Gynecologist
- You must have completed your senior secondary school from an accredited board and earned a minimum of 50% in each of the four major subjects—Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English in order to become eligible for the NEET-UG entrance examination.
- To pursue a career goal in the medical field, you must work hard and prepare for the NEET-UG entrance examination. National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test for Undergraduates (NEET-UG) is a single window entrance exam for admission to MBBS, BDS, BAMS, BUMS, BHMS, and other undergraduate medical programmes at approved/recognized Medical/Dental/AYUSH and other Colleges/Deemed Universities/Institutes (AIIMS & JIPMER) in India. After cracking the NEET-UG exam with the required score, attend the counselling process to get admitted to a medical college for an MBBS programme, which is a prime requirement for becoming a gynecologist.
- After getting admission into a medical college, complete your MBBS degree with one year rotational internship. You should pay special attention to the practical sessions, ward postings, seminars, conferences, etc. during your graduation since they establish a strong foundation for your medical career path. During your MBBS, you will be able to identify the area of interest in which you desire to pursue a postgraduate degree. You can enroll in the obstetrics and gynecology online course to get conceptual clarity over the subject and prepare for the PG entrance examinations.
- To get admission in the medical PG courses, you are required to crack the NEET PG or INI-CET entrance examination. NEET-PG is a national-level entrance examination for admission to MS/MD/PG Diploma programmes at various government and private universities and INI-CET is a national-level entrance examination for admission to MS/MD/DM (6 years)/MCh (6 years) and MDS courses at the INI Institutes, which includes AIIMS, JIPMER, etc.
- After cracking the NEET-PG exam with the required score, choose MD/MS in Obstetrics and Gynecology specialization at the time of counselling. During your three-year master’s programme, you must complete your PG dissertation and junior residency. A PG curriculum also includes conferences, symposiums, seminars, audits, clinical postings, clinical meetings, etc.
- After finishing your residency programme, get your medical certification and obtain your license to practice as an OBGYN specialist.
- You can also pursue a DM, DrNB, MCh, or DNB course. The admission to a range of DM/MCh and DrNB Super Specialty programmes is done on the basis of the marks and rank secured in the NEET-SS entrance examination. Medical professionals can also enroll in the online advanced gynecology courses on ‘Ultrasound in OBGYN made easy’ and ‘Basics of Infertility and IUI made easy’ to upskill their knowledge and practical skills in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.
Courses to pursue a Career in Gynecology
OBGYN in MBBS
To pursue a career in OBGYN, firstly you will have to complete the MBBS degree. The OBGYN subject is included in the MBBS curriculum and the syllabus includes
- Demographic and Vital Statistics
- Anatomy of the female reproductive tract
- Physiology of conception
- Development of the fetus and the placenta
- Preconception counselling
- Diagnosis of pregnancy
- Maternal Changes in pregnancy
- Antenatal Care
- Complications in early pregnancy
- Antepartum haemorrhage
- Multiple pregnancies
- Medical Disorders in Pregnancy
- Labour
- Maternal Pelvis
- Operative obstetrics
- Complications of the third stage
- Lactation
- Care of the newborn
- Normal and abnormal puerperium
- Medical termination of pregnancy
- Contraception
- Vaginal discharge
- Menopause
- Uterine prolapse
- Benign and malignant diseases of the uterus
- Cervix and the ovaries, Normal and abnormal puberty
- Abnormal uterine bleeding
- Amenorrhea
- Genital injuries and fistulae
- Genital infections, Infertility
- Uterine fibroids
- PCOS and hirsutism
- Obstetrics & Gynecological skills
The curriculum also involves clinical ward postings, seminars, conferences, etc.
PG Courses in OBGYN specialty
After completing graduation, you must pursue a three-year postgraduate (MD/MS) degree in OBGYN. The syllabus of the PG in OBGYN includes topics on Basic Sciences, Markers in Obstetrics & Gynecology, Medical Genetics, Antenatal Care, Intrapartum care, Post-Partum, Operative Obstetrics, Newborn, Clinical Gynecology and Fertility Regulation, Operative Gynecology, Family Welfare, and Demography, and Male and Female Infertility.
The PG curriculum also includes training and postings in OBGYN wards as well as in allied fields such as Neonatology, Anaesthesia, Radiology/Radiotherapy, Surgery, and Oncology.
Besides training and patient care in OPDs and wards, a PG resident also carry out minor operations under supervision and assists in major operations as a part of the second and third term. Then, in the fourth, fifth, and sixth term, you are required to perform independent duties in managing patients and major operations under the supervision of the teaching faculty.
A PG student can enroll in postgraduate courses in obstetrics and gynecology to cater to all their learning requirements. OBGYN MD is an online course crafted by the renowned practitioner and author, Dr. Aswath Kumar along with the 98 eminent faculties. Besides video lectures, notes, and self-assessment questions, there is a focus on getting the right clinical findings and taking the case history. The display of minimally invasive surgeries like hysteroscopy and diagnostic/operative laparoscopy has its own area in the course module. The in-video display of the numerous procedures being carried out will take the learnings of a medical professional to a completely new dimension.
DM Courses in OBGYN
You can pursue DM in Medical Genetics. The goal of the DM in Medical Genetics course is to create a qualified Medical Geneticist who can evaluate a patient with a potential genetic disorder, determine the likelihood of a genetic disorder, make a clinical diagnosis, be able to choose the best test to confirm the diagnosis and offer the most advanced form of treatment.
The Competency-based training for DM in Medical Genetics includes clinical evaluation, research, genetic workup requiring pre-and post-test counselling, updated knowledge and interpersonal skills to apply innovative therapies, knowledge, and abilities to develop and execute population-based preventative programmes. Also, the Geneticist must be prepared to conduct customized medicine in clinical settings in the molecular medicine era of the twenty-first century.
Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology
You have an option to pursue a 2-year Diploma in Obstetrics and Gynecology course. There are three papers in this course:
Paper I: Basic sciences related to Obstetrics and Gynaecology and recent advances
Paper II: Obstetrics including social obstetrics and diseases of newborn
Paper III: Gynaecology including fertility regulation
A medical student pursuing a Diploma in OBGYN undergoes training sessions, which include Out-patient Departments and special clinics, Inpatients, Operation Theatre, Labor Room, Writing clinical notes regularly, and maintaining records. The curriculum includes patient care in OPD, wards, casualty, and labor room, carrying minor procedures under supervision and assisting in major operations in the first and second term, and independent duties in patient management in the third and fourth term.
MCh courses in OBGYN specialty
- MCh in Gynecological Oncology
A subspecialist in gynecological oncology is someone who has completed formal training in the field and has developed specialized knowledge in gynecological oncology as well as broad-based knowledge in related fields like medical oncology, radiation oncology, gynaecological pathology, and palliative care for patients with gynecological cancers. The MCh in Gynecological Oncology course is of 3-year duration.
The course content includes:
- Diagnostic techniques and staging of gynecological cancers
- Surgery for gynaecological cancers
- Principles of radiation therapy for gynaecological malignancies
- Chemotherapy targeted therapy and Immuno-therapy for gynaecological cancers
- Palliative care for advanced and recurrent cancers
- Pathology of common gynaecological cancers
- Research methodology for clinical trials and statistics
- Writing original papers in reputed national & International scientific journals
- Knowledge related to epidemiology and preventive oncology as applied to Gynaecological Oncology
- MCh in Reproductive Medicine and Surgery
The course’s goal is to provide the medical professional with specialized knowledge in all facets of reproductive medicine and surgery as well as training in the clinical, technical, diagnostic, medical, surgical, and technological management of infertility, all of which can help people get pregnant when they’re ready. This training is designed to support gynecologists who want to provide daily care to the nation’s growing infertile population.
The course content includes:
- Basic Sciences Relating to Reproductive Medicine and Surgery
- Principles of Reproductive Medicine and Laboratory Techniques
- Fertility associated Medical and Surgical Diseases, Genetics, Counselling, Ethical and Legal issues related to ART
- Recent Advances in Reproductive Medicine and Surgery
DNB broad specialty
- To pursue a career in OBGYN, you can pursue a 3-year DNB broad specialty course in the Maternal and Child Health discipline. Admission to this 3-year Post Diploma DNB course is done through the NEET-PG entrance examination.
- You also have an option of pursuing a 2-year Post MBBS DNB course in OBGYN. Admission to a list of broad specialties in which NBEMS offers a 2-year Post Diploma DNB course is done through DNB-PDCET. The objective of a DNB programme in Obstetrics and gynecology is to make the students gain complete knowledge in Anatomy, Physiology, Pharmacology, and Pathophysiology connected to the reproductive system. Graduates will be capable of managing all normal and pathological stages and performing productively members of a team involved in teaching, research, and healthcare. The course curriculum includes the theoretical part, practical training, case presentations, seminars, Journal club, clinical audits, poster and oral presentations, and more. A medical professional gains expertise in diagnostic techniques including anesthetic procedures, and preoperative and post-operative care, and emergency situations.
The complete course syllabus of the above-mentioned courses is available on the NMC official website.
Top Medical Colleges in India:
- AIIMS, Delhi, and other AIIMS
- PGIMER, Chandigarh
- Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi
- Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Pondicherry
- Christian Medical College, Vellore
- Institute of Medical Sciences, Varanasi
- Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), Thiruvananthapuram
- Kasturba Medical College, Manipal
- Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai
- DY Patil Medical College Pune
- Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore
- SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Kancheepuram
- King George’s Medical University, Lucknow
- Lady Hardinge Medical College, Delhi
- Vardhman Mahavir Medical College & Safdarjung Hospital, Delhi
Skills required for becoming a Gynecologist
OB-GYNs require a blend of interpersonal and technical abilities. they must be subject-matter specialists as well as effective, sympathetic communicators. The gynecologist has a strong hand in Biopsy, Mammograms, STD Testing, Ultrasounds, Pap smears, Colposcopies, cancer screening, and more. Other essential knowledge and credentials for OB-GYNs include:
- Active listener
- capacity to design individualized treatment strategies
- skilled in using all the required medical equipment
- capacity to deliver precise and efficient treatment even under stress
- strict hand-eye coordination
- excellent vision and visuospatial awareness
- outstanding diagnostic and decision-making skills
- emotional fortitude, a placid demeanor, and the capacity to function successfully under pressure
- physical endurance and manual dexterity to meet the requirements of surgery and emergency situations
- Social Perceptiveness
Responsibilities of a Gynecologist
The prime task of gynecologists on a regular basis includes examining the patients, and prescribing medications and other specialized medical care to treat or prevent illness, disease, or injury. Further, explaining the treatment procedures to the patient and family members, monitoring patients’ condition and progress, and re-evaluating the treatment as necessary also comes under the responsibility of a skilled gynecologist.
The responsibilities of a highly skilled OBGYN specialist:
- Provide the community with high-quality treatment for the diagnosis and treatment of the prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal phases of healthy and unhealthy pregnancies and labour.
- Offer efficient and sufficient care to pregnant women and newborns.
- Able to perform obstetrical ultrasonography and other diagnostic techniques, including Doppler.
- Able to handle and quickly respond to all obstetrical and gynecological crises and make the proper recommendations.
- Carry out a thorough assessment of the infertile pair and have a wide-ranging understanding of assisted reproductive technologies, such as ovulation induction, gamete donation, intracytoplasmic sperm injection, in vitro fertilization, surrogacy, and the ethical and legal ramifications of these procedures.
- Offer guidance and administration of reproductive control techniques, including reversible as well as irreversible contraception, permanent contraception, etc.
- Offer women who are experiencing spontaneous abortions or who are requesting medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) and high-quality treatment and handle any difficulties that may arise.
- Control and organize the work of medical professionals such as nurses, students, assistants, specialists, therapists, and others.
- For preventing injuries and treating illnesses, hospitals, corporations, or communities plan, execute or oversee health programmes.
Career Prospects and Scope of Gynecology
The programme is undoubtedly well-regarded, career-focused, and rewarding. Obstetrics and gynecology is a profession that is always in demand in the medical sciences. This course is the best choice if you wish to work in the medical profession that deals with reproductive life. GYN/OBG provides you with a variety of employment options, rewarding compensation, additional benefits, and respectable professions both inside and outside of India. This opens up opportunities for a wide range of careers including,
- General Practitioners
- Gynecologist
- Lecturer
- Senior Medicine Consultant
- Clinical Associate
- Family Planning Consultant
- Gynecologic-oncology specialist
- Reproductive endocrinology
- Critical care specialist
- Clinical trial expert
- Reproductive Medicine Specialist
- Reproductive endocrinologists
- Senior Residents
- Researchers
Gynecologists have the option to work as private practitioners, government doctors, and private clinicians. They can also work as a gynecologist/OBGYN specialist in Nursing Homes, Private Clinics, Defense Hospitals, IVF fertility centres, and Community Health Centres. The OBGYN might also pursue research and further education in universities and research institutes.
Salary of a Gynecologist
Gynecology is a highly lucrative and demanding career in the medical field. The median salary of a gynecologist depends on a variety of factors, such as geographical area, government or private sector, experience, and specialty. A gynecologist/OBGYN specialist can earn about 10-12 lakhs per annum at the start of their career. However, the pay scale keeps on increasing with the increasing qualification and experience. However, doctors performing surgeries earn comparatively more than consultants and physicians. An academic profile also leads to a lucrative career.
Click here to read about the MRCOG membership examination.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1. How many years does it take to become a Gynaecologist?
Ans. It takes approximately 8-9 years to become a gynecologist. The MBBS is of 5.5 years, then PG(MD/MS in OBGYN) is of 3 years and further, it depends on the OBGYN specialty and course you want to pursue.
Q2. Where do gynecologists get paid the most?
Ans. The salary of a gynecologist depends on a variety of factors, such as geographical area, government or private sector, experience, and specialty. Although skilled and experienced gynecologists are paid the most in the private sector. However, doctors performing surgeries earn comparatively more than consultants and physicians.
Q3. What are the career prospects for a gynecologist?
Ans. Gynecologists have an option of working in Government and Private sectors, Nursing Homes, Private Clinics, Defense Hospitals, IVF fertility centres, and Community Health Centres. There are a variety of job profiles, such as General Practitioners, gynecologists, lecturers, Gynecologist-oncology specialists, Reproductive Medicine specialists, Senior Residents, and Researchers.
Q4. Is gynecology a good career?
Ans. Yes, Gynecology is a highly lucrative and demanding career in the medical field. A career in OBGYN provides a medical aspirant with a variety of employment options, rewarding compensation, additional benefits, and respectable professions both inside and outside of India.
Click here to get conceptual clarity in the MBBS subjects.
The MRCOG Part 3 clinical assessment aims to evaluate applicants’ aptitude for applying fundamental clinical abilities about the skills, knowledge, attitudes, and competencies outlined in the MRCOG Part 2 curriculum. One receives membership in the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists after passing the MRCOG Part 3 exam (MRCOG).
Eligibility for MRCOG Part 3
- To be eligible for Part 3, the aspirant must have passed the MRCOG Part 2 and got the Assessment of Training (AoT) approved.
- For AoT, 4 years of training in Obstetrics and Gynecology is required, of which 2 years should be within the 4 years preceding the candidate’s initial application.
Assessment of Training (AoT)
- It is a prime requirement to register for the MRCOG Part 3 or the MTI scheme.
- After completing the MRCOG Part 1 exam, you can only apply to have your training evaluated. AoT can also be filled before the Part 2 results.
- Applications for AoT can be made at any time, but you can’t take the MRCOG Part 3 exam until your application has been approved.
- Processing of AoT application takes up to 4 weeks.
- Candidates who already met the MRCOG Part 2 eligibility requirements, including having their Assessment of Training certified before July 2019, do not need to reapply.
AoT Deadlines
| Part 3 MRCOG exam | Deadline for AoT |
| Part 3 MRCOG exam- February 2023 | 24 October 2022 |
| Part 3 MRCOG exam- May 2023 | 26 January 2023 |
| MTI 2023 | 31 October 2022 |
Post-registration Training
There are two ways that post-registration training is evaluated to determine eligibility for the Part 3 MRCOG exam:
Route A: Applicable only for learners in a reputable UK specialized training programme.
Route B: Applicable for all other candidates.
Route A
Participants in an accredited specialist training programme in the UK should show evidence of the following:
- At the time of applying for the Assessment of Training, the applicant must be enrolled in intermediate training at the ST3 level or higher.
- The National Training Number must be included in the application for AoT that trainees must submit.
- There is no need for any supporting documents; if the college needs more information, candidates will be notified via email after receiving their application.
Route B
Candidates who are not enrolled in an approved specialized training programme in the UK should exhibit the following:
- A minimum of 4 years of full-time experience in obstetrics and gynecology or an equivalent post-registration position in the UK or abroad.
- Within the 4 years before a candidate’s initial application, he/she must spend at least 2 years (full-time or equivalent) in the specialty.
- A single post must have been held for at least six months straight.
- All foreign O&G hospital-based positions are welcomed.
- When applying the AoT, training must be finished.
- Flexible training in recognized positions is allowed as long as College approval is obtained in advance.
MTI 2023 Scheme
Medical Training Initiative (MTI)
International Medical Graduates (IMGs) can go to the UK under the MTI scheme for up to 2 years to train in the National Health Service (NHS). They must fulfill all the eligibility criteria and apply for the same.
MRCOG Part 3 Exam Pattern
The MRCOG Part 3 Clinical Assessment comprises 14 tasks in a circuit based on the 14 modules from the syllabus.
The duration of each task is 12 minutes including 2 minutes of initial reading time.
The assessment for the MRCOG Part 3 is done in the context of five domains:
- Patient safety
- Communication with patients and their relatives
- Communication with colleagues
- Information gathering
- Applied clinical knowledge
Types of Tasks
The MRCOG Part 3 contains two different types of tasks:
- Simulated patient/colleague tasks: The candidate will interact with a patient (actor) who has been prepared and well-prepped for the role they will play during the simulated patient/colleague tasks. The actor will be well-versed in the pertinent case information and will be prepared with some pre-written questions to ask if required.
