INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers | Free PDF Download (All 200 Qs)
Anatomy INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
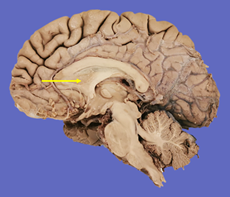
Q1. The highlighted structure in the provided image articulates with which bone?
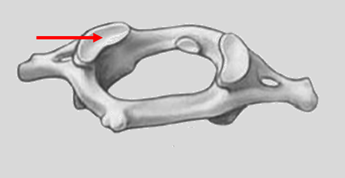
- Occipital bone
- Temporal bone
- Axis
- Sphenoid bone
Answer – A
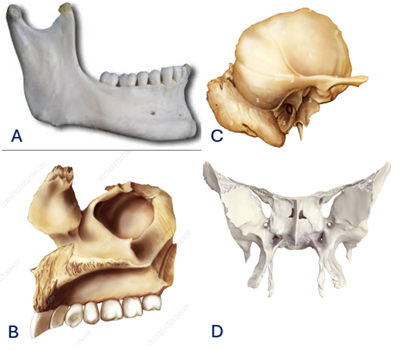
Q2. Through which of the following foramina does the nerve supplying the muscles of mastication pass?
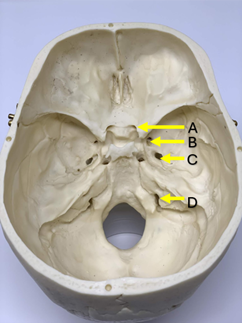
- A
- B
- C
- D
Answer – C
Q3. In the given image, which region is correctly paired with its corresponding brain structure?
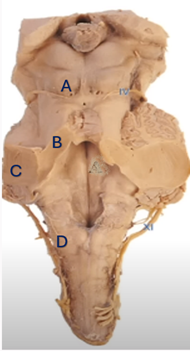
- Middle cerebellar peduncle
- Fasciculus cuneatus
- Superior cerebellar peduncle
- Inferior colliculus
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-A, 4-B
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-C, 4-A
Answer – C
Q4. Which of the following muscles is NOT typically associated with dysphagia or dysarthria?
- Stylopharyngeus
- Tensor veli palatini
- Palatopharyngeus
- Pharyngeal constrictor
Answer – B
Q5. A muscle of mastication involved in opening the mouth exhibits the following characteristics. Identify the incorrect statement about it:
- Attached to the medial surface of the mandible ramus
- Receives innervation from the mandibular nerve
- Attached close to the temporomandibular joint
- Aids in mandibular protrusion
Answer – A
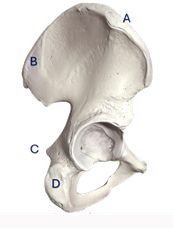
Q6. In the illustrated image, which of the following structures is NOT associated with the area marked by the arrow?
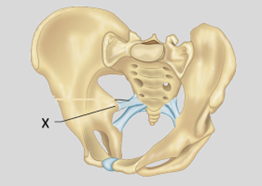
- Internal pudendal vessels
- Tendon of the obturator externus
- Ischiococcygeus
- Pudendal nerve
Answer – B
Q7. Match the following embryonic aortic arches with their respective adult derivatives:
| A. 1st Arch | 1. Maxillary artery |
| B. 2nd Arch | 2. Common carotid artery |
| C. 3rd Arch | 3. Right subclavian artery (on the right side) |
| D. 4th Arch | 4. Hyoid and stapedial arteries |
- A-2, B-4, C-1, D-3
- A-1, B-4, C-2, D-3
- A-1, B-4, C-3, D-2
- A-1, B-3, C-2, D-4
Answer – B
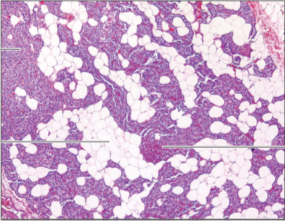
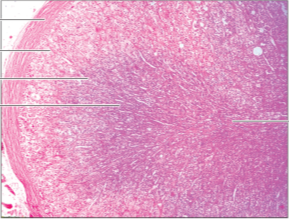
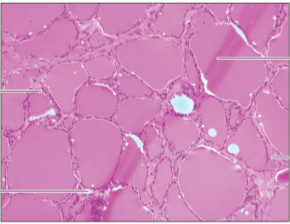
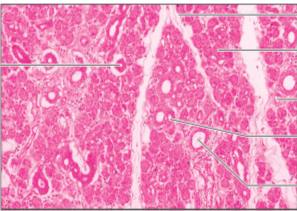
Q8. Which of the following histology images is not an endocrine structure?
Answer – D
Q9. Marked structure separates which of the following:
- Third ventricle
- Lateral ventricle
- Fourth ventricle
- Cisterna magna
Answer – B
Q10. Which of the following bones of the skull gives passage to a nerve arising from the brain
Answer – D
Q11. The muscle that contributes to both hip and knee extension originates from which of the following structures?
Answer – B
Physiology INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Which GI secretions have the lowest sodium concentration?
- Stomach
- Ileac secretions
- Duodenum
- Saliva
Answer- D
Q2. Which of the following neurotransmitters is correctly matched with its synthesis site?
- Acetylcholine- substantia nigra
- Serotonin-Raphe nucleus
- Norepinephrine- Nucleus basalis of Meynert
- Dopamine – Locus ceruleus
Answer – B
Q3. Which discovery was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology for 2025?
- Peripheral Immune Tolerance
- mRNA’s role in post-translational modifications
- RNA polymerization
- Cancer chemotherapy
Answer – A
Q4. Which hypothalamic nuclei are involved in leptin resistance?
- Ventromedial nucleus (Satiety centre, decreases hunger)
- Arcuate nucleus
- Paraventricular nucleus (PVN)
- Lateral hypothalamic nucleus
Answer – B
Q5. In the cardiac cycle, when pressure increases while volume remains constant, which phase is this?
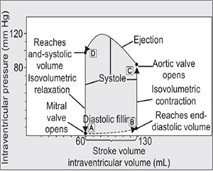
- Isovolumetric contraction
- Isovolumetric relaxation
- Rapid ventricular filling
- Ventricular ejection
Answer – A
Q6. Systolic blood pressure slightly falls during normal inspiration due to?
- Decreased pulmonary compliance
- Increased left ventricular filling
- Increased venous return to the right heart causes a transient reduction in left ventricular filling
- Increased systemic vascular resistance
Answer – C
Q7. In Myasthenia Gravis, why does repetitive nerve stimulation show a decremental response?
- Decreased release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic terminal
- Increased degradation of acetylcholine by acetylcholinesterase
- Reduced number of functional acetylcholine receptors at the postsynaptic membrane
- Autoantibodies blocking presynaptic calcium channels
Answer – A
Q8. In an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), blood glucose values are plotted over time. Which graph is most consistent with Diabetes Mellitus?
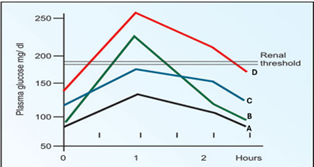
- A, B, C, D
- B, C, D only
- B, D only
- C, D only
Answer – C.
Q9. The image below is an example of which of the transport systems?
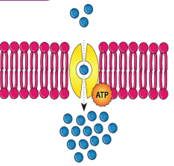
- Sodium-glucose co-transporter
- Organic anion transporter
- GLUT 4
- P glycoprotein
Answer – D
Q10. Magnesium is primarily regulated by which of the following processes?
- Urinary reabsorption
- Intestinal absorption
- Dietary intake
- Bone resorption
Answer – A
Q11. Which of the following represents the most stable and long-term Homeostasis mechanism in humans?
- Urine output
- Respiratory rate (RR)
- Oxygen saturation (SpO2)
- Heart rate
Answer – A
Q12. The below shown left ventricular pressure-volume (PV) loop is seen in –
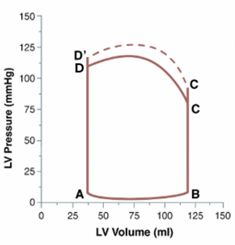
- Increased ventricular contractility
- Increased venous return
- Increased peripheral vascular resistance
- Increased aortic compliance
Answer: C
Biochemistry INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Which of the following represents the correct sequence of steps in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
- Denaturation → Annealing → Extension
- Denaturation → Annealing → Extension → Hybridization
- Annealing → Extension → Denaturation
- Extension → Denaturation → Annealing
Answer: A
Q2. In rheumatoid arthritis, increased expression of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in synovial tissue is most likely due to which epigenetic mechanism?
