LMA Airway Management: Complete Guide to Types, Indications, Insertion Technique & Difficult Airway Algorithm
Airway management is the cornerstone of safe anesthesia, emergency care and critical care practice. Failure to secure and maintain a patent airway remains one of the leading causes of anesthesia-related morbidity. Among the various airway devices available today, LMA airway management has transformed modern practice by offering a reliable, minimally invasive alternative to endotracheal intubation.
The laryngeal mask airway (LMA) bridges the gap between face mask ventilation and endotracheal tube placement making it invaluable for routine anesthesia as well as difficult airway scenarios. Its relevance extends across operating theatres, emergency rooms, ICUs and prehospital care, making it essential knowledge for anesthesia residents, emergency physicians and NEET SS aspirants.
This comprehensive guide covers everything from types of LMA and insertion techniques to airway maintenance, combi tubes and the difficult airway management algorithm with a strong clinical and exam-oriented approach.
What is LMA in Airway Management?
A Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) is a supraglottic airway device designed to sit over the laryngeal inlet, forming a low-pressure seal around the glottis. Unlike an endotracheal tube, it does not pass through the vocal cords.
Role of LMA in Airway Maintenance
- Maintains a patent airway without tracheal intubation
- Allows spontaneous or controlled ventilation
- Reduces airway manipulation and sympathetic response
When LMA is Preferred Over Endotracheal Intubation
- Short-duration surgical procedures
- Day-care anesthesia
- Anticipated difficult mask ventilation
- Rescue airway in failed intubation
In modern IMA airway management, LMAs play a vital role in ensuring effective airway maintenance with minimal complications.
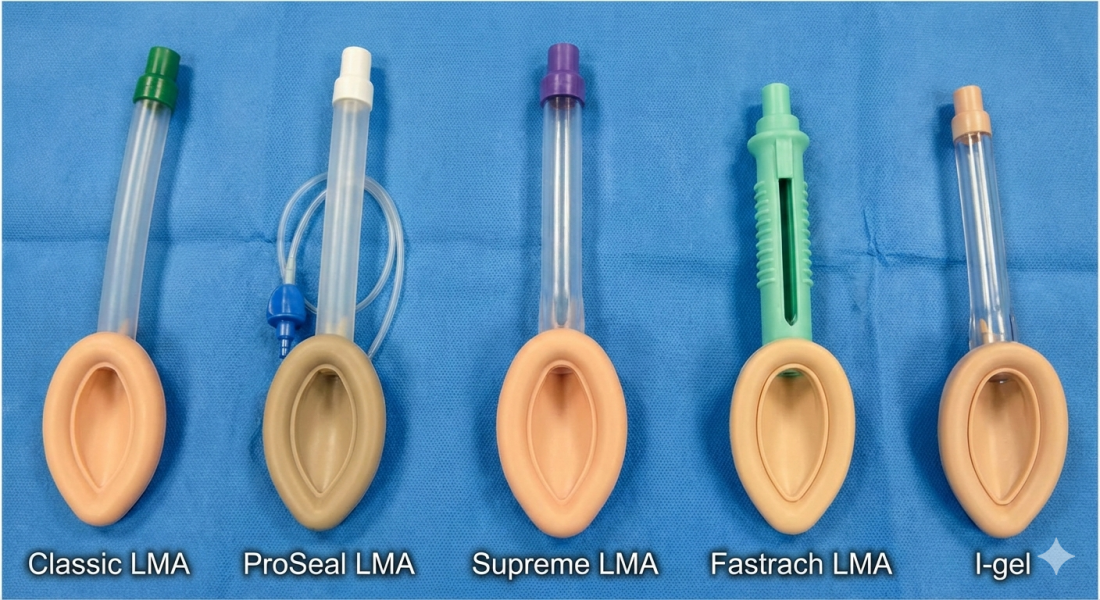
Classification & Types of Laryngeal Mask Airway
Classic LMA
- First-generation device
- Used for spontaneous or assisted ventilation
- Ideal for short, elective procedures
ProSeal LMA
- Second-generation device
- Gastric drainage tube reduces aspiration risk
- Allows higher airway pressures
Supreme LMA
- Single-use, anatomically curved
- Easier insertion with better seal
- Integrated gastric channel
Fastrach LMA
- Designed for blind or fiberoptic-guided intubation
- Crucial in difficult airway situations
I-gel vs LMA (Brief Comparison)
- I-gel has a non-inflatable cuff
- Faster insertion and less postoperative sore throat
- LMA offers wider variants and intubation options
Indications of LMA
- Short surgical procedures
- Day care anesthesia
- Difficult mask ventilation
- Emergency airway rescue
- Pediatric and adult anesthesia
Contraindication of LMA
- High risk of aspiration
- Full stomach
- Morbid obesity
- Upper airway obstruction or pathology
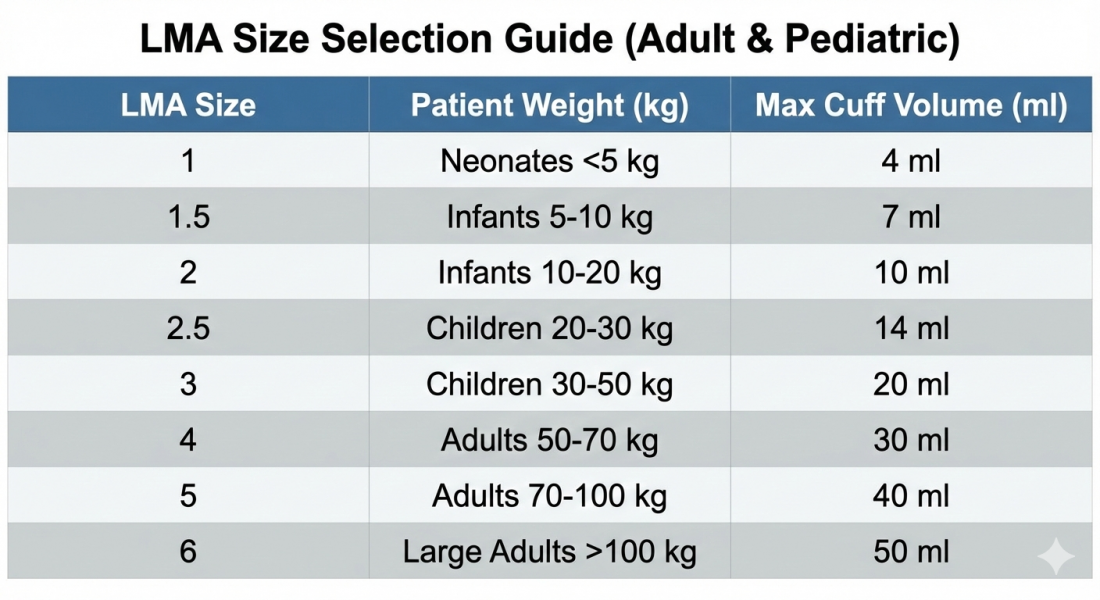
LMA Size Chart (Adult & Pediatric)
| LMA Size | Patient Weight | Cuff Volume (ml) |
| Size 1 | < 5 kg | 4 |
| Size 1.5 | 5–10 kg | 7 |
| Size 2 | 10–20 kg | 10 |
| Size 3 | 30–50 kg | 20 |
| Size 4 | 50–70 kg | 30 |
| Size 5 | 70–100 kg | 40 |
Selection Tips:
- Choose size based on patient weight
- Avoid overinflation to reduce sore throat and nerve injury
- Ensure proper seal at minimal cuff pressure
LMA Insertion Technique (Step-by-Step Guide)
Pre-Insertion Preparation
- Patient in sniffing position
- Adequate preoxygenation
- Proper lubrication of the posterior surface
Steps of LMA Insertion
- Hold LMA like a pen