- Structured discussion tasks: These tasks require the candidate to communicate directly with a clinical examiner. To prevent the candidate from running out of time, the examiner will have a list of questions and comprehensive instructions for the work that they can use to prompt the candidate. As the scenario develops, the examiner could provide the candidate with additional knowledge before posing new questions.
- A circuit may have “linked tasks,” wherein the second task is coupled to the first, to allow for more depth in the assessment of applied clinical knowledge. There can also be assignments where candidates need to write something.
How many attempts are allowed for the MRCOG Part 3?
In MRCOG Part 3, candidates are allowed 4 attempts. Candidates must retake the MRCOG Part 2 exam if they are unsuccessful after four attempts.
This does not, however, count as an attempt for candidates taking the digital remote exam for the first time.
MRCOG Part 3 Exam Date
The MRCOG Part 3 is conducted in three sessions per year.
The February 2023 MRCOG Part 3 exam is a supplemental test outside of MRCOG’s regular schedule to give the international O&G community one more opportunity to obtain an exam spot. This exam is specifically designed to give applicants outside of the UK another opportunity to take the MRCOG Part 3 exam.
February 2023 Exam Important Dates
| Deadline for all candidates to ensure the home address and email address is up to date | 2 December 2022 (Friday) |
| Closing Date for Assessment of Training | 24 October 2022 (Monday) |
| Opening Date for Booking window application | 8 December 2022 (Thursday) |
| Closing Date for Booking window application | 19 December 2022 (Monday) |
| Exam Dates | 6th – 9th February 2023
8th – 12th May 2023 6th – 10th November 2023
|
| Result Declaration | 7 March 2023 (Tuesday) |
Aspirants can apply for training assessment after passing MRCOG Part 1 exam.
MRCOG Part 3 Examination Fee
| Location | Fees (2023) |
| UK and Republic of Ireland | £563 |
| Band A | £901 |
| Band B (India comes under this category) | £840 |
| Band C | £617 |
Points to Note for the fee structure:
- India comes under Band B. Thus, the fee for the candidates having exam centres in India is £840 which is equivalent to INR 73,584.37. The amount in the Indian currency varies as per the currency change.
- Payments are linked to the country’s bandings of international membership fees.
- Banding applies to the center where you take the exam, not the candidate’s country of residence.
- You can check out on the official website under which band your exam centre country falls.
MRCOG Part 3 Pass Marks
RCOG Procedure: The standard for determining whether a candidate is competent is determined using this approach, which is based on adding the number of examiner judgments in a specific examination to an additional factor and a standard measurement error.
MRCOG Part 2 is a written examination aimed at assessing the application of knowledge of medical aspirants in clinical scenarios.
MRCOG Part 2 Exam Pattern
- MRCOG Part 2 is a computer-based test.
- The CBT consists of two papers. Both papers are worth the same number of points, hence, paper 1 and paper 2 each account for 50% of the final grade. There are two different question types on each paper:
- Single-Best Answers (SBAs) account for 40% of the final grade.
- Each question includes the following:
- A lead-in statement, i.e., question.
- A-E represents the five options on the list.
- There is no negative marking.
- Incorrect answers are marked zero.
- Extended Matching Questions (EMQs) account for 60% of the final grade.
- Each question includes a lead-in statement, which tells you clearly what to do with a list of 10-14 possible options to choose from.
- Even though it may seem like there are multiple options, you must only select the option with the highest likelihood.
- There is no negative marking.
Timetable of MRCOG Part 2
| Paper 1 and Paper 2 | |
| Particulars | Description |
| Duration | 3 hours (180 minutes) for each paper |
| Number of questions | 50 SBAs and 50 EMQs for each paper |
| Lunch break (approximately one hour) between both the papers | |
Time Management Tip: The RCOG advises devoting 110 minutes to EMQs and 70 minutes to SBAs.
Distribution of Marks
The SBAs and EMQs share a single pass mark. There is a composite pass grade that is established by establishing standards for each exam.
A total of 40% of the final grade is determined by the SBA component, and 60% is determined by the EMQ component. As a result, applicants must devote roughly 40% of their time to the SBA component and roughly 60% to the EMQ component.
How to Apply for MRCOG Part 2?
Eligibility of MRCOG Part 2
- In order to be eligible to sit for the MRCOG Part 2 exam, candidates must first pass the MRCOG Part 1 exam.
- Candidates who have passed the Part 1 MRCOG after March 2013 need to attempt the Part 2 MRCOG within 7 years of their exam date.
- To enter to UK Specialist register, you must clear both part 1 and part 2 within 6 attempts only.
How many times are you allowed to retake each test?
No matter when they make their first attempt, candidates are only allowed a total of 6 chances to pass the MRCOG Part 1 and Part 2 tests.
How to book the MRCOG Part 2 exam?
- Expression of Interest
Candidates are required to fill Expression of Interest form, within the stipulated time.
- MRCOG Part 2 Exam Calendar
The MRCOG Part 2 exam is conducted twice a year, one of which is on 17th January 2023 and the other on 5th July 2023.
a.
| Closing Date for Expression of Interest form | 14 October 2022 (Friday) |
| Opening Date for Booking window application | 10 November 2022 (Thursday) |
| Closing Date for Booking window application | 15 December 2022 (Thursday) |
| Exam Date | 17 January 2023 (Tuesday) |
| Result Declaration | 21 February 2023 (Tuesday) |
b.
| Closing Date for Expression of Interest form | 16 March 2023 (Thursday) |
| Opening Date for Booking window application | 27 April 2023 (Thursday) |
| Closing Date for Booking window application | 09 June 2023 (Friday) |
| Exam Date | 05 July 2023 (Wednesday) |
| Result Declaration | 01 August 2023 (Tuesday) |
MRCOG Part 2 Examination Fee
| Location | Fees (2023) |
| UK and Republic of Ireland | £523 |
| Band A | £631 |
| Band B (India comes under this category) | £544 |
| Band C | £434 |
Points to Note for the Fee Structure:
- India comes under Band B. Thus, the fee for the candidates having exam centres in India is £544 which is equivalent to INR 54,285.67. The amount in the Indian currency varies as per the currency change.
- Payments are linked to the country’s bandings of international membership fees.
- Banding applies to the center where you take the exam, not the candidate’s country of residence.
- You can check out on the official website that in which band your exam centre country falls under3. Choose a Country and Book into the Pearson VUE test centre
After the successful submission of the Expression of Interest form, candidates will receive an email regarding the opening date of the application window.
Candidates will then have to choose the examination country and pay the required exam fee. Then the candidates will be asked to select the Pearson VUE test centre in the respective country they have chosen and paid for.
MRCOG Part 2 Pass Marks
The standard setting is done to ensure fair examination and to accurately determine the candidate’s performance. The pass marks and the pass rate vary according to exam sitting as there is no fixed level or quota.
Angoff Method: The Angoff Method entails the evaluation of each question by a group of subject matter experts (O&G Consultants in NHS practice), who then estimate the likelihood that a borderline applicant would know the answer. The final pass mark is calculated by averaging these estimates and adding them to the measurement standard error. A measurement of an assessment’s accuracy is its standard error of measurement. It serves as a function of both the standard deviation of observed results and the test’s reliability and reveals the degree of variability in a test given to a group.
Linear Equating: In order to guarantee identical standards across subsequent examination diets, the linear equating method is used. By assessing and comparing candidate performance on a small number of “anchored” (repeated) and un-anchored questions, this technique adjusts for the relative difficulty of the papers by comparing the current results to those of previous diets.
How long should you wait to take the following MRCOG Part?
- Candidates who passed the MRCOG Part 1 after March 2013 must retake the exam within seven years after the MRCOG Part 2 exam date.
- The seven-year period is pro rata. This indicates that for trainees enrolled in less than full-time training or who take a break from training, the 7-year duration is proportionally extended, up to a maximum of 10 years.
- Candidates who passed Part 1 of the MRCOG in March 2013 or earlier must sit for Part 2 of the MRCOG within 10 years of passing Part 1.
- Candidates who complete Part 2 of the MRCOG must take Part 3 of the MRCOG within 7 years (prorated) of the Part 2 exam date.
- The amount of time between attempts for the MRCOG Part 2 or Part 3 is not limited.
- It is possible to take the Part 1 MRCOG before beginning UK specialist training.
- The MRCOG Part 2 must be taken within 10 years of the exam date of the candidate’s passed MRCOG Part 1 if they do not desire to be included in the UK Specialist Register.
There is no time limit on how frequently applicants may retake MRCOG Part 2 or Part 3 if they do not want to be added to the UK Specialist Register.
To get conceptual clarity with the help of MBBS Courses Online, Click Here.
INI-CET is a combined national-level entrance examination for admission to the medical postgraduate courses – MD, MS, DM (6 yrs), MCh (6 yrs), and MDS at INI institutes (Institute of National Importance). The INI-CET January session 2023 exam is around the corner. Getting admission to INI institutes is highly challenging and a dream for MBBS students. This is a highly competitive task to secure a seat in the renowned medical colleges in India.
Remember, Perseverance is the key.
The INI-CET exam is going to be held on 13th Nov 2022 for admission to the AIIMS INI-CET January session 2023.
Mode and Scheme of INI-CET January 2023 exam
| Particulars | Description |
| Mode of Examination | Computer-based test (CBT) |
| Duration | 3 hours (180 minutes) |
| Number of questions | 200 |
| Types of questions | Objective type |
| Marking Scheme | +1 mark for every correct response and -1/3 for every incorrect response |
Important things to know:
- If more than one candidate scores the same, then this tie-breaker situation is resolved by applying the following criteria sequentially:
-
- Less negative marks
- Older by age
- Candidates equal to 8 (eight) times the number of postgraduate seats available in each category will be called for the first and second rounds of seat distribution based on the INI-CET merit list.
- Spot Round Counseling will only be conducted if the seats will remain vacant even after the open round counseling.
List of Participating Institutes for INI-CET January 2023 Session
| S. No. | Name |
| 1 | AIIMS, New Delhi |
| 2 | AIIMS, Bhopal |
| 3 | AIIMS, Bhubaneswar |
| 4 | AIIMS, Jodhpur |
| 5 | AIIMS, Nagpur |
| 6 | AIIMS, Patna |
| 7 | AIIMS, Raipur |
| 8 | AIIMS, Rishikesh |
| 9 | AIIMS, Bibinagar |
| 10 | AIIMS, Bhatinda |
| 11 | AIIMS, Deoghar |
| 12 | AIIMS, Mangalagiri |
| 13 | AIIMS, Raebareli |
| 14 | JIPMER, Puducherry |
| 15 | NIMHANS, Bengaluru |
| 16 | PGIMER, Chandigarh |
| 17 | SCTIMST, Trivandrum |
Here’s the tentative seat distribution (Category-wise) for admission to various MS/MD/DM (6 years)/MCh (6 years)/MDS courses at AIIMS, New Delhi and other 12 AIIMS through the INI-CET entrance examination for the January session of 2023.
Table 1: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, New Delhi:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 17 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biophysics | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 9 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Lab. Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Medicine | 11 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 11 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 10 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Palliative Medicine | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 10 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 10 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis & Internventional Radiology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Surgery | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatrics & Preventive Dentistry | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MDS | Prosthodontics | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Neuro Surgery M.Ch (Direct 6 year Course) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Paediatric Surgery M.Ch (Direct 6 year Course) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DM | Infectious Diseases DM(Direct 6 year Course) | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 2: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bhopal:
| Courses | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynecology | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
Table 3: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bhubaneswar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 9 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 7 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obst. & Gynecology | 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 6 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physiology | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | PMR | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Table 4: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Jodhpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology & Critical Care | 17 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 6 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Paediatrics | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiology | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine & Blood Bank | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Paediatric Surgery (M.CH. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| DM | Radiation Oncology (D.M. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 5: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Patna:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 18 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 9 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | FMT (Forensic Medicine & Toxicology) | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Medicine | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG (Obstetrics & Gynaecology) | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 7 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | PMR | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Surgery | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MCh | Pediatric Surgery (MCh 6 Years) | 3 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 6: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Raipur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 13 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MD | Anatomy | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Dermatology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MS | ENT | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 9 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 8 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 7 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 5 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 7 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 8 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiotherapy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Pediatric and Preventive Dentistry (MDS) | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 7: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Rishikesh:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 7 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology & Venerology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Emergency Medicine | 3 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | General Medicine | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Geriatric Medicine | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Nuclear Medicine | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 6 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 5 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiation Oncology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Respiratory Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Transfusion Medicine | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Periodontics (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (MDS) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCH 6 Years | Pediatric Surgery (MCH 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Plastic, Reconstructive & Burns Surgery (M.CH. 6 Years) | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MCh | Neurosurgery (MCH 6 yrs) | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 8: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Nagpur:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Dermatology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Forensic Medicine & Toxicology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 3 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Otorhinolaryngology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MDS | Conservative Dentistry & Endodontics (MDS) | 0
|
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 9: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bibinagar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Biochemistry | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | FMT | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Obstetrics & Gynaecology | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Peediatrics | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pathology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Table 10: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Bathinda:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Ophthalmology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 11: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Deoghar:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Biochemistry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Community Medicine & Family Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Microbiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | FMT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Pathology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 12: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Mangalagiri:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Table 13: Tentative seat distribution for INI-CET January 2023 session at AIIMS, Raebareli:
| Course | Subject/Specialty | Total Number of Seats | UR | OBC | SC | ST | EWS |
| MD | Anaesthesiology | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Anatomy | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| MD | Community & Family Medicine | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| MS | ENT | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | General Medicine | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MS | General Surgery | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | OBG | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| MS | Orthopaedics | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pediatrics | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Pharmacology | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Physiology | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Psychiatry | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MD | Radiodiagnosis | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Last-Minute Tips for INI-CET Exam:
- Candidates must carry all the asked documents such as INI-CET admit card, passport size photograph, valid photo ID proof, and a copy of MCI registration certificate with them on the exam day.
- Reverify all your documents before coming to the exam hall.
- Candidates are advised to go through all the guidelines issued by AIIMS for the examination.
- Candidates must reach the INI-CET exam center before time to avoid any chaos.
- Avoid Stress and be confident.
- Eat healthy and sleep well.
- Time management is a must before and during the exam.
To get conceptual clarity on the MBBS courses online, click here
The National Medical Commission (Undergraduate Medical Education Board) has issued new guidelines and the academic calendar for MBBS 2022-2023 batch on 12th Oct 2022.
As per the new NMC guidelines, the classes for the first-year MBBS batch will start on 15th Nov 2022.
Academic Calendar for the 2022-2023 MBBS Batch
According to the new NMC guidelines, there is a change in the academic calendar of MBBS 2022-2023. However, the duration of the MBBS course is the same i.e., 5.5 years including a one-year rotational internship.
| Professional Year | Time Frame | Subjects | Months(Teaching + Exam + Results) |
| 1st | 15th Nov’22 to 15th Dec’23 | Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry | 13 months |
| 2nd | 16th Dec’23 to 15th Jan’25 | Pathology, Microbiology, and Pharmacology | 13 months |
| 3rd (III-part-1) | 16th Jan’25 to 30th Nov’25 | Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, Community Medicine/PSM | 10.5 months |
| 4th (III-part-2) | Dec’25 to May’27 | General Surgery, General Medicine, Pediatrics, Obstetrics & Gynecology, ENT, Ophthalmology |
17.5 months |
| Internship | 1st Jun’27 to 31st May’28 | As per the CRMI 2021 Regulations | 12 months |
| PG | 1st Jul ‘28 |
For the academic year 2022-2023, the one-year compulsory rotational internship will start from the 1st June 2027 and end on 31st May 2028, as per the CRMI 2021 regulations.
The following guidelines have been issued by the NMC for the 2022-23 MBBS batch:
- The MBBS batch will commence on 15th Nov 2022.
- The college vacations and examination schedules may be notified as per the affiliated universities of the respective colleges.
Other board guidelines are as follows:
- Regarding Electives – 2 blocks of 15 days each are to be adjusted by the colleges for
- Pre/para-clinical branches
- Clinical branches
- In the 2022-2023 academic batch, the supplementary exams will be conducted with a gap of 1 month from the regular exams and the results will be declared within 15 days.
- There shall be no supplementary MBBS batches.
- The remaining rules and regulations shall remain the same as per the GMER (Graduate Medical Education Regulations) 1997. You can visit the site for GMER 1997 details: https://www.nmc.org.in/rules-regulations/graduate-medical-education-regulations-1997/
- The Yoga and Family Adoption Program through village outreach shall continue for the 2021-2022 MBBS Batch.
Along with the changes in the curriculum and the guidelines mentioned above, a few more notifications have been issued by the NMC from the 2022 batch:
- The NMC has created an Anti-Ragging Committee and Dr. Aruna V. Vanikar, President, UGMEB has been appointed as the chairperson of the committee.
- In the NMC notification stated on 4 Oct 2022, the implementation of HMIS (Hospital Management Information System) is mandated in all medical colleges.
- The NEET UG counselling link is active from 11th Oct 2022 on the MCC official website: https://mcc.nic.in.
Click here to read about the NMC NExT Exam update 2023 including the guidelines, complete structure, exam dates and more.
Doctorate of Medicine in Pediatrics or Pediatrics MD Course is a three-year postgraduate degree program that primarily studies Pediatrics. It is defined as the study of medical care for infants, adolescents, and children. Candidates for an MD (Doctorate of Medicine) in Pediatrics must have a strong desire to learn about, analyze, and diagnose children’s psychosocial and physical health.