- Activation of DNA methylation
- Inhibition of DNA methylation
- Activation of histone deacetylation
- Inhibition of histone acetylation
Answer – B
Q3. Cancer cells showing an increased RNA transcript length compared to normal cells is most likely due to:
- Polyadenylation
- Alternative RNA splicing
- Gene amplification
- Gene silencing
Answer – B
Q4. The M13 bacteriophage vector used to identify specific gene sequences (e.g., viral spike proteins) represents which type of expression system?
- Phage expression
- Bacterial expression
- Yeast expression
- Mammalian expression
Answer: A
Q5. During B-cell maturation, expression of a single immunoglobulin heavy-chain allele ensuring antigen specificity occurs by which process?
- V(D)J rearrangement
- Alternate splicing of RNA transcripts
- Alternate polyadenylation sites
- Somatic hypermutation
Answer: A
Q6. The 2025 Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded for which discovery?
- Peripheral immune tolerance
- Micro RNA
- mRNA vaccine technology
- Targeted immunotherapy
Answer: A
Q7. Match the following amino acids with their respective derivatives:
|
Substance |
Derivative |
| A. Tyrosine | 1. Thyroid hormone |
| B. Tryptophan | 2. Melatonin |
| C. Glycine | 3. Taurine |
| D. Cysteine | 4. Creatine |
Options:
A. A-1, B-2, C-3, D-4
B. A-1, B-2, C-4, D-3
C. A-2, B-1, C-4, D-3
D. A-2, B-1, C-3, D-4
Answer: B
Q8. Plasma magnesium levels are primarily maintained through:
- Renal reabsorption
- Gastrointestinal absorption
- Bone resorption
- Dietary intake
Answer: A
Q9. Deficiency of which enzyme results in increased 2,3-BPG levels and low glucose values in vitro?
- Pyruvate kinase
- Phosphoglycerate kinase
- G6PD
- Hexokinase
Answer: B
Q10. A 6-month-old infant presents with hepatomegaly, a doll-like face, lactic acidosis, and anaemia. Liver biopsy reveals hepatocytes packed with glycogen and lipids, suggesting glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. Which laboratory finding is most characteristic of this disorder?
- Fasting hypoglycemia
- Elevated cholesterol levels
- Low lactate concentration
- Reduced glutathione levels
Answer: A
Q11. Which tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediate acts as a precursor for fatty acid synthesis?
- Succinate
- Citrate
- Malate
- Fumarate
Answer: B
Q12. A patient with megaloblastic anaemia is treated with folate alone, after which neurological symptoms worsen instead of improving. Which mechanism best explains this phenomenon?
- Folate trap
- Homocysteine accumulation
- Masking of vitamin B12 deficiency
- Pernicious anaemia due to intrinsic factor deficiency
Answer: A
Q13. A 28-year-old man develops fatigue, jaundice, and dark urine two days after taking an antibiotic. Lab tests show anaemia, raised LDH, elevated indirect bilirubin, and a negative Coombs test. G6PD deficiency is suspected. Which statements correctly describe features of the HMP shunt pathway?
| A. | Enzyme defect: Sphingomyelinase |
| B. | Enzyme defect: Beta-glucocerebrosidase |
| C. | Foamy macrophages are seen |
| D. | A crumpled tissue paper appearance is seen |
- 1 and 2
- 1 and 3
- 2 and 4
- 3 and 4
Answer: B
Q14. Which of the following statements about β-oxidation of fatty acids is incorrect?
- Both CAT I and CAT II transport fatty acids across the mitochondrial membrane
- ATP is required for fatty acid transport across the mitochondrial membrane
- CoA is released in the cytosol during acyl-carnitine formation
- Carnitine is released on the mitochondrial side
Answer: B
Q15. Deficiency of which cofactor shunts 3-OH-Kynurenine to the xanthurenic acid pathway?
- Thiamine
- Biotin
- Panthenic acid
- Pyridoxine
Answer – D
Q16. Which of the following best describes/true regarding the RAS gene?
- Constitutive activation of a GTP-binding protein leading to continuous MAP kinase signalling
- Enhanced DNA repair leading to genomic instability
- Inactivation of a tumour suppressor gene resulting in loss of cell cycle checkpoint control
- Increased activity of tyrosine kinase receptors through gene amplification
Answer – A
MICROBIOLOGY INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. What is the most frequent cause of viral diarrhoea in adults?
- Rotavirus
- Adenovirus 40/41
- Norovirus
- Astrovirus
Answer: C
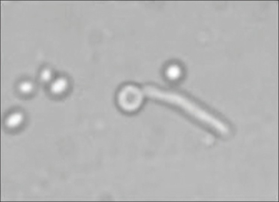
Q2. Identify the species from the given phenomenon below
- C albicans
- B parapsilosis
- C kruzei
- tropicalis
Answer: A
Q3. Which of the following infections are NOT acquired through a thorn prick injury?
- Dermatophytosis
- Chromoblastomycosis
- Mycetoma
- Sporotrichosis
Answer: A
Q4. An image shows a large operculated egg from a parasitic fluke, identified as belonging to the genus Fasciola. What is the most likely parasite?
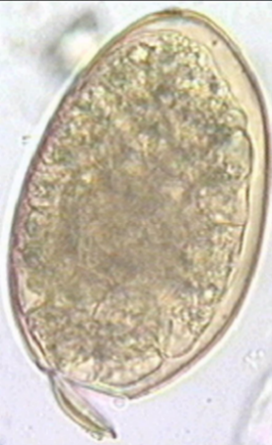
- Fasciola hepatica
- Clonorchis sinensis
- Schistosoma haematobium
- Paragonimus westermani
Ans: A
Q5. Identify the egg from the image below?
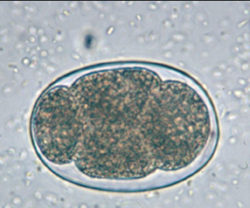
- T solium
- Ascaris lumbricoides
- H nana
- Necator americanus
Answer – D
Q6. A fungal infection of the mitral valve shows positivity on silver/Gomori stain. Which organism is most likely to cause the disease?

- Mucor
- Histoplasma capsulatum
- Aspergillus fumigatus
- Candida albicans
Answer – C
Q7. A culture of Streptococcus pneumoniae shows alpha-hemolysis and draughtsman colonies on blood agar. Which test is most useful for its identification?
- No vaccine
- Catalase positive
- Vancomycin sensitivity test
- Bile solubility test
Answer – D
Q8. Match the following parasites with the diseases they cause?
- Visceral larva migrans
- Cutaneous larva migrans
- Swimmer’s itch
- Larva currens
- Strongyloides
- Schistosomiasis
- Toxocara canis
- Ancylostoma braziliense
- 1-c, 2-d, 3-b, 4-a
- 1-a,2-b,3-c, 4-d
- 1-d,2-c,3-b,4-a
- 1-b,2-c,3-d, 4-a
Answer- A
Q9. A patient presents multiple draining sinuses releasing black granules. Which of the following organisms is most likely responsible?
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Nocardia asteroides
- Actinomyces israelii
- Madurella mycetomatis
Answer – D
Q10. The viral life cycle that corresponds to the epidermal layers—replication occurring in the spinous layer, assembly in the granular layer, and release in the cornified layer—is characteristic of which of the following viruses?
- Human papillomavirus (HPV)
- Molluscum contagiosum virus
- Varicella-zoster virus
- Herpes simplex virus
Answer: A
Q11. Which of the following is not true about the given condition?
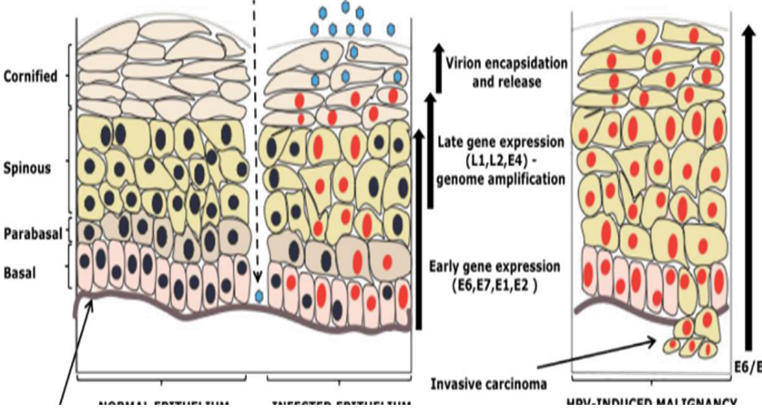
- Oncogenic virus
- Painful lesions
- RNA virus
- No vaccine available
Answer – A
Q12. Mycobacterium tuberculosis is handled in which biosafety level (BSL) laboratory?
