NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions with Answers | Free PDF Download (All 200 Qs)
Anatomy NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
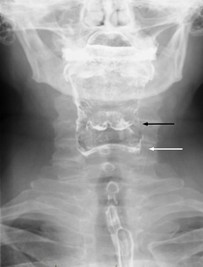
Q1. The image below highlights the jugular foramen. Which of the following structures do not pass through the marked structure “A”?
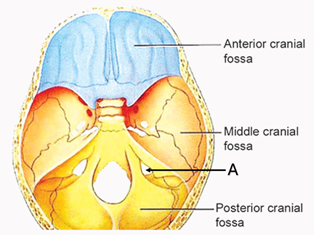
- Glossopharyngeal nerve
- Accessory nerve
- Vagus nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
Answer: D
Q2. The defect shown in the image relates to which of the following:
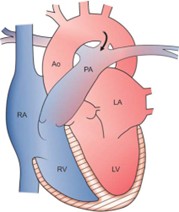
- Left 4th aortic arch
- Right 4th aortic arch
- Left 6th aortic arch
- Right 6th aortic arch
Answer: B
Q3. Which of the following is not carried by the structure marked “A” in the image?
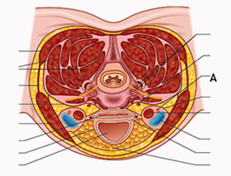
- GSA
- GVA
- GSE
- GVE
Answer: A
Q4. What are the contents of the Umbilical cord?
- 2 arteries, 2 veins
- 1 artery, 2 veins
- 2 arteries, 1 vein
- 1 artery, 1 vein
Answer: C
Q5. What is the root value responsible for Meralgia paresthetica?
- T12 and L1
- L2 and L3
- L2, L3 and L4
- L1 and L2
Answer: B
Q6. A girl presented with a foot injury and gave a history of forceful eversion of the foot. Which of the following structures is affected the most?
- Anterior talofibular ligament
- Deltoid ligament
- Posterior talofibular ligament
- Calcaneofibular ligament
Answer: B
Q7. A patient presents with muscle wasting, reduced tone, and weakness in the left hand. Fine motor movements, such as dough kneading, are impaired. Which of the following structures is most likely affected?
- Right anterior horn cells in the spinal cord
- Pyramidical lesion
- Internal Capsule
- Left Corticospinal tract in the cervical cord
Answer: A
Q8. Identify the structure where the shown epithelium is located:
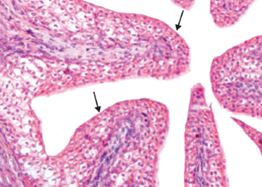
- Esophagus
- Ureter
- Fallopian tube
- Trachea
Answer: B
Q9. What is the nerve supply of the marked structure “A”?
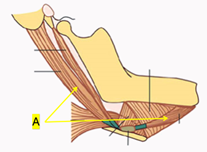
- Nerve to the mylohyoid and the facial nerve
- Facial nerve and mandibular nerve
- Mandibular nerve and spinal accessory nerve
- Facial nerve and spinal accessory nerve
Answer: B
Q10. During resection of the submandibular gland, there is accidental injury to a structure running superior to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. Which of the following structures is likely to be injured?
- Lingual nerve
- Marginal Mandibular Nerve
- Trigeminal nerve
- Hypoglossal nerve
Answer: B
Q11. A 20-year-old boy experienced severe pain due to hyperextension of the shoulder while training in the gym. The trainer expected a probable disruption of the structure marked “A” in the image below. Which site is affected?
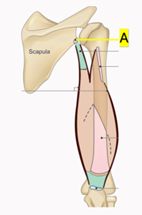
- Shaft of the humerus
- Deltoid tubercle of the humerus
- Infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
- Supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
Answer: C
Anesthesia NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q12. Patients administered sevoflurane and succinylcholine for abdominal surgery and developed post-operative muscle rigidity. What is the drug of choice here?
- Dantrolene
- Diazepam
- Propranolol
- Paracetamol
Answer: A
Q13. A patient was administered a muscle relaxant and subsequently developed erythema, facial flushing, and hypotension. Which drug is most likely responsible for these symptoms?
- Cisatracurium
- Atracurium
- Rocuronium
- Vecuronium
Answer: B
Biochemistry NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q14. In Hurler syndrome, which glycosaminoglycans accumulate and cause organ enlargement?
- Keratan sulfate and dermatan sulfate
- Keratan sulfate and heparan sulfate
- Heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate
- Keratan sulfate and hyaluronic acid
Answer: C
Q15. A child presents with gum bleeding, perifollicular haemorrhages, petechiae, and recurrent fractures. Which enzyme deficiency is most likely?
- Lysyl oxidase
- Prolyl hydroxylase
- Tyrosinase
- Alkaline phosphatase
Answer: B
Q16. A man survives 5 days without food. What is the brain’s primary energy source during this prolonged fasting period?
- Gluconeogenesis
- Glycogenolysis
- Ketosis
- Lipolysis
Answer: C
Q17. A patient has high phenylalanine levels despite normal phenylalanine hydroxylase. Which cofactor deficiency is most likely responsible?
- Tetrahydrofolate
- Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4)
- Thiamine
- Pyridoxine
Answer: B
Q18. A patient with vitamin B12 deficiency presents with anaemia, a positive Romberg sign, and elevated homocysteine levels. Which amino acid is most likely deficient?
- Cysteine
- Methionine
- Tyrosine
- Glutamate
Answer: B
Q19. A patient on long-term hydrochlorothiazide develops neuropathy, heart failure, and symmetrical paresthesia. Which nutrient deficiency is most likely responsible?
- Selenium
- Thiamine
- Vitamin B12
- Zinc
Answer: B
Q20. A frameshift mutation from nucleotide insertion at position 4 of a 900-base mRNA is observed. What is the likely outcome?
- No change in the final protein
- Partial protein production
- Complete change in protein production
- No change due to RNA editing
Answer: C
Q21. A patient develops skin cancer and worsening hyperpigmentation following sun exposure. Which DNA repair pathway is most likely impaired?
- Nucleotide excision repair
- Base excision repair
- Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ)
- Mismatch repair
Answer: A
Q22. A patient with orange-colored tonsils has a triglyceride level of 140 mg/dL and very low HDL cholesterol (5 mg/dL). What is the most probable diagnosis?
- Familial hypercholesterolemia
- Tangier disease
- Type I hyperlipoproteinemia
- Abetalipoproteinemia
Answer: B
Q23. A 10-year-old patient has high total cholesterol, tendon xanthomas, and a family history of similar findings. Triglyceride levels are normal. What type of familial dyslipidemia is most likely?
- Type I
- Type IIa
- Type IIb
- Type II
Answer: B
Q24. To diagnose a syndromic illness like meningitis, which PCR technique is most appropriate?
- Multiplex PCR
- Uniplex PCR
- Attributed PCR
- Nested PCR
Answer: A
Q25. A 45-year-old man is evaluated for electrolyte imbalance: Na⁺ = 130 mmol/L, Cl⁻ = 84 mmol/L, HCO₃⁻ = 16 mmol/L. What is his anion-gap?
- 26
- 30
- 18
- 22
Answer: B
Community Medicine NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q26. For the prevention of coronary artery disease, what is the recommended dietary cholesterol intake limit per day?
- 100 mg / 1000 kcal
- 200 mg / 1000 kcal
- 400 mg / 1000 kcal
- 500 mg / 1000 kcal
Answer: B
Q27. Toxic fumes are released after an industrial explosion. What advice should be given to the residents?
- Use the telephone and call friends
- Seal the cracks and close the windows
- Open the window for ventilation
- Use the mask
Answer: B
Q28. A new community intervention is initiated to reduce prenatal sepsis. Researchers allocated 20 PHCs to receive standard care and 20 PHCs to receive a community-based intervention. What type of study design is this?
- Cross-sectional study
- Case-control study
- Quasi-experimental study
- Cluster-randomised control trial
Answer: D
Q29. A 20-year-old resident of Andhra Pradesh presents with outward bending of the lower limbs and signs of osteoporosis. His diet mainly consists of rice and jowar roti. Which of the following interventions will not be helpful?