According to the prescribed eligibility criteria for MD Pediatrics courses, an MBBS degree issued by the Medical Council of India from a recognized university with a minimum of 55% marks in aggregate is required. Admission to MD Pediatrics is based on the marks obtained by aspiring candidates in the NEET PG or INI CET Entrance Exam.
Advantages of Pursuing Pediatrics MD Course
After completing the Pediatrics MD course, students can earn up to 1 lakh to 2 lakh per month. Many people choose to work in medicine to help others. Treating children who have been affected by an illness, accident, or other diagnosis can be highly satisfying. Not all pediatric specialties necessarily require working with critically ill children. Most of them assist in the development of healthy habits, such as immunization, exercise, and diet improvement.
MD Pediatrics Course: Specializations
- Child Abuse Pediatrics
- Pediatric Gastroenterology
- Pediatric Critical Care
- Child Neurology
- Pediatric Endocrinology
- Neonatology
- Pediatric Cardiology
- Adolescent Medicine
- Pediatric Oncology
Pediatrics MD Course: Eligibility Criteria
Typically, candidates for an MD degree must have obtained an MBBS degree from an institution recognized by the Medical Council of India (MCI) and completed one year of mandatory internship after passing the final professional examination of MBBS before the month of April of the relevant academic year.
Candidates with an MBBS degree or Provisional MBBS Pass Certificate recognized by the Indian Medical Council Act 1956, a permanent or provisional registration certificate of MBBS qualification issued by the Medical Council of India or the State Medical Council, and having completed/ completing a one-year internship on or before March 31st or April 31st of the year of admission, may apply for NEET-PG through the online application system.
Postgraduation Course in Pediatrics: Admission Process
Admission to the Pediatrics MD course is based on performance in the National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test (NEET) PG, a single window entrance examination for MD/MS/PG diploma courses in Medicine. Candidates who obtained the qualifying percentile in the National Eligibility Cumulative Entrance Test (NEET) are eligible for admission.
The exam is a computer-based test with 200 multiple-choice questions administered via a computer-based platform (CBT). The exam syllabus includes subjects chosen in accordance with the Medical Council of India’s Graduate Medical Education Regulations.
Postgraduation in Pediatrics: Career Prospects
The need for skilled experts in pediatrics guarantees that skilled doctors have higher scope in the industry. A postgraduate in pediatrics has the option of opening their own private clinic and working independently, or they can work as a pediatrician or child specialist in any of the country’s many private and public hospitals.
Pediatricians with experience and expertise in India can expect to receive a competitive salary. For new hires in the government sector, the salary ranges from INR 60,000 to INR 1 Lakh per month for senior pediatricians. Depending on experience and the repute of the institute, salaries in the private sector range from INR 60,000 to 2 Lac per month.
Successful pediatric postgraduates can establish their own specialized children’s facility and make a good living doing so. Senior pediatricians in the country make between 20 and 30 lac per year.
Best Colleges for Pediatrics MD in India
Pursuing your Pediatrics MD Course from a reputed college plays a significant role in the overall development of skills and knowledge. Let’s check out some of the best pediatrics MD colleges in India.
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 4,011
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates should have completed their MBBS degree programme and the compulsory rotational internship from a University recognized by the Medical Council of India.
- Admission Procedure: For admission to MD Pediatrics in AIIMS, a candidate has to qualify for the INI-CET examination and get into the college merit list followed by the counseling procedure.
- Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 10,000
- Eligibility Criteria: A candidate must have completed an MBBS degree from the University recognized by the Medical Council of India.
- Admission Procedure: Admission to PGIMER for MD/MS courses is done based on INI-CET rank.
- Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 8,205
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates must hold an MBBS degree that has been approved by the Indian Medical Council.
- Admission Procedure: Admission to JIPMER for MD/MS courses is done based on INI-CET rank.
- Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, Udupi, Karnataka
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 16, 33,334
- Eligibility Criteria: A medical degree from India’s Medical Council, such as an MBBS.
- Admission Procedure: Admission is based on the result of the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET).
- St. John’s Medical College, Bengaluru, Karnataka
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 12,00,000
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates should have completed their MBBS degree programme and the compulsory rotational internship from a university recognized by the Medical Council of India.
- Admission Procedure: NEET performance is used to determine selection. Candidates are required to apply through Karnataka Examination Authority to be eligible for counseling.
- Stanley Medical College (SMC), Chennai, Tamil Nadu
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 20,000
- Eligibility Criteria: A bachelor’s degree in medicine (MBBS) from any of India’s universities established by the act of the central or state legislatures.
- Admission Procedure: Admission is determined by the NEET score.
- Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham (Amrita University), Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 28,00,000
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates must have an MBBS degree from an institute recognized by the Medical Council of India.
- Admission Procedure: The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test rank is used to determine admission (NEET).
- Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh, Uttar Pradesh
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 35,000
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates must have a Medical Council of India-accredited MBBS degree.
- Admission Procedure: Admissions to MD/MS/PG Diploma courses are made through NEET. AMU does not administer a separate test for admission to the MD programme.
- Assam Medical College, Dibrugarh, Assam
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 30,000
- Eligibility Criteria: A bachelor’s degree in medicine (MBBS) from one of the Medical Council of India-approved universities. 50% of the MD/MS seats are allotted through the All India Quota (AIQ) and the rest 50% through State Quota.
- Admission Procedure: The selection is based on the NEET PG rank.
- Jagadguru Jayadeva Murugarajendra Medical College (JJM Medical College), Davangere, Karnataka
- Average Tuition fee: Rs. 1,00,000
- Eligibility Criteria: The candidate must have an MBBS degree from an MCI-recognized institution.
- Admission Procedure: Admission is based on NEET performance.
- Maharishi Markandeshwar University, Kumarhatti-Solan, Himachal Pradesh
- Average Tuition Fee: Rs. 26,36,000
- Eligibility Criteria: A MBBS degree recognized by the MCI, as well as a one-year mandatory rotatory internship, is required for admission to the MD programme.
- Admissions Procedure: Admission is based on the relative merit of the NEET PG exams. MD/MS courses are regulated by the Himachal Pradesh Govt. through centralized counseling by the Department of Medical Education.
- Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh
- Average Tuition Fee: Rs. 1,00,000
- Eligibility Criteria: An MCI-accredited MBBS degree.
- Admissions Procedure: Admission is based on the NEET-PG exam.
- Andhra Medical College, Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh
- Average Tuition Fee: Rs. 25,000
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates must hold an MBBS degree from an institution recognized by the Medical Council of India and have completed an internship before the deadline.
- Admissions Procedure: Admission is based on the rank scored in the NEET.
- Indira Gandhi Medical College, Shimla, Himachal Pradesh
- Average Tuition Fee: Rs. 39,000
- Eligibility Criteria: A bachelor’s degree in medicine (MBBS) from one of the Medical Council of India-approved universities
- Admissions Procedure: Qualifying the NEET-PG exam is a must. Admissions to MD courses are made through procedures recognized/ permitted by the Medical Council of India/ Himachal Pradesh University, strictly in accordance with the MCI and State Government conditions.
- Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka
- Average Tuition Fee: Rs. 59,070
- Eligibility Criteria: MCI-recognized MBBS degree
- Admissions Procedure: The candidate must qualify NEET-PG entrance examination. Admission to 50% of the seats is filled through the state quota, and 50% of the seats are filled through the All India Quota.
MD Course in Pediatrics: Academic Options after Pursuing the Course
Successful postgraduates can pursue further specialization in medical or surgical fields after obtaining their first postgraduate degree, i.e. MD/MS/DNB. They may even choose to pursue a Ph.D. in Pediatrics and work in research.
| Job Title | Job Profile | Average Annual Salary in INR |
| Pediatricians | Pediatricians are specialists who treat specific health issues, diseases, and disorders associated with the stages of growth and development of babies and children. The doctor in this field of medicine works closely with patients and their families. Growth and development monitoring, along with general medicine, is the foundation of any pediatrician’s practise. | 11,81,956 to 29,58,977 |
| Assistant Professor in Pediatrics | A pediatrics professor or assistant professor teaches students about infants and child physiology, trains them in preventive health maintenance for healthy children, and provides information on medical care for children, infants, adolescents, and young adults. | 6,00,000 to 9,00,000 |
| Neonatology Doctor | Neonatologists are pediatricians who specialize in the care of newborns. Clinical trials are common in neonatology research, in which doctors collaborate with pharmaceutical companies or medical device manufacturers to develop new therapies or tools to improve surgical outcomes. | 12,00,000 to 24,00,000 |
| Pediatric Intensivist or Critical Care Pediatrician | Pediatricians are critical in diagnosing, treating, and monitoring infants, children, and adolescents with life-threatening conditions. Children in critical condition require close monitoring in paediatric intensive care units (PICU). | 5,00,000 – 10,00,000 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the primary goals of Pediatrics MD course are to prepare candidates to deal with all types of pediatric diseases, provide comprehensive care for such children with long-term follow-up of chronic cases of childhood ailments, and provide medical and para-medical education to students in order to ensure a holistic training that includes theoretical and practical skills.
The course provides adequate training in providing nutritional advice to newborn babies, infants, children, and adolescents, as well as advising new parents on breastfeeding and a balanced diet. It also offers Pediatrics and Neonatology training to produce competent specialists, capable of providing basic and specialty care to neonates, infants, children, and adolescents.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ques.1 What is the salary of a pediatric doctor?
The average salary of a pediatrician is INR 7,00,000 per annum.
Ques.2 What is MD pediatrics?
MD pediatrics is a specialty that students pursue after completing their MBBS. It is concerned with diagnosing, treating and managing diseases in newborns, infants, children, and teenagers.
Ques.3 Is a pediatrician DO or MD?
MD is a doctor of medicine, and DO is a doctor of osteopathy (DO). A pediatrician can graduate from a recognised medical university with either an MD or a DO.
Ques.4 What is the scope of Pediatrics after MD?
There are a lot of opportunities for Pediatricians after MD. They can easily earn well in both the private and public sector.
Ques.5 Does a pediatrician do surgery?
Yes, some pediatric surgeons treat, diagnose, and manage surgical procedures on children.
Christian Medical College (CMC), Vellore is a private medical college, hospital, and research institute. CMC is one of the best private medical colleges in India. In and around Vellore, Tamil Nadu, India, this institute has a network of primary, secondary, and tertiary care hospitals. Dr. Ida Scudder is the founder of CMC Vellore. The college is affiliated with the Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University, Chennai. CMC, Vellore is approved by NMC (National Medical Commission). It is ranked as one of the top medical colleges in India. The institution offers admission to various disciplines of sciences: medical science, nursing, allied health sciences, some other master’s and doctoral programs, and post-graduate engineering programs.
The college offers admission to various programs including:
- Undergraduate medical course (MBBS)
- Medical postgraduate courses (diploma, degree, and higher speciality courses)
- Certification courses
- Postdoctoral fellowship courses
- Distance education program
- Undergraduate nursing program
- Nursing postgraduate courses (diploma, degree, and fellowships)
- Allied health sciences degree courses
- MBA in hospital and health systems management (HHSM)
- MS Bioengineering
- Tech. Clinical Engineering
- D. Medical Sciences
MBBS in CMC Vellore
MBBS is a four-and-a-half-year course followed by one year compulsory rotating residential internship. In CMC, Vellore, the MBBS course comes under the group A category. As per the CBME curriculum, the undergraduate course in medicine comprises three phases.
Three phases in MBBS Curriculum
| Phases in MBBS Curriculum | Duration | Subjects Included |
| 1 (Pre-Clinical Phase) | 13 months | Basic Sciences, Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Introduction to Community Medicine, Humanities, and Professional Development |
| 2 (Para-Clinical Phase) | 12 months | Pharmacology, Pathology, and Microbiology |
| 3 (Clinical Phase) | Part 1: 13 months
Part 2: 13 months |
Forensic Medicine, Community Medicine, Ophthalmology, and Otorhinolaryngology.
Medicine and Allied Specialties, Surgery & Allied Specialties, Child Health, and Obstetrics & Gynecology. |
Block postings and Internship at CMC Vellore
As per the guidelines of the National Medical Commission,
- Along with regular classes, medical students also have to undergo block postings after phase 1 of their MBBS course at community health centers, mission hospitals, and secondary care centers.
- A medical student also has to compulsorily complete the rotational internship for 12 months. They are posted in the discipline of community health, medicine, surgery, obstetrics & gynecology, orthopaedics, emergency medicine, and short elective subjects.
- At CMC, Vellore, the students are allocated community health centers, mission hospitals, and secondary care centers for internships.
Admission procedure
Admission to the MBBS undergraduate course in CMC, Vellore solely depends on the NEET-UG score. An aspirant to get admission at CMC needs to qualify and crack the NEET-UG (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) examination with a good score.
Eligibility to get admission at Christian Medical College
- Candidate must have completed 10+2 higher secondary schooling or equivalent examination, and the last two years of education must include Physics, Chemistry, and Biology/Biotechnology as major subjects with English from the Tamil Nadu State board or any other equivalent examination board.
- Candidates must have attained a minimum of 50% marks in all the subjects, Physics, Chemistry, Biology/Biotechnology, and English individually for the general category, and a minimum of 40% aggregate for BC, MBC, SC/ST candidates is required in a single attempt. The criteria mentioned are subject to change as per the state & university guidelines.
- At the time of admission, a candidate must have completed 17 years of age or should complete the mentioned on or before 31st December of the said year.
NEET-UG Exam Pattern for admission to MBBS at CMC Vellore
The NEET-UG exam is conducted by National Testing Agency (NTA) once a year. The following are some important points to keep in mind:
| Particulars | Description |
| Exam Mode | Offline (pen & paper based) |
| Type of Examination | Multiple choice questions |
| The total number of questions | 200 questions (180 MCQs must be answered) |
| NEET total marks | 720 marks |
| Marking scheme | +4 for each correct answer and -1 for every incorrect answer |
| Total duration | 3hrs 20 mins |
| Languages | The exam is conducted in 13 different languages, namely, English, Hindi, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Marathi, Odia, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, and Punjabi |
NEET Exam Section-wise Distribution:
In all 4 Subject sections, Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Zoology, there are two sections, section A comprises 35 questions and section B comprises 15 questions out of which 10 are to be answered. Each question carries 4 marks.
Number of Seats for 2022-2023 at CMC, Vellore
The total number of MBBS candidate seats is 100 and the seat distribution is as follows:
- All India open category: 16 seats
a. One candidate is selected by Govt. of India under the ‘Central Pool Scheme’.
b. 20% i.e., 3 seats are reserved for the SC/ST candidates. - Minority Network Category & CMC, Vellore staff quota: 84 Seats
Steps to get admission into CMC Vellore
- Fill out the application form for an undergraduate course from the CMC, Vellore official site.
- Provide your NEET application form details.
- Submission of the receipts of the certification forms from Minority Network Organizations (if applicable).
- Apply to the Tamil Nadu Selection Committee for the counseling process in the relevant category.
- The selection is based on the NEET-UG score and candidates are required to fill the NEET-UG score and rank on the CMC, Vellore admission site.
- Submission of the Arno & rank of TN Management Quota.
- Be updated with the release of the merit list.
- Counseling by Tamil Nadu Selection Committee, DME, Chennai.
All these steps are to be done in the stipulated period as provided by the college. So, be updated.
Admission Process after Counseling at CMC, Vellore
- After the counseling procedure, the candidate is required to register for the course by paying the tuition fees and completing other formalities, and submitting original certificates.
- The admission confirmation is approved by Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University. Until the approval, admission continues to be provisional.
- After the confirmation of the MBBS admission at CMC, Vellore, a candidate needs to submit their original required documents at the university campus.
- All the candidates getting admission to CMC, Vellore need to undergo a medical fitness check-up and the admission gets confirmed only after the medical fitness clearance by the Medical Board, CMC, Vellore.
MBBS Course Fee at CMC, Vellore
The fees to be paid at the time of registration for admissions to the MBBS course at CMC, Vellore is mentioned in the table below:
| Particulars | Fees (in rupees) |
| Tuition fees | 3,000 |
| One-time College fee at Admission | 10,300 |
| Other Annual Fee | 25,105 |
| One-time payment to the University | 14,425 |
| Total | 52,830 |
*The course fee may change in the coming years depending upon the University rules and regulations.
MBBS Cut-off at CMC, Vellore
Based upon the analysis of the previous years’ cut-offs, the estimated NEET-UG cut-off marks for the MBBS course for admission at CMC, Vellore are mentioned below:
| Category | Estimated Cut off Score |
| General | 600 |
| Minority | 380 |
| Institutional/Staff | 500 |
| SC/ST | 520 |
To get the conceptual clarity on the MBBS courses online, click here.
Medical Postgraduate Courses at CMC, Vellore
In CMC, Vellore Admission to PG Degree, Diploma, PG diploma courses, and fellowship courses come under the Group B category. Admission to the MD/MS courses is done based on the NEET-PG score. All the students need to get into the NEET-PG merit list for admission to the PG courses with the required cut-off score.
PG Courses and Number of Seats
The Christian Medical College offers admission to various post-graduate specialization courses.
- The CMC Vellore provides admission to MD courses for various subjects along with the number of seats mentioned below:
| MD Specialization Courses | Number of Seats |
| Anaesthesiology | 33 |
| Anatomy | 4 |
| Biochemistry | 2 |
| Community Medicine | 6 |
| Dermatology Venerol & Lep. | 5 |
| Emergency Medicine | 3 |
| Family Medicine | 2 |
| Geriatrics | 3 |
| General Medicine | 16 |
| Microbiology | 4 |
| Nuclear Medicine | 2 |
| Pediatrics | 20 |
| Pathology | 8 |
| Pharmacology | 2 |
| Physiology | 4 |
| Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 4 |
| Psychiatry | 12 |
| Radiodiagnosis | 12 |
| Radiation Oncology | 8 |
| Respiratory Medicine | 4 |
| Transfusion Medicine | 3 |
- The CMC Vellore provides admission to MS courses for various subjects along with the number of seats mentioned below:
| MS specialization Courses | Number of Seats |
| Otorhinolaryngology | 8 |
| General Surgery | 10 |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | 17 |
| Ophthalmology | 9 |
| Orthopaedics | 12 |
Service Obligation at CMC, Vellore
- The service obligation of 3 years is mandated for all the MS/MD candidates, except for the clinical specialties (General merit category).