- BSL-1
- BSL-2
- BSL-3
- BSL-4
Answer – C
Q13. What was incorrect about below image shown:
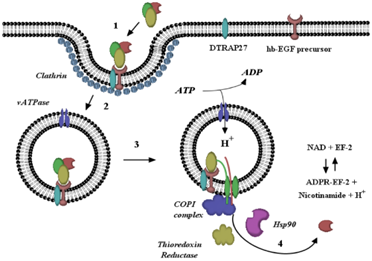
- Phage coded
- Causes myocarditis
- It is an exotoxin
- It is the most potent toxin known to man
Answer – D
Q14. An image depicting fruit bats (Pteropus species) along with the life cycle of the Nipah virus was shown. Which of the following statements regarding the Nipah virus is correct?
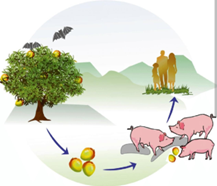
-
- Cause encephalitis
- 100% mortality once clinical symptoms appear
- DNA virus
- Humans are the most important reservoir
Answer – A
Q15. Classical case explaining lung infection with hemoptysis.
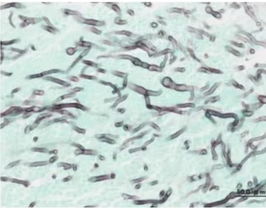
- Aspergillus with aseptate branching
- Aspergillus with septate branching
- Rhizopus with septate
- Mucormycosis with septate hyphae
Answer – B
Q16. Which of the following is an obligate intracellular organism?
- Ehrlichia chaffeensis
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Tropheryma whipplei
- Streptococcus pyogenes
Answer – A
Q17. Where is Wuchereria present during daytime, when microfilaria are not seen in blood capillaries?
-
- Spleen
- Liver
- Lungs
- Kidney
Answer – C
Pathology INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Where is Onion skin fibrosis seen?
- Primary biliary cholangitis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Biliary atresia
- Acute cholecystitis
Answer – B
Q2. Choose the correct option:
- Perls stain, iron, red
- Alizarin, Ca, black
- Van Gieson, elastin, blue
- Giemsa, mast cells, purple
- 2 & 4
- 1, 2, 3
- 2, 3, 4
- Only 4
Answer – D
Q3. A female carries an autosomal recessive mitochondrial disorder. Which of the following systems are most likely affected?
- Immune and skeletal
- Cardiac and skeletal
- Skeletal and neurogenic
- Immune and cardiac
Answer – B
Q4. What is included in the major and major criteria of Jones rheumatic fever?
- Carditis
- Polyarthralgia
- Chorea
- Shortened PR interval
- Erythema nodosum
- 1,2,3
- 2,3,4
- 1,2,3,5
- 4,5
Answer – A
Q5. What are the correct options regarding Peutz-Jeghers syndrome:
- STK 11 mutation
- Shows an arborising pattern
- Autosomal dominant
- Congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigment epithelium
- 1, 2, 3 are correct
- 1, 2, 4 are correct
- 3 & 4 are correct
- 1, 2 are correct
Answer – A
Q6. A 62-year-old man presents with generalised lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly. Peripheral smear shows small to medium-sized lymphoid cells with irregular nuclear contours. Cytogenetic analysis demonstrates a t(11;14) (q13:q32) translocation. Which of the following markers is most closely associated with the pathogenesis of this lymphoma?
- Cyclin D
- SOX 11
- CD -200
- CD 10
- 1 & 2
- 2 & 3
- 1 & 4
- 3 & 4
Answer – B
Q5. Lipid is best visualised on which technique in pathology?
- Frozen Section
- Paraffin-embedded section
- Immunohistochemistry
- Electron microscopy
Answer – A
Q6. Which of the following findings are associated with Mantle Cell Lymphoma?
- Cyclin D1
- Sox 11
- CD 200
- CD 23
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 2, 4
- 1 & 2
- 1, 2, 5
Answer – C
Q7. A patient’s blood report showing MCV = 76 fL visits the OPD. Which of the following conditions is most likely responsible for this result?
- Iron deficiency anaemia
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Thalassemia
- Lead poisoning
- A & B
- B & D
- A, C
- A, C, D
Answer – D
Q8. A patient presents with microcytic anaemia, an elevated RBC count, and a Mentzer index of less than 13. What is the next appropriate investigation?
- S. Ferritin
- Bone marrow biopsy
- S. Transferrin
- Hb electrophoresis
Answer – D
Q9. Which of the following is false regarding Gaucher’s disease?
- Crumpled tissue paper appearance
- Beta-glucocerebrosidase enzyme deficiency
- Ceramidase deficiency
- Bone pain
Answer – C
Q10. Which of the following statements about Rheumatic fever is false?
- 2 weeks post-sore throat
- Aschoff bodies seen
- Infection caused by group A, beta streptococcus
- Myocarditis, but no endocarditis
Answer – D
Q11. A boy presents with developmental delay, obesity, hypotonia, normal neurological development, and hypogonadism. His karyotype shows 46 XY with a deletion of del(15)(q11-q13). What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Prader-Willi syndrome
- Angelman syndrome
- Patau syndrome
- Cri du chat syndrome
Answer – A
Q12. Which of the following are the definitive criteria for nephrotic syndrome?
- Hyperlipidemia
- Proteinuria >3.5 g/day
- Creatinine
- Hypoalbuminemia
- 1, 2, 3
- 1, 2, 3, 4
- 1 & 3
- 2 & 4
Answer – D
Q13. Which of the following statements are correct about Retinoblastoma?
- It is always unilateral
- It is associated with an increased risk of osteosarcoma
- The RB protein is inactive (hypophosphorylated)
- Oncogenesis occurs through a loss-of-function mutation
- The gene involved is called the ‘guardian of the genome’
- B, D
- A, B, C, D
- C, D, E
- D, E
Answer – A.
Q14. A patient with microcytic hypochromic anaemia, normal or elevated RBC count, and target cells on peripheral smear is suspected of having a hemoglobinopathy. Which test would be most appropriate to confirm the diagnosis?
- Serum iron and TIBC
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Serum ferritin estimation
- Hb electrophoresis
Answer: D
Pharmacology INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. All of the following are advantages of ketamine except:
- Dissociative anesthesia
- Relief from pain
- Sedation
- Relief from depression
Answer – A
Q2. Which of the following drugs used in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension is a prostacyclin receptor agonist?
- Selexipag
- Ambrisentan
- Epoprostenol
- Iloprost
Answer: A
Q3. All of the following statements regarding Dronabinol are correct except?
- It is used for pain relief
- It is excreted unchanged in the urine
- MOA: Cannabinoid receptor agonist
- It is approved for weight loss in AIDS-associated
Answer – B
Q4. Which of the following statements about Rifampicin is incorrect?
- Resistance occurs due to mutations in the rpoB gene.
- It undergoes enterohepatic recirculation.
- It should be administered along with fatty meals.
- Its CNS penetration is limited by P-glycoprotein.
Answer – C
Q5. Which of the following medications acts by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)?
- Ranibizumab
- Pembrolizumab
- Ipilimumab
- Dostarlimab
Answer – A
Q6. Which of the following statements regarding Rimegepant is correct?
- It is administered subcutaneously
- It is indicated for the acute management of migraine
- It acts as a CGRP1 receptor agonist
- It produces vasoconstriction
Answer – B
Q7. Which regimen is considered the preferred treatment for cryptococcal meningitis?
- Amphotericin B combined with Fluconazole
- Fluconazole monotherapy
- Liposomal Amphotericin B monotherapy
- Liposomal Amphotericin B in combination with Flucytosine
Answer – D
Q8. Patient is on 2nd line ATT, now complaining about numbness & acidosis then which drug should be withdrawn?
- Linezolid
- Bedaquiline
- Delamanid
- Levofloxacin
Answer – A
Q9. Which of the following adverse effects is not associated with the use of inhaled β-adrenergic agonists?
- Pulmonary vasodilation
- Hyperkalemia
- Palpitations
- Tremors
Answer – B
Q10. Which of the following medications exerts its effect by blocking the channel labelled “C” in the diagram?
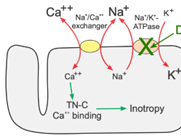
-
- Calcium channel blocker
- Ivabradine
- Nicorandil
- Digoxin
Answer – D
Q11. A patient with HIV presents with a 3-month history of cough and fever, and Miliary tuberculosis is suspected. What should be the next step in management?