- Provision of running surface water for drinking
- Change the water source
- Fluoride supplementation
- Add lime and alum to drinking water
Answer: C
Q30. A student was asked to bring the correct boxes from the lab for the Nalgonda technique:
- Alum and Gypsum
- Alum and Charcoal
- Alum and Lime
- Charcoal and Lime
Answer: C
Q31. A study is conducted to compare the mean haemoglobin (Hb) levels between two groups. Which test is most appropriate?
- Paired t-test
- Unpaired t-test
- Chi-square test
- ANOVA
Answer: B
Q32. An urban city has a population of 70,00,000, with 30% residing in slum areas. How many UPHCs are required for the slum population?
- 22
- 32
- 42
- 52
Answer: C
Q33. Identify the mosquito without a siphon tube that rests parallel to the surface of water?
- Anopheles
- Culex
- Aedes
- Mansonia
Answer: A
Q34. A 60-year-old diabetic patient with COVID-19 succumbed to death in the hospital. Which type of surveillance does this death report fall under?
- Active surveillance
- Passive surveillance
- Sentinel surveillance
- Syndromic surveillance
Answer: B
Q35. A dietary survey report indicates that the 5-year survival rate for breast cancer has increased following the introduction of a new screening method. However, autopsy data show no change in overall mortality. What type of bias does this scenario illustrate?
- Survival bias
- Lead time bias
- Berksonian bias
- Detection bias
Answer: B
Q36. In the “de facto” method of census data collection, data is collected based on which of the following?
- Place of birth
- Location at the time of enumeration
- Place of employment
- Usual place of residence
Answer: B
Q37. Which of the following is the correct sequence in a Randomised Controlled Trial (RCT)?
- Follow-up → Manipulation → Assessment → Randomization
- Randomization → Manipulation → Follow-up → Assessment
- Assessment → Randomization → Follow-up → Manipulation
- Manipulation → Assessment → Follow-up → Randomization
Answer: B
Q38. Under the Weekly Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation scheme, what is the composition of IFA tablets given to children aged 10–19 years old?
- 60 mg elemental iron + 100 µg folic acid
- 100 mg elemental iron + 500 µg folic acid
- 100 mg elemental iron + 100 µg folic acid
- 60 mg elemental iron + 500 µg folic acid
Answer: D
Q39. What is the time interval between acquiring an infection and reaching the period of maximum infectivity is known as?
- Generation time
- Communicable period
- Incubation period
- Serial interval
Answer: A
Q40. Which of the following is used to measure the degree of objective and target achievement and assess the quality of results obtained in a health program?
- Planning
- Surveillance
- Monitoring
- Evaluation
Answer: D
Q41. A young boy presents with clinical signs of rickets. Which government program specifically addresses this type of nutritional deficiency?
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS)
- National Nutritional Deficiency Control Programme
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme
Answer: A
Q42. A recently diagnosed HIV-positive patient with a CD4 count of 250 cells/mm³ also tests positive for active tuberculosis. He has not yet been started on ART. What is the correct approach to initiating treatment?
- Start ATT first, then initiate ART after 2 weeks
- Start ART first, then begin ATT after 2 weeks
- Start both ART and ATT simultaneously
- Start ATT first, then initiate ART after 8 weeks
Answer: A
Q43. Which of the following vaccines can be used in the clinics?
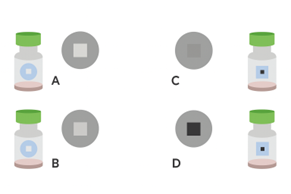
- Use A only
- Use A and B
- Use A, B and C
- Use D only
Answer: B
Dermatology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q44. A young adult presents with facial pain and painful vesicular lesions in the mouth. Tzanck smear reveals multinucleated giant cells with intranuclear inclusions. What is the most likely causative organism?
- Adenovirus
- Cytomegalovirus
- EBV
- HSV
Answer: D
Q45. What is the most common cause of Squamous cell carcinoma at the base of the tongue?
- EBV
- HPV
- HCV
- CMV
Answer: B
Q46. A patient presents with irregular swelling over the foot, multiple discharging sinuses, and black granules. A KOH mount is performed on the discharge. What is the most likely observation?
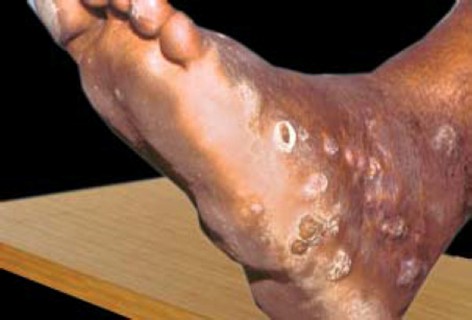
- Arthrospores
- Slender dematiaceous fungi
- Yeast
- Septate hyphae
Answer: D
Q47. A 45-year-old patient presents with a chronic granulomatous skin lesion. What is the most confirmatory diagnostic test for this condition?
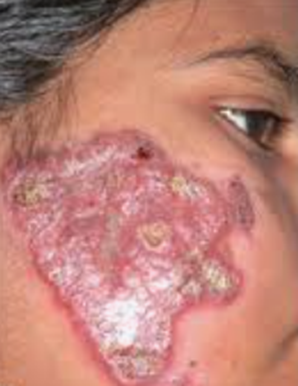
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- Slit skin smear
- Mantoux test
- Skin biopsy with histopathology
Answer: A
Q48. A 20-year-old patient presents with a non-progressive hypopigmented lesion on the trunk. On Wood’s lamp examination, there is white accentuation. Diascopy is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?

- Vitiligo
- Nevus depigmentosus
- Nevus anemicus
- Indeterminate leprosy
Answer: B
Q49. Q. A patient with an intense itchy vesicular lesion on the extensor surface presents with a history of gluten sensitivity. Likely diagnosis?
- Bullous pemphigoid
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Psoriasis
Answer: C
ENT NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q50. A patient presents with the injury shown in a lateral X-ray of the nose. What procedure can be done to manage this patient?

- Tilley’s probe
- Luc’s forceps
- Denis Browne probe
- Walsham’s forceps
Answer: D
Q51. A 78-year-old male, known case of diabetes mellitus and hypertension, presents with nasal bleeding. The initial management, such as packing, was not successful in controlling the bleed. Which of the following arteries should be ligated to control the bleeding?
- Sphenopalatine artery
- Anterior Ethmoidal artery
- Posterior Ethmoidal artery
- Greater Palatine artery
Answer: A
Q52. A 16-year-old male presents with recurrent profuse nasal bleeding in the right nasal cavity. Endoscopy shows a globular mass in the right nasal cavity. CT shows bowing of the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus. What is the most probable diagnosis?
- Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma (JNA)
- Antrochoanal polyp
- Rhinosporidiosis
- Rhinoscleroma
Answer: A
Q53. What is the marked structure?
- Thyroid cartilage
- Pyriform sinus
- Epiglottis
- Vallecula
Answer: B
Q54. A 27-year-old male presents with complaints of recurrent ear infection. Otoscopic examination shows central perforation of the tympanic membrane. The result of a tuning fork examination of the patient revealed the following: Rinne: -ve on the left and +ve on the Right; Weber: lateralisation on the left. What is the type and localisation of Hearing loss?
- Left Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Right Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Left Conductive Hearing Loss
- Right Conductive Hearing Loss
Answer: C
Q55. A 75-year-old male, a smoker, presents with complaints of hoarseness of voice, difficulty in swallowing. He has been diagnosed with large, advanced SCC and is undergoing surgery. What is the most appropriate surgical procedure done?
- Total laryngectomy
- Partial laryngectomy
- Percutaneous tracheostomy
- Standard tracheostomy
Answer: A
Q56. A 20-year-old patient presents with recurrent ear discharge. On otoscopic examination, the examiner notes the complete absence of the Tympanic membrane. What is the best option for treatment?