- Candidates admitted to the clinical specialties under the general merit category have a service obligation of 1 year.
- Candidates admitted to the pre-and para-clinical specialties under the general merit category, have no service obligation.
- For diploma courses, the service obligation period is a minimum of 2 years whereas, general merit candidates are exempted from the same.
- After the course completion, the service obligation is served at the CMC, Vellore or any of the associated mission hospitals.
Facilities available for the medical PG trainees
- Stipend
- Accommodation
- Research activity of each department
- Medical records department
- Recreation
- Staff/student health clinic
Fee Structure for the Postgraduate Medical Courses at CMC, Vellore
The fees to be paid at the time of registration for admissions to the Medical PG courses (MD/MS) at CMC are mentioned in the table below:
| Particulars | 2 yr Post Diploma Degree (in rupees) | 3 yr PG Degree (in rupees) |
| Tuition fees | 800 | 1200 |
| One-time admission fees | 1200 | 30,000 |
| University fees | 1,35,610 | 1,35,610 |
| Others | 17,600 | 19,600 |
| Total | 1,74,010 | 1,86,410 |
*The course fee may change in the coming years depending upon the University rules and regulations.
NEET-PG Cut-off Score for MS/MD admission to CMC, Vellore
Based upon the analysis of the previous years’ cut-offs, the estimated cut-off marks for the medical PG specialization courses for admission at CMC, Vellore are mentioned below:
| Specialization | Estimated Cut-off Score |
| Anesthesiology | 400 |
| Anatomy | 460 |
| Biochemistry | 430 |
| Community Medicine | 500 |
| Dip. In Clinical Pathology | 480 |
| Dermatology Venerol & Lep. | 540 |
| Emergency Medicine | 500 |
| Family Medicine | 450 |
| Geriatrics | 380 |
| General Surgery | 460 |
| General Medicine | 590 |
| Microbiology | 450 |
| Neurosurgery | 500 |
| Nuclear Medicine | 500 |
| Obstetrics & Gynecology | 380 |
| Ophthalmology | 400 |
| Orthopedics | 450 |
| Pediatrics | 440 |
| Pathology | 450 |
| Pharmacology | 600 |
| Physiology | 480 |
| Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation | 450 |
| Psychiatry | 360 |
| Radiodiagnosis | 450 |
| Radiation Oncology | 450 |
| Respiratory Medicine | 490 |
| Transfusion Medicine | 600 |
Certificate courses after MBBS
The certificate courses offered by the CMC Vellore for the MBBS graduates are mentioned below:
| Course Name | Duration | Number of Seats |
| Accident & Emergency Medicine | 2 years | 10 |
| Neonatology | 1 year | 1 |
| Palliative Medicine | 1 year | 2 |
| Acute Care Pediatrics | 1 year | 1 |
- CMC, Vellore also provides admission to various higher specialty and Postdoctoral diploma courses and allied health sciences courses.
- After completing MBBS, a medico can also pursue M.Sc. Epidemiology and Master of Public Health Administration.
CMC, Vellore Hostel Fees and Facility
- Hostel Facility for MBBS Students: MBBS students live in the campus hostels. The Bagayam campus of the CMC, Vellore has girls’ and boys’ hostels. The girls’ hostel is named as ‘Paradise on Earth’, while the boys’ hostel is named as ‘Mansion of the Gods’. Boys are required to submit the hostel charges (Deposits and advance) of10,000/- and girls Rs.8,000/-. The approximate living expenses per month for the hostel are Rs.6,000/- for boys and girls.
- Hostel facility for other courses: The women’s hostel and men’s hostel for the students of allied health courses are named as the ‘Fitch Hostel’ and the ‘Dorothy Joske Hostel’. The ‘Modale International Hostel’ is allocated for the elective course students/visitor observer students from overseas. The hostel and its charges vary as per the student’s course.
All the hostels are well equipped with all the necessities of a student and other facilities such as a Hostel Chapel, recreation room, gymnasium, library, dance room, music room, prayer room, mini kitchen, TV/Projector room. The food facility with vegetarian and non-vegetarian food is also available for all the residents.
How does DigiNerve help a medico?
DigiNerve is an EdTech initiative by Jaypee Brothers, a pioneer and market leader in health science publishing with a legacy spanning over 5 decades. It provides top-notch medical content to enhance conceptual clarity, clinical skills, and ace exams.
In terms of the calibre of the courses, the variety of subjects, the Gold Standard faculty, and the user-friendly interface, DigiNerve is unmatched.
- DigiNerve provides best online courses for MBBS subjects designed by eminent faculty as per CBME Curriculum and NEET Exam, such as
| MBBS Online Courses | Course Faculty |
| Community Medicine for UnderGrads | Dr. Bratati Banerjee |
| Forensics Medicine and Toxicology for UnderGrads | Dr. Gautam Biswas |
| Medicine for UnderGrads | Dr. Archith Boloor |
| Microbiology for UnderGrads | Dr. Apurba S Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat, Dr. Deepashree R |
| OBGYN for UnderGrads | Dr. K Srinivas |
| Ophthalmology for UnderGrads | Dr. Parul Ichhpujani, Dr. Talvir Sidhu |
| Orthopaedics for UnderGrads | Dr. Vivek Pandey |
| Pathology for UnderGrads | Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak, Dr. Debasis Gochhait |
| Pediatrics for UnderGrads | Dr. Santoah T Soans, Dr. Soundarya Mahalingam |
| Pharmacology for UnderGrads | Dr Sandeep Kaushal, Dr. Nirmal George |
| Surgery for UnderGrads | Dr. Sriram Bhat M |
- Apart from the MBBS and MD courses, DigiNerve brings the professional courses ‘Ultrasound in OBGYN Made Easy’ and ‘Basics of Infertility and IUI Made Easy’ by the top faculty Dr. Chaitanya Nagori and Dr. Sonal Panchal. After completion of the course, the candidates will earn a course completion certificate from Ian Donald Inter-University School of Medical Ultrasound.
- An Exam preparation course ‘Cracking MRCP Part 1’ by Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander and Dr. Archith Boloor, helps a medico with their preparation to crack the MRCP exam. Cracking MRCP Part 1 course is based on the curriculum devised by The Royal College of Physicians (RCP). The course has 15 online modules covering major specialties such as Clinical Sciences, Cardiology, Gastroenterology, etc. The course includes video lectures, e-chapters, 2500+ BOF questions, mock exams, and most of all high-quality notes.
FAQs
-
How many marks are required in NEET for MBBS in CMC Vellore?
Ans: The estimated cut off score for admission to CMC, Vellore is around 600+ in the NEET Examination for general category. For the OBC/SC/ST & Minority groups, the estimated cut-off score is around 500 marks. For sponsored & management quota students, the cut-off range is comparatively lower.
-
Is CMC Vellore a deemed university?
Ans: No, CMC Vellore is not a deemed University. It is a private college, affiliated with Tamil Nadu Dr. M.G.R. Medical University, Chennai run by the Christian community.
-
Is CMC good for MBBS?
Ans: CMC Vellore is ranked 3rd as per NIRF ranking 2022 after AIIMS, Delhi, and PGIMER, Chandigarh. It is one of the best medical colleges in India.
Gynecology and obstetrics both focus on the female reproductive system. Gynecology deals with non-pregnant women whereas Obstetrics deals with pregnancy and the procedures and issues that go along with it, thus obstetrics deals with both the mother and the infant. To lower the risk of newborn disease and mortality, obstetricians closely collaborate with pediatricians and neonatologists on newborn care. They also remove cancers, fibroids, etc, surgically, although many gynecological problems require hormonal and other pharmacological therapy too.
What an obstetrician does:
The duties obstetricians carry out consist of:
- Obstetricians are in charge of collaborating with midwives to monitor and support a woman’s natural birth while she is in labor.
- One of their roles is to execute an episiotomy, which entails making precise cuts over the pregnant woman’s perineum to widen the birth canal.
- In some cases, assistance may be required to hasten protracted delivery to lessen maternal exhaustion and infant suffering (rising heart rate and possible brain damage to the baby). This makes use of methods like vacuum-assisted birth and forceps delivery.
- Caesarean (or C) section, calls for the baby to be surgically removed from the mother’s womb to lessen difficulties during labor. If a C-section is not used to hurry the delivery, difficulties could ultimately result in the baby’s death or physical harm.
- Therapy and diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy. When the fertilized ovum is implanted somewhere other than the womb, it results in an ectopic pregnancy. It frequently ends up in the fallopian tubes.
What a gynecologist does:
Gynecologists employ a variety of diagnostic and curative techniques. The following are a few of the common gynecological procedures:
- Hysterectomy or uterus removal
- Removing ovaries
- Fallopian tubes are removed during surgery
- Hysteroscopy and colposcopy involve employing tools like endoscopes to inspect the uterus’ inside.
- Taking care of uterine fibroids
- Identifying and treating sexually transmitted diseases
- Diagnosing menstrual issues, such as absence, severe bleeding, irregular or no periods, etc.
- Examination of the reproductive organs with ultrasound.
Objectives of Learning OBGYN
The Obstetrics and Gynecology Department offers modern, comprehensive screening and therapeutic techniques in a sympathetic environment for women in all stages of life.
In addition to regular gynecology procedures and medical treatments, a dedicated team provides cutting-edge motherhood facilities for routine and high-risk pregnancies, post-delivery and family planning services, sterility screening and handling, and all endoscopic gynecological operations.
Moreover, the department addresses high-risk pregnancies using prenatal diagnostic tests such as infant color doppler, amniocentesis, and velocimetry investigations. It also includes colposcopy, pap smear, and HPV-CO testing for going through menopausal women for cancer screening.
Aspirants can get a variety of profitable jobs in India and overseas by enrolling in this course. You can pursue additional education, such as research studies at prestigious universities and research institutions. Medical specialties like gynecology, cancer, critical care, reproductive endocrinology, or maternal-fetal medicine are all open to you as a career option. In India, postgraduate training in obstetrics and gynecology is either a three-year master’s program or a two-year diploma program. You can pursue a sub-specialty training program in fellowships after finishing your residency training.
OBGYN in MBBS
In their fourth year of MBBS, undergraduate students who are studying OBGYN participate in case discussions in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. A medico must also do a one-month OBGYN internship in addition to this. They receive instruction in the labor room, family planning OPD and OT, and obstetrics and gynecology OPD’s wards and OTs throughout their internship.
PG in OBGYN
A three-year, full-time postgraduate programme in OBGYN aims at training students to provide care to each patient, both pregnant and non-pregnant, as well as a thorough superior assessment of the entire medical pathology associated with the female reproductive organs.
Students learn about the most recent society standards, benchmark studies, breakthroughs in PCOS, robotic surgery, and conducting clinical examinations in OBGYN MD course. In the specialty clinics, OPD, wards, labour rooms, and operating rooms, they perform the necessary tests, interpret the results, and carry out medical/surgical management. They are taught to assess pregnancy-related issues using medical skills, find solutions, and provide pertinent prognoses.
Watch this video to learn the right way to approach OBGYN MD
Ph.D. Scholars of OBGYN
Every Ph.D. candidate has the privilege of choosing their specialty area from a list that includes fetal development and growth, hereditary and genomics, gestational diabetes, parental hepatitis, preeclampsia, prenatal analysis, and screening. Additionally, topics like urogynecology, endometriosis, endometrium, and establishment, prenatal cancer, and genital level are also discussed.
List of Top 10 Colleges for OBGYN in India
Here is the most recent list of top obstetrics and gynecology colleges in India that have earned official NMC recognition. These universities have the highest rankings and are even regarded as the most reputable universities in India
| S.No. | Name of College | Affiliation |
| 1 | Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi | Delhi University |
| 2 | Kasturba Medical College, Mangalore | Manipal Academy of Higher Education (Deemed University), Manipal |
| 3 | Jawaharlal Institute Of Postgraduate Medical Education And Research (JIPMER), Pondicherry | Pondicherry University |
| 4 | Christian Medical College, Vellore | The Tamilnadu Dr. MGR Medical University, Chennai |
| 5 | Institute of Medical Sciences, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh | Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi |
| 6 | Kasturba Medical College, Manipal | Manipal Academy of Higher Education (Deemed University), Manipal |
| 7 | Christian Medical College, Ludhiana | Baba Farid University of Health Sciences, Faridkot |
| 8 | Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai | Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education & Research (Deemed to be University), Chennai |
| 9 | SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, Kancheepuram | SRM Institute of Science & Technology, Chennai |
| 10 | Dr. DY Patil Medical College Pune | Dr. D Y Patil University (Deemed), Pimpri, Pune |
Top OBGYN course online for best guidance for NEET Exam preparation
There is a great opportunity in the medical sector, particularly for OBGYNs, as the need for healthcare professionals is on the rise. Below are a few reasons why you should consider pursuing a career in OBGYN.
- Rising demand for OBGYNs
The need for female OB/GYNs has grown dramatically over the past few years, despite the perception that the health care industry is dominated by men. Today, more women than ever before are asking to consult a female specialist. Talking to other women comes more easily to women, especially when discussing sexual or pregnancy difficulties. Additionally, since more than 70% of residents are now women, supply and demand favor female OBGYNs.
- Great Earnings
The field of Obstetrics and Gynecology holds a bright future and is one of the most prestigious. Gynecology is currently one of the most lucrative medical professions. It is possible to work in government organizations, clinics, private practices, and universities, as well as in the most prestigious hospitals in India. Additionally, the candidate could open a surgical clinic. Obstetrician/Gynecologist salary in India ranges from ₹10 Lakhs to ₹ 36 Lakhs. Salary estimates are based on 199 salaries received from Gynecologists, particularly from a large hospital network.
- Fulfillment at work
One of the reasons people have named OBGYN as the most fulfilling profession in the healthcare industry is because bringing new life into this world is indeed a great sight to behold. As an OBGYN, you’ll have the opportunity to be regularly involved in childbirth and assist new mothers in making decisions that will impact the health of the infant.Only a few OBGYNs specialize in high-risk pregnancies. Patients with preterm births, a history of miscarriages, or antenatal problems that could complicate childbirth are cared for by these specialists. You’ll also have the ability as an OBGYN to advance the industry by developing novel techniques and procedures that may one day be considered best practices.
- Jobs & Career
- Salary
In OBGYN, OB refers to Obstetrics or Obstetrician, a doctor who specializes in the care of women and their babies during pregnancy and childbirth. GYN stands for Gynecology or Gynecologist, a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of female reproductive disorders. OBGYN is a branch of medicine that deals with the entire female reproductive health of pregnant as well as non-pregnant females.
OBGYNs diagnose and treat diseases of the female reproductive organs. They treat various other women’s health issues such as hormonal problems, menstruation issues, contraception, infertility, and reproductive tract infections. They also hold the responsibility of childbirth via normal delivery, cesarian sections, pregnancy complications, fetal signs, and growth and also help women with psychological distress and counseling.
ADMISSION PROCEDURE
The following steps are undertaken by students who aspire to become an OBGYN:
- From the beginning, aspirants must complete the senior secondary education with the PCB stream with at least 50% marks.
- Further, they should crack the NEET UG exam to get admission to medical college (Government/ Private).
- After obtaining an MBBS degree, they need to appear for the NEET- PG entrance examination.
- A good score in NEET-PG gives a push to admission to the medical college for the OBGYN PG course.
- Aspirants must complete a junior resident responsibility to gain a post-graduation degree.
- After the successful completion, they must obtain a license and become board certified.
ELIGIBILITY FOR BECOMING AN OBGYN DOCTOR
- Candidates should have completed an MBBS degree from a college/institution recognized by the Medical Council of India (MCI) with a minimum of 55% marks.
- They must have undergone the one-year compulsory internship after completing the course.
- Candidates must clear the NEET PG exam to be eligible for admission to recognized universities/colleges.
- For the general category, the candidate must obtain at least 50th percentile marks in NEET PG for admission to MD/MS courses. For SC, ST, and OBC, the minimum percentage requirement is the 40th
- For the candidate with benchmark disability specified under the Rights of Persons with Disability Act 2016, for the GEN-EWS and unreserved category 45th percentile is required. For, SC/ST/OBC-NCL candidates, the minimum marks shall be 40th
- In some cases, admission to post-graduate medical courses may also include a group discussion/personal interview after the entrance examination depending on the college.
- Final confirmation of admission depends on the cut-off marks and the counseling procedure.
OBGYN IN MBBS
MBBS (Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery) is an undergraduate medical sciences course with a duration of 5.5 years including an internship. Admission to the MBBS is solely based on an entrance examination. The NEET (UG) entrance examination is the only valid examination to get admission in MBBS in government or private medical colleges recognized by MCI (Medical Council of India). A student needs to get into the merit list and undergo the counseling procedure for admission to MBBS successfully.
After getting admission to medical college, a student needs to learn various subjects like microbiology, pathology, pharmacology, medicine, pediatrics, OBGYN, community medicine, surgery, and more.
Undergraduate students study OBGYN in their 4th prof, where they go through case discussions in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Along with this, a medico needs to complete a one-month OBGYN internship. During this internship, they get training in Obstetrics & Gynaecology OPD’s Wards and OTs, Labour Room, and Family Planning OPD and OT.