- Insert along the hard palate
- Advance until resistance is felt
- Inflate the cuff to the recommended volume
Alternative Techniques
- Rotational insertion
- Introducer tool technique
Confirmation of Correct Placement
- Bilateral chest rise
- Presence of end tidal CO2
- Equal air entry on auscultation
Complications of LMA
- Aspiration (rare but serious)
- Sore throat
- Nerve injury (lingual, hypoglossal)
- Gastric insufflation
- Air leak
LMA vs Endotracheal Tube
| Feature | LMA | Endotracheal Tube |
| Ease of insertion | Easy | Difficult |
| Airway protection | Partial | Complete |
| Emergency use | Excellent | Gold standard |
| Hemodynamic response | Minimal | Significant |
Role of Combitubes in Airway Management
What is a Combitube?
A dual-lumen airway device designed for blind insertion into either the oesophagus or trachea.
Indications of Combitubes
- Prehospital emergencies
- Failed intubation scenarios
- Limited airway access
When Combitube is Preferred
- Cardiac arrest
- Untrained airway providers
Comparison: LMA vs Combitube
- LMA is easier and more physiological
- Combitubes offer better protection in uncontrolled settings
Airway Maintenance in Anesthesia & Emergency Settings
Effective airway maintenance ensures oxygenation, ventilation and patient safety.
Devices Used
- Face mask
- LMA
- Combitube
- Endotracheal tube
LMA remain the most versatile option across anesthesia and emergency medicine.
Difficult Airway Algorithm
Difficulty in mask ventilation, intubation or both.
When to Suspect
- Limited mouth opening
- Obesity
- Neck immobility
- Facial trauma
Basic Principles
- Oxygenation over intubation
- Early use of supraglottic devices
Difficult Airway Management Algorithms (Step by Step)
Initial Assessment
- Airway examination
- Backup plan preparation
Failed Mask Ventilation
- Insert LMA immediately
Role of LMA in Difficult Airway
- Acts as a rescue airway
- Allows ventilation and oxygenation
Emergency Surgical Airway
- Cricothyrotomy if ventilation fails
This structured approach defines the algorithm for managing difficult airways.
Roles of LMA in Difficult Airway Management
- Rescue airway in failed intubation
- Key device in can’t intubate, can’t ventilate situations
- Reduces hypoxia-related complications
Clinical & Exam Relevance
- High-yield topic for anesthesia is PG exams
- Frequently asked in viva and OSCEs
- Crucial for NEET SS anesthesia preparation
- Strongly integrated with Anesthesiology MD Residency Course learning objectives
LMA airway management has become an indispensable component of modern anesthesia and emergency medicine. Its ease of use, versatility and life-saving role in difficult airway scenarios make it essential knowledge for every clinician. Mastery of LMA types, insertion techniques, airway maintenance, combitubes and the difficult airway management algorithm significantly improves patient safety and exam performance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- What is LMA in airway management?
Ans – It is a supraglottic airway device used to maintain a patent airway without the need for tracheal intubation. - When is LMA preferred over intubation?
Ans – In short procedures, day care anesthesia, and difficult airway rescue. - What are the complications of LMA?
Ans – Sore throat, aspiration, nerve injury, and air leak. - How is LMA used in a difficult airway?
Ans – As a rescue device when mask ventilation or intubation fails. - What is the difference between LMA and Combitube?
Ans – LMA is simpler and more physiological, while Combitubes are mainly emergency devices.
Related post