- Myringoplasty
- Radical mastoidectomy
- Ossciculoplasty
- Tympanoplasty
Answer: D
Q57. A 27-year-old male presents with complaints of reduced hearing in the left ear for 2 months. He denies tinnitus or vertigo. Pure tone audiometry is done, and the audiogram is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?

- Left ear SNHL
- Left ear CHL
- Right ear mixed hearing loss
- Normal hearing
Forensic Medicine NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q58. During an autopsy of a 35-year-old female, the doctor noted bruises below the right angle of the jaw covered with scratches over the upper border and three groups of bruises on the left side of the neck below the thyroid cartilage, and additional bruises over the shoulder blade, backside of the trunk and hip crests. What is the most likely cause of death?
- Throttling
- Garroting
- Mugging
- Ligature Strangulation
Answer: A
Q59. A 16-year-old girl and a 23-year-old man are medically examined after the girl’s parents accuse the man of rape. The girl reports that the sexual activity was consensual, and no physical injuries are noted. According to the law, which of the following is the correct statement?
- Consent is invalid as the girl is under 18 years old
- No punishment since the act was consensual
- Parents must prove that the act was non-consensual
- No punishment since there are no injuries
Answer: A
Q60. What is ZASKO’s phenomenon?
- Tendon reflex occurring after death.
- Blood clotting after death
- Gaping of the wound along skin tension lines
- Seeping of blood through bones after death
Answer: A
Q61. Under the POCSO Act 2012, which group is protected by the law?
- All children under 16 years of age
- All children under 18 years of age
- Girls under 16 years of age
- Girls under 18 years of age
Answer: B
Q62. A male patient with a recent history of RTA was brought to the hospital. His CT scan was normal, but he died within three hours of admission. His autopsy revealed a retraction ball appearance and petechial haemorrhages in the corpus callosum. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Diffuse vascular injury
- Diffuse axonal injury
- Intracerebral haemorrhage
- None of the above
Answer: B
Q63. A 68-year-old female presented with breathlessness and poor health status. She also has multiple metastases. On examination, she is awake and anxious. The doctors believed that aggressive chemotherapy, radiotherapy and ICU admission would not be helpful. However, her daughter insists on ‘trying everything’. How should the attending doctor handle such a scenario?
- Convene with family members and consider the patient’s needs
- Shift to the ICU and start aggressive treatment
- Discharge the patient and shift to palliative care
- Give placebo care to relieve anxiety
Answer: A
Medicine NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q64. Q. A 65-year-old patient with a history of atrial flutter is being considered for long-term prophylaxis to prevent recurrence. The cardiologist decides to start a calcium channel blocker for rate control and prevention of rapid ventricular response. Which calcium channel blocker is most appropriate for atrial flutter prophylaxis?
- Amlodipine
- Nifedipine
- Diltiazem
- Felodipine
Answer: C
Q65. Q. A diabetic patient on insulin glargine and metformin has persistent hyperglycemia (HbA1c 8.3%) and signs of heart failure. Which is the most appropriate medication to add next?
- Sitagliptin
- Pioglitazone
- Empagliflozin
- Gliclazide
Answer: C
Q66. Q. A patient with atrial fibrillation (AF) and mitral stenosis presents within 4 hours of symptom onset and is hemodynamically stable. What is the next best step?
- Ventricular rate control
- Cardioversion
- Anticoagulation
- Wait and watch
Answer: B
Q67. A 2-year-old child presents to the emergency department with a generalised tonic-clonic seizure lasting 3 minutes associated with high fever (39.5°C). The child has no previous history of seizures or neurological problems. The seizure has now stopped, but the parents are concerned about recurrence. What is the most appropriate immediate management for this febrile seizure?
- Ethosuximide
- Sodium valproate
- Diazepam
- No antiepileptic medication needed
Answer: C
Q68. Q. 45-year-old female presents with a 6-month history of paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, palpitations, and breathlessness. On evaluation, her blood pressure and SpO₂ are within normal limits. Jugular venous pressure is elevated, and she has an irregular pulse. Examination reveals tender hepatomegaly, a heaving apex beat, and a mid-diastolic murmur heard at the apex. She also has a history of acute rheumatic fever. Which of the following statements is false?
- This patient has an increased risk of stroke
- The ‘a wave is absent in the JVP
- This patient shows features of right heart failure
- Presystolic accentuation is a hallmark feature
Answer: D
Q69. A 15-year-old adolescent with known type 1 diabetes mellitus presents with fatigue, vomiting, and diarrhoea. Laboratory findings reveal a random blood glucose level of 700 mg/dL, serum sodium of 125 mEq/L, and potassium of 4.2 mEq/L. Which of the following is NOT recommended during the initial management of this patient?
- Administration of 3% saline
- Initiation of 0.9% normal saline infusion
- Intravenous insulin therapy
- Frequent monitoring of serum potassium levels
Answer: A
Q70. A patient with an irregular pulse and palpitations. He arrives 2.5 hours after symptom onset. No H/O diabetes, and BP is 160/100 mmHg. What is the next best step?
- Control the ventricular rate with verapamil.l
- Emergent cardioversion
- Transesophageal echo (TEE)
- Wait and watch
Answer: A
Q71. A 36-year-old woman with symmetrical small joint arthritis tests positive for anti-CCP. Which histological feature is most characteristic?
- Synovial granulomas
- Pannus formation and reactive lymphocytic infiltrate
- Uric acid crystal deposits
- Non-caseating granulomas
Answer: B
Q72. Q. A 65-year-old man presents with enlarged hat size, shin pain, elevated alkaline phosphatase, and normal calcium and PTH levels. X-ray reveals mixed lytic and sclerotic bone lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Paget’s disease
- Primary hyperparathyroidism
- Osteomalacia
- Bone metastasis
Answer: A
Q73. Q. A 64-year-old man with chronic kidney disease presents with pallor, exertional breathlessness, and signs of heart failure. Investigations reveal normocytic anaemia. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
- Oral iron
- Darbepoetin alfa
- Intravenous iron
- Blood transfusion
Answer: A
Q74. Q. A 42-year-old woman presents with enlarged hands, coarsened facial features, and an increased shoe size. Her IGF-1 level is elevated. Which of the following is the most specific test to confirm the diagnosis?
- Measurement of IGF-1 alone
- Lack of GH suppression following oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
- Lack of IGF-1 suppression after OGTT
- Random growth hormone level
Answer: B
Q75. Q. A 54-year-old man with a history of chronic hyponatremia develops sudden-onset quadriparesis after rapid sodium correction. Which investigation is most appropriate to confirm the diagnosis?
- Brainstem evoked potential
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- MRI of the brain
- Nerve conduction studies
Answer: C
Q76. Q. Which hormone is elevated in Addison’s disease, leading to hyperpigmentation?
- Cortisol
- ACTH
- Aldosterone
- Renin
Answer: B
Q77. Q. A 50-year-old man presents with altered sensorium and deep laboured breathing. ABG is given below. What is the most likely acid-base abnormality? pH: 7.20 pCO₂: 35 mmHg_x000B_HCO₃⁻: 16 mEq/L Na⁺: 130 mEq/L_x000B_Cl⁻: 84 mEq/L PaO₂: 80 mmHg
- Acute metabolic acidosis with AG 30
- Chronic metabolic acidosis with AG 30
- Acute respiratory acidosis
- Chronic respiratory acidosis
Answer: A
Q78. Q. A patient collapses with breathlessness and pink frothy sputum. Autopsy shows hemosiderin-laden macrophages. In which condition is this not seen?
- Protein-losing enteropathy
- Right heart failure
- Volume overload
- Pulmonary vein obstruction
Answer: A
Q79. Q. A 14-year-old boy presents with fatigue, mild jaundice, and splenomegaly. His haemoglobin is 10.5 g/dL, MCV is 82 fL, and MCHC is high 37 g/dL. His father had a similar history of chronic anaemia and underwent splenectomy. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia
- Hereditary spherocytosis
- Thalassemia minor
- G6PD deficiency
Answer: B
Q80. A patient arrives with hypotension, fever, joint pain, petechiae on limbs, and respiratory distress. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- Disseminated gonococcal infection
- Septic shock
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Septic arthritis
Answer: B
Q81. A critically ill patient with COVID-19 is admitted to the ICU and is currently on mechanical ventilation. The PaO2/FiO2 ratio is 100, indicating severe ARDS. Which of the following is the most appropriate ventilatory strategy to manage this patient?