PG OBGYN AFTER MBBS
OBGYN is a three-year full-time postgraduate course in medical sciences. The course consists of a comprehensive, superior examination of the complete medical pathology related to the female reproductive organs, and provision of care to each non-pregnant and pregnant patient.
Admission to OBGYN MD is done through national-level entrance examinations like NEET-PG, and INI-CET. In PG OBGYN, students get familiar with the latest society guidelines, benchmark trials, and recent advancements in PCOS, Robotic Surgery, and performing clinical examinations. They are asked for pertinent tests, decipher the results, and implement medical/surgical management in the specialty clinics, OPD, wards, labor room, and operating rooms. They learn to use medical capabilities to evaluate troubles in pregnancy and discover techniques and relevant prognoses.
Watch this video to understand this important topic of OBGYN through case-based discussion
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS FOR PURSUING PG OBGYN
MBBS students need to undergo and crack the NEET-PG entrance examination for admission to medical college for PG OBGYN. The NEET (National Eligibility cum Entrance Test) is a national-level entrance examination for admission to pursue medical sciences; NEET UG for the undergraduate medical courses (MBBS, BDS, BAMS, BHMS), and NEET PG for the doctors to get admitted to various postgraduate courses (MD/MS) and diploma courses.
Admission for PG to government and private colleges depends on the ranking of the medicos in the NEET-PG entrance Examination. The examination body of NEET PG is the National Board of Examinations and further, the Directorate General of Health Services conducts the counselling and seat allotment process.
Institutes that are exempted from admission via the NEET PG exam are:
- AIIMSs
- PGIMER
- JIPMER
- NIMHANS
- SCTIMST
These institutes come under the INI (Institute of National Importance).
To get admission to INI (Institute of National Importance) institutions, medicos must get into the merit of the INI-CET (Institute of National Importance Combined Entrance Test).
INI- CET is a combined entrance examination to the INI institutes for PG courses in medical Sciences [MD, MS, DM (6 years), MCh (6 years), and MDS]
List of Participating INI Institutes for INI-CET:
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bathinda, Punjab
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhubaneswar, Odisha
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bibinagar, Telangana
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Deoghar, Jharkhand
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur, Rajasthan
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Mangalagiri, Andhra Pradesh
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Nagpur, Maharashtra
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Patna, Bihar
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Raipur, Chhattisgarh
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh, Uttarakhand
- Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research (JIPMER), Puducherry
- Postgraduate Institute of Medical Science and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh
- National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore, Karnataka
- Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute of Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), Thiruvananathapuram, Kerala
NOTE:
MRCOG Examination:
This examination is specially designed by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists for OBGYN doctors to assess their skills, knowledge, and competencies. This exam comprises three parts- MRCOG Part 1, MRCOG Part 2 & MRCOG Part 3. Membership of RCOGs is awarded upon the successful completion of all three stages of the exam.
TOP COLLEGES FOR PG IN OBGYN
Some of the colleges for admission to PG-OBGYN are listed below:
- All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi
- Armed Forces Medical College, Pune
- IMS BHU- Indian Institute of Medical Sciences- Banaras Hindu University, Banaras
- Bangalore Medical College, Bangalore
- Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi
- Lady Hardinge Medical College, New Delhi
- JIPMER (Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research), Puducherry
- Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh
- King George Medical College, Lucknow
- Madras Medical College, Chennai
- Christian Medical College, Vellore, Tamil Nadu
- Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi
- VMMC College, New Delhi
- Goa Medical College, Panaji
COURSE STRUCTURE OF PG OBGYN
There are four papers:
PAPER I: Applied Basic sciences: Physiology and anatomy of the female reproductive system, pharmacological and hormonal roles, obstetric and gynecological markers – non-neoplastic and neoplastic, medical genetics, anatomical and physiological changes in the female reproductive tract during pregnancy, pharmacology of drugs used during labor and after birth
PAPER II: Obstetrics including Social Obstetrics & Diseases of Newborn: Prenatal Care: Risky Pregnancy, Obstetrics: Postpartum, Vaginal delivery, caesarean section, Hysterectomy, Destructive Surgery, Manipulation (external/internal pod version, manual placental removal, etc.), Medical Abortion – Safe Abortion – Case Selection, Complication Techniques, and Treatment, MTP, newborn.
PAPER Ill: Gynecology: Clinical gynecology, Family Welfare, and demography, Male and female infertility.
PAPER IV: Recent Advances in Obstetrics & Gynaecology
- Along with four theory papers, doctors pursuing MD OBGYN have to do Practical Examinations in Obstetrics and Gynecology:
Clinical long case and short case including viva of:
- Instruments
- Pathological specimen,
- Medicines and X-rays, ultrasounds, etc.
- Dummy Pelvis
- Family planning
THESIS: - Students identify relevant research questions
- Conduct a critical literature review
- Hypothesize
- Determine the most appropriate study design
- State the purpose of the research
- Preparation of test protocols
- Conduct the study according to the protocol
- Analyze and interpret research data and draw conclusions
- Write a research paper
- PG OBGYN students are also required to complete their OBGYN residency and postings.
Watch this video to learn the right way to approach OBGYN MD
SCOPE/JOB OPPORTUNITIES AFTER MD IN GYNECOLOGY & OBSTETRICS
Undoubtedly, the course is highly respected, job oriented, and lucrative. This opens doors to a variety of job prospects such as Maternal-fetal medicine specialists, Reproductive endocrinologists, Gynecologic oncologists, Female pelvic specialists, critical care medicine specialists, professors, clinical associates, junior consultants, senior residents, consultants, general physicians, researchers, private practitioners, govt. doctors, and private clinicians. Moreover, the OBGYN can go for research and higher studies in research centres and universities.
FAQs (Frequently asked questions)
Q1.What is the difference between an Obstetrician and a Gynecologist?
Ans. A gynecologist is mainly trained in female reproductive care whereas an obstetrician cares for pregnant women and newborns.
Q2. Who is the first female Surgeon General in India?
Ans. Mary Poonen Lukose was an Indian gynecologist, obstetrician, and the first female Surgeon General in India.
Q3. Can a person pursue OBGYN without an MBBS degree?
Ans. Yes, one can pursue a career in OBGYN after a BAMS degree if not MBBS. A diploma course in OBGYN can be done as well after a BAMS degree.
Q4. How can I enter the OBGYN field?
Ans. You can undergo a three-year postgraduate course in OBGYN (MS/MD) after doing MBBS or a two-year diploma program of postgraduate training in Obstetrics and gynecology.
Most students think that medical education is only about clearing the entrance exam and getting admission to MBBS. However, the reality is way different than this perception. Clearing the exam isn’t the final step, rather, is the beginning of the life of a medical student. A medical degree is considered one of the toughest degrees in the world. For a student, it’s definitely more work because of the unlimited workload and the time limit, which means a lot less sleep and a lot more stress.
Top Struggles of MBBS Students are:
- Adjusting with peers: Medical colleges are responsible for ensuring that graduates are knowledgeable, skilful, and professional to meet society’s expectations. Due to this, students have to prepare themselves for the vast syllabus while also adjusting with peers. There is huge peer pressure on medical students when it comes to adjusting themselves in the new environment due to high level of competition.
- Wow! You are smart, you should be a doctor: Medical might not be the hardest choice for aspirants but the journey is indeed very hard. Students put in all the efforts, and energy to enter the clinical world; the world that includes a lot of hard work, sleepless nights, countless hours of study, and whatnot. However, there are many students who give their 100 percent just to satisfy that One Big Dream of their family and relatives, at the cost of their happiness.
- Do you have a social life? When it comes to a medical student’s social life, the status is quite complicated. Students get trapped with books, assignments and practices, etc. that they can’t focus much on their social life. Although medicine is a very social course and being a healthcare professional, students must know how to deal with people. To take time out for social activities, students need to maintain a schedule that allows them to manage it all.
- Start the day and end the day with medicine: – The primary motivation is to enjoy studying. Exhaustion due to continuous studies can make medical college seem like a burden. So students must divert their attention from studies a bit and focus on “personal development.” This involves honing talents that fall outside the purview of academic study yet are nevertheless crucial for a doctor. For instance, participating in music or theatre can help students get used to performing or interacting in front of a large audience. This also helps them to confidently address and speak at a conference or simply to a group of their coworkers. There is a balance that needs to be achieved between working and enjoying life.
- You have to memorize so many new drugs, that your brain might explode: The most problematic situation that students face is that they need to cram names of thousands of new drugs and various syndromes, which is confusing. Also since these drugs are vast along with their own different characteristics, it is easy to forget a few. This is not the end, memorizing drugs also includes knowing their purposes, advantages, and disadvantages, after effects, and what all changes can be possible, which also includes how they respond in every individual’s body.
Watch Video to learn the right way to approach Pharmacology in MBBS
- The unending workload: – It is a popular talking point that a medical student’s life in med college is endless. The reason behind this is that medical courses are the longest courses in the educational world. It nearly takes a decade to become a fully qualified doctor. The entire journey demands a lot of hard work, sleepless nights, and a huge number of complications. It is not easy to maintain patience throughout this period and often students lose themselves in the wheel of practicals, rounds, syllabus, and examinations.
- Finance: – Finance is a huge problem for a medical aspirant. How? Not all medical aspirants belong to financially stable families, and neither do all receive government scholarships. Many students dream to become a doctor, but again finances remain a challenge. Medical studies are considered one of the most expensive education all over the world. It is a vast and expensive course. If a student does not have an adequate amount of money, pursuing a medical degree can be challenging. If this problem arises while a student is pursuing the course, students should always have a backup option.
- Exams Breakdown: – Exams have always been a huge load. Even the thought of it is scary because the syllabus is so vast that sometimes the duration of preparation tends to seem less. There’s no doubt medical life is filled with competitors, which makes the exam period even more stressful. Skipping topics is another aspect that makes it stressful while spending more time on important topics. Additionally, lack of sleep, headaches, and stress can easily lead to breakdowns.
- A good night’s sleep is a wonder for you: – Back-to-back classes, practicals, and whatnot get tiresome for them. Most students have sleepless nights because of assignments, many even suffer from sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality which is common during the internship. Researchers have paid much attention to the critical function that sleep plays in preserving mental health, advanced learning, and overall welfare. From 1st year to the final year, medical students are particularly prone to sleep-related problems due to the huge syllabus. So it is very important for students to at least have 6 – 8 hours of sound sleep.
Life of Students in the 1st year of MBBS:
Medical College is nothing like high school; it is challenging not simply because there is so much knowledge to gain, but also because students get to learn new skills. Students mostly in their first year, try to understand what kind of studying technique works to cover the syllabus. The first year is all about learning, failing and again understanding where you were wrong and then starting again.
Life in college doesn’t resemble the medical drama– Grey’s Anatomy in reality. No one goes to the clinical rounds in the first year itself. In the first year, students study Biophysics, Anatomy, and Histology and prepare for tests most of the days.
In the first year, it’s not all about saving lives. The only life students can save is theirs, by fixing a decent study routine for themselves, figuring out how to adjust their studies and things they like doing beyond studying and getting sufficient rest.
Life of Students in the 2nd year of MBBS:
It’s the best time to retrospect and make a schedule that can help students manage studies, social life, and sleep. The one benefit students have in their 2nd year is that they get familiar with the environment, faculty, and course too, so it becomes a bit easy for them to communicate and discuss their problems in the class or with the faculty. It gets even easier to make a schedule that can be followed given that students get quite familiar with the frequency of classes, practicals, and tests.
Life of Students in the 3rd year of MBBS:
It is very much like climbing one more step and reaching one step near to the goal of becoming a Top Doc. Becoming more focused on studies and attending a lot of practicals are included in the 3rd year. It is time for students to get exposed to the practical technicalities of the field. Students become familiar with everyday struggles in 3rd year; they feel the sensation of being worn out, because of classes and clinical rounds. They need to have some sort of framework, whether it be a paper journal or a schedule reminder turned on on their mobile phones.
Life of Students in the 4th year of MBBS:
The significant cause of the pressure students face in the final year is due to the major subjects like Medicine, Surgery, Pediatrics, OBGYN, Orthopaedics, etc. which are highly important for NEET PG. They experience maximum stress when they start going for rounds. Medicine is a long-distance race, not a run. Regardless of whether students complete their last year, it isn’t the end. They still need to learn a lot more because now their real life as interns and saviours begin. It’s now time to put all the knowledge into application.
Get conceptual clarity in Medicine from Dr. Archith Boloor
Passing the final exam in MBBS is crucial to starting your career as a doctor. Students must focus on conceptual clarity to clear the final exams. Discipline and dedication are the keys to mastering the syllabus. Moreover, aspirants that are pursuing the MBBS program at any medical college must complete the internship. An internship is a term of learning, or, to put it in simple words, more practical work than theoretical training. The internship phase is where you put all of the theoretical information you’ve learned over the last four years into action.
You should have a proper plan if you are going to enrol yourself as a medical student, it is a long ride with lots of struggle, hard work, failures, and whatnot. The medical course is exceptionally vast due to the volume of material that needs to be learned along with both the basic scientific principles and the clinical abilities. Keeping in mind the surreal feeling that a doctor feels while saving someone’s life is something that can’t be put into words, and furthermore, the feeling of saving somebody’s life is simply inexplicable. Once your goal is set and you are ready for it, it is definitely going to be the best chapter of your life.
Pediatricians are medical practitioners that specialise in treating children. Children experience fast physical and mental changes as they grow. Compared to adults, they undergo completely distinct physiological changes. A pediatrician is primarily responsible for managing the physical, mental, and emotional well-being of children at all stages of their development in addition to providing healthcare for children who are acutely or chronically unwell. For healthy youngsters, they also offer preventive healthcare treatments. They have a specific responsibility to transform medically and psychologically challenged kids into typical, healthy kids.
ADMISSION PROCEDURE
The following steps are undertaken by students who aspire to become Pediatricians:
- From the beginning, aspirants must complete the senior secondary education with the PCB stream with at least 50% marks.
- Further, they should crack the NEET UG exam to get admission to medical college (Government/ Private).
- After obtaining an MBBS degree, they need to appear for the NEET- PG entrance examination.
- A good score in NEET-PG gives a push to admission to the medical college for the Pediatrics PG course.
- Aspirants must complete a junior resident responsibility to gain a post-graduation degree.
- After the successful completion, they must obtain a license and become board certified.
ELIGIBILITY FOR BECOMING A PEDIATRICIAN
- Candidates should have completed an MBBS degree from a college/institution recognized by the Medical Council of India (MCI) with a minimum of 55% marks.
- They must have undergone the one-year compulsory internship after completing the course.
- Candidates must clear the NEET PG exam to be eligible for admission to recognized universities/colleges.
- For the general category, the candidate must obtain at least 50th percentile marks in NEET PG for admission to MD/MS courses. For SC, ST, and OBC, the minimum percentage requirement is the 40th
- For the candidate with benchmark disability specified under the Rights of Persons with Disability Act 2016, for the GEN-EWS and unreserved category 45th percentile is required. For, SC/ST/OBC-NCL candidates, the minimum marks shall be 40th
- In some cases, admission to post-graduate medical courses may also include a group discussion/personal interview after the entrance examination depending on the college.
- Final confirmation of admission depends on the cut-off marks and the counseling procedure.
In India, students must complete a five-and-a-half-year undergraduate programme that includes an internship to be eligible to write the entrance exam for NEET PG and pursue postgraduation in Pediatrics. This is the minimal academic requirement for becoming a doctor. In their various colleges or universities, students are required to have an MBBS degree and complete an internship.
Students who hold degrees from other nations but want to practise pediatrics in India must take the MCI exams. Students from the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and Canada are excused from taking the Medical Council Examination, but students from other nations must pass the MCI Exam to practise pediatrics in India.
In PG programmes, learning should be mostly self-directed and based on academic and clinical work. The official sessions are just intended to support this central effort. Check out the following ways to study effectively during post-graduation:
- Attend seminars or interdepartmental cases, participate in recognized scientific events (CME, symposia, and conferences), and attend webinars by eminent teachers like Prof. Piyush Gupta.
- Focus on practice-related resuscitation, basic sciences, biostatistics, research methodology, teaching style, hospital waste management, health economics, and medical ethics.
- To brush up on their knowledge of undergraduate studies, postgraduate students are required to participate in the training and instruction of interns and undergraduate students.
- During their training period, postgraduate students should keep a log book detailing the duration of their assignments and work in pediatric wards, outpatient clinics, and casualties. This should include the procedures and classes they took. They can use this to periodically assess the experience they have obtained and keep track of training-related activities.
- During their rotation, students are required to visit all of the department’s clinical facilities, including neonatology, perinatology, critical care, and emergency.
- Videos of evidence-based courses and benchmark clinical trials should be watched by students. These are easily accessible through Prof. Piyush Gupta’s renowned “PG Textbook of Pediatrics” and the DigiNerve Pediatrics MD Course.
Watch the Orientation to Post-graduation in Pediatrics to know more
DigiNerve’s Pediatrics MD Course by Prof. Piyush Gupta
To become a top pediatrician, Pediatrics MD is the most popular course for PG students. It is designed by the Chief Editor- Prof. Piyush Gupta, renowned for his best-selling “PG Textbook of Pediatrics”. This online pediatrics course is unique in its field, thanks to more than 500 years of experience and knowledge from India’s top 100 faculty. The course encourages concept-based and approach-based learning to suit all of the learning needs of the students while they pursue their master’s in pediatrics. The principles are supported by studies that serve as benchmarks or sources of proof. With an emphasis on the clinical findings and a detailed workup on how to arrive at an accurate diagnosis, the cases have been thoroughly examined.
This Pediatrics MD Course is among the best PG Pediatrics online course since the most recent society guidelines have been incorporated into each unit. The PG curriculum places a lot of emphasis on research, so a whole module has been allocated to giving students step-by-step guidance on how to do research. An interactive drug formulary has been included in the course for students’ convenience while they complete their ward rounds. The course incorporates engagement exercises including Journal Club, frequent Chat Shows, and current events.