- Start ATT, followed by initiation of ART after 2 weeks, with an increased dose of dolutegravir along with dexamethasone
- Start ART, followed by ATT after 2 weeks, with an increased dose of dolutegravir
- Administer an increased dose of dolutegravir immediately
- Initiate ART and ATT simultaneously with standard doses of dolutegravir
Answer – A
Q12. Identify the parasite in the image and select the most appropriate drug for its treatment:
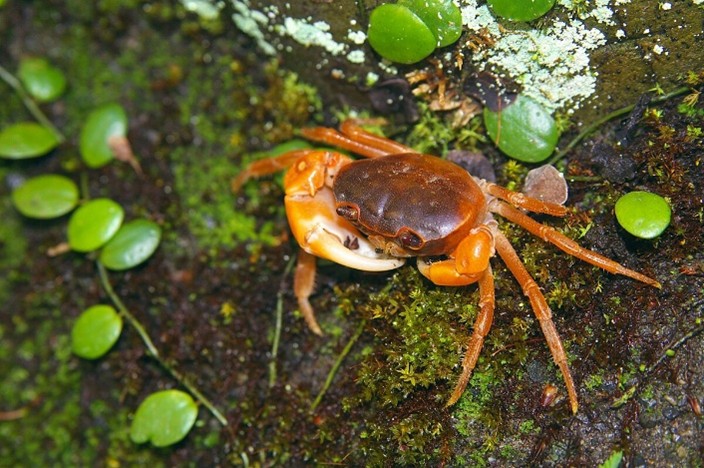

-
- Praziquantel
- Albendazole
- Niclosamide
- Ivermectin
Answer – A
Q13. The dose-response curve of acetylcholine (ACh) is shown in the graph. When an additional drug is introduced, the response to ACh increases (shifts upward). Which drug is most likely responsible for this effect?
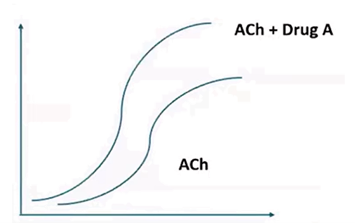
- Physostigmine
- Bethanechol
- Adrenaline
- Atropine
Answer – A.
Q14. Which DPP-4 inhibitor requires dosage modification when used with ketoconazole?
- Saxagliptin
- Linagliptin
- Sitagliptin
- Vildagliptin
Answer – A
Q15. Which of the following parasitic infections is most effectively treated with ivermectin?
- Strongyloides stercoralis and Trichinella spiralis
- Loa loa and Brugia malayi
- Onchocerca volvulus and Loa loa
- Onchocerca volvulus and Wuchereria bancrofti
Answer – D
Q16. Which of these drug combinations is recommended for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) in individuals at high risk?
- Tenofovir monotherapy
- Tenofovir + Lamivudine
- Zidovudine + Lamivudine
- Tenofovir + Emtricitabine
Answer – D
Q17. False statement about finerenone compared to spironolactone?
-
- Spironolactone causes more gynecomastia compared to finerenone.
- Both drugs are mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, but finerenone is nonsteroidal.
- Finerenone is a nonsteroidal, selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist with fewer endocrine side effects.
- Finerenone inhibits aldosterone synthesis.
Answer – C
Community Medicine INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Which of the following is not included in Bradford Hill’s criteria for establishing causation?
- Temporality
- Dose–response relationship
- Biological plausibility
- Sensitivity
Answer – D
Q2. In an emergency triage scenario, which patient should be attended to first?
- 40-year-old unconscious patient with noisy breathing
- 25-year-old woman is breathing rapidly and sweating
- 60-year-old man is conscious with blood-soaked trousers
- Child crying loudly and inconsolably
Answer – A
Q3. PM2.5 particles are considered particularly hazardous to human health because their small size allows them to penetrate deeply into which part of the respiratory tract?
- Alveoli
- Bronchioles
- Nose
- Trachea
Answer – A
Q4. A previously vaccinated healthcare worker (HCW) sustains a needle-stick injury from a Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)–positive patient. The HCW is a known non-responder. What should be done next?
- Give 1 dose of HBIG and start a complete Hepatitis B vaccination series
- No further action is required
- Give 2 doses of HBIG — one immediately and another after 4 weeks
- Give 2 doses of HBIG immediately, at separate sites
Answer – C
Q5. As per the National Program for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD), which of the following screening activities are not done at the Sub-Centre (SC) or Primary Health Centre (PHC) level?
- VIA for cervical cancer screening
- Visual inspection for oral cancer
- Mammography for screening at the primary level
- Screening starts beyond 30 years
Answer: C
Q6. Which of the following statements about the roles of the family beyond reproduction are incorrect?
- Providing support during illness
- Influencing cultural and health-related behaviour
- Providing emotional and financial security
- Regulating sexual behaviour and reproduction only
Answer: D
Q7. Which of the following statements about the NITI Aayog Health Index are incorrect?
- It is used to assess and compare the health performance of different states and UTs.
- It is meant only for evaluating government hospitals.
- It promotes healthy competition among states to improve health outcomes.
- It aids in policy planning to strengthen public health systems, especially primary healthcare.
Answer – B
Q8. A community consists of 500 individuals, and over a period of 2 years, 20 new cases of a certain disease were identified. The total observation time amounted to 950 person-years. What is the incidence rate of this disease in the population?
- 2.1 per 1000 person-years
- 2.1 per 100 person-years
- 4 per 1000 person-years
- 2 per 100 person-years
Answer – B
Q9. A research study observes that individuals who exercise regularly have a lower risk of developing heart disease. However, those who work out also tend to maintain a healthier diet, which itself lowers heart disease risk. In this scenario, diet serves as a—
- Mediator
- Effect modifier
- Confounder
- Independent variable
Answer – C
Q10. In a research study, a p-value of 0.03 was found. What does this indicate?
- There is a 3% probability that the observed result occurred due to chance.
- There is 97% confidence that the null hypothesis is true.
- The difference observed is not statistically significant.
- The null hypothesis is rejected because the chance probability is below 2%.
Answer – A
Forensic Medicine INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Crocodile-like skin is seen in which of the following?
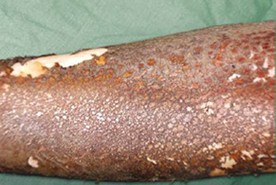
- Arsenic poisoning
- High voltage shock (10K – 12K)
- Moist burns
- Chemical burns
Answer – B
Q2. A girl was brought to the emergency in an unconscious state with a history of faintness in the bathroom, showing cherry red discolouration. She was declared dead. The bathroom was a poorly ventilated room with a newly installed geyser. Blood toxicology reports show a high concentration of an irritant gas. What could this gas be?
- CO
- CO2
- Hydrogen sulphide
- Methane
Answer – A
Q3. A case of hanging has come to the forensic department for autopsy. The autopsy, Dr. notices a ligature mark covering about 1/3rd of the neck, protruding tongue, salivary stains, opened right eye, closed left eye, and both pupils dilated. What is the probable reason for the open right eye?
- Compression of IJVs
- Compression of ICA
- Compression of the Cervical sympathetic chain
- Compression of Vagus
Answer – C
Q4. A person killed his friend because of his belief that he would poison him & later he was diagnosed as a case of schizophrenia. He was taken to court. Based on McNaughten’s rule, how is a person liable for a crime?
- Partially guilty
- Guilty
- Not guilty
- Guilty, if the act was committed with knowing it is wrong
Answer – D
Q5. Identify the grading burn Injuries:
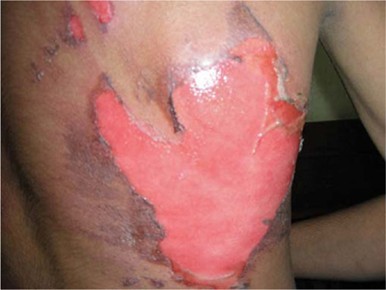
- Superficial burns
- Deep burns
- Full-thickness burns
- Partial thickness burns
Answer – D
Q6. Sexual pleasures by non-living inanimate objects are called?