- High PEEP and low tidal volume
- High PEEP and high tidal volume
- Low PEEP and low tidal volume
- Low PEEP and high tidal volume
Answer: A
Q82. Q. A 58-year-old patient has prolonged PT. Factor IX deficiency (vitamin K-dependent). Parenteral vitamin K planned. In which condition will this help?
- Hepatitis A
- Pernicious anaemia
- Haemophilia B
- Bile duct obstruction
Answer: D
Q83. Case of sudden onset of Aphasia and right arm weakness for the last 5 hours. Which is indicated investigation
- MRI barin
- Carotid Doppler
- TEE
- Transthoracic echocardiography
Answer: C
Q84. A patient already on salbutamol and ipratropium continues to have nocturnal exacerbations of asthma. What is the next step?
- Oral corticosteroids
- Montelukast
- LABA plus inhalation steroids
- Increase the dose of salbutamol
Answer: C
Q85. Q. A 32-year-old male with a history of recurrent paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is stable in sinus rhythm. What is the best choice for long-term prophylaxis?
- IV adenosine
- IV Esmolol
- Oral diltiazem
- IV amiodarone
Answer: C
Microbiology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q86. A farmer presents with a necrotic ulcerative skin lesion. Microscopy using polychrome methylene blue stain reveals capsulated bacilli showing a positive McFadyean reaction. What is the most likely causative organism?
- Clostridium perfringens
- Bacillus anthracis
- Yersinia pestis
- Francisella tularensis
Answer: B
Q87. Which structural component of Group A Streptococcus enables its attachment to pharyngeal epithelium by binding to fibronectin?
- Lipoprotein
- Lipoteichoic acid
- Capsule
- Flagella
Answer: B
Q88. Several residents in a village develop watery diarrhoea followed by bloody diarrhoea after consuming unpasteurized milk. Stool microscopy reveals Gram-negative curved bacilli with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Identify the most likely pathogen.
- Clostridium perfringens
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Campylobacter jejuni
Answer: D
Q89. A man presents with hemoptysis, fever, and breathlessness. Microscopic analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage reveals septate hyphae with acute angle branching. Which fungal infection is most likely?
- Mucormycosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Aspergillosis
- Candidiasis
Answer: C
Q90. A 5-year-old child presents with intense perianal itching, predominantly during nighttime. Microscopic examination reveals the following egg. Which organism is most likely responsible for the condition?
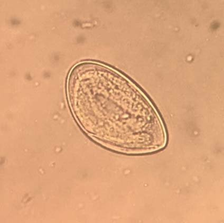
- Enterobius vermicularis
- Ancylostoma duodenale
- Hymenolepis nana
- Trichuris trichiura
Answer: A
Q91. A patient presents with chronic cough, weight loss, and intermittent low-grade fever. Fungal culture from respiratory samples shows a yeast with narrow-based budding. Which of the following is the most probable diagnosis?
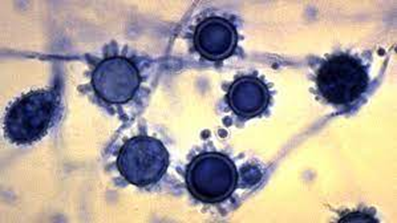
- Blastomycosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Cryptococcosis
- Coccidioidomycosis
Answer: B
Q92. A case of barin abcess reveals Gram-positive, branching, filamentous organisms on microscopy. The organism is weakly acid-fast and grows on paraffin bait media. Which is the most likely etiologic agent?
- Actinomyces israelii
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Nocardia asteroides
- Cryptococcus neoformans
Answer: C
Q93. A case of recurrent Neisseria gonorrhoeae infection is being evaluated. Which immunological investigation would best detect a complement pathway defect?
- C1 esterase inhibitor assay
- Quantitative immunoglobulin levels
- Nitroblue tetrazolium test
- Terminal complement (C5-C9) assay
Answer: D
Q94. A man from an endemic region has developed progressive leg swelling. Peripheral smear reveals the following parasitic organism. Which pathophysiologic mechanism is most likely responsible?
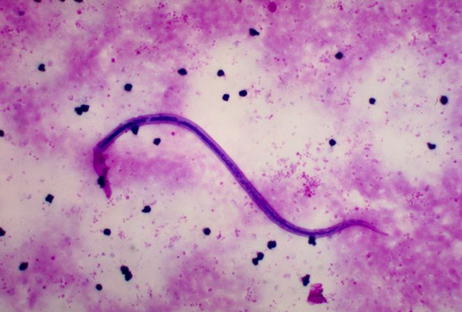
- Hypoalbuminemia
- Lymphatic obstruction
- Hypoproteinemia
- Increased hydrostatic pressure
Answer: B
Q95. A 25-year-old sewage worker presents with a fever lasting a week, followed by sudden weakness. He has scleral congestion, jaundice, and oliguria. Lab findings show raised bilirubin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Brucellosis
- Weil’s disease
- Enteric fever
- DHF
Answer: B
Obstetrics and Gynaecology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q96. 1st trimester pregnancy, previous toxoplasmosis. IgG positive. What is the advice?
- Continue pregnancy, no risk
- Abort – high risk
- Continue, risk exists
- Repeat IgM serology
Answer: C
Q97. A child born with an absent finger. Likely diagnosis?
- Amniotic band syndrome
- Arthrogryposis multiplex
- Polyhydramnios
- Congenital constriction ring
Answer: A
Q98. G2L2 delivered at home by trained dai presents with uterine prolapse. Which structure is weak?
- Round ligament
- Broad ligament
- Cardinal ligament
- Uterosacral ligament
Answer: C
Q99. Gross image of cystadenocarcinoma, CA-125 positive, heaviness in the abdomen. Diagnosis?
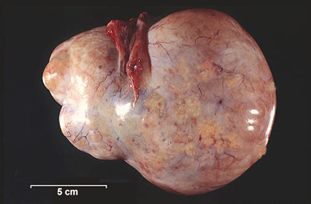
- Serous cystadenocarcinoma
- Mucinous carcinoma
- Dysgerminoma
- Yolk sac tumour
Answer: A
Q100. Q. A 28-year-old pregnant woman at 34 weeks of gestation is diagnosed with severe preeclampsia. The decision is made to start magnesium sulfate using the Pritchard regimen for seizure prophylaxis. What is the correct loading dose of magnesium sulfate in this regimen?
- 4 gm IV
- 6 gm IV + 5 gm IM each buttock
- 14 gm total
- 20 gm total
Answer: C
Q101. Sequence of repair of episiotomy:
- Mucosa → Muscle → Skin
- Skin → Muscle → Mucosa
- Muscle → Mucosa → Skin
- Mucosa → Skin → Muscle
Answer: A
Q102. During vaginal breech delivery, the baby develops winging of the scapula. Identify the manoeuvre used:
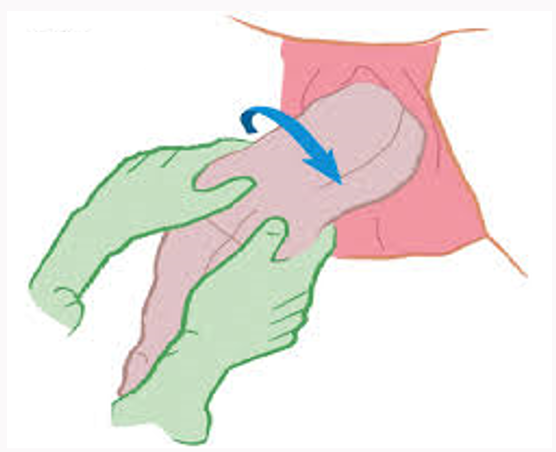
- McRoberts
- Pinard
- Lovset
- Woods corkscrew maneuver
Answer: C
Q103. A resident is performing a normal vaginal delivery. He is seen applying counterpressure above the pubic symphysis while gently pulling the umbilical cord. Which manoeuvre is being demonstrated?