Check out this Chat Show on ‘Pediatric Intensive & Critical Care’ by Prof. Piyush Gupta & Dr. Vikram Bhaskar
Careers you can pursue after PG in Pediatrics:
In order to treat a wide range of pediatric diseases and health issues, pediatricians are required to work in several settings, such as general pediatric institutions and long-term community care for children and adolescents. After postgraduation, one can choose from the following career paths:
- Gastroenterology Pediatricians: They recognise and treat serious conditions such as pancreatic insufficiency, gastrointestinal haemorrhage, inflammatory bowel disease, lactose intolerance, liver illness, vomiting, and others.
- Neonatologists: Doctors having specialised expertise in treating newborns and young children with complex, high-risk health issues.
- Pediatric Intensivists: They have significant training in detecting and treating children with life-threatening illnesses and specialise in critical care.
- Cardiologists: They specialise in the treatment of congenital cardiac disease and abnormal heart rhythms in children.
- Pediatric Endocrinologists: They identify and treat hormonal disorders in children, such as thyroid disorders, developmental problems, early or delayed puberty, and others.
- Neonatal Pediatricians: Neonatal pediatricians are particularly proficient at caring for infants who are born prematurely or with serious injuries, diseases, or birth defects, even though all pediatricians are trained to treat newborns who have just been born. They can also spot problems with the baby while it is still in the womb, which allows them to seek care from an obstetrician.
- Pediatric Hematologists and Oncologists: Leukemia, lymphomas, brain tumours, bone tumours, and solid tumours are all conditions they treat in children.
- Child Nephrologists: Kidney, bladder, and urinary tract problems in children are all treated there. They are also found to have congenital and acquired renal problems.
- Pediatric Anesthesiologists: They assure the safety of a child undergoing surgery for a condition that calls for it.
- Pediatric Allergists: They identify allergic reactions to food, air, or water that could result in asthma, a rash, or life-threatening anaphylaxis.
- Pediatric Developmentalists: They assess, advise, and treat young children and adolescents for physical deformities such as muscular dystrophy, behavioural problems like Attention Deficit Hypersensitivity Disorder (ADHD), and other developmental and behavioural problems.
- Pediatric Urologists: They treat urinary tract infections, disorders of urination like urinary retention, urinary incontinence, and others.
- Pediatric Dermatologists: They diagnose, manage, and treat skin diseases in children.
FAQs:
Q1. How many years does it take to become a Pediatrician?
Ans. A basic medical degree that lasts five and a half years and a three-year postgraduate degree is required in India to become a pediatrician, which adds up to eight and a half years of education.
Q2. Does a Pediatrician perform surgery?
Ans. It is a pediatrician’s duty to identify and treat common ailments in children. Treatment for conditions like diabetes, asthma, ear infections, strep throat, and pneumonia are included. Along with providing medical care, they also perform surgery and provide prescriptions for drugs.
Q3. What are the skills that a pediatrician requires?
Ans. Problem-solving, empathy, teamwork, communication skills, ability to relate to children, analysing laboratory results, and awareness of different cultures and traditions.
The specialised area of medicine known as ophthalmology is dedicated to eyes’ health. It covers the physiology, anatomy, and disorders that could impact the eyes. A professional doctor who deals with the prevention, diagnosis, and medical care of the eyes is an ophthalmologist. Ophthalmologists are trained in both surgical techniques and pharmacological therapies because this could involve both. M.D.s have the specialised training to offer the complete range of eye care, from performing intricate and delicate eye surgery to dispensing contact lenses and spectacles. Research into the causes and treatments for eye disorders and vision issues is another area of expertise for many eye doctors.
What does the PG Ophthalmology course focus on?
PG Ophthalmology programme lasts 3 years after students complete their MBBS degree. The course helps train students to treat eye conditions such as glaucoma, which damages the optic nerve and impairs vision, with the potential to result in blindness, iritis, which is an inflammation of the iris that may be caused by a systemic disease, chemical burns, orbital cellulite. Higher education and training in a variety of subspecialties are made available to enrolled students, from performing critical eye surgery to prescribing glasses and contact lenses. The course is well-structured for doctors to address any eye issues that may arise.
The course covers the fundamentals of ophthalmology as well as more complex topics such as disorders of the optical nerve system and the uvea and vitreoretinal tissues. According to analyses obtained through the use of medication, surgery, diet, and other therapies, doctors are taught how to cure eyes. The curriculum is developed to equip MD students with the knowledge and skills necessary to provide total eye care, including vision services, eye examinations, medical and surgical eye procedures, and the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders and other visual difficulties.
DigiNerve’s Ophthalmology MD Course by Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna
Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna, the Editor-in-Chief of Ophthalmology MD has designed the course along with India’s 55 renowned faculty. Their collective expertise will help students remarkably to gain an in-depth knowledge of concepts. The course is designed from an academic, clinical, and surgical point of view. The in-video demonstration of various surgeries will give a whole new dimension to students’ postgraduate learning.
The Ophthalmology MD course is a thoughtfully compiled collection of topics from prominent ophthalmologists from across the nation. Around 400 topics that are significant from an academic, clinical, and surgical perspective are collected in the course. All of the course’s topics have been carefully chosen with consideration given to frequently asked questions and troublesome regions for postgraduate students to provide adequate knowledge.
This programme is one of the best PG Ophthalmology courses for students who are seeking to fare well in post-graduation. Components of the course appropriately match the requirement of students in the pre-operative workup, helping them to perform surgical skills and even handle post-operative difficulties. To meet all of the students’ learning needs, it promotes concept and approach-based learning.
Postgraduate students who are taking exams have a special section with an innovative examination corner. For frequently encountered ocular disorders, particular focus is placed on obtaining the proper clinical findings by following the proper case and history-taking procedures.
With the use of surgical videos combined with 3D animated sequences of every surgical step, practitioners could also develop clinical/surgical ophthalmic skills. The conceptual knowledge will take on a completely new dimension, thanks to the in-video display of the numerous surgeries being carried out.
To help students gain a full understanding of each topic and to prepare them for exams, the lectures are richly illustrated with clinical/surgical and radiological pictures, as well as flowcharts, tables, and boxes, wherever necessary. For many illnesses, recent evidence-based recommendations have been added to familiarise readers with recent developments in the field. The important diagnostic procedures and techniques have been covered in detail along with a drug chart for quick reference for the students with a special focus on drug dosages, adverse effects, and their indications/contraindications.
Table of Content – Ophthalmology MD by Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna
Cataract
Lens
Anesthesia for Cataract Surgery
Preoperative Evaluation of Cataract Surgery
IOL Power Calculation
Ocular Viscosurgical Devices
Manual Extracapsular Cataract Extraction
Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery – Basics
Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery – Complications
Applications of Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery
Secondary IOL Implantation Through Sclero-Corneal
Phacodynamics
Phacoemulsification Techniques
Cortical wash – Coaxial and Bimanual Irrigation Aspiration Techniques
Foldable IOLs, Loading and Implantation
Complications of Phacoemulsification
Applications of Phacoemulsification
Repositioning of IOL and IOL Exchange
Femto Laser Assisted Cataract Surgery
Lens Induced glaucoma
Instrument Sterilization
Cornea
Cornea Basics
Corneal Topography
Specular Microscopy
Confocal Microscopy
Bacterial Keratitis
Fungal Keratitis
Acanthamoeba Keratitis
Microsporidial Keratitis
Herpes Simplex Keratitis
Herpes Zoster Keratitis
Non Healing Keratitis/Non Healing Corneal Ulcers
Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis I -General concepts
Corneal Ectasia
Pterygium
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency
Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid
Chemical Injuries of the Eye
Limbal Epithelial Transplantation (SLET and CLET, Buccal)
Amniotic Membrane Transplantation
Keratoprosthesis
Management of Ocular Trauma
Contact Lens
Corneal retrieval and Eye banking
Penetrating keratoplasty
Therapeutic keratoplasty
Graft Rejection
Refractive Surgeries
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty
Descemet Stripping Automated Endothelial Keratoplasty
Glaucoma
The Angle of Anterior Chamber
Aqueous Humour Dynamics
Tonometry
Central Corneal Thickness and Glaucoma
Gonioscopy
Pathogenesis of Glaucomatous Optic Neuropathy
Clinical Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head
Optic Nerve Head Changes in Glaucoma
Interpreting Humphrey Visual Field Reports
Interpreting Octopus Perimetry Reports
Anterior Segment Imaging Imaging – Ultrasound Biomicroscopy and Anterior segment Optical Coherence Tomography
Optic Nerve Head Imaging/Role of OCT in Glaucoma
Classification of the Glaucomas
Ocular Hypertension
Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
Normal-Tension Glaucoma
Primary Angle Closure Disease
Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma
Pigmentary Glaucoma
Lens Induced glaucoma
Uveitic Glaucoma
Neovascular Glaucoma
Glaucoma Associated with Ocular Trauma
Nanophthalmos and Other Secondary Angle Closure Glaucomas
Glaucoma after Vitreoretinal Surgery
Steroid Induced Glaucoma
Glaucoma following Penetrating Keratoplasty
Glaucoma Associated with Corneal Disorders
Classification and Early Diagnosis of Pediatric Glaucoma
Primary Congenital Glaucoma
Juvenile Open Angle Glaucoma
Glaucoma in Phacomatoses
Target Intra Ocular Pressure
Medical Management of Glaucoma
Newer Ocular Hypotensive Medications
Neuroprotection
Lasers in Glaucoma
Trabeculectomy
Glaucoma Drainage Devices
Non-Penetrating Deep Sclerectomy
Minimally Invasive Glaucoma Surgery
Cyclodestructive Procedures
Neuro-Ophthalmology
Practical Pearls in Neuro-ophthalmology
Neuro-ophthalmic Cases: Case Scenarios
Approach to Neuroimaging in Neuro-ophthalmology
Evaluation of a Case of Double Vision
Optic Neuritis
Optic Atrophy
Papilloedema
Myasthenia and Myopathies
Nystagmus-Evaluation
Double Vision A 10-step Assessment Plan
Myasthenia Gravis and its Mimickers
Neuro-Ophthalmic Examination: An Overview
MRI Making Sense of the Images
Neuroimaging for Ophthalmologists
Evaluation of a Pale Optic Disc
Optic Neuropathy
Pupil Pathways and Inference
Bilateral Ocular Motility Disorders – A Differential Diagnosis
An Approach to Swollen Optic Discs
Visual Fields in Neuro-ophthalmology
Ocular-Microbiology
Basic Microbiology
Antibiotics: Therapy and Testing
Molecular Diagnosis in Ocular Microbiology
Orbit
Anatomy of the Orbit
Lacrimal Apparatus
Imaging of the Orbit: Computed Tomography Scan
Orbital Decompression for Thyroid Orbitopathy
Proptosis- General Concepts
Orbital trauma- Considerations and principles
Orbital fractures and management
Orbit Infections
Fungal Infections of the Orbit
Parasitic Infections of the Orbit
Orbital Inflammations
Anophthalmic Socket
Contracted Socket
Benign tumors of the Orbit
Vascular Lesions of the Orbit
Reconstructive Socket Surgeries: Enucleation, Evisceration and Exenteration
Blepharoptosis: Evaluation and Management
Eyelid Retraction
Ectropion
Entropion
Esthetic Eyelid Surgery
Basics of Eyelid Reconstruction
Overview of Eyelid Reconstruction
Lacrimal Drainage System: Anatomy and Anomalies
Evaluation of the Lacrimal System
Congenital NasoLacrimal Duct Obstruction
Adult NasoLacrimal Duct Obstruction
Botulinum Toxin in Ophthalmology
Orbitotomy- Introduction
Lateral Orbitotomy
Orbitotomy – Other Approaches
Oncology
Pediatric Ophthalmology
Development of Visual System
Typical Development of Visual Milestones
Estimating Visual Acuity in a Child
Estimating Visual Acuity in Infant
Childhood Refractive Errors and Guidelines on Management
Lazy Eye
Red Eye in a Child and Vitamin A Deficiency
Syndromes with Ocular Manifestation
Low Vision (Visual Impairment)
Vision Assessment in Children with Low Vision
Low Vision Aids – Optical
Non Optical Aids and Rehabilitation
Headaches in Children
Ocular Causes of Headache
Retina
Macular Function Tests
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography
Indocyanine Green Angiography
Optical Coherence Tomography
OCT Angiography
USG + UBM
Fundus Autofluorescence and Multicolor Imaging
Retina
Anatomy, Physiology and Embryology of Vitreous
Evaluation of Retina and Vitreous
Diabetic Retinopathy
Hypertension and the Eye
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Pachychoroid Spectrum Disease – Introduction and Pachychoroid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Central Serous Chorio-Retinopathy
Pachychoroid Neovasculopathy & Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV)
Peripapillary Pachychoroid Syndrome & Focal Choroidal Excavation
Hereditary Macular Dystrophies
Macular Pathologies
Peripheral Retinal Degenerations
Retinopathy of Prematurity
Melanoma PG 1
Retinoblastoma
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy
Vascular Tumors of Retina and Choroid
Lasers in Retina
Intravitreal Injections
Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
Non Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
Posterior Segment Trauma
Systemic Diseases with Retinal Manifestations
Principles of Vitreoretinal Surgery
IOFB and its Management
Endophthalmitis
AI in Ophthalmology
Vitreoretinal Interface Diseases of the Macula – Epiretinal Membrane
Strabismus
Extra-Ocular Muscles & Orbital Fascia Applied Anatomy
Physiology of Extra Ocular Muscles
Binocular Single Vision
Strabismus – Classification & Etiology
Approach to a Comitant Deviation Patient
Diplopia
Hess Charting
Comitant Horizontal Strabismus: Esodeviation
Comitant Horizontal Strabismus: Exodeviation-
Vertical Deviation a. Approach to vertical deviations
Pattern Strabismus
Paretic Strabismus
Diagnosis and Management of Oculomotor Palsy
Diagnosis and Management of Trochlear Nerve Palsy
Diagnosis and Management of Abducent Nerve
Duanes Retraction Syndrome
Restrictive Strabismus
Browns Syndrome
Monocular Elevation Deficiency
Thyroid Related Strabismus
Congenital Fibrosis of Extra Ocular Muscles
Non-surgical Management of Strabismus
Surgical Management of Strabismus
Complications of Strabismus Surgery
Uvea
Uveal Tract
The SUN Classification & Terminologies of Uveitis
Systematic Work Up in Uveitis
Construction of Differential Diagnosis in Uveitis
Art of Ordering Lab Investigations in Uveitis
Immunosuppressives and New Biologicals
Management of Uveitic Cataracts
Ocular Tuberculosis
Viral Anterior Uveitis
Viral Uveitis
CMV – Posterior Uveitis
Leptospirosis & Syphilitic Uveitis
Ocular Toxoplasma
HIV and Opportunistic Infections Non Infectious Uveitis
Autoimmune Diseases and Uveitis
Sarcoidosis
VKH
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
The Masquerades
Refraction
Visual Acuity
Refractive Errors
Retinoscopy
Subjective Refraction
Accommodation and Convergence
Presbyopia Mechanism, Optical Correction and Surgical Procedures
Spectacle Lenses, Frames and Vertex Distance
Bifocals/Trifocals
Progressive Additional Lenses
Prisms
Contact Lenses
Colour Vision Contrast Sensitivity and Higher Order Aberrations
Aberrometer
Keratometry
Lensometer
Low Vision Aids
Examination Corner
How to Write a Theory Paper
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Uveitis Case?
FAQs in a Uveitis Case
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Cornea Case
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Retina Case?
FAQs in a Fundus Case Pertaining to the Retinal Vessels
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Glaucoma Case?
How to Describe Clinical Finding in a Orbit Case?
FAQs in a Orbit Case
How to Describe Management in Examinations
Investigations
OSCE Glaucoma
OSCE in Posterior Segment
OSCE in Neuro-ophthalmology
Ophthalmic Instruments
Best Way to Study Ophthalmology MD
- The postgraduate students should actively participate in lecture demonstrations, seminars, symposia, and inter and intradepartmental meetings. Through participation in symposia, CMEs, and journal clubs, they are exposed to contemporary developments. This will help them to focus on the aim, methods, remarks, conversations, and conclusions.
- They should gain clinical training by going through maximum clinical case discussions. Case discussions based on student-written patient records will assist students to hone their diagnostic and decision-making abilities.
- They should participate in presentations and discussions in a variety of ways. Using a problem-oriented approach will help students with decision-making.
- They should indulge in discussions with their senior postgraduate students before presenting in the symposium. The postgraduate students can prepare for a class-wide debate by participating in these discussions.
- Postgraduate students should indulge in bedside conversations during rounds and outpatient instruction which will help create an impact on patient management.
- Students should take interest in consultant’s case presentations which help in the solution of challenging issues and provide a forum for the debate of intriguing instances.
- The postgraduate students must take part in the training and instruction of interns and undergraduate students to brush up on their knowledge.
- They should attend monthly chat shows by eminent faculty, like the ones provided by the DigiNerve app.
- The student must take up rotations in the specialty clinics- Anterior segment and cataract, Glaucoma, Oculoplastics, Paediatric ophthalmology and strabismus, Retina and Uvea, Cornea, Contact lens and low vision, Neuro-ophthalmology, and Refractive Clinic.
- The postgraduate students should take the postings very seriously since they familiarize students with the typical ophthalmic issues. They must work freely and accept new and old cases, including refractions.
- The postgraduate student should make sure to keep an in-depth history and case record.
- MD students need to focus on basic sciences, biostatistics, research technique, teaching methodology, hospital waste management, health economics, medical ethics, and legal concerns connected to the practice of ophthalmology.