- Fetischism
- Voyeurism
- Exhibitionism
- Froutterism
Answer – A
Q7. Identify the condition shown in CT
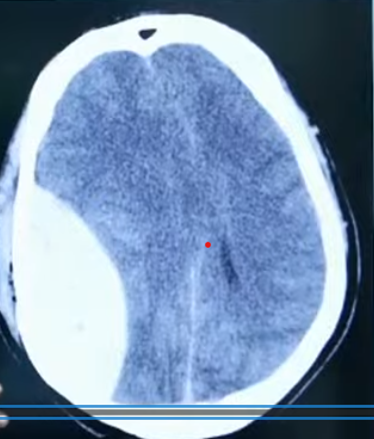
- EDH
- SDH
- SAH
- ICH
Answer – A
Q8. Match the following poisoning with its treatment:
| 1. Arsenic | A. Naloxone |
| 2. Methanol | B. Fomepizole |
| 3. Benzodiazepine | C. Flumnazenil |
| 4. Opioid | D. BAL |
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-D, 2-B, 3-C, 4-A
- 1-A,2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
Answer – A
Q9. Match the following poisoning with its agents:
| 1. Deliriant | A. Alcohol |
| 2. Inebriant | B. LSD |
| 3. Hallucinogenic | C. Opium |
| 4. Somniferous | D. Datura |
- 1-D, 2-A, 3-B, 4-C
- 1-D, 2-B, 3-C, 4-A
- 1-A,2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-C, 3-A, 4-D
Answer – A
Q10. A patient comes to OPD with soddened burn injury over his right thigh with erythema, blisters & line of demarcation. Which of the following is true of this case?
- Moist burn
- Chemical burn
- Dry burn
- Electric burn
Answer – A
Q11. A 17-year-old juvenile is brought by police, and as alleged by police, the school certificate shows the age as 17, but there is evidence of overwriting in the certificate. According to the police, the age is 19 years. Which X-rays will you recommend to prove the age is>18 years?
- Pelvis, sternum
- Pelvis, skull
- Wrist, medial end of clavicle & pelvis
- Elbow, shoulder
Answer – C
Q12. An 18-year-old girl was brought to the hospital by her mother with a history of sexual assault by her 24-year-old coworker in the factory. The mother doesn’t want to inform the police. What will you do as the doctor in charge?
- Ask the guardian for permission to do a medicolegal examination
- Do a medicolegal examination with the consent of the victim
- Do not collect materials required as forensic evidence
- Do not inform the police
Answer – B
Q13. Which of the following is not a seminal test in a case of rape?
- Barberio test
- Acid phosphate test
- Reineche test
- Florence test
Answer – C
Ophthalmology INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. A patient reports a sudden onset of intense eye pain, headache, blurred vision, and colored halos. Examination reveals a mid-dilated fixed pupil, hazy cornea, and markedly raised intraocular pressure. What is the most probable diagnosis?
- Secondary angle closure due to anterior uveitis
- Acute endophthalmitis
- Orbital cellulitis
- Acute primary angle closure glaucoma
Answer – D
Q2. A contact lens user presents with severe ocular pain, photophobia, and blurred vision. Corneal examination shows a ring-shaped infiltrate, as shown in the image. Which staining technique helps in identifying the causative organism?
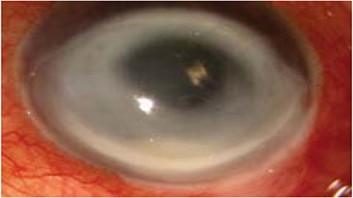
- Zinc stain
- Calcofluor white stain
- Gram stain
- GMS silver stain
Answer – B
Q3. Krukenberg spindle formation on the corneal endothelium is a characteristic finding of which type of glaucoma?
- Pigmentary glaucoma
- Malignant glaucoma
- Acute angle closure glaucoma
- Neovascular glaucoma
Answer -A
Q4. All of the following are used to assess visual acuity in preverbal children, except:
- Optokinetic nystagmus drum
- Teller acuity cards
- ETDRS chart
- Landolt C chart
Answer – C and D. (ETDRS and Landolt C chart are for literate adults, not preverbal children)
Q5. A young myopic patient with astigmatism presents with acute red eye, history of frequent spectacle change, and eye rubbing. On examination, corneal hydrops is seen, and an intracameral gas injection was performed. What is the likely diagnosis and management procedure shown?
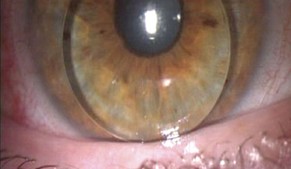
- Descemet’s stripping endothelial keratoplasty (DSEK)
- Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK)
- Intracameral gas injection with C3F8 for acute hydrops
- Collagen cross-linking
Answer – C
Q6. Which part of the cortex is responsible for scanning the visual field?
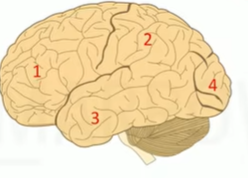
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer – A
ENT INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. A 65-year-old male complains of difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds. Which region of the cochlea is primarily damaged?
- Apex of the cochlea
- Base of the cochlea
- Stria vascularis
- Tectorial membrane
Answer – B
Q2. A patient is diagnosed with carcinoma of the larynx involving the entire right true vocal cord, anterior commissure, and one-third of the left true vocal cord, with extension into the paraglottic space and inner thyroid cortex. The right vocal cord is completely immobile. What is the most likely tumour stage?
- T1
- T4
- T3
- T2
Answer – B
Q3. Which of the following hearing tests is not performed in infants?
- OAE (Otoacoustic Emissions)
- BERA (Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry)
- PTA (Pure Tone Audiometry)
- Free-field audiometry
Answer: C
Q4. Arrange the following steps of Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) in the proper order:
- Uncinectomy
- Bullectomy
- Open the maxillary sinus
- Ethmoidectomy
Options:
- ABDC
- CABD
- ACBD
- CBAD
Answer: C
Surgery INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. A patient is diagnosed with recurrent peptic ulcers and a nodule in the first part of the duodenum. Which of the following tests should be done next to confirm the diagnosis?
- Serum prolactin levels
- Serum gastrin levels
- 24-hour urinary catecholamine levels
- Serum parathyroid hormone levels
Answer: B
Q2. A patient presents with a rapidly growing breast lump (20×15 cm), erythema, and peau d’orange (PDO), with a family history of breast cancer. She is diagnosed with inflammatory breast cancer. What is the appropriate treatment?
- Neoadjuvant chemotherapy followed by MRM
- MRM followed by chemotherapy
- Neoadjuvant therapy followed by BCT and SLNB
- Palliative care
Answer – C
Q3. A patient presents with 24 hours of abdominal pain and is diagnosed as acute appendicitis. Which of the following statements are incorrect?
- McBurney’s point is the classical site of tenderness
- Oschner Sherren is used in the appendicular lump
- Immediate appendectomy is performed after conservative management in all cases
- Ultrasound is the investigation of choice in children
Answer – C
Q4. Which of the following absorbable sutures causes the maximum tissue reaction?
- Polygalactin
- Catgut
- Polypropylene
- Polydioxanone
Answer – B
Q5. A patient presents for follow-up after obesity treatment, with a surgical image shown. Which procedure was performed?
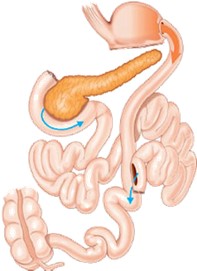
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
- Mini-gastric bypass
- Duodenal switch
- Biliopancreatic diversion
Answer – D
Q6. TIGAR-O classification is used in which type of pancreatitis?
- Acute pancreatitis
- Chronic pancreatitis
- Autoimmune pancreatitis
- Alcoholic pancreatitis
Answer – B
Q7. An intraoperative image of an inguinal hernia is shown. Which type is depicted?
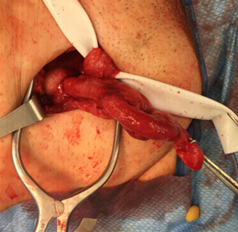
- Littre
- Amyand
- Garengeot
- Grynfelt
Answer – B
Q8. Arrange the following steps of surgery in order:
- Creating pneumoperitoneum
- Dissection of hepatocystic triangle
- Ligation of the cystic duct and artery
- Separation of the gallbladder from the liver bed
- A-B-C-D
- A-C-B-D
- B-A-C-D
- D-A-B-C
Answer – A
Q9. Arrange the steps of hernioplasty in the correct order:
- Skin incision
- Identify the sac and reduce its content
- Place the mesh
- Wound closure
- a-b-c-d
- b-c-a-d
- a-d-c-b
- b-a-d-c
Answer – A
Q10. The angle of laparoscopy between the left- and right-hand working ports is known as:
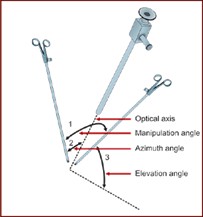
- Manipulation angle
- Azimuth angle
- Elevation angle
- Extreme angle
Answer – A
Q11. A 60-year-old female with a history of cholecystectomy and abdominal tube insertion 10 days ago presents with abdominal pain. What is the next step in management?