- Controlled cord traction
- Replacement of the prolapsed cord
- Manual removal of placenta
- Delivery of the shoulder using the Lovset manoeuvre
Answer: A
Q104. A postmenopausal woman presents with blood-stained discharge. Her BP is 170/100 mm Hg. What is the next best step?
- Reassure
- PV exam, Pap smear, TVUSG
- Refer to a cardiologist
- Wait and watch
Answer: B
Q105. Q. A 65-year-old postmenopausal woman presents with bleeding per vagina. She undergoes a total hysterectomy. What is the most likely diagnosis?
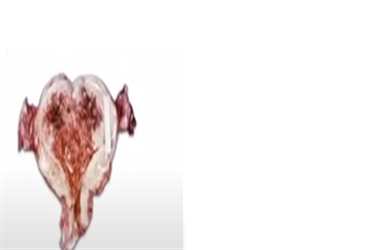
- Fibroid
- Endometriosis
- Adenomyosis
- Endometrial cancer
Answer: D
Q106. Postpartum anticoagulant of choice:
- LMWH
- Warfarin
- Aspirin
- Clopidogrel
Answer: A
Q107. A 36-year-old P2L2 with 9 months of secondary amenorrhea has FSH 36, LH 56, and AMH 0.5. What is the diagnosis?
- PCOS
- Premature ovarian failure
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Hypothalamic amenorrhea
Answer: B
Q108. A 46-year-old woman presents with heavy menstrual bleeding. USG shows endometrial thickness of 16 mm. Next best step?
- Hysterectomy
- Endometrial biopsy
- HPV testing
- Progesterone therapy
Answer: B
Q109. Atonic PPH is not responding to medical management. Next best step?
- Uterine devascularization
- Hysterectomy
- Bakri balloon tamponade
- Compression suture
Answer: C
Q110. Correct order of manoeuvres in shoulder dystocia:
- McRoberts → Rubin → Gaskin → Zavanelli
- Zavanelli → McRoberts → Gaskin → Rubin
- Rubin → Gaskin → McRoberts → Zavanelli
- McRoberts → Suprapubic pressure → Rubin → Zavanelli
Answer: A
Q111. A 30-year-old G2P1 woman presents in labour. Previous cesarean, active labour, fetal bradycardia, maternal tachycardia, cervix 8 cm. Next step?
- Instrumental delivery
- ARM
- Increase oxytocin dose
- Emergency Cesarean Section
Answer: D
Q112. Day 21 of 28-day cycle. Which hormone profile is correct?
- ↑P, ↑E, ↓FSH, ↓LH
- ↑P, ↓E, ↓FSH, ↓LH
- ↓P, ↓E, ↑LH, ↑FSH
- ↑E, ↓P, ↑LH, ↓FSH
Answer: B
Q113. A female in labour presents with cord prolapse. What is the next best step?
- Push the cord back into the cervix
- Emergency C-section
- Head-low, lift part, fill bladder
- Vaginal delivery with forceps
Answer: B
Q114. Cervical cancer with hydronephrosis. FIGO stage?
- IIA
- IIIA
- IIIB
- IV
Answer: C
Q115. A woman presents with amenorrhea, linea nigra, nausea, vomiting, bluish vagina. These are:
- Probable signs of pregnancy
- confirmed pregnancy
- Menopause
- Normal menstrual cycle
Answer: A
Q116. A woman presents with Chronic lower abdominal Pain and dysmenorrhea. MRI is shown. Diagnosis?
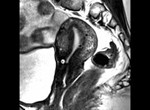
- Adenomyosis
- Endometriosis
- endometrial carcinoma
- Fibroid
Answer: A
Q117. A woman is first antenatal visit reports her LMP 2 months ago. Which ultrasound parameter is most accurate for dating pregnancy at this stage?
- Biparietal diameter
- Mean gestational sac diameter
- Abdominal circumference
- Crown-rump length
Answer: D
Q118. 36 weeks pregnant, ↓fetal movements. NST 1 accel, no decel in 20 min. Next step?
- Emergency C-section
- Induce labor
- Wait and observe
- Continue NST for 40 min
Answer: D
Ophthalmology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q119. An elderly patient presents with white dandruff-like deposits on the anterior lens capsule seen on slit-lamp examination. What is the most likely diagnosis?
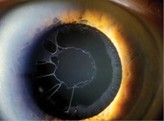
- Anterior capsular opacity
- Iris cyst
- Pseudoexfoliation syndrome
- Pigment dispersion syndrome
Answer: C
Q120. The device shown in the image is “INTACS.” What is the primary indication for its use?
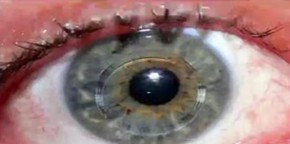
- Glaucoma
- Cataract
- Keratoconus
- Corneal ulcer
Answer: C
Q121. A 16-year-old female presents with a gradually enlarging, painless orbital swelling that has persisted for 10 years. What is the most likely diagnosis?

- Dermoid cyst
- Capillary Hemangioma
- Lacrimal gland carcinoma
- Osteoma
Answer: A
Q122. A patient presents with guttate lesions in one eye and bullous keratopathy in the other. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy
- Viral corneal ulcer
- Interstitial keratitis
- Keratoconjunctivitis
Answer: A
Q123. Which of the following is true about orbital cellulitis?
- The inflammation is confined anterior to the orbital septum
- Ethmoidal sinusitis is the most common cause in all age groups
- It presents with proptosis, but pupillary reflexes and extraocular movements remain normal
- Broad-spectrum topical antibiotics are the treatment of choice
Answer: B
Q124. Identify the A and B components from the image about binocular vision
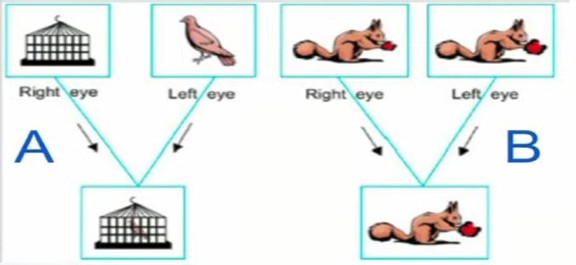
- A. Simultaneous perception and B-Stereopsis
- A-Simultaneous perception and B-Fusion
- A- Fusion and Simultaneous Perception
- A- Stereopsis and B-Fusion
Answer: B
Orthopaedics NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q125. Q. A 27-year-old individual presents with chronic lower back pain that improves with physical activity and is associated with early morning stiffness. There is a past history of anterior uveitis. A recent X-ray of the sacroiliac joints appears normal. What is the most appropriate next step in evaluation?
- MRI of the sacroiliac joints
- Anti-CCP antibody testing
- Repeat plain radiograph
- CT scan of the sacroiliac joints
Answer: A
Q126. What is the most appropriate diagnosis for the image below?
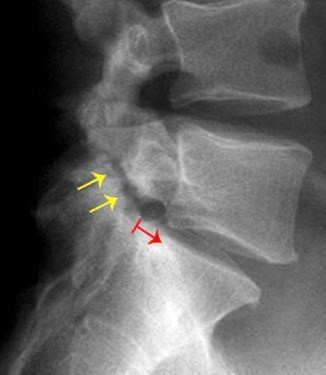
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spondylolysis
- Vertebral compression fracture
- Degenerative disc disease
Answer: A
Q127. A 11-year-old boy presented with a complaint of painless limp. An X-ray was done, and the following image was obtained. What is the most likely diagnosis?