FAQs
Q1. What is the highest degree in ophthalmology?
Ans. Doctor of Medicine in Ophthalmology is the highest degree gained in the field of ophthalmology.Q2. What is the future of ophthalmology?
Ans. By 2025, there will be a need for about 22,000 ophthalmic surgeons, according to an estimate from the Health Resources and Services Administration in 2016. It also predicted that there will be more than 6,000 more doctors needed to meet the demand than there are currently available ophthalmologists.
Q3. What are the subspecialties in Ophthalmology?
Ans. Subspecialties in Ophthalmology include Glaucoma, Strabismus/pediatric ophthalmology, neuro-ophthalmology, anterior segment/cornea, retina/uveitis, oculoplastics/orbit, and ocular oncology.
The 3-year MD Obstetrics & Gynecology programme focuses on the comprehensive clinical pathology of the female reproductive organs and care of both pregnant and non-pregnant patients. At the end of the first semester in the MD Obstetrics & Gynecology, students are evaluated as a unit on what they choose to do from among the available courses. As a result, an analytical topic is selected based on the student’s interests. The program’s methods for delivering instruction include conversations, presentations, in-class performances, assignments, attendance, and seminars.
The area of medicine known as obstetrics deals with the treatment of pregnant women before, during, and after childbirth. The basic goal of obstetrics is to protect and preserve a woman’s general health throughout her pregnancy. This includes pregnancy, labour, childbirth, and the postpartum period. Obstetricians can assist with labour and delivery, and do surgery. Some operate a solo or private practice where they offer their services while others provide services in a bigger healthcare facility or medical group.
On the other hand, the area of medicine dedicated to the bodies and reproductive health of women is known as gynecology. It covers reproductive system diagnosis, care, and therapy for women. This includes the fallopian tubes, ovaries, and vagina. In this area of medicine, problems with women’s breasts are also screened for and treated. Gynecology deals with women’s health through puberty and adulthood. It represents most of the reproductive care a patient receives during their lifetime.
Best Way to Study OBGYN MD
- Postgraduate students should attend lectures, seminars, symposia, departmental meetings as well as journal clubs, and interdepartmental meetings.
- They must focus on presenting their theses under ethical approval, sound clinical practice standards and acceptable research methodologies.
- In addition to brushing up on their knowledge of undergraduate studies, postgraduate students should participate in the training and instruction of interns and undergraduate students.
- They should take part in chat shows like those provided by DigiNerve’s OBGYN MD course and other forms of interactions with distinguished faculty across the country.
- They must get familiar with the latest society guidelines, benchmark trials, and recent advancements in PCOS, Robotic Surgery, etc. These can be accessed easily with DigiNerve’s OBGYN MD course by Dr. Aswath Kumar.
- Students should emphasize self-learning, group discussions, and case presentations.
- They should concentrate on taking correct notes, performing a clinical examination, recommending or ordering pertinent tests, deciphering the results, and implementing medical/surgical management in the specialty clinics, OPD, wards, labour room, and operating rooms.
- They must take down clinical notes regularly while maintaining records.
- Students should attend dummy/model demonstrations with utmost attention and dedication before performing on real patients later.
- They should attend CMEs and conferences where they can present papers.
- Postgraduate students should keep a log book during the training time that details the length of their rotations and work in wards, outpatient departments, and casualties. This should list the operations and classes they attended. They can use this to periodically assess the experience they have obtained and keep track of training-related activities.
- Students must visit the department’s clinical units during rotations including anesthesiology, neonatology, and radiology/radiotherapy. In Obstetrics & Gynecology, NST, and Partogram, students should be competent to perform and interpret ultrasonography.
DigiNerve’s OBGYN MD course by Dr. Aswath Kumar
The course is designed by the chief editor Dr. Aswath Kumar along with 98 eminent faculty. Students will benefit greatly from their accumulated knowledge of more than 500 years as they learn ideas in depth. The course covers crucial obstetrics and gynecology concepts as well as case discussions on regular and uncommon cases. The students’ practical application of concepts will be enhanced through lectures on the management of labour, abnormal labour, abnormal presentations, and medical abnormalities in pregnancy. These lectures will also give the students a road map for how to treat these conditions successfully.
In order to help PG students prepare for their university examinations, the OBGYN MD course has been created based on the question papers from the country’s numerous universities during the previous 20 years. For students looking for a master’s in gynecology or master’s in obstetrics, this course is among the best postgraduate OBGYN courses available. To meet all of the students’ learning needs, it promotes concept-based and approach-based learning. Along with case discussions on often seen as well as uncommon instances in clinical practice, it covers significant obstetrics and gynecology issues. All of the course’s topics have been carefully chosen with consideration for the postgraduate students who struggle to obtain information on them as well as frequently asked questions.
The PG students studying gynecology and obstetrics have presented their cases as part of an open discussion with the relevant professors in the course. There is a focus on getting the right clinical findings and taking the case and history in the right way. The discussion between the faculty and students has been done in a way that would assist the viewers in approaching a case with the proper differential diagnosis and developing a strategy for correct diagnosis. To familiarise the students with contemporary developments in the field, the course contains current evidence-based guidelines for the management of a variety of conditions.
The display of minimally invasive surgeries like hysteroscopy and diagnostic/operative laparoscopy has its own area. This will give students’ learning a practical orientation. They will be thrilled with the lecture on Robotic laparoscopic surgery focusing on its relevance, application, and implications in the field of obstetrics and gynecology and how it is a boon from a future perspective. The concepts will take on a whole new dimension, thanks to the in-video display of the various surgeries being carried out.
The students’ practical application of concepts will be enhanced through lectures on the management of labour, abnormal labour, abnormal presentations, and medical abnormalities in pregnancy. These lectures will also give the students a road map for how to treat these conditions successfully. The crucial diagnostic techniques and procedures, such as the use of ultrasound in gynecology and prenatal examination, have been described in detail. A complete drug chart has been supplied for rapid reference by the students with a special focus on medications, doses, and their indications/contraindications in pregnancy and labour. To help students gain a complete understanding of each topic and to prepare them for exams, the lectures are profusely illustrated with clinical and radiological pictures, as well as flowcharts, tables, and boxes, when applicable.
We have also come up with the comprehensive OBGYN MD printed notes for existing users as well as new users to enhance the learning. The key features of our two volume OBGYN MD notes include:
- Our lecture notes are comprehensive yet condensed, keeping the vital details from lectures, textbooks, and extra material while still being clear and simple to read. No more turning pages or searching through pointless information!
- The carefully designed notes feature exam-oriented material and questions from past years, assisting students in concentrating their study efforts on the most crucial subjects and improving their chances of success.
- For busy students, our lecture notes are a time-saving lifesaver. The course content will be presented in a well-organized and condensed form so that students may learn more effectively and devote more time to practise and revision.
- Our lecture notes include visual learning components like charts, graphs, and diagrams to help memory retention. This makes difficult subjects simpler to understand and recall during tests.
- We think everyone should have access to a high-quality education at an affordable price. Our cost-effective lecture notes give students a method to succeed academically without going over budget.
Table of Content – OBGYN MD by Dr. Aswath Kumar Raghu
GYNECOLOGY LECTURE
Gynecological Anatomy
Development of Female Genital System
Anatomy of Female Genital System
Course of Pelvic Ureter, Anatomical Sites Susceptible to Injury
Pelvic Floor
Internal Iliac Artery
Lymphatic Drainage of Genital Tract
Menstrual Physiology
Physiology of Menstrual Cycle – Part I
Physiology of Menstrual Cycle – Part II
Gynecological Surgery
Thromboembolism Prevention in Gynecological Surgery
Developmental Anomalies of the Genital Tract
Developmental Anomalies of Female Genital Tract – Part I
Developmental Anomalies of Female Genital Tract – Part II
Menstrual Abnormalities
Cryptomenorrhea
Turners Syndrome
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome
Physiology of Menopause and Menopause Hormonal Therapy
Dysmenorrhea
Premenstrual Syndrome
Postmenopausal Bleeding
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Endometrial Hyperplasia
Hormonal Abnormalities in Gynecology
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
Hirsutism
Adrenal Steroidogenesis and Clinical Implications
Ovarian Pathology
Ovarian Torsion
Benign Ovarian Tumors
Borderline Ovarian Tumors
Uterine Abnormalities
Endometriosis- Management of Infertility and Pain
Fibroid uterus- I
Fibroid uterus – II
Treatment of Fibroid Uterus
Reproductive Medicine
Step by Step Approach To Male Infertility
Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Recent Updates in PCOS
Physiology of Ovulation
Ovulation Induction – I
Ovulation Induction – II
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
Pathology/Infection of the Female External Genitalia
Trichomonas Vaginitis
Bacterial Vaginosis
Vulvo-Vaginal Candidiasis
Pathologies of the Female External Genitalia
Non Neoplastic Lesions of Vulva
Pelvic Infection
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pediatric Gynecology
Puberty and Precocious Puberty
Urinary Tract Abnormalities/Infections
Stress Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Incontinence
Overactive Bladder
Urodynamic Study
Genital Fistula -VVF and RVF
Malignancy of the Genital Tract
Premalignant Lesion of Cervix
HPV Vaccination: Cornerstone of Cervical Cancer Elimination in India
Fallopian Tube Carcinoma
Carcinoma Vagina
Carcinoma Vulva
Cancer Cervix Management
Minimally Invasive Surgery
Hysteroscopy
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy Complications
Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
Robotic Surgery – Hype or Hope
Pregnancy Prevention
Updates on Contraception
Medical Termination of Pregnancy
Septic Abortions
Miscellaneous Topics of Gynecology
Radiation Therapy in the Management of Gynecological Malignancies
USG in Gynecology
OBSTETRICS LECTURE
Obstetric Anatomy, Physiology, and Embryology
Maternal Pelvis and Fetal Skull
Physiology of Lactation
Ovarian Steroidogenesis
Fetal Circulation
Antenatal Assessment
Antepartum Fetal Surveillance
Doppler in FGR
First Trimester USS
Second Trimester Ultrasound
Invasive and Non-Invasive Prenatal Diagnosis
Non Invasive Prenatal Testing
Chorionic Villus Sampling
Amniocentesis
Screening of Down Syndrome
Preconceptional Counseling
Complications of Pregnancy
Preterm Labor Prevention, Diagnosis and Management
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease and Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Abortions
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss – Practical approach
Management of Twin Pregnancy
Monochorionic Twins Surveillance, Complications, Management
Abruptio Placentae
Placenta Previa
Placenta Accreta Spectrum
Vasa Previa
Prediction and Management of Intra Uterine Fetal Growth Restrictions
HELLP Syndrome
Antihypertensives in Preeclampsia
Cervical Incompetence
Post Term Pregnancy
Abnormal Presentation
Malpresentations Breech Presentation
Transverse Lie
Face and Brow Presentation
Occipito Posterior Position
Deep Transverse Arrest
Medical Disorders in Pregnancy
SLE in Pregnancy
Liver Disorders in Pregnancy – Part I
Liver Disorders in Pregnancy – Part II
Thyroid Disorders in Pregnancy
Epilepsy in Pregnancy
Heart Disease in Pregnancy
Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnancy
Varicella in Pregnancy
Malaria in Pregnancy
TORCH Infection in Pregnancy
HIV in Pregnancy
Sepsis in Pregnancy: an Overview to Diagnosis and Management
COVID Complicating Pregnancy
Labor (Normal and Abnormal)
Mechanism of Labor
Induction of Labor
Premature Rupture of Membrane
External Cephalic Version
Monitoring during Labor
Partogram
Intrapartum Fetal Surveillance
Operative Delivery
Instrumental Deliveries – Dying art
Third Stage of Labor and its Complications
Retained Placenta
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Puerperium and its Complications
Normal Puerperium
Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative
Pulmonary Edema in Pregnancy
Thromboembolism in Pregnancy
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy
Psychiatric Disorders in Pregnancy
Obstetric Emergencies
Shoulder Dystocia
Cord Prolapse
Obstructed Labor
DIC in Pregnancy
Obstetric Hysterectomy
Rupture Uterus
Amniotic Fluid Embolism
Safe Motherhood/Epidemiology of Obstetrics
Maternal Mortality
Miscellaneous Topics during Antepartum and Intrapartum Period
Immunization in Pregnancy
Nutrition in Pregnancy
Labor Analgesia
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Pharmacotherapeutics in Obstetrics
Drugs in Obstetrics and Gynecology
Disease of the Fetus and Newborn
Neonatal Resuscitation
Miscellaneous Topics of Obstetrics
Role of Genetics in Obstetric Practice
GYNECOLOGY CASE DISCUSSION
Primary Amenorrhea
Secondary Amenorrhea
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Fibroid uterus
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Endometriosis
Adenomyosis
Infertility
Carcinoma Cervix
Endometrial Carcinoma
Carcinoma Ovary
OBSTETRICS CASE DISCUSSIONS
Antepartum Hemorrhage
Rh Negative Pregnancy
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss – I
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss – II
Twin Pregnancy
Fetal Growth Restriction
Hypertension in Pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy
Anemia in Pregnancy
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Cephalopelvic Disproportion
Previous Cesarean Section
Breech Presentation
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Scope of OBGYN after PG
- Maternal-fetal medicine specialists
High-risk pregnancies are managed by specialists in maternal-fetal medicine. They focus on the woman and baby’s health and may also manage challenging or high-risk deliveries like breech delivery.
- Reproductive endocrinologists
They are infertility specialists. They identify infertility issues and create treatment strategies. Several provide In-Vitro fertilisation (IVF) treatments.
- Gynecologic oncologists
A doctor who focuses on treating cancer is known as an oncologist in medicine. Ovarian and cervical cancer are two examples of the cancers that gynecological oncologists treat.
- Female pelvic specialists
Specialists in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery concentrate on diseases and injuries of the pelvic floor and adjacent structures. They could conduct surgery to fix prolapsed pelvic organs, address incontinence, or offer pelvic floor physical therapy.
FAQs
Q1. Who is an obstetrician-gynecologist?
Ans. An obstetrician-gynecologist is an expert in pregnancy and childbirth as well as female reproductive health. Some provide a broad range of general medical treatments, much like a primary care physician while some concentrate on the treatment of the female reproductive system.
Q2. Can a gynecologist deliver babies?
Ans. A gynecologist is an expert in the female reproductive system; he/she does not treat pregnant patients or assist in childbirth, instead, an obstetrician delivers babies. These two branches of medicine are frequently combined by students.
Q3. Can a male be a gynecologist?
Ans. Yes, many renowned gynecologists in the country and even across the world are male.
Q4. How many years does it take to become a gynecologist?
Ans. It takes around 7.5-8 years to become a gynecologist including 5.5 yrs of MBBS and 2 yrs of MD.
Pediatrics is the field of medicine dedicated to treating infants, children, and teenagers. In addition to being a distinct specialty, pediatrics is a collaborative one that incorporates other specialties. By 2030, pediatrics aims to lower infant mortality rates, stop the spread of infectious diseases, and help adolescents with their mental health, and physical capabilities. PG Pediatrics in Post-graduation specifically aims to prepare candidates to handle a variety of pediatric diseases and provide comprehensive care to children with long-term follow-up of chronic cases. It aims to educate students in medicine and paramedicine to ensure holistic understanding that includes both theoretical and practical knowledge.
The duration of Post-graduation in Pediatrics is 3 years, which may be increased or decreased as per the policies of various institutions. To ensure the students’ complete development of both academic and practical abilities, PG in Pediatrics provides sufficient expertise in offering dietary advice to new parents regarding breastfeeding and a healthy diet for children and adolescents. Additionally, it offers training in pediatrics and neonatology to make qualified experts capable of offering fundamental and specialised treatment to newborns, infants, children, and teenagers.
PG Pediatrics focuses on:
- The crucial relevance of children’s health in the context of the nation’s top health priority.
- The degree programme offers solid foundations for the additional research study.
- The significance of growth and development in the field of pediatrics and working with each child to attain his or her full potential in this regard.
- Carrying out pertinent investigative and therapeutic procedures on the patients.
- Nutritional guidance on nursing, weaning, and a balanced diet for newborns, infants, kids, and teenagers.
- Conducting pertinent research for diagnostic and prognostic evaluation while taking into account the costs, advantages, and risks involved.
- Analysing information gleaned through anthropometric measurements and developmental evaluations, as well as assessing nutritional status and deciding whether the child is receiving enough food.
- Offering sound advice on healthy and hygienic activities in order to prevent illnesses, disorders, injuries, accidents, and poisoning.
DigiNerve’s Pediatrics MD by Prof. Piyush Gupta
Pediatrics MD is a remarkable course designed by the Chief Editor- Prof. Piyush Gupta, renowned for his best-selling “PG Textbook of Pediatrics”. India’s top 100 faculty have enriched this online pediatrics course with over 500 years of combined experience and knowledge, making it unique in its field.
All the topics have been carefully chosen to address postgraduate students’ pain areas, for which they struggle to find adequate information. In order to meet all of the learning needs of the students while they pursue their master’s in pediatrics, the course promotes concept-based and approach-based learning. Benchmark/evidence-based studies have been used to support the principles. The cases have been thoroughly explored, with a focus on the clinical findings and a thorough workup on how to get the correct diagnosis. To refresh students’ memories, discussions about investigations such as ECGs, echocardiography, and other reports have also been had. The lectures include a live demonstration of systemic examination as well.
One of the PG exam’s most commonly asked topics is Neurology. As a result, this specialty has taken up around 20% of the course, and the professors have used an organised method to make the concepts easier for the students. The most recent society guidelines have been incorporated into each topic, making this Pediatrics MD Course one of the best online pediatrics postgraduate courses. Due to the significance of research in the PG curriculum, a complete module has been devoted to providing students with step-by-step instructions on how to do research. For the students’ convenience, while conducting their ward rounds, an interactive drug formulary has been included in the course. This covers all the important medications and includes pertinent dosages, contraindications, and common brand names. The course includes engagement activities including monthly Chat Shows, Journal Club, and recent updates.