- Immediate percutaneous drainage
- Exploratory laparotomy
- ERCP and stenting/sphincterotomy
- Conservative management
Answer – C
Q12. A 17-year-old presents with recurrent abdominal pain for 3 months. Amylase and lipase are raised. What is the likely diagnosis based on USG and MRCP findings?
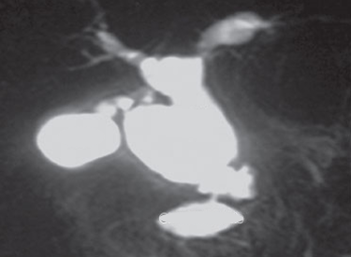
- Choledochal Cyst
- Annular Pancreas
- Pancreas Divisum
- CBD stone
Answer – A
Q13. Which of the following statements about intestinal stomas is incorrect?
- The ileostomy loop is generally kept with pouting
- Maximum malabsorption of electrolytes and nutrients is seen with colostomy
- The stoma of a colostomy is everted above skin level
- Only the muscular layer is taken in sutures while creating an ileostomy
Answer – C
Q14. During triage, who should receive the highest priority?
- 6-year-old child crying
- 45-year-old unconscious with noisy breathing/grunting sounds
- 23-year-old conscious with breathing difficulty
- 60-year-old conscious patient with blood-soaked pants
Answer – B
Q15. A patient presents with abdominal pain and has elevated mucin and CEA levels but normal amylase. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN)
- Pancreatic cystic neoplasm
- Mucinous adenoma
- Pancreatic pseudocyst
Answer – C
Medicine INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. A patient with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) presents with the deformity shown. What is the correct name of the deformity?
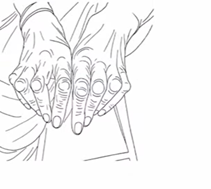
- Piano key sign
- Z deformity
- Boutonniere deformity
- Swan neck
Answer: C
Q2. A patient presents with Horner’s syndrome and absence of sweating on one side of the face. Which of the following structures is most likely compressed?
- Sympathetic chain
- Internal carotid plexus
- Vagus nerve
- Common carotid artery
Answer – A
Q3. A 22-year-old athlete collapses and dies suddenly during a game. Autopsy reveals ventricular hypertrophy. What is the most likely underlying cause?

- He died of valvular disease
- The image shows features of chronic heart failure
- Coronary artery disease due to increased cholesterol
- HOCM needs to be screened in case of a family history
Answer – D
Q4. A 45-year-old man with known alcoholic cirrhosis presents with confusion and 3 days of hematemesis. Examination reveals icterus, hepatosplenomegaly, tense ascites, and asterixis. Vitals: BP 100/60 mmHg, pulse 104/min. Which of the following is NOT appropriate in the initial management of this patient?
- Start propranolol to stop variceal bleeding
- Perform a diagnostic ascitic tap to rule out spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)
- Start IV antibiotics and IV octreotide infusion
- Give IV albumin after large-volume paracentesis or if renal dysfunction develops
Answer- A
Q5. According to the GOLD guidelines, what is the FEV1 (% predicted) cutoff associated with clinically significant resting hypoxemia in patients with chronic COPD?
- 50%
- 20%
- 40%
- 30%
Answer: D
Q6. According to the GOLD guidelines, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of a patient who smokes and has a chronic COPD exacerbation with a respiratory rate of 30/min, pulse of 110/min, with increased sputum, resting SpO2 of 90% on room air, and pCO2 of 80 mm Hg?
- Antibiotics
- Systemic Corticosteroids
- Antiviral treatment
- Nebulized bronchodilators
Choose the correct combination
- A, B, D
- A, C, D
- B, C, D
- A, B, C, D
Answer: A
Q7. A patient with chronic productive cough and progressive breathlessness is diagnosed with COPD. He develops type II respiratory failure. Which of the following statements regarding his condition is not true?
- Bronchial wall inflammation is a characteristic finding
- Increased Reid index
- Lung compliance is decreased
- FEV₁/FVC ratio is <70%
Answer – C
Q8. Which of the following has the highest risk of causing invasive pulmonary aspergillosis?
A. Febrile neutropenia
B. CD4 <50 cells/μL
C. Severe protein-energy undernutrition
D. Bronchial asthma\
Answer – A
Q9. A patient presents to the OPD with the complaint of back pain and weakness in both lower limbs. Which of the following findings would suggest compressive myelopathy?
- Hypotonia
- Absent Babinski sign
- Normal cremasteric reflex
- Knee clonus
Answer: D
Q10. A patient comes to the OPD with a history of fever for 4 days, no bleeding manifestations, and stable vitals. Blood work shows Hb = 9 g/dL, platelet count = 20,000/mL. What is the next step in management during the first hour?
- PCM
- Antibiotics
- Platelet transfusion
- Steroids
- A, B, C, D
- A, B, C
- A, B
- A
Answer: A
Q11. A patient presents with exertional dyspnea and pedal oedema. His echocardiogram shows a dilated left ventricle with reduced systolic function. Which of the following statements regarding this condition is false?
A. Pulmonary hypertension may develop in this patient
B. Ejection fraction will be reduced in this condition
C. Long-term anticoagulation is not needed for this patient
D. Beta blockers are indicated in chronic management
Answer – C
Q12. A 28-year-old male presents with involuntary jerky movements of the face and limbs, along with noticeable personality changes and increasing forgetfulness. An MRI of the brain is shown. What is the most likely diagnosis?
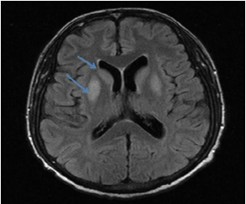
- Wilson’s disease
- Sydenham’s chorea
- Prion disease
- Huntington’s disease
Answer: D
Q13. Which of the following conditions is associated with large P waves on an ECG?
- Mitral stenosis
- Tricuspid stenosis
- Aortic regurgitation
- Systemic hypertension
Answer – B
Q14. Which of the following conditions does NOT share the same underlying mechanism that contributes to the development of heart failure, as seen in the other conditions?
- Anemia
- Fever
- High salt intake
- Thyrotoxicosis
Answer: C
Q15. A 25-year-old female with systemic lupus erythematosus presents with weight gain, moon facies, buffalo hump, and hirsutism. Which of the following is the most appropriate investigation to confirm the diagnosis?
- Serum ACTH and low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
- Low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
- High-dose dexamethasone suppression test
- Serum ACTH and cortisol levels
Answer: D
Q16. Which of the following findings is NOT typically seen in Conn’s syndrome?
- Hypernatremia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypertension
- Metabolic alkalosis
Answer: A
Q17. What is the most common site of a berry aneurysm in the Circle of Willis?
- Basilar artery
- Vertebral artery
- Anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- Middle cerebral artery (MCA)
Answer: C
Q18. A patient with hypothyroidism recently completed a 13–14-hour flight. Which of the following factors contribute to the risk of developing pulmonary deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
- Prolonged immobilisation due to long flights
- Smoking
- Hypothyroidism
- Oral contraceptive pills (OCP)
Choose the correct combination:
- C, D
- A, B
- A, B, D
- A, B, C, D
Answer: C
Q19. Which of the following clinical conditions are correctly matched with their respective anion gap status?
- Starvation – Increased anion gap
- Diabetic ketoacidosis – Increased anion gap
- Severe vomiting – Increased anion gap
- Only A is correct
- A and C are correct
- A and B are correct
- Only B is correct
Answer – C
Q20. A woman with dry mouth, gritty eye sensations, and bilateral salivary gland enlargement presents for evaluation. Laboratory tests show hypokalemia and metabolic acidosis. What is the most appropriate diagnostic test to confirm the diagnosis?
- Schirmer’s test and autoantibody profile
- Serum acetylcholine receptor antibody
- Salivary gland scintigraphy
- Serum calcium and ACE levels
Answer – A
Q21. A child develops signs of central obesity, moon face, and striae. What is the most likely underlying cause?
- Progression of the disease
- Use of exogenous steroids
- Adrenal hyperplasia
- Pituitary adenoma
Answer: B
Obstetrics and Gynaecology INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Which of the following instruments are commonly used during a cesarean section?