- Perthes disease
- Developmental dysplasia of the Hip
- TB Hip
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
Answer: A
Q128. A 25-year-old male presents to the emergency department following a motorbike accident. He has sustained a closed midshaft tibial fracture. Six hours later, he complains of severe pain disproportionate to the injury, which worsens with passive dorsiflexion. The pain is not relieved by analgesics. Distal pulses are palpable, but there is loss of sensation in the first web space. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
- Elevate the limb and observe
- Immediate fasciotomy
- Administer opioid analgesics
- Apply a cast and schedule follow-up
Answer: B
Q129. A male patient sustains a road traffic accident with closed midshaft fractures of the femur and tibia. Two days later, he develops breathlessness, tachycardia, and petechial rash on the chest and conjunctiva. What is the most probable diagnosis?
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- Fat embolism syndrome
- Pulmonary embolism
- Sepsis
Answer: B
Q130. A 45-year-old male presents with discomfort in his joints. Synovial fluid aspiration reveals rhomboid-shaped shaped positively birefringent crystals under polarised light microscopy. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Gout
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Pseudogout
Answer: D
Pathology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q131. Q. Which of the following types of cell death involves activation of caspase enzymes?
- Necrosis and Apoptosis
- Apoptosis and Pyroptosis
- Apoptosis and Necroptosis
- Apoptosis only (+ Pyroptosis)
Answer: B
Q132. Q. Anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA) is most commonly seen in:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Primary biliary cholangitis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Answer: B
Q133. Q. Which of the following conditions is most likely to follow this pattern of inheritance?
- Prader-Willi syndrome
- Marfan syndrome
- Kearns-Sayre syndrome
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Answer: B
Q134. Q. A 68-year-old man presents with complaints of persistent fatigue. On examination, there is generalised lymphadenopathy. CBC shows leukocytosis with an absolute lymphocyte count of 35,000/µL. Which of the following is the investigation of choice to confirm the diagnosis and determine CD markers of CLL?
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Flow cytometry of peripheral blood
- Serum LDH levels
- Lymph node excisional biopsy
Answer: B
Q135. Q. A 35-year-old woman undergoes abdominal imaging for nonspecific RUQ pain. A liver mass is identified and surgically excised. The gross specimen is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?

- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Focal nodular hyperplasia
- Hepatic adenoma
- Metastasis
Answer: B
Q136. Q. A patient with H/o cough, chest pain and dyspnea. Imaging reveals giant cells, granuloma formation and stellate inclusions. Likely diagnosis?
- Tuberculosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Lung cancer
- Fungal infection
Answer: B
Q137. Q. A very tall man presents with visual problems and is found to have ectopia lentis on ophthalmological evaluation. Which gene is most likely defective in this patient?
- FBN1 ✅ (chromosome 15)
- COL1A1
- FGFR3
- PAX6
Answer: A
Q138. Q. A patient presents with hearing loss and balance problems. Histopathology of the lesion shows Antony A and Antony B areas and Verocay bodies. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Schwannoma ✅
- Ependymoma
- Meningioma
- Medulloblastoma
Answer: A
Q139. Q. A child presents with visual disturbances and delayed growth. Imaging reveals a suprasellar mass, and histopathology shows the presence of wet keratin compact, eosinophilic, anucleate keratin. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Medulloblastoma
- Rathke pouch cyst
- Pituitary adenoma
- Craniopharyngioma
Answer: D
Q140. Q. Which of the following lab techniques is most commonly used to compare and quantify CD markers in cells?
- ELISA
- Western blot
- Flow cytometry
- IHC
Answer: C
Q141. Q. Anti-SCL 70 antibody is most strongly associated with
- GAVE
- B. Calcinosis cutis
- Interstitial lung disease
- Myositis
Answer: C
Q142. Q. A 30-year-old man presents with a painless testicular mass. An ultrasound shows a well-circumscribed, homogeneous, non-hemorrhagic tumour. Histology is shown. What is the likely diagnosis?
- Yolk sac tumour
- Choriocarcinoma
- Teratoma
- Seminoma
Answer: D
Q143. Q. A lymphoma characterised by the presence of centrocytes and centroblasts, along with BCL2 positivity and CD10 expression, is most commonly associated with which chromosomal translocation?
- t(2;5)
- t{11;14)
- t(14;18)
- t(11;14)
Answer: C
Q144. Q. A 68-year-old man presents with bleeding. Peripheral smear shows a “faggot cell.” Which translocation is associated?
- t(15;17)
- t(14;18)
- t(11;14)
- t(8,21)
Answer: A
Q145. Q. A middle-aged woman presents with dry eyes and mouth. Laboratory tests reveal positive anti-Ro (SSA) and anti-La (SSB) antibodies. What is the most likely underlying pathological mechanism?
- Destruction of exocrine glands by neutrophils
- IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction
- Lymphocytic infiltration and destruction of salivary and lacrimal glands ✅
- Deposition of amyloid in salivary glands
Answer: C
Q146. Q. A patient has a neck mass with odynophagia and dyspnea. Histology shows amyloid deposition. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Follicular thyroid carcinoma
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
Answer: C
Q147. Q. A patient is diagnosed with AML M3. Which chromosomal translocation is characteristically associated with this condition?
- t(9;22)
- t(8;21)
- t(15;17)
- t(11;14)
Answer: C
Pediatrics NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q148. A 3-year-old child is brought to the emergency department with generalised convulsions following a high-grade fever. Which of the following is the most appropriate first-line medication to manage seizures in this acute febrile episode?
- Diazepam
- Valproate
- Fosphenytoin
- Doxycycline / Amoxicillin
Answer: A
Q149. A 6-month-old infant presents with frequent infections and failure to thrive. Tests show adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. Which immunodeficiency disorder is most likely responsible?
- Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)
- Hypogammaglobulinemia
- DiGeorge Syndrome
- Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
Answer: A
Q150. A family pedigree reveals multiple individuals with symptoms such as progressive eye movement limitation, retinal pigment changes, and disturbances in cardiac conduction. Based on these findings and the inheritance pattern, which of the following is the most probable diagnosis?
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Kearns–Sayre Syndrome
- Friedreich Ataxia
- Myotonic Dystrophy
Answer: B
Q151. A 2-year-old child has choked on a peanut. What is the most appropriate immediate management?
- Chest compressions
- Back blows
- Abdominal thrusts
- Endotracheal intubation
Answer: C
Q152. A child demonstrates progressive neurological decline and a cherry-red spot on fundus examination. Enzyme analysis reveals a deficiency in hexosaminidase A. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- GM1 gangliosidosis
- GM2 gangliosidosis
- Niemann-Pick disease
- Gaucher disease
Answer: B
Q153. A child with coarse facial features and developmental delay is found to have an α-L-iduronidase deficiency on enzyme testing. Which substances are expected to accumulate in this disorder?
- Dermatan sulfate + Chondroitin sulfate
- Only Dermatan sulfate
- Dermatan sulfate + Heparan sulfate
- Heparan sulfate + Chondroitin sulfate
Answer: C
Q154. A 7-month-old infant has just started complementary feeding using the ‘katori method.’ What is the recommended quantity and frequency of feeding during the first day?
- ½–1 katori, 4 times daily
- ½–1 katori, 5 times daily
- ½–1 katori, 6 times daily
- ½–1 katori, 8 times daily
Answer: A
Q155. A neonate is born to an HIV-positive mother with a viral load of 1200 copies/mL. What is the recommended antiretroviral prophylaxis for the newborn?
- Nevirapine for 6 weeks with exclusive breastfeeding
- Nevirapine + Zidovudine for 6 weeks with exclusive breastfeeding
- No prophylaxis needed as the mother is on ART
- Nevirapine + Zidovudine for 12 weeks with exclusive breastfeeding
Answer: D
Q156. A 5-year-old child with known chronic kidney disease presents with bowing of the legs. Lab results reveal: Normal calcium, Elevated phosphate, Increased alkaline phosphatase, Low 25(OH) Vitamin D. What is the most appropriate next intervention?
- Calcium supplementation with a phosphate binder
- Phosphate binder
- Oral calcium with Vitamin D
- Growth hormone therapy
Answer: A
Q157. A 1-day-old newborn with significant respiratory distress is admitted to the ICU. A chest radiograph is performed. What is the most probable diagnosis based on the clinical and radiological findings?