Table of Content – Pediatrics MD by Prof. Piyush Gupta
Introduction
Indicators of Child Health and Vital Statistics
Resources for Learning in Pediatrics
Nutrition
Assessment of Nutritional Status
Nutritional Status of Children and National Programs in India
Micronutrient Supplementation: Key Issues
Infant and Young Child Feeding
JUNCS Guidelines & Way Forward
Severe Acute Malnutrition
Infectious Diseases
Immunization Dialogue
Prevention of Hospital-Acquired Infections
Principles of Antibiotic Therapy
Antimicrobial Resistance
Resistant Bacterial Infections
Tuberculosis
COVID -19
Anti-Viral Therapy
Helminthiasis: Current Perspectives
Neonatology
Assessment of Gestational Age
Neonatal Reflexes
Neonatal Resuscitation
X-ray and ECG in Neonates
Neonatal Jaundice
Comprehensive New-Born Screening for Birth Defects
HIE, IVH and White Matter Injury
Follow-up of High-risk Newborn
Critical Care
Shock
Fluid and Electrolytes
ABC of ABG
Cardiopulmonary Resucitation
Oxygen Therapy and Ventilation
Genetics and Metabolic Disorders
Approach to Diagnosis of Inborn Errors of Metabolism
Approach to Diagnosis of Genetic Disorders
Chromosomal Disorders
Newborn Screening in India
Approach to Skeletal Dysplasia
Gastroenterology
Examination of abdomen
Approach to a Child with Hepatosplenomegaly
Approach to a Child with Jaundice
Interpretation of Liver Function Tests with Case Scenarios
Persistent Diarrhea
Approach to Chronic Liver Disease
Portal Hypertension and Ascites
Upper GI Bleed: Diagnosis & Management
Approach to A Child with Constipation
Approach to a Child with Malabsorption
Endocrinology
Growth and Growth Charts
Approach to Short Stature
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Diabetes Type 1
Approach to Pubertal Disorders
Disorders of Sex Development: A Practical Approach
Hematology
Approach to a Child with Anemia
Hemolytic Anemia: Thalassemia
Nutritional Anemia
Bleeding Disorders in Pediatric Practice
Approach to Coagulation Disorders
Cardiology
Examination of Cardiovascular System in Children
Basic ECG and Arrhythmias in Children
Approach to a Child with Congenital Heart Disease
Left-to-Right Shunts
Approach to Cyanotic Heart Diseases
Cyanotic Heart Disease (Fallot Physiology)
Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease
Cardiomyopathies and Congestive Heart Failure
Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension
Nephrology
Urinary Tract Infections
Proteinuria & Nephrotic Syndrome in Children
Approach to Hematuria and Acute Nephritic Syndrome
Renal Tubular Disorders
Acute Kidney Injury
Chronic Kidney Disease
Hypertension in Children
Respiratory System
Examination of Respiratory System
Bronchial Asthma
Pneumonia: Differential Diagnosis and Management
Pleural Effusion: A Case-based Discussion
Neurology
Clinical Neuroanatomy
Higher Mental Function Assessment
Cranial Nerve Examination
Demonstration of Motor System in Children
Examination of Sensory System, Cerebellar and Meningeal Signs
Case-based Understanding of Localization in Neurology
How to summarize and Present a Neurological Case
Bare Basics of Interpreting Neuroimaging
Understanding the Basics of EEG
Principles of Developmental Evaluation
Developmental Assessment First 6 Months of Life
Developmental Examination (6 months–2 years)
Developmental Examination (2-5 years)
Case Scenarios in Developmental Deviations
How to Present a Case of Cerebral Palsy
Case Presentation of TBM
Case Presentation of DMD
Case Based Discussion of Seizure and Epilepsy in Children
Common Case Scenarios Presenting with Epilepsy in Children
Movement Disorders: Phenotypic/Clinical Spectrum
Case Based Approach to Hydrocephalus and Neural Tube Defects
Pediatric Stroke: Challenges in Diagnoses and Management
Approach to Floppy Infant
Rheumatic Disorders
Approach to a Child with Rheumatic Disorder & pGALS Exam
Rational Diagnostics for Rheumatic Disorders
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Mimics
Childhood-onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (cSLE)
Approach to Pediatric Vasculitis
Macrophage Activation Syndrome
Principles of Management of Pediatric Rheumatological Disorders
Approach to Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases
Research in Pediatrics
Study Designs
Steps of Conducting Research the ABC (RQ, Aim, Objectives)
Principles of Statistical Analysis
Sample Size Estimation
Drug Formulary
Best Way to enhance knowledge during PG in Pediatrics
Learning in PG programmes should primarily come from clinical and academic work and be self-directed. The formal sessions are merely meant to supplement this core effort. Following are some of the ways you can study effectively during post-graduation:
- Attend seminars or interdepartmental cases, participate in reputable scientific gatherings (CME, symposia, and conferences), and attend webinars by eminent faculty like Prof. Piyush Gupta.
- Focus on practice-related resuscitation, basic sciences, biostatistics, research methodology, teaching technique, hospital waste management, health economics, and medical ethics.
- Postgraduate students must take part in the training and instruction of interns and undergraduate students which will also brush up their knowledge of undergraduate studies.
- Postgraduate students should keep a log book during the training time that details the length of their posts and work in pediatric wards, outpatient departments, and casualties. This should list the operations and classes they attended. This will assist them in keeping track of the training-related activities and can be used to evaluate the experience gained periodically.
- Students must visit all of the department’s clinical units during their rotation including neonatology, perinatology, intensive care, and emergencies.
- Students should go through evidence-based video lectures and benchmark clinical trials. These can be accessed easily with DigiNerve’s Pediatrics MD course by Prof. Piyush Gupta, author of the renowned ‘PG Textbook of Pediatrics’.
Career Options after Pediatrics MD:
Pediatricians are required to operate in a variety of settings including long-term community care for children and adolescents, and general pediatric facilities to treat a variety of diseases and health concerns related to children. After postgraduation in pediatrics, one can opt for the following career paths:
- Neonatologists: Medical professionals with specialised training in managing complex, high-risk health problems in babies and young children.
- Cardiologists: They specialise in treating children’s heart issues, such as congenital heart disease and irregular heart rhythms.
- Critical Care Pediatricians or Pediatric Intensivists: They specialise in critical care and have extensive training in diagnosing and treating children with life-threatening diseases.
- Pediatric Endocrinologists: They diagnose and treat hormonal abnormalities in children including developmental issues, early or delayed puberty, thyroid disorders, and others.
- Gastroenterology Pediatricians: They identify and manage major issues including gastrointestinal haemorrhage, inflammatory bowel disease, lactose intolerance, liver disease, vomiting, pancreatic insufficiency, and others.
- Pediatric Hematologists and Oncologists: They treat children suffering from leukemia, lymphomas, brain tumours, bone tumours, and solid tumours.
- Neonatal Pediatricians: Although all pediatricians are trained to care for newborns who have just been born, neonatal pediatricians are particularly skilled in caring for infants who are born prematurely or with serious injuries, illnesses, or birth defects. Additionally, they can identify issues with the infant while still in the womb so that they can consult an obstetrician for treatment.
- Child Nephrologists: They treat kids with bladder, urinary tract, and kidney issues. Additionally, congenital and acquired renal issues are identified in them.
- Pediatric Allergists: They diagnose allergic reactions caused by food, air, or water that could cause asthma, a rash, or life-threatening anaphylaxis.
- Pediatric Anesthesiologists: Special medical skills are required for procedures like surgery. They are qualified to assure the safety of a child undergoing surgery if they are dealing with a condition that calls for it.
- Pediatric Developmentalists: They are equipped with skills to evaluate, counsel, and provide treatment for children during their early age and adolescence; if they have physical defects like muscular dystrophy, or if they have Attention Deficit Hypersensitivity Disorder (ADHD) and other behavioural and developmental issues.
- Pediatric Dermatologists: They are the pediatricians who are experts in the diagnosis, management, and treatment of skin diseases in children.
- Pediatric Urologists: They attend to children with urinary tract infections, disorders of urination like urinary retention, urinary incontinence, and others.
FAQs
Q1. Is MD Pediatrics a good career?
Ans. Graduates in MD Pediatrics can find employment in both the public and private sectors in India, according to their interests, abilities, and preferred field of work.
Q2. How long is MD in Pediatrics?
Ans. MD in Pediatrics is a 3-year long postgraduate program in the medical field.
Q3. Which is the best book for Paediatrics MD?
Ans. PG Textbook of Pediatrics by Prof. Piyush Gupta is the most renowned Pediatrics textbook in post-graduation.
COVID-19 has devastated families, institutions, and livelihoods while also scarring those at the front lines who witness it every single day. The strain put on our mental health during COVID-19 cannot be understated and the lockdown spent watching the news during such a time of extreme crisis has pressured our mental health further. It can be helpful to take moments out of your day to truly reflect on COVID-19’s impact on education and the mental health of students that might be fractured at the moment.
For those looking to pursue medicine, seeing crippling amounts of pressure being put on the healthcare system might be personally worrying. However, it is especially important to consider the mental health of students at such a critical juncture. To help take care of your mental health during covid-19, keep the following tips in mind to reduce stress.
- Free Headspace Subscription – Headspace is a US-based meditation app that announced a free subscription to all healthcare workers in India to tackle their mental health during COVID-19. Headspace has conducted numerous studies to reach the definitive conclusion that with just 30 days of guided meditation and practicing mindfulness, there has been a 30% stress reduction, greatly boosting mental health of students during COVID-19. If you are searching for a sense of peace in your days, consider signing up for Headspace.
- Take Care of Your Health – It can be difficult to separate your own life from those you care for but finding time to ensure that you are getting the exercise and nutrition you need is essential for myriad reasons. Firstly, an adequate diet that is supplemented with vitamins and nutritious food is essential to building up your immune system, an important factor when amid a pandemic. Secondly, as physical and mental health during covid-19 are interrelated, exercise regularly, try and sleep for full 8 hours, and eat healthy.
- Communicate Often – One of the best ways to destress and find a connection in an isolating time is to talk to other people. Be it friends, family, or a counselor, consider finding a connection and a way to unwind. Especially when considering COVID-19’s impact on the education and mental health of students during covid-19, these forms of socialization may provide a much-needed respite.
- Limit News – The endlessness of social media coupled with the stress of news can seriously harm the mental health of students during covid-19 and adults alike. While we all must remain alert about further developments in the pandemic, limit the amount of time that you ingest news.
If you find moments of solace through submerging yourself into challenging but rewarding tasks, perhaps signing up for an online course is a good way to spend your day. To get started, click here to view DigiNerve’s medical course options.
DigiNerve is an online medical education platform by Jaypee Brothers, and it is here to solve all the tutoring needs of medical undergraduate students, postgraduate students, and professionals. It aims to provide top-notch content to improve concept-building, acquire clinical skills, and crack exams by top-class faculty, accessible anytime, anywhere.
There are four categories of courses offered by DigiNerve: UnderGrad, PostGrad, Professional, and Exam Prep.
UnderGrad Category includes courses for 2nd, 3rd, and 4th year MBBS subjects:
- Microbiology for UnderGrads by Dr. Apurba S Sastry, Dr. Sandhya Bhat & Dr. Deepashree R
- Pathology for UnderGrads by Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak & Dr. Debasis Gochhait
- Pharmacology for UnderGrads by Dr. Sandeep Kaushal & Dr. Nirmal George
- Forensic Medicine and Toxicology for UnderGrads by Dr. Gautam Biswas
- Ophthalmology for UnderGrads by Dr. Parul Ichhpujani & Dr. Talvir Sidhu
- Community Medicine for UnderGrads by Dr. Bratati Banerjee
- Pediatrics for UnderGrads by Dr. Santosh T Soans & Dr. Soundarya Mahalingam
- Orthopaedics for UnderGrads by Dr. Vivek Pandey
- Medicine for UnderGrads by Dr. Archith Boloor
- Surgery for UnderGrads by Dr. Sriram Bhat M
- OBGYN for UnderGrads by Dr. K Srinivas
Additionally, two combos are also available in the UnderGrads section,
- Basic Sciences Combo: This combo includes the second professional courses (Microbiology, Pathology, and Pharmacology) along with Clinics to provide them a clinical foundation in 2nd prof.
- Clinical Combo: This combo includes Medicine, Surgery, OBGYN, Orthopaedics, Ophthalmology, Community Medicine, Pediatrics and Forensic Medicine & Toxicology course.
PostGrad Category includes PG specialisation courses:
- OBGYN MD by Dr. Aswath Kumar
- Dermatology MD by Dr. Rashmi Sarkar & Dr. S. Sacchidanand
- Ophthalmology MD by Dr. N. Venkatesh Prajna
- Pediatrics MD by Prof. Piyush Gupta
- Medicine MD by Dr. Jyotirmoy Pal and Dr. Shashank R Joshi
- Surgery MS by Prof. (Dr.) Nilay Mandal
Professional Category includes the following courses:
- Ultrasound in OBGYN Made Easy by Dr. Sonal Panchal & Dr. Chaitanya Nagori
- Basics of Infertility & IUI Made Easy by Dr. Chaitanya Nagori & Dr. Sonal Panchal
- Ganga Videos on Spine Surgery by Prof. Rajasekaran Shanmuganathan, Dr. Ajoy Prasad Shetty & Dr. Rishi Mukesh Kanna
- Advance Course in Ultrasound and Infertility by Dr. Sonal Panchal and Dr. Chaitanya Nagori
- Critical Care Simplified by Dr. Yatin Mehta, Dr. Subhal Dixit, and Dr. Kapil G. Zirpe
- Organ Donation Simplified by Dr. Kapil G. Zirpe and Dr. Rahul Pandit
- Cosmetic Botulinum Toxin Simplified by Dr. Rasya Dixit, Dr. Urmila Nischal and Dr. K.C. Nischal
Exam Prep Category includes the following courses:
- Cracking MRCOG Part 1- Comprehensive Course by Dr. Richa Saxena
- Cracking MRCOG Part 1- Mock Exam by Dr. Richa Saxena
- Cracking MRCOG Part 2- Comprehensive Course by Dr. Richa Saxena
- Cracking MRCOG Part 2- Mock Exam by Dr. Richa Saxena
- Cracking MRCOG Part 3- Live OSCEs Engagement by Dr. Richa Saxena
- Cracking MRCOG Part 3- Non-Interactive OSCEs by Dr. Richa Saxena
- Cracking MRCP Part 1 by Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander and Dr. Archith Boloor
Why Choose DigiNerve?
The course content offered by DigiNerve is not only as per the respective curriculums but is also brought to students easily and interactively. The courses include highly illustrative video lectures, competitive self-assessment questions, progress analysis, and specially curated notes while always focusing on concept-based learning. Here are a few other aspects of DigiNerve that set it as the best guide a student can have during their Top Doc journey:
- Esteemed Faculty: Each course on DigiNerve is curated and taught by Gold Standard Faculty in the respective field. For example, ‘Cracking MRCP Part-1’ is taught by the highly acclaimed Dr. Gurpreet Singh Wander and Dr. Archith Boloor, each of whom has published research papers and taught at renowned medical universities. Similarly, ‘Ultrasound in OBGYN Made Easy’ is structured and mentored by the distinguished faculty, Dr. Sonal Panchal and Dr. Chaitanya Nagori, who have years of expertise and have published successful books on gynecology. Also, UG courses such as Microbiology for UnderGrads is taught by the maestro himself, Dr. Apurba S Sastry along with Dr. Sandhya Bhat & Dr. Deepashree R, Pathology for UnderGrads by Prof. Harsh Mohan, Prof. Ramadas Nayak & Dr. Debasis Gochhait. These faculties already have an irreplaceable place on the shelves of every medical student. Thus, all students can be assured that no matter which course they choose, DigiNerve has got their back.
- Credible Content: Since all course content is structured by renowned faculty, all students get the latest medical breakthroughs, practically relevant material, clinical case demonstrations & discussions, and the benefit of over 50-year trusted medical legacy that Jaypee provides. All of this results in courses that have credible and valuable information to help students not only ace their medical and entrance exams but also develop their professional abilities as doctors.
- Easy to Use: DigiNerve is designed to be as student-friendly as possible. With an efficient and detailed website and a virtual classroom experience that is based on interactivity, all students can access courses and navigate with ease. Further, students can learn from their respective courses and content anytime and anywhere via the DigiNerve App. The app also has other great features, such as the Continue Journey Widget, Split View option to access the video lectures and notes simultaneously, Video Indexing, and ‘Ask a doubt’ feature.
- Specialization Courses: Apart from providing students with courses to help them crack competitive exams, DigiNerve also has specialized courses for doctors looking to hone in on a particular skill or for postgraduate students looking to enhance their practical knowledge. One such course is ‘Ultrasound in OBGYN Made Easy’. The course provides students with detailed knowledge of ultrasounds that is essential for gynecology and radiology practice. It also specifically teaches cutting-edge fetal medicine knowledge to help doctors reach a diagnosis.
- International Certification: On completion of the specialized courses offered in Infertility and IUI and Ultrasound in OBGYN, DigiNerve facilitates internationally recognized certificates for its students. Thus, boosting their CV, opening doors for higher pay and international practice in the respective specialization. For some courses like the USG course, students on completion receive a certificate from the prestigious Ian Donald Inter-University School.
DigiNerve is unparalleled in the quality of courses offered, the range of material taught, the Gold Standard faculty that structure and teach the courses, and the easily navigable interface. Thus, giving students helpful courses at a competitive price that provide them with conceptual clarity, allowing them to excel in their exams, and also offering practical guidance.