- Green amytage forceps
- Shirodkars clamp
- Doyens retractor
- Scalpel with BP holder
- Allis forceps
- Cusco and Karman
- a, c, d, e
- b, c, d, f
- a, b, e, f
- a, c, e, f
Answer: A
Q2. A 36-week pregnant woman is being evaluated for possible eclampsia. Which of the following symptoms are not indicative of imminent eclampsia?
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Pedal edema
- Epigastric pain
Answer: C
Q3. A pregnant woman with placenta previa presents with mild bleeding. There are no uterine contractions, her blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and the fetal heart rate is 140 bpm. What is the best next step in management?
- Hospitalisation and expectant management
- Oxytocin induction of labour
- Immediate lower segment cesarean section (LSCS)
- ARM
Answer: A
Q4. A primigravida with a normal vaginal delivery develops postpartum haemorrhage not controlled by uterine massage. What should be the next step in management?
- Uterine artery embolisation
- Hysterectomy
- Balloon tamponade
- Pelvis-specific embolization
Answer: C
Q5. Identify the condition based on the image provided
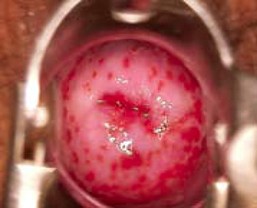
- Trichomoniasis
- Candidiasis
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Chlamydial cervicitis
Answer: A
Q6. A patient presents with intermenstrual bleeding, and the pap smear report shows atypical glandular cells. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
- Conization of the cervix
- Repeat Pap smear after 6 months
- Colposcopy with endometrial sampling
- Hysterectomy
Answer – C
Q7. A 45-year-old postmenopausal woman has an endometrial thickness of 15 mm on transvaginal ultrasound. What should be the next step in management?
- Endometrial biopsy
- MRI Pelvis
- Hysterectomy
- Repeat transvaginal ultrasound after 6 weeks
Answer – A
Q8. Postpartum intrauterine contraceptive device (IUCD) insertion should ideally be performed within which of the following time frames?
- Within 24–48 hours
- Within 10 minutes of placental delivery
- At 4 weeks postpartum
- After 6 weeks postpartum
Answer – B
Q9. Which of the following statements about shock is accurate?
- Uterine inversion in the postpartum period causes neurogenic shock initially
- Gram-positive bacteria cause endotoxic shock
- Severe shock occurs with more than 20% blood loss
- Hypoperfusion with increased cardiac output
Answer – A
Q10. Which of the following is NOT a test of ovarian reserve during the early follicular phase?
- FSH
- E2
- AMH
- AFC
Answer: B
Paediatrics INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. The term neonate presents with respiratory distress, chest X-ray showed hyperinflation with prominent fissure/bulging of the middle fissure. If the baby got well after 2 hours, what is the likely diagnosis?
- Transient Tachypnea of Newborn
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Congenital Pneumonia
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Answer: A
Q2. A 7-year-old child with stunting is brought for evaluation of short stature. His height is below -2 SD for age. Developmental milestones are normal. On examination, the upper-to-lower segment ratio is 1.4. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Achondroplasia
- Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia
- Nutritional cause
- GH deficiency
Answer: A
Q3. Which of the following features are characteristic of Hirschsprung’s disease?
- Failure of migration of ganglia
- Causes intestinal obstruction postnatally
- Distal segment dilated
- Proximal segment constricted
- 1, 2, 3 are correct
- 1, 2 are correct
- 3, 4, 5 are correct
- 3 & 4 are correct
Answer – B
Q4. A boy is brought for evaluation; he has stunting with excessive weight gain. His height is below -2 SD for age, and his weight is above +2 SD. Developmental milestones are normal. He has a history of recurrent respiratory infections for which he frequently receives oral medications. What is the next best step to take?
- Promote physical activity as the Child is overweight
- Screen children for Growth hormone deficiency
- Check TFT, as the child has congenital hypothyroidism
- Test for Cushing Syndrome secondary to steroid use
Answer: D
Q5. An infant with 3 months of progressive jaundice, pale stools, high colored urine. The child was healthy, gaining weight and feeding well. HIDA scan showed no excretion. What is the next step?
- Breast milk jaundice, stop for 2 weeks and give formula feed
- Galactosemia, do tests to confirm
- Metabolic condition requiring further testing
- Liver biopsy
Answer: D
Q6. A child with fever and abdominal pain tested positive for Dengue on day 5 of fever. His BP was 110/70 mm Hg, platelet counts were 20,000/mm3, but there were no bleeding manifestations. What is the next step?
- Platelet transfusion
- 10 ml/kg/hr RL
- 7 ml/kg/hr RL
- 20 ml/kg RL
Answer: C
Q7. A 10-year-old child presents with generalised oedema. Urinalysis shows +3 proteinuria, and 24-hour urine protein is more than 3.5 g/day. There is no hypertension or hematuria. Serum albumin is low. Kidney biopsy shows segmental fibrosis and hyalinosis. The child shows a poor response to steroids. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Minimal Change Disease
- Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
- Membranous Glomerulopathy
- IgA Nephropathy
Answer: B
Q8. A 10-year-old child presented with hyperglycemia. He was diagnosed with Severe DKA, HCO3 of 4, pH of 7.0, RBS of 450, And + 4.5. Management?
- 10 ml/kg NS over 30 min (10% deficit correction) followed by insulin infusion, with KCl 20 mmol/l & bicarbonate
- 20 ml/kg NS (10% deficit correction) over 30 min followed by insulin infusion & fluid with KCl 40 mmol/l added
- 10 ml/kg RL bolus (7% deficit correction) followed by insulin infusion and KCl
- 20 ml/kg RL over 30 min (7% deficit correction) followed by insulin infusion, bicarbonate and KCl
Answer: B
Q9. Identify the correct match of milestone & corresponding normal age of attainment?
- Mature Pincer grasp – 9 months
- Making a tower of 2 blocks – 2 years
- Bidextrous approach – 6 months
- Transfers objects from one hand to another – 6 months
Answer: D
Q10.A child presents with recurrent pneumonia and respiratory distress but no cyanosis. A continuous murmur is heard below the left clavicle. What is the most probable diagnosis?
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
- Atrial septal defect (ASD)
- CoA
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Answer – D
Q11. Which is not used in status epilepticus?
- Valproate
- Ethosuximide
- Fosphenytoin
- Levetiracetam
Answer – B
Orthopedics INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. A 7-year-old boy presents to the emergency department after falling on an outstretched hand. X-ray shows an extension-type supracondylar fracture of the humerus. On examination, he is unable to make an ‘OK’ sign with his thumb and index finger. Which structure is most likely injured?
- Median nerve
- Ulnar nerve
- Radial nerve
- Brachial artery
Answer – A
Q2. A 60-year-old man presents with generalised bone pain and easy fatigability. X-rays show diffuse osteoporosis, and hypercalcemia is noted. Which of the following investigations is most appropriate to confirm the diagnosis?
- CT scan
- Bone marrow biopsy
- MRI
- Sestamibi scan
Answer: D
Q3. A 13-year-old boy presents with waxing and waning pain and swelling over the mid-shaft of the humerus for 3 weeks—no trauma history. X-ray shows a periosteal reaction with a suggestion of medullary involvement. What is the next best diagnostic investigation?
- MRI
- Biopsy
- Blood investigation
- CT
Answer: A
Q4. A 30-year-old man presents after a fall. He complains of severe shoulder pain and the inability to move his arm. On examination, the arm is slightly abducted and externally rotated. The X-ray is given. What is the most likely diagnosis?
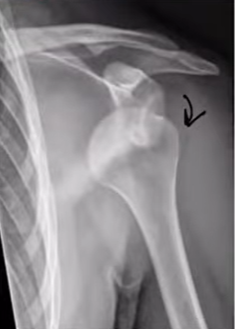
- Anterior dislocation
- Posterior dislocation
- Fracture clavicle
- Proximal humerus fracture
Answer – A
Q5. Match the following:
| A) Equinus | 1. Longitudinal arch of foot extended dorsally |
| B) Planus | 2. Longitudinal arch of foot flattened |
| C) Cavus | 3. Foot in dorsiflexion |
| D) Calcaneus | 4. Foot in plantar flexion |
- A) 1, B) 2, C) 3, D) 4
- A) 1, B) 4, C) 3, D) 2
- A) 3, B) 1, C) 4, D) 2
- A) 4, B) 2, C) 1, D) 3
Answer: D
Psychiatry INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. A patient on Haloperidol develops Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (rigidity, fever). What is the most appropriate treatment?