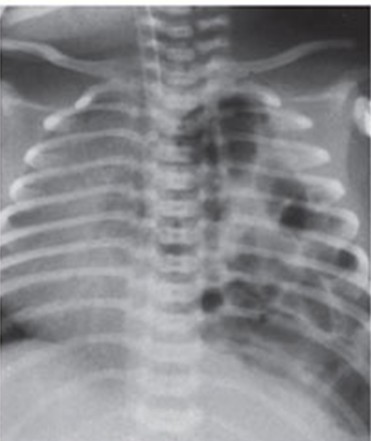
- Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation (CPAM)
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH)
- Congenital lobar emphysema
- Neonatal pneumonia
Answer: B
Pharmacology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q158. Which receptor does Benralizumab act on?
- IL-5
- IL-4
- IL-1
- TNF – α
Answer: A
Q159. What is the drug of choice for chemoprophylaxis in close contacts of a patient diagnosed with meningococcal meningitis?
- Doxycycline
- Amoxicillin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Vancomycin
Answer: C
Q160. Which of the following, if given in large volumes, can lead to hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis?
- Dextrose in NS (DNS)
- Normal saline (NS)
- 5% dextrose in water
- Ringer lactate
Answer: B
Q161. Q. A 60-year-old man with ischemic cardiomyopathy and palpitations is started on amiodarone. Which phase of the cardiac action potential is its primary site of action?

- Phase 0 – Rapid depolarisation
- Phase 2 – Plateau
- Phase 3 – Repolarisation
- Phase 4 – Resting potential
Answer: C
Q162. Q. A patient presents with headache, palpitations and diaphoresis with elevated 24-hour urine metanephrine levels. Which of the drugs is given preoperatively
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Esmolol
- CCB
- Labetalol
Answer: D
Q163. A 35-year-old woman is diagnosed with migraine and has a family history of coronary artery disease. She has been previously treated with sumatriptan. What is the drug of choice for migraine prophylaxis?
- Propranolol
- Topiramate
- Ergotamine
- Naratriptan
Answer: A
Q164. A patient with tumour lysis syndrome has elevated uric acid levels and is prescribed Pegloticase. What is the mechanism of action of Pegloticase?
- Xanthine oxidase inhibition
- URAT-1 receptor inhibition
- Oxidises uric acid
- Hydrolysis of uric acid
Answer: C
Q165. A 40-year-old male patient presents with GERD. Which of the following drugs helps in the contraction of the lower oesophageal sphincter and increases gastric emptying?
- Metoclopramide
- Pantoprazole
- Vonoprazan
- Sodium alginate
Answer: A
Q166. A patient presents with the following lesions and has burning sensations on eating spicy food. Which of the following drugs is responsible here?
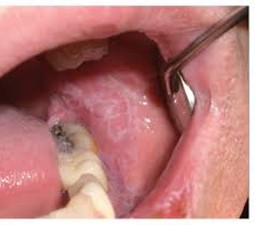
- Lithium
- Beta blockers
- Fluconazole
- Ciprofloxacin
Answer: A
Q167. A patient with a history of hypertension presents with renal stones. He was started on hydrochlorothiazide. Which statement is true regarding the choice of a drug?
- Increased calcium excretion
- Decreased calcium excretion
- Increased oxalate absorption
- Decreased citrate excretion
Answer: D
Q168. A patient with HIV has recently been diagnosed with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. What is the appropriate regimen, and what should the patient be monitored for?
- BPaLM; monitor for immune reconstitution syndrome
- INH + Levofloxacin + Pyrazinamide + ethambutol, monitor for hepatotoxicity
- INH + Levofloxacin + Streptomycin + Ethionamide, monitor for pyridoxine deficiency
- INH + Clarithromycin + Pyrazinamide + Ethambutol, monitor for optic neuritis
Answer: A
Physiology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q169. In a patient with pulmonary embolism, there is a complete obstruction of blood flow. Which point on the V/Q graph indicates the effect of pulmonary
embolism
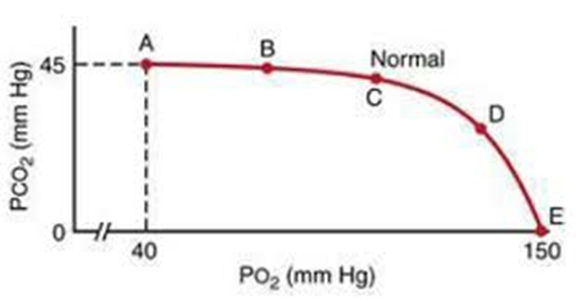
- A
- B
- C
- D
Answer: D
Q170. A patient has the following Starling forces measured at the capillary level: Capillary hydrostatic pressure: 18 mmHg, Capillary oncotic pressure: 27 mmHg, Interstitial oncotic pressure: 7 mmHg. If there is no net movement of fluid across the capillary wall, what is the value of the interstitial hydrostatic pressure?
- 0 mmHg
- +1 mmHg
- +2 mmHg
- –2 mmHg
Answer: D
Q171. A patient flying to a high altitude (3700 m) develops headache, nausea, dyspnea, and dizziness. What explains these symptoms?
- Hypoxia causing vasodilation
- Hypoxia causing vasoconstriction
- Metabolic acidosis causes oedema
- high PO2 causing vasoconstriction
Answer: A
Q172. In an experimental study, blood glucose levels were elevated to 2–3 times the normal level and maintained at that level. What is the most likely pattern of insulin secretion in response?
- Rapid rise followed by a fall
- Gradual rise followed by a fall
- Remains persistently elevated
- Initial rise followed by sustained elevation
Answer: D
Q173. In the sarcomere length–tension relationship curve, at which point is the maximum active tension generated due to optimal overlap between actin and myosin filaments?
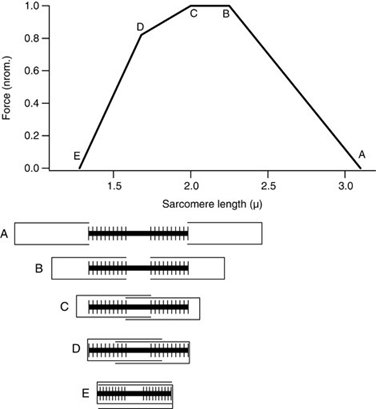
- Point A
- Point B
- Point C
- Point D
Answer: B
Q174. A patient presents with fatigue, muscle cramps, and strong salt cravings. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Addison’s disease
- Conn’s disease
- Cushing’s disease
- Hypopituitarism
Answer: A
Q175. What acid-base disturbance is expected in a person trekking at high altitude due to hyperventilation?
- Metabolic acidosis
- Metabolic alkalosis
- Respiratory acidosis
- Respiratory alkalosis
Answer: D
Q176. A woman presenting with amenorrhea and galactorrhea is diagnosed with a pituitary adenoma and elevated prolactin levels. What is the most likely cause of her amenorrhea?
- Low GnRH
- High pulsed LH
- High FSHD
- Inhibition of GnRH by prolactin
Answer: A
Psychiatry NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q177. A schizophrenia patient on haloperidol was responding well for the last 2 years. Now presented with orofacial dyskinesia, choreiform, tick-like movements, and dystonia features. What can be the probable diagnosis and treatment?
- Acute dystonia – Ropinirole
- Tardive dyskinesia – Valbenazine
- Akathesia – Propranolol
- Oral tremor – amantadine
Answer: B
Q178. A patient says that he follows the way birds fly whenever he is in an open place because god is giving him instructions through the birds. What is the diagnosis?
- Delusional perception
- Visual hallucination
- Delusional memory
- Sudden Delusional ideas
Answer: A
Q179. Mr. K was brought to a psychiatrist by his friend, saying that Mr. K needs everything to be in perfect order and has difficulty getting rid of things stored with him, both of which are affecting his work quality. He is a perfectionist. However, Mr. K denies such complaints. What is the diagnosis?
- Narcissistic Personality
- Obsessive Compulsive Personality Disorder
- Paranoid Delusion
- Dependent personality
Answer: B
Q180. A patient is brought in by a social worker after a recent earthquake. He has been living in a town different from his place of origin and is unaware of how he travelled 110 km away from home. He cannot recall his identity. There’s no substance abuse history. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Dissociative amnesia
- Dissociative fugue
- DID
- Selective amnesia
Answer: B
Q181. A 21-year-old female presents with amnesia of events following her father’s death in a road traffic accident. Symptoms have persisted for 2 weeks, and she experiences flashbacks. What is the most probable diagnosis?
- Dissociative disorder
- Major depression
- PTSD
- Acute stress disorder
Answer: D
Q182. A person attacks his co-worker, complaining that the co-worker has been plotting to harm him. He hears voices. On examination, the person is found to have a disorganised speech. What is the next step in this case?
- Refer for anger management.
- Refer for psychiatric assessment and check if he is fit for trial.
- He is not responsible because he is mentally ill
- Start immediate trials and punishment
Answer: B
Radiology NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q183. What is correct regarding the image shown?
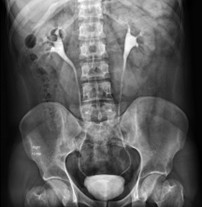
- Non-invasive and the gold standard of cancer
- Non-invasive and can diagnose PUJ obstruction
- Percutaneous method
- Invasive and therapeutic for bladder lithiasis
Answer: B
Q184. What is the most appropriate diagnosis for the image below?
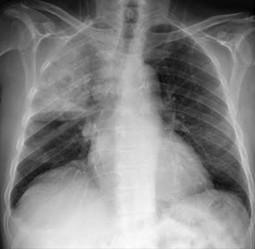
- Collapse of the right upper lobe
- Consolidation of the right upper lobe
- Right lung abscess
- Right upper lobe bronchogenic carcinoma
Answer: A
Q185. A 35-year-old male presents with a complaint of recurrent headaches. On further investigation, the following MRI was received. What is the most likely diagnosis?
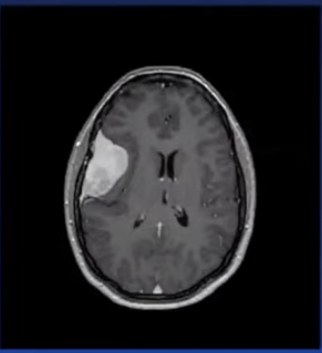
- Meningioma
- Glioma
- Medulloblastoma
- Pilocystic astrocytoma
Answer: A
Q186. A 32-year-old male presents with dysphagia and regurgitation. A barium swallow image is shown. Which investigation is considered the gold standard for confirming the diagnosis?
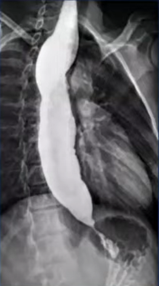
- CECT
- Esophageal manometry
- Endoscopy
- NCCT
Answer: B
Surgery NEET PG 2025 Recall Questions
Q187. A patient presents with dyspnea and tachycardia 7 days after undergoing knee replacement surgery. Which investigation will confirm the diagnosis?
- V/Q ratio
- D-dimer
- Chest X-ray
- CT Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA)
Answer: D
Q188. Q. A 35-year-old man diagnosed with pheochromocytoma is scheduled for surgery. Which medication should be given as preoperative preparation?
- Clonidine
- Phenoxybenzamine
- Esmolol
- Aspirin
Answer: B
Q189. During a complex duodenal surgery, a vessel posterior to the duodenum is cut, resulting in massive bleeding and blood collection. Which vessel is most likely injured?
- Superior mesenteric artery
- Inferior vena cava
- Aorta
- Portal vein
Answer: B
Q190. A patient presents with the fingertip changes shown in the image. What is the most likely diagnosis?
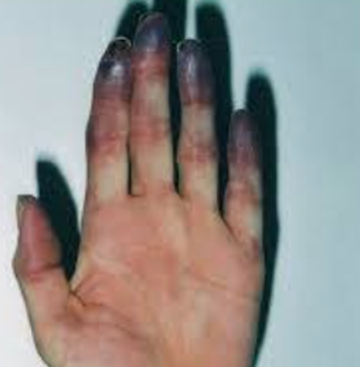
- Wet gangrene
- Raynaud’s phenomenon
- Dry gangrene
- Frostbite
Answer: A
Q191. A patient presents with the breast condition shown in the image. According to TNM staging, what stage would this represent?
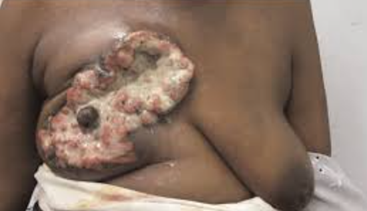
- Stage IIIB
- Stage IIIC
- Stage IVD
- Stage IIB
Answer: C
Q192. A 50-year-old patient presents with a slowly growing, painless neck mass at the angle of the mandible… ‘Lyre’s sign’ is observed. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Thyroid nodule
- Lymphadenopathy
- Carotid body tumour
- Branchial cyst
Answer: C
Q193. The knot shown in the image is commonly used in surgical procedures. What type of knot is depicted?
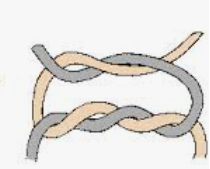
- Surgeon’s knot
- Granny’s knot
- Square knot
- Slip knot
Answer: A
Q194. A 35-year-old male with a stab wound to the epigastrium, hypotension, and guarding. What is the immediate intervention of choice?
- FAST
- DPL
- CT Scan
- Exploratory Laparotomy
Answer: D
Q195. Based on Park’s classification, identify the type of anorectal fistula shown in the image.

- Intersphincteric
- Suprasphincteric
- Extrasphincteric
- High transsphincteric
Answer: A
Q196. A 56-year-old with chronic venous changes in the lower limb. Which statement is true?
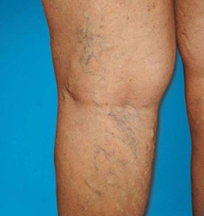
- Sclerotherapy is preferred
- Eczema or lipodermatosclerosis may develop
- Telangiectasia is uncommon
- Venous ulcer not expected
Answer: B
Q197. Regarding polydioxanone suture material, which of the following is accurate?
- Non-absorbable
- Monofilament
- Braided multifilament
- Derived from collagen
Answer: B
Q198. A 3-year-old boy has painful urination and ballooning of the foreskin. Likely diagnosis?

- BXO
- True phimosis
- Recurrent balanoposthitis
- Recurrent UTI
Answer: B
Q199. A woman with deep partial-thickness burns on the lower limb. The image shows the procedure. What is the procedure?
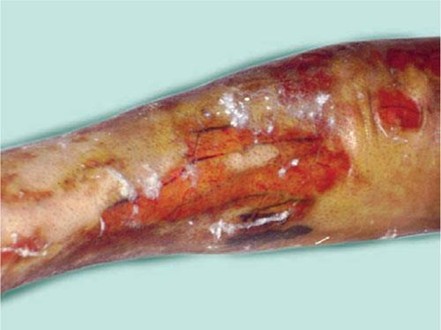
- Escharotomy
- Surgical debridement
- Excision of healthy fat or fascia
- Early skin grafting
Answer: B
Q200. A known case of anal carcinoma with a mass near the anal opening comes for a follow-up. Which of the following lymph nodes are most likely involved?
- Superficial inguinal lymph nodes
- Deep inguinal lymph nodes
- External iliac lymph nodes
- Internal iliac lymph nodes
Answer: A
PDF Download link – NEET PG Recall Question with Answers
🚀 Crack NEET PG 2025 with Expert Guidance!
Don’t just rely on recall questions—master every subject with DigiNerve’s NEET PG Course. Get video lectures by top faculty, PYQ discussions, QBank, mock tests, and smart study tools.
👉 Enrol Now & Boost Your NEET PG Rank
Read More –
Top 10 Highest Paying Careers for Doctors in India 2025
MD vs. DNB: Which Postgraduate Medical Degree is Better
Expected NEET PG 2025 Cut-Offs Based on Difficulty Level
How to Choose the Right Medical PG Branch: Passion vs. Scope vs. Salary
Related post