- Stop the antipsychotic and give dantrolene/bromocriptine
- Give Acetylcholine
- Atropine
- IV fluids and continue the antipsychotic
Answer: A
Q2. A patient develops sudden vision loss after a traumatic event. Eye examination is normal, and the patient is unconcerned about blindness. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Somatoform Disorder
- Conversion Disorder
- Factitious Disorder
- Malingering
Answer: B
Q3. A 7‑year‑old child has had severe recurrent anger outbursts for 1 year, disproportionate to the situation, with persistent irritability between episodes. Most likely diagnosis?
- Oppositional Defiant Disorder
- Conduct Disorder
- Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder
- Intermittent Explosive Disorder
Answer: C
Q4. Match the types of delusions with their descriptions:
- Persecution
- Grandiosity
- Nihilistic
- DInfluenceDescriptions:
- False belief of being controlled by external forces
- False belief of having great powers or importance
- False belief that the body/world does not exist
- False belief of being harmed or conspired against
A–4, B–2, C–3, D–1
B. A–3, B–1, C–4, D–2
C. A–2, B–4, C–3, D–1
D. A–1, B–2, C–3, D–4
Answer: A
Dermatology INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Match the following:
| a. Auspitz sign | 1. Psoriasis |
| b. Darier’s sign | 2. Discoid lupus erythematosus |
| c. Carpet tack sign | 3. Cutaneous mastocytosis |
| d. Flag sign | 4. Kwashiorkor |
A.a-3, b-2, c-1, d-4
B.a-4, b-3, c-1, d-2
C.a-1, b-3, c-2, d-4
D.a-1, b-2, c-3, d-4
Answer – C
Q2. The most common site of melanoma in Indians is:
- Trunk
- Hands and feet
- Genitals
- Face
Answer – B
Q3. Which of the following is NOT a part of syndromic management in males?
- Urethral discharge
- Genital discharge
- Inguinal swelling
- Lower abdominal pain
Answer – D
Q4. A farmer presents with a lesion that discharges black-colored granules. What is the causative agent?
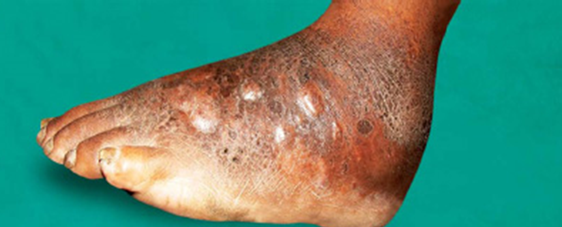
- Madurella mycetomatis
- Actinomadura Madurae
- Nocardia brazilensis
- Streptomyces somaliensis
Answer – A
Q5. A lesion is observed at the same site on three separate occasions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
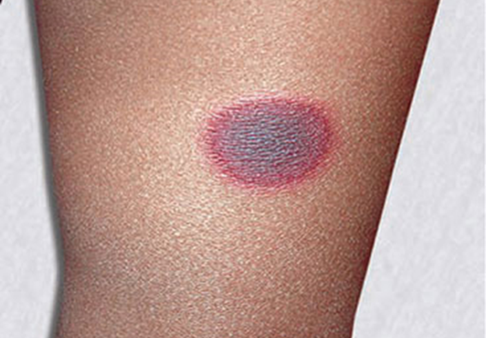
- Cutaneous mastocytosis
- Fixed drug eruption
- HSV1
- Erythema multiforme
Answer – B
Q6. A 70-year-old female presents with intense itching and a white plaque in the genital region. Histopathological examination shows loss of rete ridges, abundant collagen, and thinned epithelium. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Lichen planus
- Lichen sclerosis
- Candidiasis
- Vulvar leukoplakia
Answer – B
Anaesthesia INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. Identify the nerve block demonstrated in the given intraoral image?
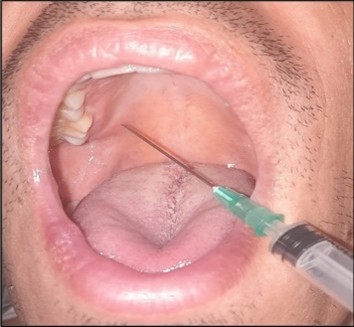
- Inferior alveolar nerve block
- Anterior ethmoidal nerve block
- Maxillary nerve block
- Greater palatine nerve block
Answer – D
Q2. For benzodiazepines and barbiturates, which of the following statements are true?
- Both act on GABA
- Cause additive sedation with alcohol
- Thiopentone has a short duration of action due to metabolism
- Flumazenil is an antidote for barbiturates
- Both A & B are correct
- Only A is correct
- Only C is correct
- All are correct
Answer – A
Radiology INI-CET 2025 Recall Questions with Answers
Q1. A trauma patient presents with two episodes of vomiting and loss of consciousness. CT brain shows a biconvex hyperdense lesion. What is the next step in management?
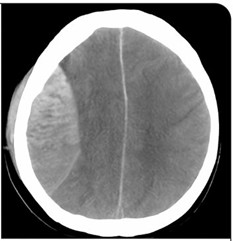
- Craniectomy
- ICU observation
- Conservative management
- Burr hole and evacuation
Answer – D
Q2. A patient with retroviral infection presents with low-grade fever, cough, and one episode of hemoptysis. What is the most probable diagnosis based on the chest X-ray findings?
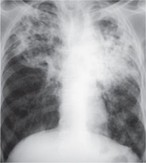
- Tuberculosis
- Pneumothorax
- Lung abscess
- Pulmonary metastasis
Answer – A
Q3. A 60-year-old male with tingling and numbness in the arm develops visual disturbances in one eye. Chest X-ray shows a suspicious lesion. What is the definitive diagnostic investigation?
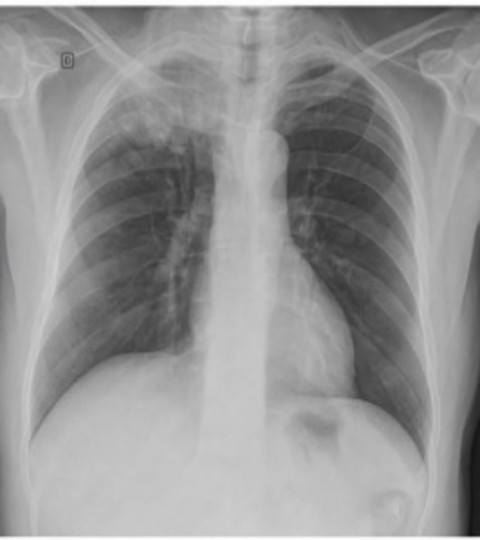
- Ultrasound
- Cardiovascular evaluation
- CT-guided biopsy
- Sputum microscopy
Answer – C
Q4. A 13-year-old presents with upper arm swelling and pain. X-ray reveals a diaphyseal lesion in the humerus with mild ESR elevation. What should be the next investigation?
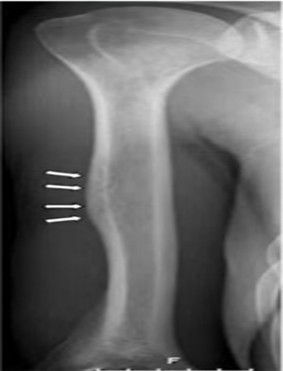
- PET scan
- MRI
- Humeral lesion biopsy
- Bone marrow biopsy
Answer: B
Q5. Identify the labelled structure in the given image?
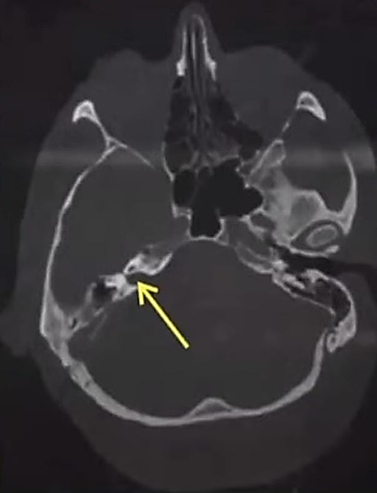
- Internal auditory canal
- Aqueduct
- External auditory canal
- Carotid canal
Answer: A
Q6. A 36-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden shortness of breath. The CT thorax shows evidence of air in the pleural cavity with partial lung collapse. What is the immediate next step in management?
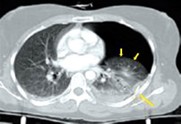
- Needle decompression
- Intercostal chest tube insertion
- Sputum microscopy and culture
- Thoracic ultrasound
Answer – A
PDF Download link – INI-CET Recall Question with Answers
Related post